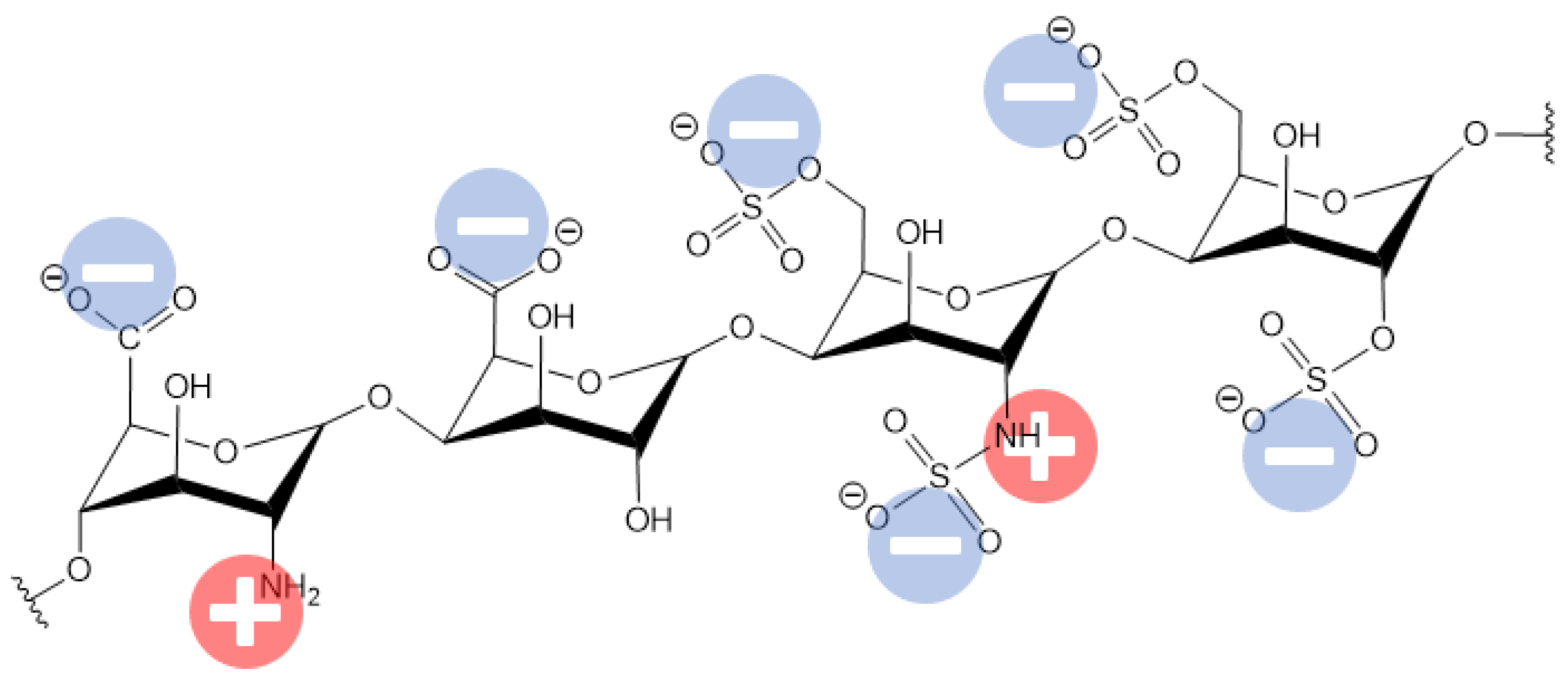
Hemodialysis (HD) is a life-sustaining extracorporeal blood purifying treatment for end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients. However, this membrane-based therapy is associated with acute side effects, life-threatening chronic conditions, and unacceptably high morbidity and mortality rates. Numerous surface coatings have been developed to improve the blood compatibility of biomaterials. Heparin is a widely used anticoagulant substance that increases the clotting time and increases the membrane hemocompatibility in terms of platelet adhesion and protein adsorption and anti-clotting activity. However, using heparin is challenging due to its severe or life-threatening side effects such as heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), in addition to heparin induced thrombocytopenia and thrombosis (HITT). In addition, heparin is strongly electronegative and exhibits a binding affinity for the positive active sites of human serum proteins, which is an additional challenge. Consequently, covalently immobilized heparin would create a more charged surface to induce more blood–membrane interactions, and consequently more adsorbed human serum proteins and biochemical pathway activations, which can negatively affect dialysis patients.
- hemodialysis membrane
- heparin
- hemocompatibility
- anticoagulant
- immobilization
1. Introduction
2. Current Challenges of Heparin-Coated Dialysis Membranes

3. Factors Affecting Hemocompatibility of Heparin-Grafted Membranes
| Human Serum Protein | pI |
|---|---|
| Albumin (HSA) | ~5 |
| Fibrinogen (FB) | 5.8 |
| Transferrin (TRF) | ~6 |
| β-2 Microglobulin | 5.3 and 5.7 (isoforms) |
4. Methods for Enhancing Dialysis Membrane Hemocompatibility
4.1. Biopassive Antifouling Surface
4.2. Bioactive Surfaces
5. Heparin-Immobilized Dialysis Membranes
Moreover, improvement in the recovery of blood vessel function was observed for implanted heparin-coated vascular grafts into 24-month-old Sprague Dawley rats due to promoting the proliferation of endothelial cells and preventing thrombosis. The examples of using heparin through different approaches of its immobilization on various surfaces and the resulting outcomes are listed in Table 2.
