Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Polymer Science
Polysaccharides are biocompatible nontoxic natural polymer compounds. They are widely used as functional soft-matter for exploration in the food industry, drug delivery, regenerative medicine, and other biomedical research and applications. The tunable macroscopic properties of gels should meet case-dependent requirements. The admixture of proteins to polysaccharides and their coupling in more sophisticated structures opens an avenue for gel property tuning via physical cross-linking of components and the modification of gel network structure.
- protein–polysaccharide gels
- κ-carrageenan
- galactan
- structure
- crosslinking
- FTIR-spectroscopy
- molecular modelling
1. Introduction
Polysaccharides are biocompatible nontoxic natural polymer compounds. They are widely used as functional soft-matter for exploration in the food industry, drug delivery, regenerative medicine, and other biomedical research and applications [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. Polysaccharides are widely spread in bacterium, plant, and animal nature: produced by algae (alginate and carrageenan), plants (cellulose, pectin, and guar gum), bacterium (dextran and chitin) and animals (hyaluronan, chondroitin, and heparin). Polysaccharides with diversity of chemical modification represent a wide range of molecular weights. This work is devoted to carrageenans, one of the representatives of galactans. Galactans are a unique class of natural polysaccharides, distributed in plants (red algae, lupine seeds, citrus peel, etc.), also found in animals and microorganisms.
Carrageenans are linear, sulfated, hydrophilic non-toxic polysaccharides from red algae. Their molecules consist of galactose repeat units, one ring per disaccharide can be (3,6)-anhydro, connected by alternating α-(1,3)- and β-(1,4)-glycosidic links with a variable proportion of sulfate groups at different positions [13]. There are different types of carrageenans (are widely used in technologic developments), carrying from one to three sulfate groups per monomeric unit of polymer (Figure 1). Among natural galactans the carrageenans are ideal candidates for different applications in wound healing and drug delivery [14]. Together with other sulfated polysaccharides [15], they are often considered as mimetics of glycosaminoglycans (GAG), the matrix polysaccharides of mammals, and have a potential to be used for tissue engineering [16]. In addition, the application of carrageenans is omnipresent in dairy products due to their strong interaction with food proteins [17].
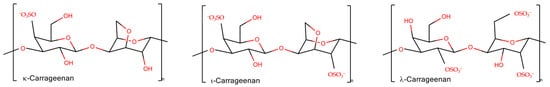
Figure 1. The schematic representation of disaccharide units of carrageenans.
Gels, one of the essential states of polysaccharides, represent a three-dimensional crosslinked polymer network immersed in a confined continuous fluid phase. If the fluid totals more than 90% of volume, it is referred to as hydrogel in the case of water or organogel in the case of organic fluid. Gels are classified as chemical or physical depending on the cross-linker’s nature [19]. In the first case, the polymeric chains are held together by covalent chemical bonds. Mostly technologically advanced are physical hydrogels, which are typical of many natural biopolymers, in which a three-dimensional polymer network exists owing to the mechanical weave of the polymer molecules and/or stabilized by intermolecular interactions, including ionic bridges, hydrogen bonding, and hydrophobic interactions.
2. Crosslinking in Polysaccharide Gels
The molecular weight of polysaccharides ranging from several hundred thousand to millions of Daltons allows them to form gels at concentrations lower than those required for protein gelation. Usually, less than 1 mass% of polysaccharide is necessary for its gelation via various intermolecular interactions [17]. Gel formation may occur via the long chain entanglement and formation of ordered structures in the junction zones. The packing of chains in junction zones is generally accompanied with the structuring of flexible polysaccharide chains and results in the increase of gel elasticity, whilst the simple entanglement contributes to the gel viscosity. Several types of chain–chain interactions in polysaccharide gels upon chain ordering have been proposed.
2.1. Chain Ordering in Carrageenans
Thermoreversible gels are formed by ι- and κ-carrageenans. The gel melts above a certain temperature and becomes firm when cooled. The firmness of the gel versus temperature may reveal hysteresis being dependent on the process direction. The melting temperature depends on the salt present, that is the type and concentration of counterions. The presence of two sulfate groups per one disaccharide in ι-carrageenan requires divalent cations to screen the repulsion of approaching chains and make a bridge between them stabilizing the gel formation. The κ-carrageenan needs monovalent cations, like K+, and to a lesser extent divalent cations. For λ-carrageenan, its gelation was reported only in the case of the presence of Fe3+ [34]. More detailed information about carrageenan gel rheology can be found in recent reviews on this topic [35,36].
