Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Biology
Worsening renal function is associated with poor outcomes in heart failure and often accompanies the initiation and up-titration of guidelines-directed heart failure therapy.
- cardiorenal syndrome
- heart failure
- chronic kidney disease
1. Introduction
Many patients with heart failure (HF) suffer from chronic kidney disease (CKD), which not only worsens prognosis but also complicates guidance of medical HF therapy [1,2]. Initiation or up-titration of guidelines-directed HF therapy often goes along with a decrease in renal function [3,4,5,6,7]. This interaction is unpleasant from a clinical point of view; however, HF therapies such as renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS) antagonists largely improve the prognosis of HFrEF and slow the progression of renal dysfunction in the medium and long term.
Most pivotal randomized-controlled trials testing drugs for the treatment of HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) excluded patients with more severe chronic kidney disease (CKD). By consequence, evidence guiding implementation of HF drugs in patients with more severe CKD is limited (Table 1). Therefore, most clinicians are watchful when implementing HF drugs that interact with renal function, and are often inert with respect to increasing the guidelines-recommended drugs to the target dose. Figure 1 illustrates the mechanisms of heart failure and evidence-based treatments for renal function in HFrEF.
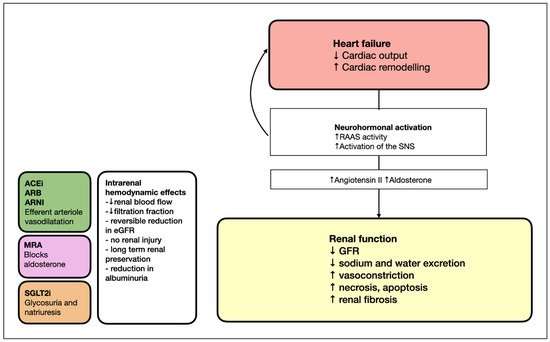
Figure 1. Mechanisms of heart failure and evidence-based treatments for renal function in HFrEF. ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; ARNI, angiotensin receptor blocker–neprilysin inhibitor; GFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; MRA, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; RAAS, renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system; SGLT2i, sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor; SNS, sympathetic nervous system.
Table 1. Recommendation of drug dosing in HFrEF in patients without and with CKD, based on available evidence and the SWISS medicinal product licensing body (SWISSMEDIC).
| Drug Class | Medical Therapy | Target Daily Dose in Heart Failure Clinical Trials | Drug Dose Recommendations in Advanced CKD |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACE inhibitors (ACEis) | Enalapril | 20 mg BD | Maximum dose of 5 mg D for enalapril |
| Lisinopril | 50 mg D | Maximum dose of 5 mg D for lisinopril | |
| Captopril | 75 mg BD | Maximum dose of 6.25 mg D for captopril | |
| Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs) | Candesartan | 32 mg D | Candesartan untested in eGFR < 15 mL/min |
| Valsartan | 160 mg BD | Valsartan untested in eGFR < 10 mL/min | |
| Angiotensin Receptor–Neprilysin Inhibitor (ARNI) | Sacubritril/Valsartan | 200 mg BD | No adjustment recommended |
| Steroidal Mineralocorticoid receptor Antagonist (MRA) | Spironolactone | 50 mg D | Contraindicated with eGFR < 30 mL/min |
| Eplerenone | 50 mg D | Contraindicated with eGFR < 30 mL/min | |
| Nonsteroidal Mineralocorticoid Antagonist | Finerenon | 10 mg D | Not recommended with eGFR < 25 mL/min |
| Beta-blockers | Carvedilol | 50 mg BD | No adjustment recommended for carvedilol, cardvedilol, or bisoprolol |
| Bisoprolol | 10 mg D | ||
| Metoprolol | 200 mg D | ||
| Sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor (SGLT2i) | Dapaglifozin | 10 mg D | No adjustment recommended |
| Empaglifozin | 10 mg D | Not recommended with eGFR < 20 mL/min (results of the EMPA-Kidney pending) | |
| Practice guidelines recommend up-titration of evidence-based medications at trial doses for all HF patients, as tolerated. Close monitoring of blood pressure, serum potassium and kidney function is recommended | |||
ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; ARNI, angiotensin receptor blocker–neprilysin inhibitor; BD, twice a day; CKD, chronic kidney disease; D, daily; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; MRA, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; SGLT2i, sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor.