Table 2. The effects of the different approaches of heparin immobilization.
|
No. |
System |
Preparation Method |
Outcome in Hemocompatibility and Performance |
Ref. |
|
1 |
PTFE HD arteriovenous graft with attached heparin |
Commercial product. |
No benefit of using heparin. The number of cases of open or percutaneous thrombectomy was significantly higher for heparin-coated grafts as well as the number of any intervention performed to maintain graft patency. Kaplan–Meier survival curve also shows no positive effect of using heparin. |
[61] |
|
2 |
Low-molecular weight heparin injections |
|
Heparin prevents blood coagulation. |
[62] |
|
3 |
Heparin injections |
|
Heparin increases the activated clotting time (ACT) from 150 s to 300 s depending on dosage. Survival is improved by increased heparin administration independent of the ACT. |
[63] |
|
4 |
Heparin (fractioned and unfractioned) injections |
|
When fractioned heparin was used, it resulted in increasing the density of lipoproteins that is associated with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Unfractionated heparin reduces these effects. |
[64] |
|
5 |
Barium alginate microcapsules with conjugate heparin |
Alginate microcapsules were incubated with avidin with further treatment with heparin solution. |
Immobilized heparin reduces pericapsular fibrotic overgrowth (PFO) both in syngeneic and allogeneic rat transplantation models by ~65% and ~43%, respectively (in-vivo experiments). |
[39] |
|
6 |
Pullulan acetate (PA)/polyethylene glycol (PEG) membrane with conjugated heparin |
Heparin was immobilized using PEG spacer and N-hydroxysuccinimide. |
Improved resistance to platelet adhesion. |
[65] |
|
7 |
Alginate capsules covered with poly-l-lysine (PLL) heparin |
Alginate capsules were covered with positively charged poly-L-lysine with further immobilization of heparin or acrylic acid. |
Use of heparin resulted in the appearance of fibroblasts and macrophages on the capsules (in-vivo rat tissues). When heparin was replaced by poly-acrylic acid, this effect was not observed. |
[40] |
|
8 |
Low-molecular weight heparin injections |
|
Use of heparin in a coagulation preventive dose caused heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) type 1 and 2 |
[66–78] |
|
9 |
Polyurethane (PU) coated with chitosan/heparin layer-by-layer. |
Heparin / chitosan was immobilized on PU surface using 1,6-diisocyanatohexane in the presence of dibutyltin dilaurate. |
Increase in blood clotting and recalcification time in the in vitro experiments. Thromboresistance was 83.94 ± 8.12% − 86.22 ± 5.29% after 20–240 min. In vivo hemolysis ratio was less than 0.01%. |
[49] |
|
10 |
Covalently attached heparin to membrane for artificial lung use. |
Commercial product. |
Heparin reduces activated coagulation time (ACT) from approx. 250 s to 150 s compared to the non-heparinized membrane. Lung performance parameters remained approximately the same |
[79] |
|
11 |
Heparin coated circuit parts |
Commercial product. |
Reduction in the terminal complement complexes when using heparin. Improvement in biocompatibility. |
[80] |
|
12 |
PTFE coated with bovine serum albumin (BSA)/heparin multilayers |
Heparin/BSA was immobilized using cross-link by glutaraldehyde or without it. |
The BSA/heparin layer, cross-linked by glutaraldehyde, prevented fibrinogen adsorption and platelet adherence on the PTFE surface. |
[51] |
|
13 |
TiO2 surface coated with heparin |
TiO2 surface was coated with conjugate of polydopamine (PDA) and poly(ethyleneimine) (PEI). Then heparin was attached to this conjugate using N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) and N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N’-ethylcarbodiimide (EDC). |
Increase of activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) from 35 s (pristine TiO2) to 55–57 s for heparin-coated TiO2. Heparin-coated TiO2 also inhibited platelet adhesion. |
[81] |
|
14 |
Titan surface coated with laminin/heparin complex |
Laminin/heparin complex was covalently immobilized onto poly-L-lysine (PLL) coated titan surface with help of 1-ethyl-3-dimethylaminopropyl carbodiimide (EDC), N-hydroxy-2,5-dioxopyrol-idine-3-sulfonicacid sodium salt (NHS) and 2-morpholinoethane sulfonic acid (MES). |
