1. Multiple Myeloma
The malignant transformation process is preceded by key alterations of DNA content or structure [
66,
90,
114,
115,
116,
123,
124,
125,
126]. Several genomic alterations, such as DNA-damage-induced events, chromosome abnormalities, and epigenetic modifications, contribute to the high genomic instability observed in cancer [
124,
127,
128,
129]. Multiple Myeloma (MM) is an incurable disease of plasma cells characterized by the accumulation of aberrant cells in the bone marrow and secretion of immunoglobulin called M protein [
130,
131]. MM is the latest stage of a progressive disease preceded by two precursor asymptomatic stages (monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance, MGUS, and smoldering multiple myeloma, SMM) [
132]. The progression from MGUS to SMM and, ultimately, to MM is associated with numerical and structural chromosomal alterations, such as gains or losses of chromosomes and chromosome translocations, which may promote disease progression [
133,
134,
135]. MM can be defined as high-risk based on the presence of genomic abnormalities, such as aneuploidies (gains or losses) in chromosomes 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 15, 19, and 21, as well as translocation events that mostly comprise the immunoglobulin heavy-chain (
IGH) locus, placed on chromosome 14 [
136,
137].
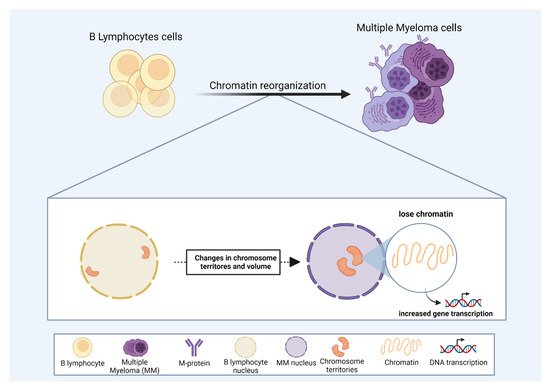
One of the key regulators of gene expression is the chromatin state. The availability of chromatin sites to the transcriptional machinery can dictate gene expression [
141,
142]. In MM, recent studies have shown an association between chromatin status and altered gene expression [
136,
143,
144]. Moreover, CT volumes increase in MM compared to normal B-lymphocytes [
145] (
Figure 3). This observation supports the idea that an open chromatin state in MM would facilitate the expression of key genes involved in MM development and progression [
141,
145]. The analysis of chromatin structure, using 3D Structured Illumination Microscopy in MGUS and MM derived patient samples, revealed that MM has a less condensed and an open chromatin state compared to normal B-lymphocytes, even in the precursor stage of MGUS [
146], suggesting that chromatin state could be used to identify MM in early stages of the disease development.
Figure 3. The role of chromosome territories in multiple myeloma (MM). Correlation of chromosome position and chromatin state as drivers of the malignant progression in MM. For details, please see
Section 3.1. In MM, some chromosomes display altered positions, towards the nuclear center, compared to regular B lymphocytes. Some chromosome territory volumes also increase in MM, and changes in nuclear organization may favor MM progression by modulating gene expression.
Chromatin localization inside the nucleus can also modulate gene expression in MM. In MM-derived patient samples, the territories occupied by chromosomes 4, 9, 11, 14, and 18 are internally located compared to normal B-lymphocytes [
145] (
Figure 3). These altered CT positions associated with an open chromatin state might play an important role in deregulating gene expression, ultimately leading to MM progression (
Figure 3). According to this concept, Broyl et al. (2010) and Chen et al. (2021) reported that several genes located on chromosomes 4, 9, 11, and 18 were up-regulated in MM-derived patient samples [
147,
148]. These studies provide insight that a high-level chromatin regulation could be critical for MM progression and highlight chromosome position and chromatin state as important prospective targets for MM therapeutical strategies.
2. Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Secondary Leukemia
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) accounts for the majority of cases of secondary leukemias [
149]. The most common chromosomal abnormality associated with AML is
t (8;21) (q22;q22.1) [
150], where up to 20% of these cases are secondary AML. This translocation leads to a novel chimeric gene
RUNX1-
RUNX1T1 on chromosome 8. When not translocated,
RUNX1 and
RUNX1T1 do not share the same CT [
151]. Rubtsov et al. (2008) showed that the treatment of primary embryonic normal human male fibroblasts with the Topoisomerase II (Topo II) poison etoposide leads to a reposition of the
RUNX1T1 gene. After Topo II treatment,
RUNX1 and
RUNX1T1 were found in closer proximity [
151]. The authors did not observe a direct contact between the two genes in fibroblasts after etoposide treatment. Only human lymphoid cells (Jurkat cells) displayed a juxtaposition of
RUNX1 and
RUNX1T1 after the treatment, suggesting a cell type-specific relationship [
152].
