Shape memory elastomers have revolutionised the world since their introduction in the 20th century. The ability to tailor chemical structures to produce a family of materials in wide-ranging forms with versatile properties has propelled them to be ubiquitous.
1. Introduction
Smart materials, also known as intelligent or responsive materials, are a useful name for a broad group of different chemical substances. A common characteristic is that one or more properties may change significantly, even reversibly, in response to the specific stimulus input of preset form and extent over short or appropriate timescales and return to its original shape as the stimulus is taken away. The stimulus could be strain, stress, temperature, pressure, electric and magnetic fields, irradiation, or chemicals. Examples of smart materials include coatings that transform colour owing to the presence of chemicals, materials that have a shape memory at specific temperatures and paint that self-heals when it is scratched [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7]. Smart materials can acquire, convey, or process a stimulus and reply by creating a ‘useful’ effect. This ability offers opportunities for responsive materials in applications such as actuation, shape memory, and sensing in industries including biomedicine, aerospace, textiles, and so on [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14].
Shape memory polymers (SMPs) can memorise an original shape and can be tailor-made to some temporary shapes, whereas they naturally return to their original permanent shape from the temporary deformations upon simultaneous disclosure to various (even multiple) stimuli without additional mechanical effort. Typically, SMPs exhibit at least two phases: the first is a stable form that stabilises the SMP and is responsible for the retention of the original shape and the second that responds to the external trigger [
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25]. SMPs can be categorized into one of four types depending on their chemical structure: thermosets, rubbers, thermoplastics, and block copolymers. This classification decides the mechanisms of the shape memory of the SMP [
26,
27,
28,
29,
30].
Generally, SMPs are rigid and non-elastomeric at the application temperature [
31,
32,
33,
34]. In contrast, shape memory elastomers (SMEs) are softer and more elastomeric than SMPs since elastomers are polymers with the property of “elasticity”, typically having low tensile strength and high elongation at breakage. Therefore, elastomers can withstand high elastic deformation without rupture. Moreover, elastomers are relatively soft and deformable at ambient temperatures due to their low glass transition temperatures (
Tg) [
35,
36,
37,
38,
39]. Some key differences between polymers and elastomers are summarised in
Table 1. The high viscoelasticity of elastomers leads to a strong influence of ‘transformation temperature’ on the shape memory properties of an SME. The transformation temperature is typically 15–20 °C higher than the
Tg, though it may be in the vicinity of or even below that of the
Tg. When passing the
Tg from the glassy to the rubbery state, it is known that the network deformability goes through a maximum [
24]. A sample model of an SME is presented in
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Characteristic behaviour of shape memory elastomers: (i) deformation of the material transforms the original ‘equilibrium’ shape into a temporary shape, and (ii) external stimuli trigger and affect the return to the original shape from the temporary shape.
Table 1. Key differences between polymers and elastomers relevant to shape memory behaviour.
SMEs are elastic polymer networks, which are an appearing type of active elastomer, and have a dual-shape (or multi-shape) architecture. Generally, SMEs exhibit two types of structure: original shape and deformed (temporary) shape, which can be switched reversibly under specific conditions. A category of smart materials, SMEs react to external stimuli such as temperature, pressure, electromagnetic fields, chemicals (and pH), water, light, and so on. The responsive physical properties could be stiffness, shape, and damping, among others [
1,
9,
14,
24,
40,
41,
42].
Table 2 lists examples of SMEs, their chemical nature and potential triggers, and their applications studied in the literature.
Table 2. Example SMEs and their potential applications.
SMEs such as polyurethane and natural rubber typically comprise two regions: amorphous and crystalline. The amorphous region supports the stabilisation and retention of the original shape, and then the deformation of this region induces shape recovery. In contrast, the crystalline region is responsible for obstructing shape recovery until a critical condition is met [
23,
41,
56,
57].
Current applications of SMEs are principally in the consumer products sector (
Table 3). In the present era of health and fitness, comfort fitting is becoming an increasingly important consideration in choosing personal products such as clothing, footwear, insoles, and orthotic devices [
58]. For footwear, the demand for more comfort and functionality makes the characteristics of SMEs attractive and appealing to footwear design [
59]. In 2021, the International Trade Centre revealed that the sale of sports shoes had grown 31% compared to 2020, with the market worth USD 2320 million, and bedding sales had grown 17% compared to 2020, with the market worth USD 115 million. Moreover, for thermoplastic elastomers, a market research report by MarketsandMarkets™ revealed that the market was worth USD 5.1 billion in 2021, with a compound annual growth rate of 5.8% between 2021 and 2026 (
Table 3).
