Indian Himalayan region (IHR) supports a wide diversity of plants and most of them are known for their medicinal value. Humankind has been using medicinal plants since the inception of civilization. Various types of bioactive compounds are found in plants, which are directly and indirectly beneficial for plants as well as humans. These bioactive compounds are highly useful and being used as a strong source of medicines, pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, food additives, fragrances, and flavoring agents. Apart from this, several plant species contain some toxic compounds that affect the health of many forms of life as well as cause their death. These plants are known as poisonous plants, because of their toxicity to both humans and animals.
- Indian Himalaya
- pharmaceuticals
- poisonous plants
- bioactive compounds
- toxicity
1. Introduction
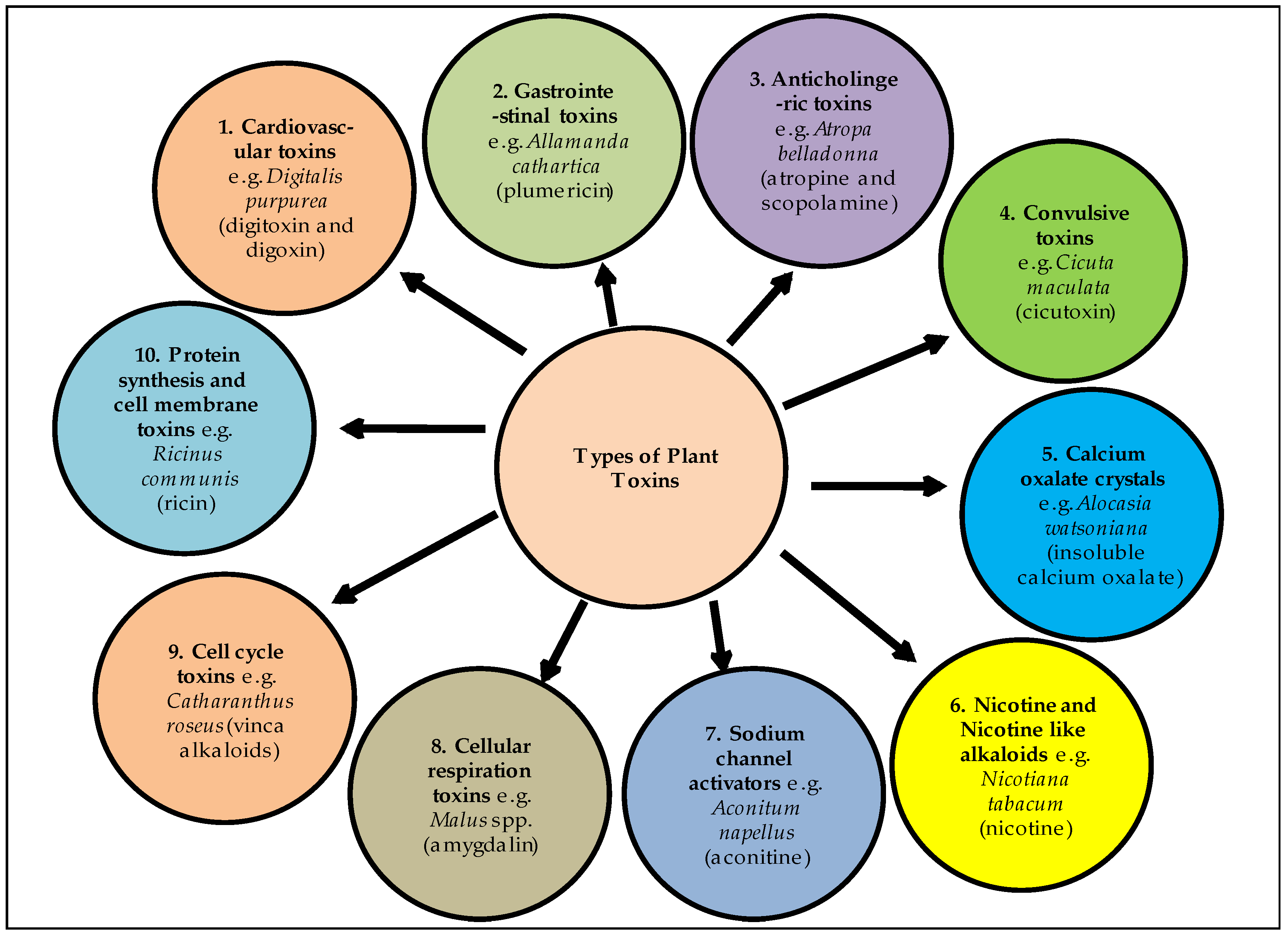
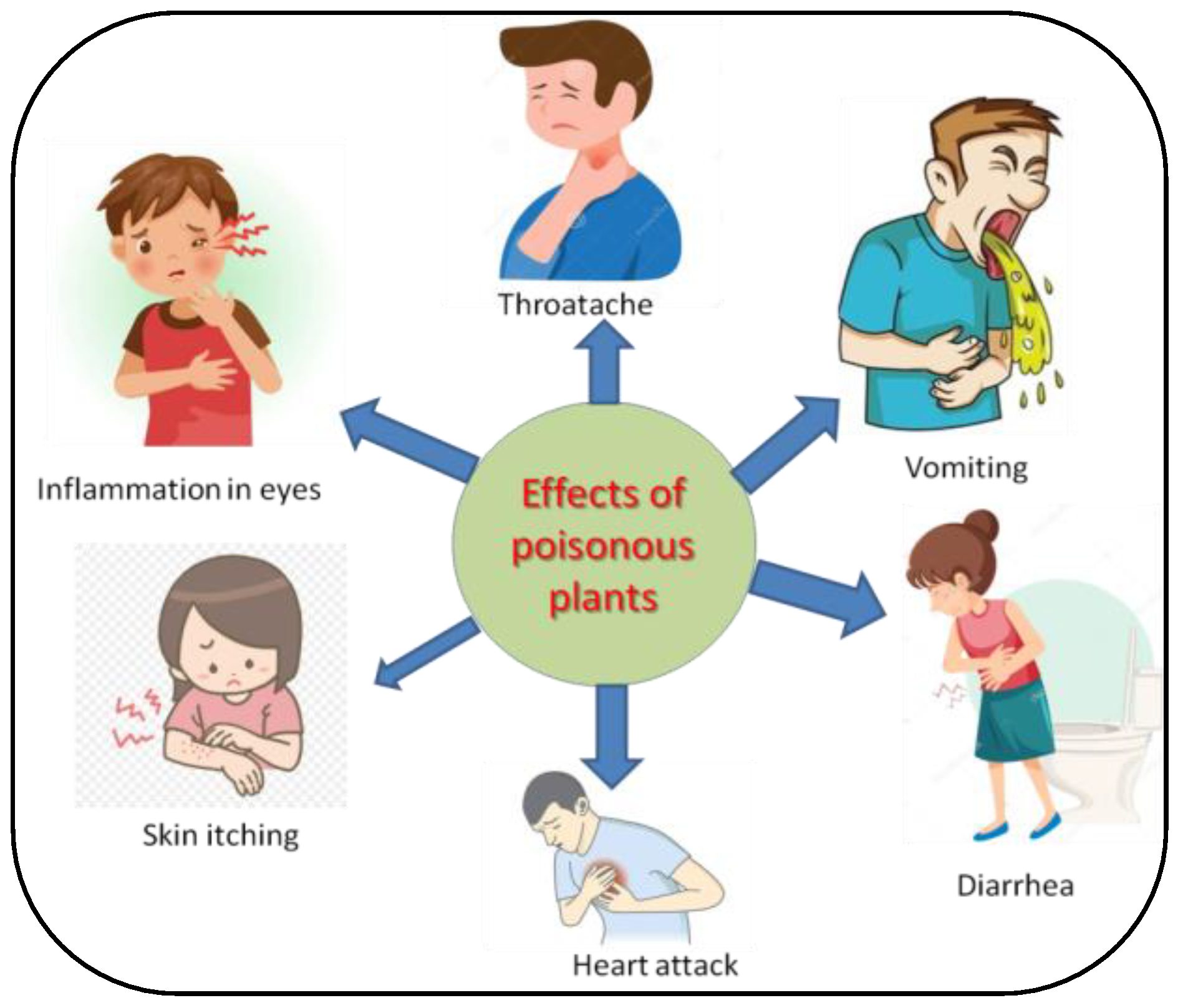
2. Poisonous Plants of Indian Himalaya
2.1. Abrus precatorius Linn.
2.2. Aconitum ferox Wall. Ex Ser. (Syn Aconitum Atrox Walp)
2.3. Aconitum hookeri Stapf.
2.4. Aconitum lethale Griff. (Syn Aconitum Balfourii Stapf.)
2.5. Aconitum napellus Linn.
2.6. Aconitum spicatum (Brühl) Stapf.
2.7. Aquilegia pubiflora Wall. Ex Royle
2.8. Aesculus indica (Wall. Ex Camb.) Hoof. f.
2.9. Cannabis sativa Linn.
| S. No. | Plant Species | Family | Toxic Compound | Symptoms | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Abrus precatorius Linn. | Fabaceae | Abrin | In humans, it causes vomiting, nausea, difficulty in swallowing, throat pain, high fever, weakness irritation in eyes, severe diarrhoea and even death. After ingestion by livestock it causes nasal discharge, salivation, severe diarrhoea, abortion and eventual death in pregnant animals. | [14] |
| 2 | Aconitum chasmanthum Stapf ex Holmes |
Ranunculaceae | Aconitine, diterpenoid alkaloid | Cardiotoxins and neurotoxins, skin contact cause numbness. | [27][58] |
| 3 | Aconitum ferox Wall. ex Ser. | Ranunculaceae | Pseudoaconitine and bikhaconitine | Cardio and neurotoxicity. | [38][39] |
| 4 | Aconitum lethale Griff. | Ranunculaceae | Pseudoaconitine and aconitine, balfourine | Cardio and neurotoxicity. | [43][44] |
| 5 | Aconitum laeve Royle | Ranunculaceae | 8-methyllycaconitine, 14-demethyllycaconitine, and N-deethyllycaconitine-N-aldehyde | Cardio and neurotoxicity. | [59][60] |
| 6 | Aesculus indica (Wall. Ex Camb.) Hoof. f. | Hippocastanaceae | Escin or aesculin | After consumption it causes gastro-intestinal problems, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, headache, fatigue and pruritus, while excessive consumption may cause paralysis and death. | [54] |
| 8 | Ageratum conyzoides Linn. | Asteraceae | Pyrrolizidine alkaloids | Due to contact with the plant, it causes skin problems such as as itching and rashes in susceptible individuals. Animals usually avoid browsing it, but accidental consumption causes very high fever, diarrhoea, anorexia and finally death within few hours. | [61] |
| 9 | Aloe vera (L.) Burm.f. | Xanthorrhoeaceae | Aloin or barbaloin an anthraquinone glycoside | Excessive consumption may cause nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, hyperkalemia and cardiac dysrhythmias. | [17] |