2. Chronic Kidney Disease in Heart Failure—The Real-World Data
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the most prevalent comorbidity in HF and is associated with a high risk for all-cause mortality and HF hospitalization [5,9,10]. At least 60% of HF patients have mild renal dysfunction, and around 20% have moderate-to-severe kidney dysfunction [11]. In addition, CKD is a key risk factor of suboptimal use of guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) as shown in the in the CHAMP-HF registry (Change the Management of Patients With Heart Failure). CKD was the most frequent reason for the absence of evidence-based therapy up-titration in HFrEF patients in the BIOSTAT-CHF trial [12,13,14]. Furthermore, the TRANSLATE-HF trial recently showed that GDMT was applied less frequently with increasing severity of CKD. In fact, among patients with HFrEF, treatment with three classes of GDMT was used in only 15% and 5% when the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was 30 to 44 mL/min/1.73 m2 or <30 mL/min/1.73 m2, respectively [15]. Patients with HFrEF and CKD are therefore at double risk of having an adverse prognosis.
Due to strict eligibility criteria for HF patients included in randomized controlled trials (RCTs), study results are often considered to be of limited applicability for real-world HF patients, while registry data are thought to map the typical HF patient more accurately. However, recent results obtained from a retrospective observational study including 17,106 de novo HFrEF patients indicate that higher treatment intensity is associated with lower mortality and lower rehospitalization risk [16]. Moreover, triple GDMT HF therapy at discharge was associated with a 32% decrease in the incidence of death or rehospitalization. These results extend the applicability of the RCT findings to HF patients with a more severe comorbidity burden, as 54% of the study participants had diabetes and 34% had CKD.
3. Definition of Worsening Kidney Function
Many HF studies have defined worsening renal function (WRF) as a decrease in the eGFR, but there is great variability in the definition of WRF, and the biomarkers used for grading severity of WRF vary (serum creatinine, cystatin C or estimated GFR). This inhomogeneity makes it difficult to compare studies with each other. For example, when WRF is defined by the increase in absolute creatinine, it inhomogeneously weighs the percentage of worsening of renal function between patients with mild and moderate-to-severe CKD. Nonetheless, there is a general consensus that WRF is an increase of 26.5 µmol/L of serum creatinine, as this increase is associated with a significant elevation in the risk of mortality and morbidity [17,18].
4. Antagonists of the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System (RAAS)
4.1. Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs)
4.1.1. ARB in HFrEF with Kidney Dysfunction
The multicenter Valsartan in Heart Failure Trial (Val-HeFT) study evaluated the effect of valsartan on the incidence of all-cause mortality and morbidity among patients with HFrEF (left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) < 40%) when added to standard-of-care HF therapy [19]. Valsartan treatment reduced the incidence of the primary combined endpoint by 13.2%, and this improvement was primarily due to a lower number of patients hospitalized for treatment of HF. HFrEF patients with a creatinine level > 220 µmol/L were excluded from study participation; however, in patients with renal impairment at baseline (n = 2346; 46.8% of the study participants), the benefit of valsartan treatment was even more pronounced, with a 24% reduction in the incidence of the primary endpoint (hazard ratio (HR) 0.76, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.66–0.88; p = 0.0002).
Among study participants with WRF during the observation time, 8.6% had a decrease in the eGFR > 20% within 1 month after randomization while 91.4% had a decrease in the eGFR ≤ 20%. In study, for participants whose eGFR decreased while on valsartan therapy, the risk for the combined endpoint was significantly reduced (HR 0.83, 95%CI 0.75–0.92; p = 0.0005), and this benefit was also present in study participants whose renal function declined rapidly (HR 0.63, 95%CI 0.45–0.89; p = 0.0086). Altogether, valsartan decreased the incidence of the combined endpoint independent of pre-existing kidney dysfunction or WRF [4]. Nonetheless, patients with early worsening of renal function had a higher risk of cardiovascular (CV) death and hospitalization for HF compared with those without early worsening renal function (HR 1.44, 95%IC 1.21–1.71; p < 0.0001).