The amount of immobilized heparin depends on the amount of used laminin. When high concentrations (more than 150 μg/mL) of laminin were used, it significantly increased the activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) to more than 190 s while the uncoated Ti surface possessed an APTT of 30 s. A lower amount of laminin increased the APTT to 90–120 s. |
[44] |
|
15 |
PLA surface coated with heparin |
Heparin was conjugated with chitosan coated polylactic acid (PLA) surface. |
Chitosan/heparin complex prevented platelet adhesion and their activation in blood contact in the in vitro tests. At the same time, the L929 fibroblast adhesion test showed that the PLA surface adsorbed only 20% of cells, whereas the chitosan/heparin coating increased this value to 70%, which was greater than for the PLA coated with chitosan only (40% relative adsorption). |
[43] |
|
16 |
The extracorporeal circuit of low-flux cellulose dialyzers was rinsed with heparin solution |
Commercial product. |
75% of heparin-treated dialyzers showed a decrease in the vascular endothelial basic fibroblast growth factor VEGF165. It was more profound for patients with ischemic heart disease. |
[82] |
|
17 |
Fixation of heparin on biological tissue |
Fresh porcine pericardia was used as biological tissue. For ionic immobilization, the tissue was treated with 2.1% protamine sulfate with further treatment with 0.625% glutaraldehyde or genipin. For covalent immobilization tissue was treated with 0.625% glutaraldehyde or genipin with further treatment with 2% water-soluble carbodiimide, 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide hydrochloride. |
Heparin increased the surface hydrophilicity and reduced fibrinogen and platelet adsorption. At the same time, covalently attached heparin resulted in a greater hydrophobic surface and increased the amount of adsorbed fibrinogen and platelets compared with ionically immobilized heparin. |
[42] |
|
18 |
Polyurethane (PU) films coated with chitosan/heparin |
PU film was treated with plasma with further growing polyacrylamide. Then, films were treated with glutaraldehyde with the further addition of chitosan (CH) and heparin (Hep). |
Both surfaces were shown to possess antibacterial properties with some improvement for PU-CH-Hep. |
[83] |
|
19 |
Glass and PVC surfaces coated with heparin |
PVC surface was treated with radiofrequency SF6 plasma with further chemical vapor deposition from heparin/isopropanol and heparin/hexamethyldisiloxane solutions. |
The coagulation time of blood was increased by about 20–60%. |
[84] |
|
20 |
Electrospun bilayered bioresorbable small-diameter vascular grafts (SDVG) based on blends of poly(L-lactic acid) (PLLA) and segmented polyurethane (PHD), coated with heparin |
Electrospun fibers were treated with allyl glycidyl ether with further addition of poly(ethylene glycol) bis(amine). Then heparin was immobilized with help of 2-(4-Morpholino) ethanesulfonic acid (MES), 1-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium salt (sNHS). |
Heparin-coated surface promoted a stable and functional endothelial cell layer. |
[85] |
|
21 |
Alkylated polyelectrolyte thin film surface with immobilized heparin |
Heparin was chemically modified by end-point conjugation to biotin and immobilized onto membrane-mimetic thin films via biotin–streptavidin interactions. |
Heparin promoted ATIII-mediated thrombin inactivation. |
[86] |
|
22 |
Polysulfone (PSf) membrane coated with heparin/polydopamine (PDA)/polyethyleneimine (PEI) |
PSf membranes were treated with PDA/PEI mixture. Then membrane was incubated into heparin and 1-Ethyl-3-(aminopropyl)carbodiimide (EDC)/N-hydroxysucciimide (NHS) mixture solutions |
Heparin-modified PSf membranes possessed high selectivity for LDL removal and a reduction in the rate of platelet adhesion. |
[87] |
|
23 |
Stainless steel with covalently attached heparin-liposomes complex. |
Stainless steel surfaces were treated with plasma with further deposition of acrylic acid and heparin-liposomes. |
Increase in blood coagulation time. |
[88] |
|
24 |