| 10 | Anagallis arvensis Linn. | Primulaceae | Primin | Consumption of the plant causes an acute headache, nausea, unconsciousness, anorexia, body pains, general weakness, bloody diarrhoea, sudden drop in body temperature and eventually death. | [14][62] |
| 11 | Aquilegia pubiflora Wall. ex Royle | Ranunculaceae | Isovitexin, isoorientin, vitexin, chlorogenic acid, orientin, cumeric acid, sinapic acid, ferulic acid | Cardiogenic toxins cause gastroenteritis and heart palpitations. | [63] |
| 12 | Argemone Mexicana Linn. | Papaveraceae | Sanguinarine and dihydrosanguinarine alkaloids present in Argemone oil. | Seeds are toxic and cause nausea, intense headaches, vomiting, severe diarrhoea, oedema of legs and feet. | [14][64] |
| 13 | Arisaema tortuosum (Wall.) Schott | Juncaceae | Raphide (Calcium oxalate) | Intake of tubers causes irritation of the skin and mucous membrane, mouth and body pain, slow breathing and suffocation. | [65] |
| 14 | Arisaema triphyllum (L.) Schott | Araceae | Raphide (Calcium oxalate) | Irritation of the skin and the mucous membrane and body pain. | [65] |
| 15 | Artemisia nilagirica (C.B. Clarke) Pamp. | Asteraceae | Lactones | Ingestion of large doses by animals causes headaches, nausea, vomiting and abortion of pregnant animals as a result of contraction of the uterus. | [14][66] |
| 16 | Atropa belladonna Linn. | Solanaceae | Atropine and Scopolamine | Plant ingestion may cause vomiting, nausea, diarrhea and abdominal cramps. | [17] |
| 17 | Calotropis procera (Aiton) W.T.Aiton | Asclepiadaceae | Uscharin, Calotoxin, Calotropin, Calactin, and Calotropage | The milky latex of this plant act as the skin and mucous membranes irritant, that causes blisters in both humans and animals. Accidental exposure to latex can cause eye swelling and redness. Both the leaves and the latex cause diarrhea in livestock and abortion of pregnant animals. | [14][67] |
| 18 | Caltha palustris Linn. | Ranunculaceae | Protoaneminin | Poison severity of this plant is low but this plant can be toxic, and ingesting large amounts of the plant’s leaves can lead to burning of the throat, vomiting, bloody diarrhea and gastric illness. Poisonous to human beings in mature stages. | [68][69] |
| 19 | Cannabis sativa Linn. | Cannabaceae | Cannabidiol, 9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) | Skin allergy. | [27] |
| 20 | Capsicum chinense Jacq. | Solanaceae | Capsaicin | Consuming excessive amounts may cause stomach irritation. | [17] |
| 21 | Cassia occidentalis Linn. | Fabaceae | Achrosin, aloe-emodin, emodin | Accidental intake of pods causes nausea, vomiting, restlessness, high fever, purging and ataxia in adult humans, whereas the accidental intake of seeds in childhood causes severe brain disease. In animals it causes gastroenteritis. | [14][70][71] |
| 22 | Celtis australis Linn. | Ulmaceae | Not reported | Regular consumption of leaves causes weakness and increase in body temperature in animals. | [14] |
| 23 | Chelidonium majus Linn. | Papaveraceae | Chelidonine | Ingestion causes the severe irritation of oral mucosa. | [14] |