Corresponding observations were reported from the CHARM-Alternative trial testing in HFrEF patients the efficacy of candesartan for the reduction in the composite endpoint of cardiovascular mortality and hospitalizations for HF. Overall, candesartan reduced the incidence of the composite primary endpoint by 23% (HR 0.77, 95%CI 0.67–0.8; p = 0.0004) [20]. As in the Val-HeFT study, the incidence of the combined endpoint was increased in study participants with WRF (odds ratio (OR) 2.29, 95%CI 1.75–3.00; p < 0.001). However, the incidence of the combined endpoint was numerically less important in the candesartan treatment group (HR 1.29, 95%CI 0.96–1.73; p = 0.71) when compared to patients with WRF in the placebo group (HR 1.51, 95%CI 1.02–2.22; p = 0.039). In summary, results from the Val-HeFT as well as the CHARM-Alternative trials indicate beneficial effects of antagonist of the angiotensin II receptor in HFrEF patients with or without renal dysfunction at baseline or WRF during the course of the study.
4.1.2. ARB in HFpEF with Kidney Dysfunction
The CHARM-Preserved trial included 3023 HF patients in New York Heart Association (NYHA) Class II-IV with an LVEF ≥ 40% and previous hospitalization [21]; 64% of patients had hypertension, and 28% had diabetes mellitus. The difference in the primary outcome, a composite of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for HF, failed to reach statistical significance (HR 0.89, 95%CI 0.77–1.03; p = 0.12). The results nonetheless suggest that the use of ARBs reduces recurrent hospitalizations for HF; however, since the primary endpoint of the study was not significantly changed, the statistical robustness of a hierarchical secondary endpoint remains questionable.
The Irbesartan in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction study (I-PRESERVE) compared irbesartan versus a placebo in 4133 patients with HFpEF, of whom 88% had hypertension and 27% diabetes mellitus [22]. Unfortunately, I-PRESERVE lacked statistical power due to a high rate of study discontinuation (34%) and the concomitant use of ACE inhibitors in 39% of patients in the placebo group and 40% of patients in the irbesartan group. Therefore, a firm conclusion regarding the efficacy of irbesartan in patients with HFpEF is not possible. In this study, the incidence of WRF at 8 weeks was 6.4% (n = 229), and patients randomized to irbesartan treatment experienced WRF more often when compared with patients in the placebo group (8.4% vs. 4.3%, OR 2.07; 95%CI 1.56–2.75; p < 0.001). Worth noting is that WRF after initiation of irbesartan treatment in HFpEF patients was associated with excess risk in the unadjusted analysis but not in the adjusted analysis. This observation differed according to WRF in the test group of the Val-HeFT or the CHARM-Alternative trial, where candesartan lowered the risk when compared to WRF in the placebo group [23]. However, these results mandate thoughtful interpretation since the primary endpoint of the I-Preserve trial was negative, and the secondary endpoints therefore cannot claim a causal relationship.
Nonetheless, irbesartan showed beneficial effects in patients with diabetic kidney disease (DKD) as suggested by the Irbesartan Diabetic Nephropathy (IDN) trial. This trial included 1715 participants with type 2 diabetes, hypertension, urine protein excretion ≥ 0.9 g/day and mean serum creatinine of 150 micromol/L. Patients were randomly assigned to irbesartan (75 to 300 mg once daily), amlodipine (2.5 to 10 mg once daily) or a placebo [24]. At 2.6 years, the likelihood of a doubling of serum creatinine was lower in patients with irbesartan (17%) compared with study participants in the amlodipine (25%) or placebo groups (24%). In addition, irbesartan numerically reduced the incidence of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) (14 vs. 18% for amlodipine and placebo, respectively). In this study, irbesartan was shown to be effective in protecting against the progression of nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes, independent of the action of blood pressure reduction. The IDN trial did not include patients with symptomatic HF, but type 2 diabetes mellitus and HF often coexist, with diabetes mellitus occurring in ≈25% of patients with chronic HF [25]. In fact, in the IDN trial, secondary endpoints, including the incidence of heart failure, did not differ between treatment groups, suggesting that this trial enrolled patients with asymptomatic stage B HF at baseline.