PVC tubing coated with heparin |
Commercial product. |
It was demonstrated that the immobilization of heparin altered the composition of surface-adsorbed proteins and promoted the AT-mediated inhibition of surface adsorbed FXIIa and FXIa, unlike free heparin in solution. |
[89] |
|
25 |
Polyacrylonitrile HD membrane coated with chitosan/heparin conjugate |
Chitosan (CS)/heparin (HEP) polyelectrolyte complex (PEC) was covalently immobilized onto the surface of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) membrane with help of glutaraldehyde and 1-ethyl-3-(3-di-methylaminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC). |
Coated PEC reduced protein adsorption, platelet adhesion, and thrombus formation. Additionally, immobilized PEC could suppress the proliferation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. |
[90] |
|
26 |
Graphene oxide with covered heparin, incorporated in polyetherimide membranes |
Heparin was immobilized on the graphene oxide surface with the help of dopamine hydrochloride. Then, film and hollow fiber-based membranes with inclusions of modified graphene oxide were prepared. |
Heparin reduced the platelet adhesion/activation (103 times), increased the blood clotting time (APPT 235 s), and lowered thrombin generation. Hemolysis ratio was less than 2%. Outstanding removal of uremic toxins after 4 h (Urea 77 ± 2.5%, creatinine 68 ± 2%, and lysozyme 44 ± 2%) and ~95% retention of human serum albumin was shown. |
[91] |
|
27 |
Heparin injections during HD |
|
Skin necrosis due to the proposed acquired antithrombin III deficiency. Multiple erythematous, tender lesions developed over the abdomen. |
[92] |
|
28 |
HD procedure with heparin |
|
Heparin-associated antiplatelet antibody (HAAb) positive patients experienced higher risk of thromboembolic and hemorrhagic complications (60% vs. 8.7% for control group) and higher related mortality (28.6% vs. 4.35% for control group). |
[93] |
|
29 |
Heparin-bonded polytetrafluorethylene HD arteriovenous graft (AVG) |
Commercial product. |
Rates of reintervention and thrombectomy were higher for the heparin-coated PTFE AVGs. |
[94] |
|
30 |
Heparin-coated polyacrylonitrile HD membrane |
Heparin-coated polyacrylonitrile membrane (AN69ST) was compared with regional Citrate Anticoagulation. |
Heparin-coated PAN membrane resulted in blood clotting in 39% of HD sessions, whereas no or 13% clotting occurred for citrate anticoagulation depending on citrate concentration. |
[95] |
|
31 |
Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) electrospun scaffold and heparin-poly(vinyl alcohol) (heparin-PVA) hydrogel coating HD membranes |
Heparin was chemically attached to PVA with help of glutaraldehyde. Then, it was mixed with PAN and electrospun. |
Heparin reduced membrane fouling with proteins and improved anticoagulation. |
[96] |
|
32 |
Immobilized heparin on PVDF membranes with microporous structures |
First, polyacrylic acid was grafted on the PVDF surface. Then, heparin was covalently attached using (1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide hydrochloride. |
Heparin reduced platelet adhesion |
[97] |
|
33 |
Dopamine-covered 316 L stainless steel surface coated with heparin/poly-L-lysine nanoparticles |
Stainless steel was covered with dopamine with the further addition of heparin/poly-L-lysine nanoparticles. |
Heparin prolonged the APTT and TT times, although a heparin density of more than 20 μg/cm2 was unsuitable for vascular cell proliferation and endothelium regeneration. |
[48] |
|
34 |
Polycarbonate film with immobilized heparin |
Heparin was attached to the PCL surface via aminolysis modification. |
Heparin increased the surface negative charge, resulting in increased protein adsorption. |
[98] |
|
35 |
GORE-TEX1 vascular grafts (PTFE) with immobilized heparin |
Commercial product. |
Heparin-coated PTFE grafts remained patent and had significantly greater thrombus-free luminal surface. The bioactivity of heparin was retained for a period of up to 12 weeks. |
[99] |
|
36 |
liquid crystalline hydroxypropyl cellulose ester film with immobilized heparin |
Heparin was directly attached to cellulose surface using NaOH. |