| 24 | Colchicum luteum Baker | Liliaceae | Colchicine | Prolonged consumption may cause salivation with frothing in the mouth, colic, polydipsia, fetid diarrhea, dizziness and eventually death in a few cases. | [14] |
| 25 | Commelina benghalensis Linn. | Commelinaceae | n-octacosanol, n triacontanol, n-dotriacontanol | The plant is bitter in taste and after ingestion it causes stomach irritation in animals. | [14] |
| 26 | Convallaria majalis Linn. | Asparagaceae | Cardenolides | Neurotoxic, ingestion may cause cardiac dysrhythmia and hyperkalemia. | [27][72][73] |
| 27 | Cuscuta reflexa Roxb. | Cuscutaceae | Cuscutin, cuscutatin, beta-sitosterol, luteolin, bergenin and kaempferol | It causes vomiting, stomach ache, anorexia and purgation in animals, and its consumption can cause abortion in pregnant animals. | [14] |
| 28 | Daphne oleoides Schreb | Thymelaeaceae | Not reported | Berries and leaves consumption creates mouth sensation, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, restlessness, numbness and unconsciousness. | [14] |
| 29 | Datura innoxia Mill. | Solanaceae | Atropine | In humans the strong pungent smell of the leaves causes nausea and severe headaches. Contact with the leaves causes several skin problems. Unintentional consumption of the seeds by humans and animals causes dryness and sensation of the mouth and throat, stomach ache, numbness, anorexia, mydriasis, polydipsia and restlessness. | [14] |
| 30 | Datura stramonium Linn. | Solanaceae | Atropine | Accidental ingestion of the leaves or seeds by either humans or animals may cause drowsiness, dryness and sensation of the mouth and throat, bulging of the eyeballs, mydriasis, blurred vision, startling movements, convulsions, unconsciousness and finally death. | [14] |
| 31 | Delphinium brunonianum Royle | Ranunculaceae | Diterpenoid, alkaloids, Methyllycaco-ninite | Skin allergy. | [27] |
| 32 | Digitalis purpurea Linn. | Plantaginaceae | Digitoxin and Digoxin | Ingestion of the plant may cause nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, excessive urination, abnormal heartbeats and finally death. | [17] |
| 33 | Ephedra sinica Stapf. | Ephedraceae | Ephedrine | Plant ingestion may cause nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, hyperkalemia and cardiac dysrhythmias. | [17] |
| 34 | Eupatorium adenophorum Spreng. | Asteraceae | 2-deoxo-2-(acetyloxy)-9-oxoageraphorone, 9-oxo-10, 11-dehydroageraphorone, 10Hβ-9-oxoageraphorone, and 10Hα-9-oxo-ageraphorone | Ingestion of the plant may cause coughing, increased respiratory effort and weight loss in horses. | [74][75] |
| 35 | Gloriosa superba Linn. | Colchicaceae | Colchicine | Every part of this plant is poisonous, especially the tuberous rhizome, and after ingestion it may cause nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, numbness, burning in the throat and bloody diarrhea, which leads to dehydration. | [76] |
| 36 | Heracleum canescens Lindl. | Apiaceae | Furanocoumarins | Skin contact with furanocoumarins caused sensitization when exposed to sunlight or UV light. Furanocoumarins enter to the nucleus and binds with DNA and causes cell death and inflammation. | [77] |