The rheological properties are coupled with structural transitions of the carrageenan chains. The secondary structure changes from the coil to the helix state upon gelling. It still remains a matter of debate if carrageenans form single [37,38] or intertwined double helices [39,40].
The double helix formation with further cation mediated association in stacks is a widely accepted model for the junction zones in carrageenan gels. The double helix formation is supported by a large amount of data [17] including X-ray diffraction [39,41] and ultrasonic relaxation [42]. X-ray diffraction on crystalline ι-carrageenan revealed a parallel three-fold double helix with pitch around 26 Å [43]. Although experimental data for κ-carrageenan cannot be interpreted in terms of geometry [34], the modelling suggests a three-fold double helix with pitch of 25 Å, where both parallel and antiparallel chain orientations are possible [44]. A similar 25 Å pitch of helix was reported for λ-carrageenan [34]. Wide-angle X-ray diffraction on carrageenan solids packed in a form of membranes showed double-helical structure for ι- and κ-carrageenans and a single-helical one for λ-carrageenan [45]. Computer modelling favored a single helix [46].
Using high-resolution AFM microscopy, Schefer et al. [38,47] provided direct evidence of single helix formation in ι- and κ-carrageenans, similar to some other polysaccharides [48]. The monovalent ion-induced coil-helix transition is coupled with non-monotonic tendency of chain stiffening with persistent length variations from 10 to 20 nm [38]. In contrast, in the presence of NaCl, λ-carrageenan retains a random coil conformation [38]. Single helices may laterally associate into supercoils in the fashion of tertiary structure of proteins or/and to coil-coiled helices similar to quaternary structures and after this they can form supramolecular gels [49].
Recently, the researchers group applied Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy to provide deeper insights into the coupling of ion binding with coil-helix transitions in κ-carrageenan upon the temperature-induced formation and melting of gels [10]. Because of pronounced overlapping of spectral bands, which is typical for polysaccharides, the set of spectra, recorded along the perturbation coordinate (i.e., temperature), was decomposed into orthogonal variants. Based on the splitting of the νasSO3 complex band (1300–1200 cm−1) the orthogonal variants were attributed to sulfate groups in the free state and with weakly or strongly bound ions. Two orthogonal components in the region of skeletal vibrations (1200–1000 cm−1), interchanging in a cooperative fashion along the temperature, were the hallmark of helical and coil conformation. Further analysis coupled with quantum chemical calculations revealed the following sequence of events [10]: (1) upon cooling down the strong K+ binding becomes prevalent over weak contacts, (2) the strong K+ binding requires the neocarrabiose units to be in a conformation determined by the values of the phi and psi angles as those in the helix; at this stage the “seeds” of helical conformation are stabilized by bound potassium ions, (3) the further cooling of the system results in the full chain conversion to the helix conformation (Figure 2a).
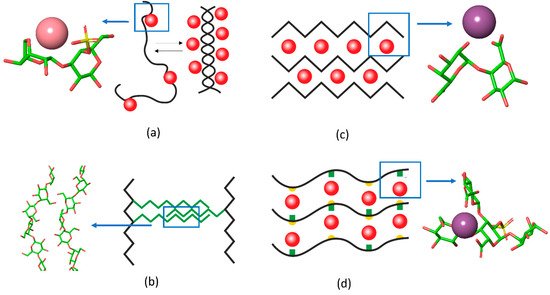
Figure 2. The schematic representation of interchain junctions and the atomistic representation of (a) key interactions in carrageenan, (b) 1,4-β-galactan in RG-I, (c) pectin gels, and (d) in Infernan gel. In the schemes, cations are shown as red balls, side chains are given in green, the location of sulfate groups in Infernan is indicated by yellow semicircles. K+ in the complex with κ-carrageenan is shown in pink and Ca2+ in complex with pectin and Infernan is shown in violet.
The FTIR-spectral patterns of helix and coil conformations of κ-carrageenan can be used for the in situ detection of the polysaccharide conformational state in protein–carrageenan gels, which is illustrated in Section 3.
2.2. 1,4-β-Galactan Crosslinking
Another type of gel formation via galactan chains was reported recently for rhamnogalacturonan I (RG-I), which is usually present as a hairy region of the pectin molecule. The RG-I from gelatinous fibers of flax, which does not have homogalacturonan fragments and is branched with long 1,4-β-galactan side chains, can form physical gels under microwave irradiation [12]. In this type of gel, the RG-I molecules are entangled by galactan side chains. Interestingly, the 2D-correlation FTIR spectroscopy [9] together with molecular modelling [11] showed that in such gels 1,4-galactan has a regular helical structure, the side chains interact in a side-by-side antiparallel fashion (Figure 2b).