Heparin increased the activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) and prothrombin time (PT) as well as the plasma re-calcification time (PRT) and reduced coagulation activation. |
[100] |
|
37 |
Alginate microbeads covered with polyallylamine (PAV)/macromolecular heparin conjugates |
Heparin/PAV complex was attached to alginate microbeads using poly-L-lysine. |
Heparin–PAV complex increased anticlot activity, lowered cytotoxicity, reduced elevated complement, leukocyte CD11b, and fibrotic overgrowth. |
[50] |
|
38 |
Hollow-fiber based PES HD membrane, modified with tannic acid (TA)/poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) (PEtOx)/heparin |
PES hollow fibers were covered with TA, then partially hydrolyzed PetOx was added with the further immobilization of heparin. |
TA/PEtOx/Hep complex protected cardiomyocytes (H9C2) and vascular endothelial cells (HUVEC) from oxidative damage. Additionally, activated partial thromboplastin time was prolonged and complement activation was reduced. |
[45] |
|
39 |
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) tubes and capillary membrane oxygenators with heparin-modified hollow fibers |
Commercial product. |
Immobilization of heparin resulted in reduced attachment of activated C3 and C5b-9 to the membrane surface in the invitro experiment and improved long-term hemocompatibility. |
[101] |
|
40 |
PVC surface coated with heparin and nitric oxide. |
Heparin/copper nanoparticles and NO-generating substances were immobilized via tyrosinase (Tyr)-mediated reaction. |
Heparin/copper nanoparticles/NO-generating generating complex demonstrated reduced inflammatory response and improved the adaptation of implants in vivo. Additionally, the complex promoted endothelialization and inhibited coagulation and platelet activation |
[102] |
|
41 |
PES HD membrane. |
Heparin was added during HD. |
In vitro, heparin reduced the rate of superoxide release from separated 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)-stimulated peripheral blood polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNLs). In vivo, the rate of superoxide release from PNMLs was significantly reduced for heparin use. |
[103] |
|
42 |
Cellulose membrane with covalently attached heparin |
Visking@ dialysis tubes were modified with heparin (HE), dextran sulfate (DX), dermatan sulfate (DS), and endothelial cell surface heparan sulfate (ES-HS) using the photochemical heterobifunctional reagent 4-azido-lfluoro-2-nitrobenzene (AFNB). |
Heparin-coated membrane showed 50% reduced platelet adhesion. ES-HS modified membranes demonstrated no platelet adhesion. |
[104] |
|
43 |
Polyetherimide (PEI) with attached heparin |
Heparin was covalently attached to the PEI surface via the amide group reaction. |
Heparin caused a significant reduction in the platelet adhesion as well as the reduction in cell growth and metabolic activity |
[105] |
|
44 |
Bio-based poly(lactic acid) (PLA) membrane with attached heparin |
Heparin was immobilized to the PLA membrane surface via reaction with dopamine. |
Suppressed platelet adhesion, prolonged plasma recalcification time, and decreased the hemolysis ratio. |
[106] |
|
45 |
Styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) copolymer-based membrane with immobilized poly-vinylpyridine/heparin |
Heparin was attached to polymer surface using poly-vinylpyridine. |
Reduced adsorption of albumin and fibrinogen. |
[46] |
|
46 |
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) based sodium selective membrane electrode coated with chitosan/heparin |
Heparin/chitosan was attached using carbonyldiimidazole (CDI). |
Reduced platelet adhesion |
[107] |
|
47 |
Heparin grafted HD dialyzers based on polyaryethersulfone/polyamide, polysulfone, polyethersulfone, polyarylethersulfone, cellulose triacetate |
Dialyzers from several manufacturers. |
Increase in the success rate of the HD sessions for heparin-grafted dialyzers (68.5% versus 50.4% for the control group). |
[108] |
|
48 |
Gold covered SUS316L stainless steel (SS) sheet |
Alternatively immobilized chondroitin 6-sulfate (ChS) and heparin (HEP) layers on gold-coated SS. |
Increase in the blood clotting time |
