Underground sewerage systems (USSs) are a vital part of public infrastructure that contributes to collecting wastewater or stormwater from various sources and conveying it to storage tanks or sewer treatment facilities. A healthy USS with proper functionality can effectively prevent urban waterlogging and play a positive role in the sustainable development of water resources. Since it was first introduced in the 1960s, computer vision (CV) has become a mature technology that is used to realize promising automation for sewer inspections.
- survey
- computer vision
- defect inspection
- condition assessment
- sewer pipes
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Defect Inspection Framework
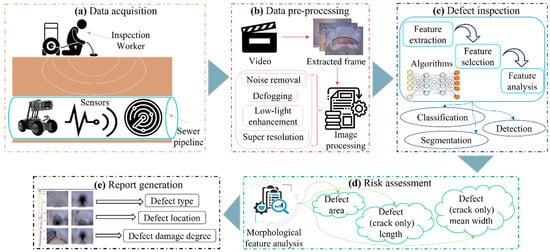
2. Defect Inspection
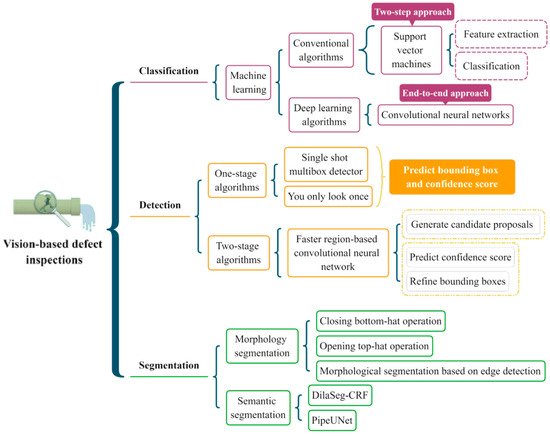
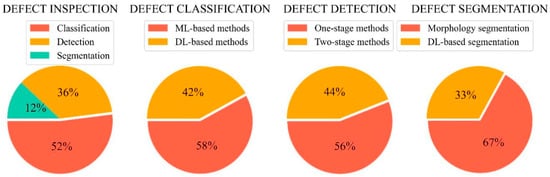
2.1. Defect Classification
2.2. Defect Detection
2.3. Defect Segmentation
3. Dataset and Evaluation Metric
3.1. Dataset
3.1.1. Dataset Collection
|
Name |
Company |
Pipe Diameter |
Camera Feature |
Country |
Strong Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CAM160 (https://goolnk.com/YrYQob accessed on 20 February 2022) |
Sewer Robotics |
200–500 mm |
NA |
USA |
● Auto horizon adjustment ● Intensity adjustable LED lighting ● Multifunctional |
|
LETS 6.0 (https://ariesindustries.com/products/ accessed on 20 February 2022) |
ARIES INDUSTRIES |
150 mm or larger |
Self-leveling lateral camera or a Pan and tilt camera |
USA |
● Slim tractor profile ● Superior lateral camera ● Simultaneously acquire mainline and lateral videos |
|
wolverine® 2.02 |
ARIES INDUSTRIES |
150–450 mm |
NA |
USA |
● Powerful crawler to maneuver obstacles ● Minimum set uptime ● Camera with lens cleaning technique |
|
X5-HS (https://goolnk.com/Rym02W accessed on 20 February 2022) |
EASY-SIGHT |
300–3000 mm |
≥2 million pixels |
China |
● High-definition ● Freely choose wireless and wired connection and control ● Display and save videos in real time |
|
Robocam 6 (https://goolnk.com/43pdGA accessed on 20 February 2022) |
TAP Electronics |
600 mm or more |
Sony 130-megapixel Exmor 1/3-inch CMOS |
Korea |
● High-resolution ● All-in-one subtitle system |
|
RoboCam Innovation4 |
TAP Electronics |
600 mm or more |
Sony 130-megapixel Exmor 1/3-inch CMOS |
Korea |
● Best digital record performance ● Super white LED lighting ● Cableless |
|
Robocam 30004 |
TAP Electronics’ Japanese subsidiary |
250–3000 mm |
Sony 1.3-megapixel Exmor CMOS color |
Japan |
● Can be utilized in huge pipelines ● Optical 10X zoom performance |
3.1.2. Benchmarked Dataset
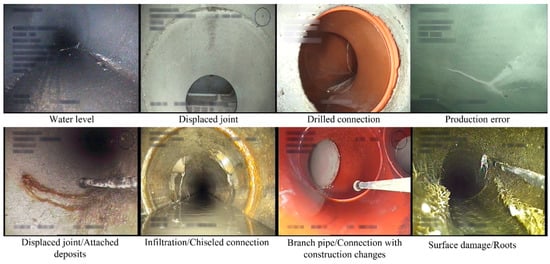
|
ID |
Defect Type |
Image Resolution |
Equipment |
