Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Antimicrobial resistance to conventional drugs has resulted in high global rates of recurrent invasive infections, facilitating disease progression and reducing the likelihood of effective treatments.
- antimicrobial peptides
- photochemotherapy
1. Introduction
In 2020, the World Health Organization warned about the appearance of strains increasingly resistant and difficult to control. The indiscriminate use of antimicrobial drugs is facilitated by inadequate medical prescriptions and substandard medications [1].
Considering the challenges related to antimicrobial resistance, other strategies for controlling infections have been suggested [2][3][4][5]. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (aPDT) has been used to inactivate microorganisms and treat infections [2][3][4][5]. aPDT involves the application of a photosensitizing agent (PS), an LED source corresponding to the absorption band of the PS, and the presence of oxygen. This therapy has several advantages in the treatment of infections from microorganisms, such as the wide spectrum of action and a low mutagenic potential in exposed cells [5].
When comparing aPDT with other therapies, it has the advantage of local PS application, restricting the treatment to the area of interest, thus preventing systemic side effects. There is also an immediate onset of action and elimination of virulence factors secreted by resistant microorganisms [6]. Lastly, the literature did not report the development of bacteria and fungi resistance to aPDT [3][7].
Studies have shown that microbial biofilms reduce the susceptibility to aPDT compared to planktonic cultures [3]. Considering the protection endowed by the extracellular matrix (ECM), it is difficult for the PS to penetrate the deeper layers of the microbial biofilm, impairing aPDT activity [8]. To overcome this limitation, aPDT associated with enzymes or antifungal agents was more effective for microbial inactivation than aPDT alone [4][8]. Additionally, antimicrobial peptides (AMP) have been used alone [9][10], combined with aPDT [11][12], or by conjugating a PS to the AMP molecule [13][14][15][16][17][18][19][20][21][22][23][24][25][26][27][28][29][30], presenting satisfactory results in pathogenic microorganism inactivation.
AMP are molecules expressed by all living organisms and responsible for the innate defense system against pathogen infection, including viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites [31]. AMP are oligopeptides with up to 50 amino acids with a broad spectrum of action against microorganisms [32][33]. This new class of compounds has boosted science for new methodologies for synthesizing, isolating, purifying, analyzing, and quantifying peptides [34]. The presence of cationic residues (Arg and Lys) in AMP promotes a positive liquid charge for this structure, resulting in the interaction with the negative cell membrane of the target organism, such as bacteria [34]. Another important aspect of the construction of the AMP amphipathic structure is the high fraction of hydrophobic amino acids (>50%) [35], which is vital for membrane penetration. The biological activity of AMP is closely related to their structure, and these could be classified as α-helix, β-sheet, extended peptides, and both α-helix and β-sheet peptides [36], with the first two appearing more frequently [37]. Although the molecular target of some peptides is inside the cell, as non-membrane disruptive AMP [38], most peptides interact with the anionic components of the membranes of microorganisms and damage this structure [31].
The literature has described the association of AMP and aPDT to explore the best properties of both treatments, increasing the effectiveness and decreasing the time of application [11][12]. AMP can form pores in cell membranes and present biofilm activity [10], which leads to the penetration of the PS into the membrane, facilitating the inactivation of structures through LED photoexcitation [11]. Other advantages of association treatments are reduced effective dose, minimized toxicity potential, and reduced treatment costs [11][39].
2. Synthesis of Results
The results of the systematic review show that all articles had an in vitro experimental design and 3 of them were both in vitro and in vivo experimental studies [27][29][30]. Moreover, of the 20 articles analyzed, 18 performed the therapy with a portion of the PS redirected to AMP and only 2 studies performed the therapy combined with AMP [11][12]. The shortest and longest irradiation times were 30 s [13] and 20 h [20][21], respectively. The most commonly used PS were chlorin e6 [11][12][23][27][29][30] and porphyrin [13][15][16][18][20][21][24][25]. Additionally, the most frequently used microorganism in the assay was Staphylococcus aureus [11][13][14][16][17][18][19][20][21][23][25][26][28][29][30], followed by Escherichia coli [11][13][15][16][17][18][19][20][21][25][26][29][30]. Most of the studies analyzed evaluated the microorganisms in suspension (planktonic culture) and only 4 evaluated the therapy in a biofilm culture [11][23][27][30] (Table 1).