[109] |
|
49 |
Titanium surface covered with chitosan (CS)/heparin (Hep) |
Heparin was covalently immobilized on the alkali treated titanium surface with further immobilization of CS with electrostatic bonding. |
Reduction in protein absorption, blood clot mass, and platelet adhesion. Additionally, antibacterial activity was observed. |
[47] |
|
50 |
Polyisobutylene-based thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) with immobilized heparin |
Heparin was immobilized using 1-ethyl-3-(dimethyl-aminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDAC) and azidobenzoic acid/propine acid |
Hindered accessibility of the heparin active site to antithrombin. |
[110] |
|
51 |
Hydrophobic polyethylene (PE) porous membrane covered with poly-dopamine/heparin |
Heparin was covalently attached to the PE surface with dopamine. |
Suppressed platelet adhesion and improved anticoagulation in vitro. |
[111] |
|
52 |
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) with a heparin-immobilized extracellular matrix (ECM) coating |
Heparin was attached to the ECM coating. |
Reduced endothelial cell (EC) growth and improved smooth muscle cell (SMC) proliferation, though platelet adhesion was observed at a low heparin surface density (4.89 ± 1.02 μg/cm2). |
[112] |
|
53 |
Heparin-coated dialyzer membrane modules |
Commercial dialyzers. |
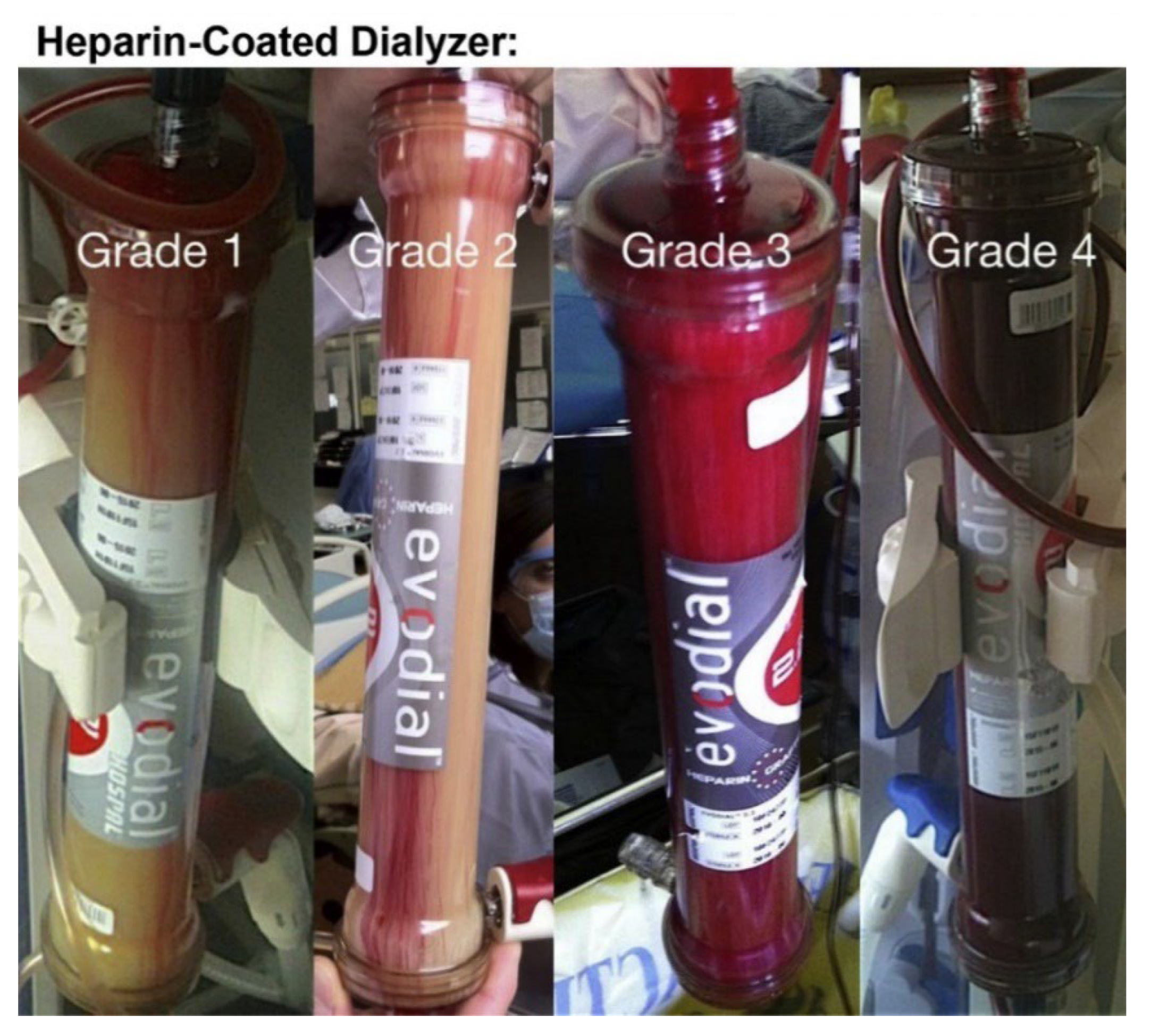
73% of HD sessions ended up with Grade 3 and Grade 4 clotting. No significant benefit of using heparin over vitamin E was shown. |
[2] |
6. Conclusions
The development of antifouling and anti-clotting materials is of great importance for hemodialysis and biomedical applications. The current tendency in the development of biocompatible materials is to design a membrane with near-zero charge due to the immobilization of zwitterionic molecules or pseudo-zwitterionic complexes. Achieving a near-zero charge dialysis membrane will minimize any possible electrostatic interaction with human serum proteins or other molecules, whose adsorption can provoke further cascade reactions and related undesired consequences.
The possibilities of current chemistry allow us to synthesize tunable structures with the desired properties that are potentially capable of replacing heparin and providing ultimate hemocompatibility. At the same time, it is also possible to use heparin for the creation of complex conjugates that eliminate heparin drawbacks, although this approach seems to be less promising than the controlled synthesis of heparin-mimicking polymers.
Achieving a biopassive antifouling surface that possesses minimal adsorption of proteins and blood cells is urgently required, since this phenomenon is considered as the very first step for further thrombotic response, blood clotting, and biochemical cascade reaction, which result in severe health problems for HD patients. Though the aim of biopassive surfaces is to minimize triggering immune response reactions, the effectiveness of this approach for long-term applications is still a major concern. Hence, a bioinactive surface is hardly suitable for biomedical implants, but is a good option for short-term or single-use applications such as hemodialysis. On the other hand, a bioactive surface utilizes the immobilization of bioactive compounds that minimize the immune response by interacting with key blood components or by releasing bioactive compounds.
Furthermore, with the methods mentioned, it is more suitable for modifying flat-sheet membranes. However, studies to date on the heparin or heparin-mimicking modification of hollow fibers are not sufficient or well-tested. Therefore, in future studies, much more attention should be paid to the surface modification of hollow fiber membranes.
A few studies have succeeded in the mimicking of heparin conformation, since the anticoagulant of heparin is not only derived from the chemical groups, but also because the specific conformation of heparin may also promote the binding of coagulant factors. Thus, with a further understanding of heparin, the ultimate goal should be to design advanced heparin-mimicking polymers with both mimicking groups and conformations.