Table 3. Growth rate and value of market size of SME products.
|
Products
|
Growth Rate
|
Value (USD)
|
|
Sports shoes [60]
|
31%
|
2320 million
|
|
Bedding [61]
|
17%
|
115 million
|
|
Thermoplastic elastomers [62]
|
5.8%
|
5.1 billion
|
2. Thermodynamic Aspects Governing SMEs
From an elastomer transition state point of view, all movements of the elastomer molecules are fixed in the glassy region of the elastomer’s character (below its glass transition temperature). When the temperature is increased, the rotation surrounding the elastomer bonds also increases approaching the rubbery region, indicating that the elastomer molecules are close to entangled. Most of the macromolecules form a highly coiled conformation with the maximum entropy based on the Boltzmann equation [
63]. In the rubbery state, an elastomer with sufficient molecular weight can be stretched along the alignment of the external force. When the force is applied at a high speed or over short periods of time, the local entanglement of the elastomer molecules can block the movement of the molecule. Consequently, the elastomer will recover to its original shape once the applied force is taken away, exhibiting what is known as a viscoelastic response. In this way, the elastomer with a randomly coiled state possesses a type of memory of its initial state thereby exhibiting a memory effect. In contrast, when the applied force is applied at a low speed or over long periods of time, a relaxation process will take place. This relaxation is due to the slipping and disentangling of the elastomer chains from each other into new positions, which enables the molecules to form other random coil conformations with favourable entropy (
Figure 2). The described slipping or flow of the elastomer molecules under force can be prevented by crosslinking the molecules. Chemically crosslinked elastomers form insoluble elastomers; their structure is linked during the crosslinking process and then cannot be transformed afterwards [
64].
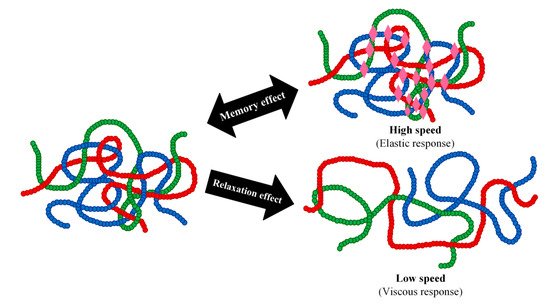
Figure 2. Entangled elastomer chains (with different colours illustrating different chains) respond to externally applied force in different ways. If we quickly stretch an elastomer, the entangled chains will make provisional knots that oppose the movement of the chains. The elastomer displays an elastic response (memory effect). On the other hand, if we slowly stretch the entangled chains, they have time to relax and restrain and rearrange themselves. The elastomer chains flow similar to a liquid, thereby showing a viscous response. Thus, the response of an elastomer to external stress is always the result of the balance between the rate of molecular agitation (which increases with high temperatures) and the rate of external stress (which increases with high frequencies or short times). These behaviours are the origin of one of the characteristic properties of polymers: the law of time–temperature superposition.
Therefore, molecular mobility is the main cause of the shape memory effect for polymers as mentioned before. For example, Oikonomou et al. (2021) [
65] studied the relationship between free volume and molecular mobility using the Couchman−Karasz and Gordon−Taylor equations, which are numerical approaches to describing molecular mobility in poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) blends. The results revealed that molecular mobility increased with the increasing free volume in the blend system.
During the transition of a shape memory elastomer from its original shape to a temporary shape and then its return to the original shape based on the stimuli-response environment, there are two types of phases or domains in the system [
66]. This is related to the phase diagrams, which are a graphical representation of the various material domains of stability at equilibrium. Phase diagrams are most commonly constructed in temperature–pressure–composition space, or Gibbs free energy composition space. Other coordinate systems, though not yet as widely used, may find increasing practical applications, especially in predicting changes in the internal structure of shape memory. A system that is equilibrated in some initial domain on the map and then placed in another domain with a different equilibrium structure, such as by simply changing its temperature, undergoes a series of microstructure transformations that take it towards its new equilibrium state. Microstructures with optimum properties can be selected by interrupting this process and quenching (i.e., rapid cooling) in the structure, which is then the state in which the shape memory elastomer is used.
A system is considered to be unary (single phase) if for the range of states under study it consists of a single chemical component. Each of the elements forms a unary system over its full range of existence. Molecular compounds such as synthetic polyisoprene (
cis–1,4–polyisoprene) may be treated as unary systems over most of the range of temperatures and pressures normally encountered in the laboratory. Under conditions in which it may decompose or change to form significant quantities of other molecules, it cannot be treated as a unary system. From a thermodynamic point of view, a system is homogeneous if it consists of a single phase. More specifically, when a system consists of a single phase, its intensive properties are similar. A heterogeneous system consists of more than one phase. Some of its intensive properties exhibit discontinuities at the boundaries between the phases in a heterogeneous system. In the case of SMEs, the thermodynamic equilibrium is not always reached with regard to compatibility (as opposed to miscibility). Miscibility always relates to small molecules. The definition of compatibility is linked to the properties of the mixture as natural latex (
cis–1,4–polyisoprene molecules with non–rubber components); if the response of a mixture to the input force is one model or one characteristic, the mixture is compatible. Therefore, thermodynamics is a significant property-governing character in the investigation and development of shape memory elastomers [
67].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/polym14163276