| 37 | Hedera nepalensis K.Koch | Araliaceae | Saponins | When the skin comes in contact with the leaves it causes skin problems such as rashes and severe swelling in susceptible individuals. Consumption of leaves is poisonous for animals, causing paralysis and finally death. | [14] |
| 38 | Hyoscyamus niger Linn. | Solanaceae | Tropane alkaloids | Ingestion causes dry mouth, dysphonia, tachycardia, dysphagia, mydriasis, headache, urinary retention and confusion. | [27] |
| 39 | Hypericum perforatum Linn. | Hypericaceae | Hypericin, pseudohypericin, and hyperforin | Plant intake during flowering phases causes itching, photosensitization and inflammation of affected areas of skin, dry cough, trembling of limbs, extreme body pains, cold sweat and intense fatigue are some other symptoms after ingestion. | [14] |
| 40 | Ichnocarpus frutescens (L.) W.T. Aiton | Apocynaceae | Not reported | Consumption of leaves by animals’ causes indigestion, sour belching, vomiting and stomach irritation. | [14] |
| 41 | Lantana camara Linn. | Verbenaceae | Lantadenes | Jaundice, diarrhea, weakness, lethargy, loss of appetite, photosensitivity and hepatotoxicity in grazing animals. | [78] |
| 42 | Melia azedarach Linn. | Meliaceae | Tetranortriterpenes (meliatoxins) | Neurotoxin, gastrointestinal. | [27][79] |
| 43 | Nerium indicum Mill. | Apocynaceae | Oleandrin | Consumption of this plant causes mild to severe symptoms such as increased blood pressure and heart rate, sweating and vomiting. Its excessive consumption leads to heart attack and sudden death. | [14] |
| 44 | Physalis minima Linn. | Solanaceae | Solanine | Consumption of unripe berries causes abortion in pregnant animals. | [14] |
| 45 | Prunus persica (L.) Batsch | Rosaceae | Cyanide | Excessive consumption of the newly developed leaves affects brains and causes severe symptoms, i.e., seizures, loss of consciousness, abdominal pain, convulsions, choking, and finally death within a few hours in animals. | [14] |
| 46 | Ranunculus arvensis Linn. | Ranunculaceae | Protoanemonin | This plant may cause skin inflammation and injury of mucous membranes. The fresh leaf juice causes cracks, itching and sores in the skin of humans and animals. | [14][80] |
| 47 | Ranunculus sceleratus Linn. | Ranunculaceae | Protoanemonin | When the skin or mucosa comes in contact with the injured part of the plant, it causes itching and skin rashes and blisters. Poison ingestion may cause dizziness, nausea, vomiting, acute hepatitis, jaundice and finally paralysis. | [81][82] |
| 48 | Rhamnus triquetra Wall. | Rhamnaceae | Rhamnetin, quercitin and rhamnazin | Fruits and leaves of this species are highly toxic for livestock and excessive consumption affects the working ability of their brain resulting in loss of mental balance. | [14] |
| 49 | Rhododendron campanulatum D.Don | Ericaceae | Andromedotoxin | After ingestion of flowering buds and leaves by livestock it causes salivation, diarrhea, loss of energy and finally death. | [83][84] |
| 50 | Ricinus communis Linn. | Euphorbiaceae | Ricin | In humans, it causes mild to severe symptoms after ingestion, i.e., pain in throat, inflammation in eyes, high fever, profuse cold sweat, difficulty in swallowing, vomiting, diarrhoea, nausea, weakness, trembling of hands, inability to stand and finally death. | [17] |