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
| HIT | Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia |
| PF4 | Platelet factor 4 |
| HD | Hemodialysis |
| C3 | Complement component 3 |
| HSA | Human serum albumin |
| FB | Fibrinogen |
| TRF | Transferrin |
| SH | Superhydrophobic |
| ZW | Zwitterionic |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| ECC | Extracorporeal circuits |
| PVC | Polyvinyl chloride |
| KL | The Klotho Gene |
| SIS | Small intestinal submucosa |
| PES | Polyethersulfone |
| PDA | Polydopamine |
| PNIPAM | Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide |
| EDC | 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide |
| NHS | N-hydroxysuccinimide |
| DCS | Decellularized scaffold |
| PVA | Poly(vinyl alcohol) |
| LbL | Layer-by-layer |
| APTT | Activated partial thromboplastin time |
| PRT | Plasma recalcification time |
| PT | Prothrombin time |
| TT | Thrombin time |
| DHI | Dihydroxy-iron |
| BPSs | Bovine pericardial scaffolds |
| PU | Polyurethane |
| PCL | Poly(ε-caprolactone) |
| AEMA | 2-aminoethyl methacrylate |
| PTFE | Poly-tetrafluoroethylene |
| ACT | Activated clotting time |
| PFO | Pericapsular fibrotic overgrowth |
| PA | Pullulan acetate |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| PLL | Poly-L-lysine |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| PEI | Poly(ethyleneimine) |
| MES | Morpholinoethane sulfonic acid |
| PLA | Polylactic acid |
| VEGF165 | Vascular endothelial basic fibroblast growth factor |
| CH | Chitosan |
| Hep | Heparin |
| SDVG | Small-diameter vascular grafts |
| sNHS | N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium salt |
| PSf | Polysulfone |
| PEC | Polyelectrolyte complex |
| PAN | Polyacrylonitrile |
| HAAb | Heparin-associated antiplatelet antibodies |
| AVG | Arteriovenous graft |
| PVDF | Poly-vinylidene fluoride |
| PAV | Polyallylamine |
| TA | Tannic acid |
| PEtOx | Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) |
| HUVEC | Human umbilical vein endothelial cells |
| Tyr | Tyrosinase |
| PMA | Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate |
| PMNLs | Polymorphonuclear leukocytes |
| DX | Dextran sulfate |
| DS | Dermatan sulfate |
| ES | Endothelial cell surface |
| HS | Heparan sulfate |
| AFNB | 4-azido-lfluoro-2-nitrobenzene |
| SBS | Styrene-butadiene-styrene |
| CDI | Carbonyldiimidazole |
| SS | Stainless steel |
| ChS | Chondroitin 6-sulfate |
| TPE | Thermoplastic elastomer |
| EDAC | 1-ethyl-3-(dimethyl-aminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride |
| PE | Hydrophobic polyethylene |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| SMC | Smooth muscle cells |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/jcs6090244
References
- Shen, J.I.; Winkelmayer, W.C. Use and safety of unfractionated heparin for anticoagulation during maintenance hemodialysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2012, 60, 473–486.
- Islam, M.S.; Hassan, Z.A.; Chalmin, F.; Vido, S.; Berrada, M.; Verhelst, D.; Donnadieu, P.; Moranne, O.; Esnault, V.L. Vitamin E-Coated and Heparin-Coated Dialyzer Membranes for Heparin-Free Hemodialysis: A Multicenter, Randomized, Crossover Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 68, 752–762.
- Harter, K.; Levine, M.; Henderson, S.O. Anticoagulation drug therapy: A review. West J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 16, 11–17.
- van Rein, N.; Biedermann, J.S.; van der Meer, F.J.M.; Cannegieter, S.C.; Wiersma, N.; Vermaas, H.W.; Reitsma, P.H.; Kruip, M.; Lijfering, W.M. Major bleeding risks of different low-molecular-weight heparin agents: A cohort study in 12 934 patients treated for acute venous thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 1386–1391.
- Nelson-Piercy, C. Hazards of heparin: Allergy, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and osteoporosis. Baillikres Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 1997, 11, 489–509.
- Abdelrasoul, A.; Shoker, A. Induced Hemocompatibility of Polyethersulfone (PES) Hemodialysis Membrane using Polyvinylpyrrolidone: Investigation on Human Serum Fibrinogen Adsorption and Inflammatory Biomarkers Released. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 177, 615–624.
- Eduok, U.; Westphalen, H.; Abdelrasoul, A.; Shoker, A. Influence of UV-irradiation intensity and exposure duration on the hemobiocompatibility enhancement of a novel synthesized phosphobetaine zwitterions polyethersulfone clinical hemodialysis membranes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2022, 110, 573–586.
- Saadati, S.; Eduok, U.; Westphalen, H.; Abdelrasoul, A.; Shoker, A.; Choi, P.; Doan, H.; Ein-Mozaffari, F.; Zhu, N. In situ Synchrotron Imaging of Human Serum Proteins Interactions, Molecular Docking and Inflammatory Biomarkers of Hemocompatible Synthesized Zwitterionic Polymer Coated-Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Dialysis Membranes. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 27, 101505.
- Saadati, S.; Westphalen, H.; Eduok, U.; Abdelrasoul, A.; Shoker, A.; Choi, P.; Doan, H.; Ein-Mozaffari, F.; Zhu, N. Biocomptability Enhancement of Hemodialysis Membranes using Novel Zwitterionic: Experimental, in situ Synchrotron Imaging, Molecular Docking, and Clinical Inflammatory Biomarkers Investigations. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 117, 111301.
- Westphalen, H.; Saadati, S.; Eduok, U.; Abdelrasoul, A.; Shoker, A.; Choi, P.; Doan, H.; Ein-Mozaffari, F. Case studies of clinical hemodialysis membranes: Influences of membrane morphology and biocompatibility on uremic blood-membrane interactions and inflammatory biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–18.