Altogether, these results indicate that irbesartan is appropriate for the management of DKD, like other RAAS-inhibiting molecules, and may not be harmful in patients with HFpEF.
4.2. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACEIs)
4.2.1. ACEI in HFrEF with Kidney Dysfunction
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors are widely used for treatment of HF, and remain the cornerstone treatment for patients with HFrEF despite the availability of other vasodilator molecules. Among 6797 patients randomized to enalapril or a placebo in the Studies Of Left Ventricular Dysfunction (SOLVD) trial, 9.5% experienced early WRF [3]. Early WRF was associated with increased mortality in the placebo group (HR 1.2, 95%CI 1.0–1.4; p = 0.037) but not in the enalapril treatment group. Furthermore, a survival benefit was maintained with enalapril therapy in patients remaining on the study drug despite early WRF. This mortality benefit was also demonstrated in a post hoc analysis of SOLVD focusing on HF and more severe CKD [26]. In CONSENSUS (Cooperative North Scandinavian Enalapril Survival Study), 11% of patients assigned to enalapril experienced doubling of serum creatinine [27]. The doubling of serum creatinine occurred early in most study participants, and serum creatinine returned back to within 30% of baseline values in the majority of these patients [28]. Altogether, these observations provide consistent evidence that ACEI in HFrEF patients preserves a beneficial effect even in the context of WRF.
4.2.2. ACEI in HFpEF with Kidney Dysfunction
The Perindopril in Elderly People with Chronic Heart Failure (PEP-CHF) study with its 850 study participants remains the largest trial to date investigating the use of ACE inhibitors in HFpEF. The trial included patients older than ≥70 years with an LVEF ≥ 45% [29]. The study failed to meet sufficient power for its primary endpoint, which was a composite of all-cause mortality and HF hospitalization due to a lower event rate than expected. However, the PEP-CHF study showed a significant reduction in HF hospitalization within the first year, but this beneficial result was not maintained for the entire duration of follow-up. Only 25% of the study participants had a serum creatinine level > 110 µmol/L because patients with a serum creatinine level > 200 µmol/LL were excluded from study participation. Given the relatively small number and the overall neutral effect of perindopril treatment, it remains unclear whether there is a benefit of ACEIs in HFpEF patients with kidney dysfunction.
4.2.3. ACEI in Diabetic Kidney Disease
The best data supporting ACEI in patients with type 1 diabetes come from a trial including 409 adult participants with a mean urine protein excretion ≥ 500 mg/day and a serum creatinine level ≤ 221 micromol/L [30]. Patients were randomly assigned to captopril (25 mg three times daily) or a placebo. At 3 years, captopril reduced the rate of death or ESKD (11% vs. 21%) and reduced the likelihood of doubling of serum creatinine (12% vs. 21%).
4.3. Angiotensin Receptor–Neprilysin Inhibitor (ARNI)
4.3.1. ARNI in HFrEF with Kidney Dysfunction
In the PARADIGM-HF study (Prospective Comparison of ARNi with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor to Determine the Impact on Global Mortality and Morbidity in), sacubitril–valsartan, an angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitor, was shown to be superior to enalapril in reducing the incidence of the primary composite endpoint of hospitalization for CV mortality and hospitalization for worsening HF. All-cause mortality and a decline in renal function, among others, were prespecified secondary endpoints [31]. On the basis of the results of the PARADIGM-HF study, it is recommended that an ACE-I (or ARB) is replaced by sacubitril–valsartan in ambulatory HFrEF patients when patients remain symptomatic on ACEI or ARB treatment. Symptomatic HF was essentially defined by elevated brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) concentrations, and patients with an eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 were not included. In a prespecified subgroup analysis of PARADIGM-HF, treatment with sacubitril–valsartan slowed the decrease in the eGFR both overall and in patients with CKD while modestly increasing albuminuria [32].