Number of Images |
Country |
Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Broken, crack, deposit, fracture, hole, root, tap |
NA |
NA |
4056 |
Canada |
[9] |
|
2 |
Connection, crack, debris, deposit, infiltration, material change, normal, root |
1440 × 720–320 × 256 |
RedZone® Solo CCTV crawler |
12,000 |
USA |
[48] |
|
3 |
Attached deposit, defective connection, displaced joint, fissure, infiltration, ingress, intruding connection, porous, root, sealing, settled deposit, surface |
1040 × 1040 |
Front-facing and back-facing camera with a 185∘ wide lens |
2,202,582 |
The Netherlands |
[49] |
|
4 |
Dataset 1: defective, normal |
NA |
NA |
40,000 |
China |
[69] |
|
Dataset 2: barrier, deposit, disjunction, fracture, stagger, water |
15,000 |
|||||
|
5 |
Broken, deformation, deposit, other, joint offset, normal, obstacle, water |
1435 × 1054–296 × 166 |
NA |
18,333 |
China |
[70] |
|
6 |
Attached deposits, collapse, deformation, displaced joint, infiltration, joint damage, settled deposit |
NA |
NA |
1045 |
China |
[41] |
|
7 |
Circumferential crack, longitudinal crack, multiple crack |
320 × 240 |
NA |
335 |
USA |
[11] |
|
8 |
Debris, joint faulty, joint open, longitudinal, protruding, surface |
NA |
Robo Cam 6 with a 1/3-in. SONY Exmor CMOS camera |
48,274 |
South Korea |
[71] |
|
9 |
Broken, crack, debris, joint faulty, joint open, normal, protruding, surface |
1280 × 720 |
Robo Cam 6 with a megapixel Exmor CMOS sensor |
115,170 |
South Korea |
[52] |
|
10 |
Crack, deposit, else, infiltration, joint, root, surface |
NA |
Remote cameras |
2424 |
UK |
[66] |
|
11 |
Broken, crack, deposit, fracture, hole, root, tap |
NA |
NA |
1451 |
Canada |
[104] |
|
12 |
Crack, deposit, infiltration, root |
1440 × 720–320 × 256 |
RedZone® Solo CCTV crawler |
3000 |
USA |
[98] |
|
13 |
Connection, fracture, root |
1507 × 720–720 × 576 |
Front facing CCTV cameras |
3600 |
USA |
[99] |
|
14 |
Crack, deposit, root |
928 × 576–352 × 256 |
NA |
3000 |
USA |
[97] |
|
15 |
Crack, deposit, root |
512 × 256 |
NA |
1880 |
USA |
[116] |
|
16 |
Crack, infiltration, joint, protruding |
1073 × 749–296 × 237 |
NA |
1106 |
China |
[122] |
|
17 |
Crack, non-crack |
64 × 64 |
NA |
40,810 |
Australia |
[109] |
|
18 |
Crack, normal, spalling |
4000 × 46,000–3168 × 4752 |
Canon EOS. Tripods and stabilizers |
294 |
China |
[73] |
|
19 |
Collapse, crack, root |
NA |
SSET system |
239 |
USA |
[61] |
|
20 |
Clean pipe, collapsed pipe, eroded joint, eroded lateral, misaligned joint, perfect joint, perfect lateral |
NA |
SSET system |
500 |
USA |
[56] |
|
21 |
Cracks, joint, reduction, spalling |
512 × 512 |
CCTV or Aqua Zoom camera |
1096 |
Canada |
[54] |
|
22 |
Defective, normal |
NA |