The mixed-lineage leukemia gene (
MLL) is also frequently rearranged in secondary leukemias [
153]. The breakpoint cluster region of
MLL has a Topo II cleavage site [
154,
155]. Glukhov et al. (2013), after treating human lymphoid cells with etoposide, observed many cleavage sites of the
MLL gene (~17% of nuclei). They showed that ~9% of these broken
MLL alleles were repositioned outside their CT [
156].
MLL can be translocated with more than 40 different partners [
157,
158]. Gué et al. (2006) measured the relative positions of
MLL to
AF4 and ENL genes (a commonly involved gene and a less frequent gene in MLL translocations, respectively). Interestingly,
MLL and
ENL genes were closer to each other in comparison to
MLL and
AF4 [
159,
160]. The “breakage first” model states that breaks formed at distant locations could scan for potential partners and move to produce translocations, which could explain their observation. There are many models contraposing the “breakage first” model; among them, figures the “contact-first” model. In this model, translocations preferentially occur between chromosomes that are in close spatial proximity, a hypothesis based on the observation that chromosomes are not randomly distributed in the interphase nuclei [
160,
161,
162].
3. Radiation Effects on CT in Hematological Malignancies
Ionizing radiation is known to be one of the main causes of genetic instability [
163]. Several studies demonstrated that chromosomal proximity plays a key role in translocations arising after irradiation [
164]. Lukásová et al. (1997) compared
ABL and
BCR gene nuclear localizations in bone marrow cells from patients with chronic myeloid leukemia and control donors. After irradiation, both genes were shifted to the central area of the nucleus in approximately 15% of the cells [
165]. Kozubek et al. (1997) also showed in lymphocytes exposed to radiation that
BCR and
ABL genes are shifted to the nuclear center in closer proximity. Bártová et al. (2000) also showed increased proximity of
ABL and
BCR in lymphocytes after irradiation. Interestingly, closer proximity was found between
c-MYC and
IGH genes in approximately 8% of the lymphocytes. Those two genes are involved in the
t (8;14), a translocation present in 98% of Burkitt’s lymphoma cases [
166,
167]. In irradiated lymphocytes,
c-MYC is shifted closer to the nuclear center. However, after 24 h of radiation exposure,
c-MYC returns to its original territory [
102].
Cafourková et al. (2001) also irradiated normal lymphocytes to verify CT alterations among 11 selected chromosomes. They observed many CT interactions after irradiation where the interactions were associated with chromosome size, as expected due to the increased probability of CT contact increases for larger chromosomes [
168]. Similarly, Boei et al. (2006), using FISH, observed alterations in chromosomes 1, 4, 18, and 19 of lymphocytes exposed to ionizing radiation. They also found an association between chromosome size and CT distribution. The frequency of CT changes was associated with the density of ionizing radiation, presenting higher frequencies with densely ionizing radiation than with the sparse one [
169]. Anderson et al. (2002) reported that complex chromosome aberrations (chromosomal exchanges involving three or more breaks in two or more chromosomes) arise in peripheral blood lymphocytes after exposure to high-linear energy transfer (LET) α-particle radiation [
170]. Later, in 2006, they analyzed the formation of complex chromosomal abnormalities and reconstructed their probable origin. This model proposed by Anderson et al. (2006) suggests that in the individual high-LET α-particle-induced complex chromosomal abnormalities arise from the misrepair of damaged chromatin in single physical locations. The complexity is influenced by the number of CTs that are affected by alpha particles, which corroborates previous studies with irradiation. Due to their size, chromosome q-arms are more prone to translocations with different chromosomes [
170,
171]. Recently, Balajee et al. (2018) used multicolor FISH (m-FISH) to investigate CTs in interphase nuclei of lymphocytes and B-lymphoblastoid cells [
139]. They analyzed cells before and after exposure to ionizing radiation using metaphase chromosome analysis. Up to 50% of the ionizing radiation-induced translocations were associated with the proximity of pre-existing CTs in both cell lines. Chromosome conformation capture (Hi-C) was used to measure the frequencies of interactions between different chromosomes and gene loci, and it highly correlated with the findings using FISH. There were also interactions between loci of the genes
BCR and
ABL in lymphoblastoid cells, which increased after exposure to X-ray. However, in the fibroblasts, this association was not observed [
139]. Collectively, these studies provide a new layer of knowledge on the explanations for why some translocations are more likely to occur after exposure to radiation, one of the most studied factors known to increase the risk of hematological malignancies.