| 51 | Solanum xanthocarpum Schrad. & H. Wendl. | Solanaceae | Solasonine and solamargine | After ingestion it causes headaches, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach ache, burning of the throat, itching, eczema, thyroid problems and pain and inflammation in the joints. | [85] |
| 52 | Taxus baccata Linn. | Taxaceae | Taxanes or Taxines, Taxol | Seeds and leaves are highly toxic, causing nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain bradycardia and respiratory muscle paralysis. | [86] |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/metabo12060540
References
- Husaini, D.C.; Bush, C.J.; Coc, I.; Guerra, E.; Perez, A.W.; Wu, C.-Y. Poisonous plants of Belize: A mini toxicological review. Adv. Tradit. Med. 2020, 1–11.
- Benzeid, H.; Gouaz, F.; Touré, A.H.; Bouatia, M.; Idrissi, M.O.B.; Draoui, M. Inventory of toxic plants in Morocco: An overview of the botanical, biogeography, and phytochemistry studies. J. Toxicol. 2018, 2018, 4563735.
- Khan, M.S.A.; Ahmad, I. Chapter 1—Herbal medicine: Current trends and future prospects. In New Look to Phytomedicine; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 3–13.
- Painuli, S.; Quispe, C.; Herrera-Bravo, J.; Semwal, P.; Martorell, M.; Almarhoon, Z.M.; Seilkhan, A.; Ydyrys, A.; Rad, J.S.; Alshehri, M.M. Nutraceutical Profiling, Bioactive Composition, and Biological Applications of Lepidium sativum L. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 2910411.
- Tewari, D.N. Report of the task force on conservation and sustainable use of medicinal plants. In Bulletin of Planning Commission; Government of India: New Delhi, India, 2000.
- Neupane, P.; Lamichhane, J. Estimation of total phenolic content, total flavonoid content and antioxidant capacities of five medicinal plants from Nepal. Vegetos 2020, 33, 360–366.
- Semwal, P.; Painuli, S. Antioxidant, antimicrobial, and GC-MS profiling of Saussurea obvallata (Brahma Kamal) from Uttarakhand Himalaya. Clin. Phytosci. 2019, 5, 12.
- Alonso-Amelot, M.E.; Oliveros, A.; Calcagno-Pisarelli, M.P. Phenolics and condensed tannins in relation to altitude in neotropical Pteridium spp.: A field study in the Venezuelan Andes. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2004, 32, 969–981.
- Semwal, P.; Painuli, S.; Tewari, D.; Bussmann, R.W.; Palni, L.M.S.; Thapliyal, A. Assesment of non-timber Brahma Kamal (Saussurea obvallata (DC.) Edgew.), an important Himalayan. Ethnobot. Res. Appl. 2020, 19, 1–15.
- Zlatić, N.M.; Stanković, M.S. Variability of secondary metabolites of the species Cichorium intybus L. from different habitats. Plants 2017, 6, 38.
- Semwal, P.; Painuli, S.; Painuli, K.M.; Antika, G.; Tumer, T.B.; Thapliyal, A.; Setzer, W.N.; Martorell, M.; Alshehri, M.M.; Taheri, Y. Diplazium esculentum (Retz.) Sw.: Ethnomedicinal, Phytochemical, and Pharmacological Overview of the Himalayan Ferns. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 1917890.
- Jamloki, A.; Bhattacharyya, M.; Nautiyal, M.; Patni, B. Elucidating the relevance of high temperature and elevated CO2 in plant secondary metabolites (PSMs) production. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07709.