CCTV (Fisheye) |
192 |
USA |
[57] |
|
23 |
Deposits, normal, root |
1507 × 720–720 × 576 |
Front-facing CCTV cameras |
3800 |
USA |
[72] |
|
24 |
Crack, non-crack |
240 × 320 |
CCTV |
200 |
South Korea |
[106] |
|
25 |
Faulty, normal |
NA |
CCTV |
8000 |
UK |
[65] |
|
26 |
Blur, deposition, intrusion, obstacle |
NA |
CCTV |
12,000 |
NA |
[67] |
|
27 |
Crack, deposit, displaced joint, ovality |
NA |
CCTV (Fisheye) |
32 |
Qatar |
[103] |
|
29 |
Crack, non-crack |
320 × 240–20 × 20 |
CCTV |
100 |
NA |
[100] |
|
30 |
Barrier, deposition, distortion, fraction, inserted |
600 × 480 |
CCTV and quick-view (QV) cameras |
10,000 |
China |
[110] |
|
31 |
Fracture |
NA |
CCTV |
2100 |
USA |
[105] |
|
32 |
Broken, crack, fracture, joint open |
NA |
CCTV |
291 |
China |
[59] |
3.2. Evaluation Metric
|
Metric |
Description |
Ref. |
|---|---|---|
|
Precision |
The proportion of positive samples in all positive prediction samples |
[9] |
|
Recall |
The proportion of positive prediction samples in all positive samples |
[48] |
|
Accuracy |
The proportion of correct prediction in all prediction samples |
[48] |
|
F1-score |
Harmonic mean of precision and recall |
[69] |
|
FAR |
False alarm rate in all prediction samples |
[57] |
|
True accuracy |
The proportion of all predictions excluding the missed defective images among the entire actual images |
[58] |
|
AUROC |
Area under the receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve |
[49] |
|
AUPR |
Area under the precision-recall curve |
[49] |
|
mAP |
mAP first calculates the average precision values for different recall values for one class, and then takes the average of all classes |
[9] |
|
Detection rate |
The ratio of the number of the detected defects to total number of defects |
[106] |
|
Error rate |
The ratio of the number of mistakenly detected defects to the number of non-defects |
[106] |
|
PA |
Pixel accuracy calculating the overall accuracy of all pixels in the image |
[116] |
|
mPA |
The average of pixel accuracy for all categories |
[116] |
|
mIoU |
The ratio of intersection and union between predictions and GTs |
[116] |
|
fwIoU |
Frequency-weighted IoU measuring the mean IoU value weighing the pixel frequency of each class |
[116] |
|
ID |
Number of Images |
Algorithm |
Task |
Performance |
Ref. |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Accuracy (%) |
Processing Speed |
|||||
|
1 |
3 classes |
Multiple binary CNNs |
Classification |
Accuracy: 86.2 Precision: 87.7 Recall: 90.6 |
NA |
[48] |
|
2 |
12 classes |
Single CNN |
Classification |
AUROC: 87.1 AUPR: 6.8 |
NA |
[48] |
|
3 |
Dataset 1: 2 classes |
Two-level hierarchical CNNs |
Classification |
Accuracy: 94.5 Precision: 96.84 Recall: 92 F1-score: 94.36 |