2.3. Egg-Box Assembly in Pectins and Alginates
A famous example of polysaccharide chain fine-tuning via ion cross-linking in gel junction zones is the packing of alginates and pectins in the form of an egg-box. The gelation of alginate, composed of (1→4)- linked α-L-guluronic and β-D-mannuronic residues of varying sequence, takes place under mild conditions with the sol-gel transition independent of temperature. Divalent cations induce chain–chain association by means of physical cross-linkage of guluronic acid blocks of neighboring alginate molecules, known as the “egg-box model” [50]. Another example is the homogalacturonan, a major domain of the pectin molecule, built up by the (1→4)- linked α-D-galacturonate residues. The GalpA residues offer their carboxylate groups for the ion coordination in the form of an egg box [51,52]. A recent review sums up the differences between pectin and alginate structure of the egg-box [53]. The progression of such a structure results in the formation of firm bunches of polysaccharide chains (Figure 2c).
The chain stiffness of a polymer influences its properties and its capability to interact with other molecules [59]. Thus, the polysaccharide chain ordering that effects charge exposure is of high importance for rational design of novel materials. Probing the conformational state of such flexible matter as polysaccharides is a challenging task to which computer methods contribute significantly revealing the statistically relevant cases of both individual molecule conformation in solution and their assembly [60]. Among promising experimental methods to probe the polysaccharide state with high resolution, along with AFM microscopy, a fascinating tool should be mentioned which studies the conformational landscape of an oligosaccharide molecule, sampled by exciting a gas-phase molecular conformer to an ensemble using soft molecule–surface collision [61]. Despite the atomistic depicture of the polymer structure through these methods, the detection of the structure in molecular complexes in soft matter remains challenging. FTIR-spectroscopy is one of the non-destructive methods sensitive to the conformational state of both polysaccharides and proteins, which is able to observe the conformations of both species in gels in situ. It is shown in the next section that the method is highly informative for protein–carrageenan gels where both components have remarkable conformational changes.
3. Protein–Polysaccharide Gels
In recent decades, protein–polysaccharide gels have attracted attention due to the broad variability of the tuning gel properties [62]. Other strategies to tune the carrageenan gel structure and properties include the use of sugar and polyols as cosolvents [63] or the admixture of other polysaccharides [64].
Protein–polysaccharide gels can be formed in mixtures of gelling polysaccharides and non-gelling proteins [65], gelling proteins and non-gelling polysaccharides [66], or when both agents gel [67]. Depending on the chemical structure of the biopolymers and the environmental conditions, the gel network is formed due to interpenetration, phase-separation, or coupling of components [68,69]. In the interpenetrating network, two independent gel networks are formed where each network is made by the individual biopolymer [70,71]. The phase-separated network is formed in segregative conditions upon demixing of protein and polysaccharide, the resultant structure of such gels is determined by the rate of coarsening and crosslinking of the gelling components. Since segregation is stopped by gelling, the final morphology depends on the relative rates of these processes [72,73]. The coupled gel network forms in associative conditions when two biopolymers interact with formation of modified junction zones. Often both mixing and demixing behavior is electrostatically driven [74,75].
The ability of proteins to form binary gels with polysaccharides depends on pH, ionic strength, and type of salt, that determine the balance between attractive and repulsive forces. Eleya and Turgeon [76] reported that β-lactoglobulin, one of the whey proteins, being co-gelled with κ-carrageenan in the course of heating, demonstrates the pH-depending behavior. Above the protein pI, in the region of pH 5–7, the rheological behavior of binary gels upon their formation and melting was attributed to the presence of a phase-separated type of network. While at pH 4.0, below the protein pI, their behavior implies the association of biopolymers with the formation of one continuous network, which significantly enhances the protein gel strength.
Thus, gel formation driven by repulsive forces and phase separation is associated with changes of microstructure to which the rates of demixture and gelling contribute. The microstructure of such gels is rather characterized by spatially separated aggregates of individual components. The apparent changes of gel rheology may be explained by the level of the individual components network intactness and by the increase of the local concentration of components.