- Al-Qura’n, S. Ethnobotanical survey of folk toxic plants in southern part of Jordan. Toxicon 2005, 46, 119–129.
- Bhatia, H.; Manhas, R.; Kumar, K.; Magotra, R. Traditional knowledge on poisonous plants of Udhampur district of Jammu and Kashmir, India. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 207–216.
- Mendieta, M.d.C.; Souza, A.D.Z.d.; Ceolin, S.; Vargas, N.R.C.; Ceolin, T.; Heck, R.M. Toxic plants: Importance of knowledge for realization of health education. J. Nurs. UFPE/Rev. Enferm. 2014, 8.
- Tamilselvan, N.; Thirumalai, T.; Shyamala, P.; David, E. A review on some poisonous plants and their medicinal values. J. Acute Dis. 2014, 3, 85–89.
- Banasik, M.; Stedeford, T. Plants, Poisonous (Humans). In Encyclopedia of Toxicology, 3rd ed.; Wexler, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 970–978.
- Serrano, R. Toxic plants: Knowledge, medicinal uses and potential human health risks. Environ. Ecol. Res. 2018, 6, 487–492.
- Habermehl, G.G. Highlights on Plant Toxins in Toxicon; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 44, pp. 341–344.
- Harvey, A.; Bradley, K.; Cochran, S.; Rowan, E.; Pratt, J.; Quillfeldt, J.; Jerusalinsky, D. What can toxins tell us for drug discovery? Toxicon 1998, 36, 1635–1640.
- Katewa, S.; Galav, P.; Nag, A.; Jain, A. Poisonous plants of the southern Aravalli hills of Rajasthan. Indian J. Tradit. Knowl. 2008, 7, 269–272.
- Ekor, M. The growing use of herbal medicines: Issues relating to adverse reactions and challenges in monitoring safety. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 4, 177.
- Petrovska, B.B. Historical review of medicinal plants’ usage. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2012, 6, 1.
- Coleman, J.J.; Ferner, R.E.; Evans, S.J.W. Monitoring for adverse drug reactions. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 61, 371–378.
- Casarett, L.J.; Klaassen, C.D.; Watkins, J.B. Casarett and Doull’s Essentials of Toxicology; McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.: New York, NY, USA, 2003.
- Huai, H.; Xu, J. Indigenous knowledge: An inexhaustible “information bank” for toxin research. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2000, 38, 745–746.
- Gupta, S.M.; Manikyaprabhu, K.; Dwibedi, S. Himalayan toxic plants of defense importance. Acta Sci. Med. Sci. 2018, 2, 44–48.
- Maharani, B.; Vijayakumari, N. Profile of poisoning cases in a Tertiary care Hospital, Tamil Nadu, India. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 3, 91.
- Unnikrishnan, B.; Singh, B.; Rajeev, A. Trends of acute poisoning in south Karnataka. Kathmandu Univ. Med. J. (KUMJ) 2005, 3, 149–154.
- Haritha, C.; Khan, S.; Manjusha, K.; Banu, A. Toxicological aspects of common plant poisoning in ruminants. Indian Farmer 2019, 6, 812–822.
- Gupta, V.K.; Singh, G.D.; Singh, S.; Kaul, A. Medicinal Plants: Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Therapeutics; Daya Publishing House: New Delhi, India, 2010; Volume 1.
- Bhatia, M.; Siddiqui, N.; Gupta, S. Abrus precatorius (L.): An evaluation of traditional herb. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 3, 3296–3315.
- Narayanan, S.; Surendranath, K.; Bora, N.; Surolia, A.; Karande, A.A. Ribosome inactivating proteins and apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 1324–1331.
- Karthikeyan, A.; Amalnath, S.D. Abrus precatorius poisoning: A retrospective study of 112 patients. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. Peer-Rev. Off. Publ. Indian Soc. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 21, 224.
- Polunin, O.; Stainton, A. Flowers of the Himalaya; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1984.
- Ghimire, S.K.; Sapkota, I.; Oli, B.; Parajuli, R. Non-Timber Forest Products of Nepal Himalaya: Database of Some Important Species Found in the Mountain Protected Areas and Surrounding Regions; WWF Nepal; WWF: Gland, Switzerland, 2008; ISBN 978-99946-837-9-6.
- Agnihotri, P.; Husain, D.; Katiyar, P.; Husain, T. Notes on the typification of four Himalayan aconites. Kew Bull. 2016, 71, 1–7.
- Hanuman, J.B.; Katz, A. Isolation and identification of four norditerpenoid alkaloids from processed and unprocessed root tubers of Aconitum ferox. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 801–809.
- Hanuman, J.B.; Katz, A. Isolation of quinolinones from ayurvedic processed root tubers of Aconitum ferox. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1993, 3, 227–231.
- Rokaya, M.B.; Münzbergová, Z.; Timsina, B. Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants from the Humla district of western Nepal. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 130, 485–504.