1.109 h for 200 videos |
[69] |
|
Dataset 2: 6 classes |
Accuracy: 94.96 Precision: 85.13 Recall: 84.61 F1-score: 84.86 |
|||||
|
4 |
8 classes |
Deep CNN |
Classification |
Accuracy: 64.8 |
NA |
[70] |
|
5 |
6 classes |
CNN |
Classification |
Accuracy: 96.58 |
NA |
[71] |
|
6 |
8 classes |
CNN |
Classification |
Accuracy: 97.6 |
0.15 s/image |
[52] |
|
7 |
7 classes |
Multi-class random forest |
Classification |
Accuracy: 71 |
25 FPS |
[66] |
|
8 |
7 classes |
SVM |
Classification |
Accuracy: 84.1 |
NA |
[41] |
|
9 |
3 classes |
SVM |
Classification |
Recall: 90.3 Precision: 90.3 |
10 FPS |
[11] |
|
10 |
3 classes |
CNN |
Classification |
Accuracy: 96.7 Precision: 99.8 Recall: 93.6 F1-score: 96.6 |
15 min 30 images |
[73] |
|
11 |
3 classes |
RotBoost and statistical feature vector |
Classification |
Accuracy: 89.96 |
1.5 s/image |
[61] |
|
12 |
7 classes |
Neuro-fuzzy classifier |
Classification |
Accuracy: 91.36 |
NA |
[56] |
|
13 |
4 classes |
Multi-layer perceptions |
Classification |
Accuracy: 98.2 |
NA |
[54] |
|
14 |
2 classes |
Rule-based classifier |
Classification |
Accuracy: 87 FAR: 18 Recall: 89 |
NA |
[57] |
|
15 |
2 classes |
OCSVM |
Classification |
Accuracy: 75 |
NA |
[65] |
|
16 |
4 classes |
CNN |
Classification |
Recall: 88 Precision: 84 Accuracy: 85 |
NA |
[67] |
|
17 |
2 class |
Rule-based classifier |
Classification |
Accuracy: 84 FAR: 21 True accuracy: 95 |
NA |
[58] |
|
18 |
4 classes |
RBN |
Classification |
Accuracy: 95 |
NA |
[59] |
|
19 |
7 classes |
YOLOv3 |
Detection |
mAP: 85.37 |
33 FPS |
[9] |
|
20 |
4 classes |
Faster R-CNN |
Detection |
mAP: 83 |
9 FPS |
[98] |
|
21 |
3 classes |
Faster R-CNN |
Detection |
mAP: 77 |
110 ms/image |
[99] |
|
22 |
3 classes |
Faster R-CNN |
Detection |
Precision: 88.99 Recall: 87.96 F1-score: 88.21 |
110 ms/image |
[97] |
|
23 |
2 classes |
CNN |
Detection |
Accuracy: 96 Precision: 90 |
0.2782 s/image |
[109] |
|
24 |
3 classes |
Faster R-CNN |
Detection |
mAP: 71.8 |
110 ms/image |
[105] |
|
SSD |
mAP: 69.5 |
57 ms/image |
||||
|
YOLOv3 |
mAP: 53 |
33 ms/image |
||||
|
25 |
2 classes |
Rule-based detector |
Detection |
Detection rate: 89.2 Error rate: 4.44 |
1 FPS |
[106] |
|
26 |
2 classes |
GA and CNN |
Detection |
Detection rate: 92.3 |
NA |
[100] |
|
27 |
5 classes |
SRPN |
Detection |
mAP: 50.8 Recall: 82.4 |
153 ms/image |
[110] |
|
28 |
1 class |
CNN and YOLOv3 |
Detection |
AP: 71 |
65 ms/image |
[108] |
|
29 |
3 classes |
DilaSeg-CRF |
Segmentation |
PA: 98.69 mPA: 91.57 mIoU: 84.85 fwIoU: 97.47 |
107 ms/image |
[116] |
|
30 |
4 classes |
PipeUNet |
Segmentation |
mIoU: 76.37 |
32 FPS |
[122] |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/s22072722