When the gel formation is driven by electrostatic attraction the complexation between protein and polysaccharide may lead to a significant alteration of the structure of junction zones. For example, Duran with co-authors [89,90] showed that in quinoa protein–ι-carrageenan gels both biopolymers are synergically responsible for the formation of the gel matrix. The mixtures between the male gonad hydrolysates of scallop Patinopecten yessoensis and κ-carrageenan [91] suggest electrostatic interactions involved in the maintenance of the gel network. In their turn, the protein–polysaccharide complexation via electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonds, and hydrophobic interactions leads to a well-distributed network structure supporting the stronger gel rigidity [91]. The increasing level of ι-carrageenan results in a more compact network of soya meat analogues [92]. Synergistic interactions of κ-carrageenan with milk proteins promote the development of a cross-linked network in whipped cream [27]. The addition of ι-carrageenan to scallop Patinopecten yessoensis male gonad hydrolysates can result in a 116-fold increase of storage modulus compared to that of protein alone [93]. The emulsion-based gels of whey protein isolate with κ- and ι-carrageenans increase the strength and elasticity together with increase of carrageenan content; the network coupled with ι-carrageenan was stronger than that with κ-carrageenan [94]. In turn, the influence of λ-carrageenan on the gel strength was higher than that of ι-carrageenan [95]. Furthermore, the gels formed by κ-carrageenan with hagfish slime show synergistic effects by exhibiting high values of elasticity and viscosity [96]. κ-Carrageenan enhances yolk properties via electrostatic interactions with proteins [97].
Molecular interactions between proteins and polysaccharides occur upon coacervate formation in solution. FTIR- [98] and NMR-spectra [99] can detect the complex formation between charged biopolymers. Le and Turgeon [100] proposed the following mechanism of associative gelation in the β-lactoglobulin and xanthan gum mixtures [62]. The gelation starts by establishing interactions between negatively charged groups of polysaccharide and positively charged moieties of protein with the formation of soluble complexes. Then, along with the change of surface charge of these soluble complexes, interpolymer association occurs where one protein molecule may interact with several polysaccharide chains forming junction zones. This cross-linking process continues further until the completion of the sol-gel transition [100].
Protein–polysaccharide complexation in the cross-linked gel network as well as in coacervates may result in conformational changes in both the protein and polysaccharide, which, in turn, can be one of the factors for the modified gel rheology.
However, despite the fact that the analysis of gel microstructure has accompanied most research dealing with the properties of binary gels, the information about their nano-scale structure and conformational adjustment of counter-parts in complexes is rather scarce.
To have a vision of protein conformation alteration upon binary protein–polysaccharide coacervate formation, some spectroscopic techniques are informative. Several studies report on significant changes in protein secondary structure content. Siddiqui and co-authors [101] reported that purified almond cystatin mixing with λ-carrageenan at 25 °C showed a significant shift in the FTIR-peak intensity, which depicts the helix-to-β-sheet change in the secondary structure of cystatin. The CD spectra confirmed the helix to β-sheet transition. Tang and co-authors [102] observed a decrease of the relative content of α-helixes and β-turns and an increase of β-sheets and random coils in salted duck egg white with the addition of κ-carrageenan. According to the Raman spectroscopy data, a small content of κ-carrageenan promoted the conformational transition of surimi protein from α-helix to β-sheet [103]. In contrast, Zheng and co-authors [104] observed none-to-minimal shift of the β-sheet and the α-helical protein structure in the gels of κ-carrageenan with krill protein isolate. A tendency of globular protein structure to shift from order to disorder was concluded on the basis of low-temperature DSC-curve shift and CD-spectra of lysozyme–κ-carrageenan gels [65].
The conformation of both protein and polysaccharide may be influenced by its counter-part. For example, the unwinding of the ι- and κ-carrageenans double helix was reported to be induced by β-casein [105]. This unwinding is due to preferable electrostatic interaction with the coil polysaccharide chain since the conformational change is fully reversible in conditions of sufficiently high ionic strength [105].
Apparently, in a gel with coupled network the conformational adjustment of polymers, together with the concentration of polymers, pH, and ionic strength, becomes a factor of tunable gel rheology. Then the rational design of the binary composition requires a deep fundamental understanding of structural adjustment upon complex formation. The lack of information about the mutual conformational influence of protein and polysaccharide determines, in particular, the lack of appropriate methodology. CD-spectroscopy, widely useful for protein and polysaccharide conformation probing in solution [106], is not appropriate for gels. Suffering from light scattering, it results in distorted spectra of colloid particles that can mislead the analysis. FTIR-spectroscopy may work with the samples of any phase states, if the characteristic bands of protein and polysaccharides do not overlap (not critical if any) and is suited perfectly to probe simultaneously the conformation of protein and polysaccharide in binary gels in situ. Below, some examples of the application of FTIR-spectroscopy in probing the protein–polysaccharide mutual conformational adjustment in protein–κ-carrageenan gels are given [108,110].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/gels8050287
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