- Regmi, P.; Ravikrishna, S.; Bhat, S.; Hebbar, C. Ethno-botanical and Toxicological comparison on varieties of Vatsanabha (Aconitum ferox Wall.) available in Nepal. Int. J. Ayurveda Tradit. Med. 2020, 2, 3–9.
- Kalita, B.C.; Gogoi, B.J.; Hui, P.K. Diversity and Traditional Uses of Some Poisonous Plants of Arunachal Pradesh. Int. J. Adv. Res. Innov. Ideas Educ. 2017, 3, 57–64.
- Sharma, E.; Gaur, A. Aconitum balfourii Stapf: A rare medicinal herb from Himalayan Alpine. J. Med. Plants Res. 2012, 6, 3810–3817.
- Khetwal, K.; Joshi, B.; Desai, H.; William Pelletier, S. Alkaloids of Aconitum balfourii Stapf. Heterocycles 1992, 34, 441–444.
- Khetwal, K.; Pande, S. Constitutens of high altitude himalayan herbs part XV: A new norditerpenoid alkaloid from the roots of Aconitum balfourii. Nat. Prod. Res. 2004, 18, 129–133.
- Khetwal, K.S.; Desai, H.; Joshi, B.S.; Pelletier, S.W. Norditerpenoid alkaloids from the aerial parts of Aconitum balfourii Stapf. Heterocycles 1994, 38, 833–842.
- Sher, H.; Jan, H.A.; Ur Rahman, I.; Hussain, W.; Kunwar, R.M.; Bussmann, R.W.; Paniagua-Zambrana, N.Y. Aconitum balfourii Stapf. Aconitum ferox Wall. ex. Ser. Aconitum heterophyllum Wall. ex Royle Aconitum laeve Royle Aconitum naviculare (Brühl) Stapf. Aconitum spicatum Stapf. Aconitum violaceum Jacq. ex Stapf var. violaceum Ranunculaceae. In Ethnobotany of the Himalayas; Kunwar, R.M., Sher, H., Bussmann, R.W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switerland, 2021; pp. 139–154.
- Agnihotri, P.; Husain, D.; Husain, T. Assessment of diversity, endemism and distribution of the genus Aconitum Linnaeus (Ranunculaceae) in India. Pleione 2015, 9, 95–102.
- Gao, L.M.; Wei, X.M.; Yang, L.; Gao, L. Two new norditerpenoid alkaloids from Aconitum spicatum Stapf. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2005, 16, 475–478.
- Manandhar, N. Ethnobotany of Jumla District, Nepal. Int. J. Crude Drug Res. 1986, 24, 81–89.
- Aziz, N.; Khan, M.N.; Ul Haq, F.; Ahmed, F.; Ali, A.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Musharraf, S.G. Erythroid induction activity of Aquilegia fragrans and Aquilegia pubiflora and identification of compounds using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2021, 33, 101227.
- Jan, H.; Usman, H.; Shah, M.; Zaman, G.; Mushtaq, S.; Drouet, S.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H. Phytochemical analysis and versatile in vitro evaluation of antimicrobial, cytotoxic and enzyme inhibition potential of different extracts of traditionally used Aquilegia pubiflora Wall. Ex Royle. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 1–19.
- Kaur, L.; Joseph, L.; George, M. Phytochemical analysis of leaf extract of Aesculus indica. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 3, 232–234.
- Yadav, N.; Singh, A.P.; Rana, A.C.; Kumar, S.; Kaur, P.; Singh, J.; Jangra, A.; Kumar, D. Aesculus indica: An updated review on its pharmacognosy, phytochemistry and pharmacological profile. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2022, 9, 125–135.
- Plants of the World Online, w.p.o. Available online: www.plantoftheworldonline.org (accessed on 22 May 2022).
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Guo, H.; Trindade, L.M.; Salentijn, E.M.J.; Guo, R.; Guo, M.; Xu, Y.; Yang, M. Latitudinal Adaptation and Genetic Insights Into the Origins of Cannabis sativa L. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1876.
- Breijyeh, Z.; Jubeh, B.; Bufo, S.A.; Karaman, R.; Scrano, L. Cannabis: A toxin-producing plant with potential therapeutic uses. Toxins 2021, 13, 117.
- Ameri, A. The effects of Aconitum alkaloids on the central nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 1998, 56, 211–235.
- Shaheen, F.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, M.T.H.; Jalil, S.; Ejaz, A.; Sultankhodjaev, M.N.; Arfan, M.; Choudhary, M.I. Alkaloids of Aconitum laeve and their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and tyrosinase inhibition activities. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 935–940.
- Ulubelen, A.; Mericli, A.; Mericli, F.; Kolak, U.; Arfan, M.; Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, H. Norditerpenoid alkaloids from the roots of Aconitum leave Royle. Pharmazie 2002, 57, 427–429.
- Diallo, A.; Eklu-Gadegbeku, K.; Amegbor, K.; Agbonon, A.; Aklikokou, K.; Creppy, E.; Gbeassor, M. In vivo and in vitro toxicological evaluation of the hydroalcoholic leaf extract of Ageratum conyzoides L. (Asteraceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 1214–1218.