- Abdelrasoul, A.; Shoker, A. Influence of Hydration Shell of Hemodialysis Clinical Membranes on Surrogate Biomarkers Activation in Uremic Serum of Dialysis Patients. Biomed. Eng. Adv. 2022, 4, 100049.
- Bolten, S.; Rinas, S.; Scheper, T. Heparin: Role in protein purification and substitution with animal-component free material. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 8647–8660.
- Kristyn, S.; Bohl, J.L.W. Nitric oxide-generating polymers reduce platelet adhesion and smooth muscle cell proliferation. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2273–2278.
- Tousoulis, D.; Kampoli, A.M.; Tentolouris Nikolaos Papageorgiou, C.; Stefanadis, C. The Role of Nitric Oxide on Endothelial Function. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2012, 10, 4–18.
- Handa, H.; Brisbois, E.J.; Major, T.C.; Refahiyat, L.; Amoako, K.A.; Annich, G.M.; Bartlett, R.H.; Meyerhoff, M.E. In vitro and in vivo study of sustained nitric oxide release coating using diazeniumdiolate-oped poly(vinyl chloride) matrix with poly(lactide-co-glycolide) additive. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3578–3587.
- Grossi, L.; Montevecchi, P.C. A Kinetic Study of S-Nitrosothiol Decomposition. Chem. Eur. 2002, 8, 380–387.
- Frost, M.C.; Meyerhoff, M.E. Controlled Photoinitiated Release of Nitric Oxide from Polymer Films Containing S-Nitroso-N-acetyl-DL-penicillamine Derivatized Fumed Silica Filler. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 1348–1349.
- Broniowska, K.A.; Hogg, N. The chemical biology of S-nitrosothiols. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2012, 17, 969–980.
- Roberts, T.R.; Neufeld, M.J.; Meledeo, M.A.; Cap, A.P.; Cancio, L.C.; Reynolds, M.M.; Batchinsky, A.I. A metal organic framework reduces thrombus formation and platelet aggregation ex vivo. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2018, 85, 572–579.
- Wo, Y.; Brisbois, E.J.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Major, T.C.; Mohammed, A.; Wang, X.; Colletta, A.; Bull, J.L.; Matzger, A.J.; et al. Reduction of Thrombosis and Bacterial Infection via Controlled Nitric Oxide (NO) Release from S-Nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine (SNAP) Impregnated CarboSil Intravascular Catheters. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 349–359.
- Douglass, M.E.; Goudie, M.J.; Pant, J.; Singha, P.; Hopkins, S.; Devine, R.; Schmiedt, C.W.; Handa, H. Catalyzed Nitric Oxide Release Via Cu Nanoparticles Leads to an Increase in Antimicrobial Effects and Hemocompatibility for Short Term Extracorporeal Circulation. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 2539–2548.
- Große-Berkenbusch, K.; Avci-Adali, M.; Arnold, M.; Cahalan, L.; Cahalan, P.; Velic, A.; Maček, B.; Schlensak, C.; Wendel, H.-P.; Stoppelkamp, S. Profiling of time-dependent human plasma protein adsorption on non-coated and heparin-coated oxygenator membranes. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 156, 106843.
- Zhao, P.; Fang, Q.; Gao, D.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Ao, Q.; Wang, X.; Tian, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, H.; et al. Klotho functionalization on vascular graft for improved patency and endothelialization. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2022, 133, 112630.
- Rose, I.I.; Kather, M.; Roth, H.; Dünkelberg, H.; Rein, L.; Klimosch, S.N.; Schmolz, M.; Wessling, M. Single-step chitosan functionalized membranes for heparinization. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 655, 120567.
- Lu, Y.T.; Zeng, K.; Fuhrmann, B.; Woelk, C.; Zhang, K.; Groth, T. Engineering of Stable Cross-Linked Multilayers Based on Thermo-Responsive PNIPAM-Grafted-Chitosan/Heparin to Tailor Their Physiochemical Properties and Biocompatibility. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 29550–29562.
- Sun, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Jiang, X.; Yang, L.; He, L.; Song, S.; Zhang, J.; Shen, J.; Qiao, T. Chitosan-Heparin Polyelectrolyte Multilayer-Modified Poly(vinyl alcohol) Vascular Patches based on a Decellularized Scaffold for Vascular Regeneration. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 2928–2934.
- Nguyen, M.T.N.; Tran, H.L.B. Heparinization of the bovine pericardial scaffold by layer-by-layer (LBL) assembly technique. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2022, 7, 100405.
- Kim, S.E.; Jeong, S.I.; Shim, K.M.; Jang, K.; Park, J.S.; Lim, Y.M.; Kang, S.S. In Vivo Evaluation of Gamma-Irradiated and Heparin-Immobilized Small-Diameter Polycaprolactone Vascular Grafts with VEGF in Aged Rats. Polymers 2022, 14, 1265.