Table 1. Summary of the characteristics of the studies included.
| Study (Year) | Study Design | Peptide | Irradiation Time | Wavelength | Photosensitizer | Microorganism | Culture Type | Sample Size | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bourré et al. 2010 [13] | In vitro | Tat | 30, 43, 60, and 120 s | 410 nm | Tetracks (phenol) and porphyrin | Escherichia coli Staphylococcus aureus Pseudomonas aeruginosa Streptococcus pyogenes |
Suspension | ND | Reduction in the concentration of 1 uM from 3 to 6 log10 CFU/mL. The greatest effect was in the first 30 s. |
| Yang et al. 2011 [14] | In vitro | WLBU2 | 100 s | 652 nm | Temoporfin + WLBU2 | S. aureus (methicillin resistant) P. aeruginosa |
Suspension | 3 | Reduction by 100% for S. aureus (aPDT only and aPDT + peptide) and reduction by 2 log10 CFU/mL for P. aeruginosa (aPDT + peptide). |
| Liu et al. 2012 [15] | In vitro | WI13WF (YVLWKRKRKFCFI-amide) | 2, 5, and 10 min | 400 to 900 nm | Protoporphyrin IX | E. coli Salmonella enteric Klebsiella pneumoniae |
Suspension | ND | Peptide and PS conjugate 99% lethal. |
| Dosseli et al. 2013 [16] | In vitro | Apidaecin | ND | 600–750 nm 390–460 nm |
Porphyrin | E. coli S. aureus |
Suspension | ND | Reduction by 100% for E. coli. |
| Johnson et al. 2013 [17] | In vitro | (KLAKLAK)2 | 30 min | 525 nm | (KLAKLAK)2 + Eosin Y | Acinetobacter baumannii P. aeruginosa E. coli S. aureus Staphylococcus epidermidis |
Suspension | ND | Reduction by 99% for all microorganisms. |
| Dosseli et al. 2014 [18] | In vitro | Magainin Buforin |
ND | 390–460 nm | Porphyrin | E. coli S. aureus (methicillin resistant) |
Suspension | ND | Reduction by 100% for all microorganisms. |
| Johnson et al. 2014 [19] | In vitro | (KLAKLAK)2 | 2 min 5 min 30 min |
525 nm | (KLAKLAK)2 + Eosin Y | E. coli S. aureus |
Suspension | 3 | Reduction by 50% for all microorganisms (2 min of irradiation). Reduction by 90% (5 min of irradiation). Reduction by 99.99% (30 min of irradiation). |
| Le guern et al. 2017 [20] | In vitro | Polymyxin B | 20 h | 420 nm | Porphyrin | S. aureus E. coli P. aeruginosa |
Suspension | ND | Antibactericidal activity of the PS and peptide association on 3 strains. |
| De Freitas et al. 2018 [11] | In vitro | Aurein 1.2 (AU) | ND | 660 nm | Methylene blue Chlorin e6 |
S. aureus A. baumannii E. coli Enterococcus faecium |
Suspension | 9 | S. aureus reduction
A. baumannii reduction
E. coli reduction
E. faecium reduction
|
| Le guern et al. 2018 [21] | In vitro | Polymyxin B modified by lysine | 20 h | 420 nm | Porphyrin | S. aureus E. coli P. aeruginosa |
Suspension | ND | Reduced antibacterial activity of polymyxin modified by lysine. |
| Nakonieczana et al. 2018 [22] | In vitro | CAMEL Pexiganan |
668 s 1335 s 2668 s |
514 nm | Rose-bengal (RB) | P. aeruginosa | Suspension | 3 | Reduction by 2.06 log10 CFU/mL for RB + CAM. Reduction by 6.00 log10 CFU/mL for RB + PEX. |
| Gao et al. 2019 [23] | In vitro | Magainin I | 2 min 4 min 8 min |
660 nm | Magainin I + Chlorin e6 | P. aeruginosa S. aureus (methicillin resistant) |
Biofilm | ND | P. aeruginosa 2 min (0.385 log10 CFU/mL reduction) 4 min (1.645 log10 CFU/mL reduction) 8 min (6.724 log10 CFU/mL reduction) S. aureus 2 min (0.922 log10 CFU/mL reduction) 4 min (3.796 log10 CFU/mL reduction) 8 min (6.586 log10 CFU/mL reduction) |
| De Freitas et al. 2019 [12] | In vitro | AU (GLFDIIKKIAESF-NH2) (AU)2K[(GLFDIIKKIAESF)2-k] |
ND | 664 nm | Methylene blue Chlorin e6 |
Enterococcus faecalis S. aureus E. faecium |
Biofilm | 9 | Reducing the early biofilm stage
|
| Feese et al. 2019 [25 | In vitro | Alkyne 1-Zn TMPYP |
5, 15, and 30 min | 400 to 700 nm | Porphyrin | Mycobacterium smegmatis | Suspension | Inactivation of 4 Log10 CFU/mL when associated with porphyrin and 1-Zn. | |
| Zhang et al. 2019 [25] | In vitro | (KLAKLAK)2(KLA) | 5 min (in vivo) 10 min (in vitro) |
660 nm | PpIX PPK = PpIX + (KLAKLAK)2(KLA) |
S. aureus E. coli |
Suspension | ND | Inhibition rate S. aureus = 100% for both PS E. coli = 100% (PPK)/50% (PpIX) |
| Chu et al. 2021 [26] | In vitro | Bacitracin | 5 and 30 min | 610 nm | Phthalocyanine | E. coli S. aureus |
Suspension | 9 | High phototoxicity of the Peptide with PS. The group without light 99% reduced. |
| Gao et al. 2021 [27] | In vitro/in vivo | PEGylated polypeptide | 5 min | 660 nm | PEGylated polypeptide + Chlorin e6 | P. aeruginosa | Biofilm | ND | Total eradication of P. aeruginosa biofilms. |
| Judzewitsch et al. 2021 [28] | In vitro | ZnTTP-AC | 30 min | Green-light irradiation | ZnTTP-AC | S. aureus P. aeruginosa |