4. Lymphomas
Hodgkin’s lymphoma is a disorder characterized by the presence of mono-nucleated Hodgkin cells and bi- to multi-nucleated Reed–Sternberg cells [
172,
173]. Guffei et al. (2010) demonstrated that chromosomes 9 and 22 have altered CTs in both mono- or multi-nucleated cells [
174]. These data are consistent with previous results showing that the transition from Hodgkin to Reed–Sternberg cells is marked by changes in the three-dimensional nuclear organization of telomeres [
175]. The nuclear telomeric architecture of Hodgkin’s and Reed–Sternberg cells was significantly different at diagnosis for cases with recurring/relapsed disease when compared to the non-relapsed group [
176]. These data on Hodgkin’s lymphoma imply that changes in nuclear architecture, including CTs, are a key factor for the occurrence of chromosomal translocations and nuclear genome remodeling found in this disorder.
Roix et al. (2003) reported that the genes frequently translocated in B-cell lymphomas are positioned at a closer distance in normal human B cells.
MYC was found in significantly closer proximity with
IGH and
IGL but distant from its rare translocation partner
IGK. Furthermore, normal fibroblasts, when compared to lymphocytes, present longer distances between
MYC and
IGH loci. This provides strong evidence for the role of cell-specific CT proximity since translocations involving these two genes do not occur in cell types other than B cells [
120]. Furthermore, several factors are involved in the origin of lymphomas, and there is a significant association with several types of viral infection. Patients infected by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) present an increased risk of developing lymphoma. Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is one of the most predominant lymphomas associated with HIV infection. Most cases of BL have the
MYC-IGH translocation. Interestingly, Germini et al. (2017) showed that the HIV Tat protein, a key factor in the HIV pathogenesis, when injected into circulating B-cells, generates DNA damage and changes in
MYC gene CT. In this context,
MYC moves to the nuclear center, colocalizing with the
IGH (10-fold when compared to controls) [
177].
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) is a non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of cells expressing CD30. The translocation
t (2; 5) (p23; q35) is found in approximately half of the ALCL cases [
178]. Mathas et al. (2009) studied an ALCL cell line without this translocation, and they visualized close proximity between the two chromosomal regions involved in the t(2;5) (p23;q35). In order to further investigate the role of close proximity in facilitating translocation between these two chromosomal regions, the authors induced DSBs in the negative ALCL cells. The
t (2;5) (p23; q35) was found in these cells after DNA repair [
179].
Klein et al. (2011), investigating the nature of chromosomal rearrangements in mouse B lymphocytes, demonstrated that proximity between DSBs, transcriptional activity, and CTs were key factors of rearrangements. One part of the rearrangements was associated with CT, in which intra-chromosomal joining was more common than trans-chromosomal rearrangements after DSB formation. Remarkably, the rearrangements were preferentially found at the transcription start sites of actively transcribed genes [
119].
CTs in human lymphocytes can interact more than previously anticipated. Recently, Steininger et al. (2018) applied the chromosome conformation capture (Hi-C), a technique used for the investigation of genome-wide chromatin interactions in a T-cell lymphoma cell line. They found higher probabilities of interaction between chromosomal segments than an earlier report [
180]. Branco and Pombo (2006) used cryo-FISH (a FISH method using cryosections of approximately 150 nm thick of sucrose-embedded fixed cells or tissues) in human lymphocytes and reported that approximately 40% of each chromosome intermingled with the rest of the genome. A highly significant correlation was found between the extension of CT intermingling and the frequency of translocations in lymphocytes (
p < 0.0001). It was also estimated that approximately 19% of the nuclear volume is composed of intermingling regions [
117]. Tavares-Cadete et al. (2020) have shown different results, indicating that contact/entanglement of chromosomes and chromosomal domains are not so frequent. However, in this study, they used different cells (HeLa S3 cell line) [
181].
There was a significant achievement in demonstrating that the spatial proximity of chromosomes increases the probability of translocations in hematological malignancies such as myeloma, leukemia, and lymphoma. However, only a few genes and chromosomes were investigated; a significant part of the studies was not confirmed later or were conducted using cell lines. There are still many potential genes involved in translocations of these diseases, and this offers a wide field to be explored. This field of study has gained remarkable new possibilities since new genome-wide/single-cell techniques are being tested. The biogenesis of chromosomal translocations is a highly complex phenomenon. Although differentiation, exposure to radiation, and cytotoxic drugs were associated with changes in CTs, which elevates the risk of chromosomal translocations, many other factors predisposing these alterations could also be studied in the context of CTs. Due to the complexity of the mechanisms behind the occurrence of translocation, it is essential to mention that although CTs are clearly associated with specific chromosomal abnormalities, many others still lack explanations. In this sense, CT comprises a critical candidate to explain such an important cancer hallmark.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/cells11081368