4.3.2. ARNI in HFpEF with Kidney Dysfunction
In the PARAGON-HF trial (LVEF ≥ 45%; n = 4796), treatment with sacubitril–valsartan compared with valsartan was associated with a numerically modest but nonsignificant reduction in the composite primary endpoint total hospitalizations for HF and cardiovascular death (RR 0.87; 95% CI 0.75 to 1.01; p = 0.06). A prespecified analysis of patients enrolled in this trial showed that the combined endpoint of serious adverse renal outcomes (defined as either a ≥50% reduction in the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) or progression to end-stage renal disease) was reduced by sacubitril–valsartan regardless of baseline renal function [33]. In addition, a subgroup analysis showed that addition of sacubitril–valsartan rather than valsartan alone appears to slow progress of renal dysfunction when added to mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA). Moreover, this combination was not associated with an increase in severe hyperkalemia. These data support the potential added value of sacubitril–valsartan in combination with MRA in patients with HFpEF, but again, caution is needed in interpreting this result because of the neutral primary outcome [34].
4.3.3. ARNI in Diabetic Kidney Dysfunction
Sacubitril–valsartan blocks the RAAS and inhibits neprilysin, a ubiquitous vasopeptidase enzyme breaking down >50 vasoactive peptides, including the biologically active natriuretic peptides, bradykinin, angiotensin I and II, endothelin 1, glucagon, glucagon-like peptide-1 and insulin-B chain. There is some evidence to suggest an improvement in glucose metabolism through inhibition of the renin–angiotensin system, although this effect is most likely modest, whereas there are a number of potential mechanisms by which inhibition of neprilysin may lead to improved glycemic control. Because these mechanisms are not fully understood, detailed mechanistic studies, as well as large randomized clinical trials in patients with DM, are needed to further clarify beneficial metabolic properties of sacubitril–valsartan [35].
4.4. Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist (MRA)
4.4.1. MRA in HFrEF with Kidney Dysfunction
Complete suppression of the RAAS axis with the help of an MRA in addition to recommended HF therapy has a beneficial impact in more severely symptomatic HFrEF patients, as first demonstrated in the Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study (RALES) [36]. The RALES study compared the effect of 25 mg of spironolactone with a placebo on all-cause mortality in severe heart failure patients in NYHA functional class IIIb and IV on standard therapy. The mean follow-up was 24 months. A post hoc analysis of the RALES trial showed that the incidence of the composite endpoint of all-cause mortality and the secondary endpoint combining all-cause death or HF hospitalization was not increased in study participants with an eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 in the placebo arm [37]. In the spironolactone treatment arm of the RALES, the eGFR declined more often during the first 4 weeks when compared with the placebo group (17% vs. 7%), and the eGFR remained reduced thereafter. However, while WRF was associated with an increased adjusted risk of death in the placebo arm, no such change was observed in study participants with WRF in the treatment group.
The risk of hyperkalemia was higher in the spironolactone treatment group when compared to the placebo group, particularly in study participants with an eGFR < 60 at baseline (OR 3.7, 95% CI 2.5–5.7) or those with WRF (OR 3.8, 95% CI 1.2–6.4). Thus, spironolactone treatment was significantly more often reduced or discontinued in study participants with an eGFR < 60 (OR 2.3, 95% CI 1.2–4.7) but not in study patients with an eGFR ≥ 60. MRAs are therefore more commonly underused in patients with impaired kidney function.
A recent Cochrane meta-analysis including 44 studies suggests that an aldosterone blockade may reduce proteinuria and kidney function when added to ACEis or ARBs [38]. However, treatment effects did not prevent progression of CKD towards kidney failure, and did not reduce major cardiovascular events or all-cause death. Furthermore, this Cochrane analysis suggested that aldosterone antagonists in combination with ACEis or ARBs (or both) increase the risk of hyperkalaemia, similar to result from the RALES.
This increased risk may relate to the substantial change of pharmacokinetic properties of spironolactone in patients with moderate-to-severe kidney dysfunction as suggested by the AMBER randomized trial, in which spironolactone (25 to 50 mg/d) was administered for 12 weeks as an add-on therapy in patients with resistant hypertension and moderate CKD (eGFR of 25–45 mL/min per 1.73 m2) [39]. After stopping treatment, more than half of the initial blood pressure reduction remained sustained for another 2 weeks after drug discontinuation, which suggests accumulation of active metabolites of spironolactone in the circulation of these patients. This can also explain why discontinuation of spironolactone treatment for hyperkalemia may not restore normokalemia immediately.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/kidneydial2030033
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