- Kotb, F.T. Medicinal Plants in Libya; Arab Encyclopedia House: Beirut, Lebanon, 1985; p. 830.
- Tilford, G.L. Edible and Medicinal Plants of the West; Mountain Press Publishing: Missoula, MT, USA, 1997.
- Shelar, M.; Bafna, A.; Wahile, A.; Tupkari, S. Evaluation of edible oils for Argemone mexicana seed oil adulteration. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 927–936.
- Ali, H.; Yaqoob, U. Traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicity of Arisaema (Areaceae): A review. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2021, 45, 1–19.
- da Silva, J.A.T. Mining the essential oils of the Anthemideae. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 3, 706–720.
- Iyadurai, R.; Gunasekaran, K.; Jose, A.; Pitchaimuthu, K. Calotropis poisoning with severe cardiac toxicity—A case report. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2020, 9, 4444.
- Plants, N. Plant Database. Agalinis purpurea, A. setacea, A. strictifolia, A. heterophylla, Perideridia americana, Osmorhiza longistylis, Taenidia integerrima. 2014. Available online: https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=SOSE3 (accessed on 22 May 2022).
- Liakh, V.; Konechna, R.; Mylyanych, A.; Zhurakhivska, L.; Hubytska, I.; Novikov, V. Caltha palustris. Analytical overview. Sci. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 2020, 51–56.
- Alves, A. Pharmacological study of the root of Cassia occidentalis. Anals Fac Farm. Porto 1965, 24, 65–119.
- Vashishtha, V.; Nayak, N.; Jacob John, T.; Kumar, A. Recurrent annual outbreaks of a hepato-myo-encephalopathy syndrome in children in western Uttar Pradesh, India. Indian J. Med. Res. 2007, 125, 523–533.
- Knight, A. A Guide to Poisonous House and Garden Plants; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007.
- Moxley, R.; Schneider, N.; Steinegger, D.; Carlson, M. Apparent toxicosis associated with lily-of-the-valley (Convallaria majalis) ingestion in a dog. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1989, 195, 485–487.
- Bhardwaj, R.; Singh, A.; Sharma, O.P.; Dawra, R.K.; Kurade, N.P.; Mahato, S.B. Hepatotoxicity and cholestasis in rats induced by the sesquiterpene, 9-oxo-10, 11-dehydroageraphorone, isolated from Eupatorium adenophorum. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2001, 15, 279–286.
- Oelrichs, P.B.; Calanasan, C.A.; Macleod, J.K.; Seawright, A.A.; Ng, J.C. Isolation of a compound from Eupatorium adenophorum (Spreng.) causing hepatotoxicity in mice. Nat. Toxins 1995, 3, 350–354.
- George, P. Death related to herbal therapy for joint pains–A rare case of Gloriosa superba poisoning. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2011, 5, 379–380.
- Del Río, J.A.; Díaz, L.; García-Bernal, D.; Blanquer, M.; Ortuno, A.; Correal, E.; Moraleda, J.M. Furanocoumarins: Biomolecules of therapeutic interest. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2014, 43, 145–195.
- Negi, G.; Sharma, S.; Vishvakarma, S.C.; Samant, S.S.; Maikhuri, R.K.; Prasad, R.C.; Palni, L. Ecology and use of Lantana camara in India. Bot. Rev. 2019, 85, 109–130.
- Oelrichs, P.B.; Hill, M.W.; Vallely, P.J.; MacLeod, J.K.; Molinski, T.F. Toxic tetranortriterpenes of the fruit of Melia azedarach. Phytochemistry 1983, 22, 531–534.
- Sedivy, C.; Piskorski, R.; Müller, A.; Dorn, S. Too low to kill: Concentration of the secondary metabolite ranunculin in buttercup pollen does not affect bee larval survival. J. Chem. Ecol. 2012, 38, 996–1002.
- Lewis, R.A. Lewis’ Dictionary of Toxicology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998.
- Yilmaz, B.; Yilmaz, B.; Aktaş, B.; Unlu, O.; Roach, E.C. Lesser celandine (pilewort) induced acute toxic liver injury: The first case report worldwide. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 285.
- Rai, I.D.; Singh, G.; Rawat, G. Plants of Kedarnath Wildlife Sanctuary, Western Himalaya: A Field Guide; Bishen Singh Mahendra Pal Singh: Dehradun, India, 2017.
- Bhattacharyya, D. Rhododendron species and their uses with special reference to Himalayas—A review. Assam Univ. J. Sci. Technol. 2011, 7, 161–167.
- Siddiqui, B.; Siddiqui, S.; Faizi, S. Studies in the Chemical Constituents of the Fresh Berries of Solanum xanthocarpum Schrad. and Wendle. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2011, 5, 99.
- Willaert, W.; Claessens, P.; Vankelecom, B.; Vanderheyden, M. Intoxication with Taxus baccata: Cardiac arrhythmias following yew leaves ingestion. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2002, 25, 511–512.