Suspension | 3 | 4.5 log10 CFU/mL reduction for S. aureus. Total reduction for P. aeruginosa. |
| Qiu et al. 2021 [a] [29] | In vitro/in vivo | GKRWWKWWR-RPLGVRG | 5 min | 660 nm | GKRWWKWWR-RPLGVRG + Chlorin e6 | S. aureus E. coli |
Suspension | 3 | Total reduction for S. aureus 90% reduction for E. coli |
| Qiu et al. 2021 [b] [30] | In vitro/in vivo | GKRWWKWWRR | 10 min 20 min 30 min |
660 nm | GKRWWKWWRR + Chlorin e6 + AuNPs | S. aureus E. coli |
Biofilm | 3 | S. aureus 10 min (~50% viability) 20 min (~20% viability) 30 min (~2.5% viability) E. coli 10 min (~60% viability) 20 min (~42.5% viability) 30 min (~10% viability) |
ND: not documented; s: seconds; min: minutes: h: hour; PS: photosensitizer; ~: approximately; MB: methylene blue; RB: rose-bengal; Ce6: chlorin e6.
3. Risk of Bias Assessments for In Vitro Studies
The criteria from the OHAT Rob tool were applied to all articles included in the systematic review. The most frequent biases regarded blinding procedures. Moreover, the problem with internal validity was the lack of methodological details in the statical analyses and the performance of treatments only in microorganism suspensions (Table 2).
Table 2. Risk of bias assessment in the articles included, according to the OHAT criteria.
| Studies/Questions | Was the Dose or Exposure Level Administered Adequately Randomized? | Was the Allocation to Study Groups Adequately Concealed? | Were the Experimental Conditions Identical Across Study Groups? | Were Research Personnel Blind to the Study Group During the Study? | Were the Outcome Data Complete without Attrition or Exclusion from the Analysis? | Is the Exposure Characterization Reliable? | Is the Outcome Assessment (Including Blinding of Assessors) Reliable? | Were There No Other Potential Threats to Internal Validity? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bourré et al. 2010 [13] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
| Yang et al. 2011 [14] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
| Liu et al. 2012 [15] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
| Dosseli et al. 2013 [16] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | -- | ++ | -- | -- |
| Johnson et al. 2013 [17] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
| Dosseli et al. 2014 [18] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
| Johnson et al. 2014 [19] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
| Le Guern et al. 2017 [20] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
| De Freitas et al. 2018 [11] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
| Le Guern et al. 2018 [21] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
| Nakonieczana et al. 2018 [22] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
| Gao et al. 2019 [23] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
| De Freitas et al. 2019 [12] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
| Fesse et al. 2019 [24] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
| Zhang et al. 2019 [25] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
| Chu et al. 2021 [26] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
| Gao et al. 2021 [27] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
| Judzewitsch et al. 2021 [28] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
| Qiu et al. 2021a [29] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
| Qiu et al. 2021b [30] | ++ | ++ | ++ | -- | ++ | ++ | -- | -- |
++: direct evidence of positive finding; --: direct evidence of negative finding.
4. Meta-Analysis
The meta-analysis was performed only in 3 studies [12][14][22]. The reduced number of studies included in the quantitative analysis is due to the lack of data (e.g., sample size) and the absence of a study group evaluating only aPDT application. The experimental group included microorganisms treated with aPDT associated with peptides (aPDT + AMP), while the control group included microorganisms treated only with aPDT (aPDT). The microbial load was the outcome evaluated in the meta-analysis.
The Peto method was used to perform the meta-analysis due to the sparse data. The results were transformed into odds, and, therefore, the odds ratio (OR) was used as the effect measure. The result was significant (OR = 0.14/p = 0.0235/I-squared = 0%), showing better outcomes for aPDT associated with peptides than those for aPDT alone for controlling the microbial load (Figure 1A). Moreover, small-study effects in the meta-analysis and consequently publication and meta-analysis biases were verified with the trim-and-fill method. However, there were no biases (Figure 1B).
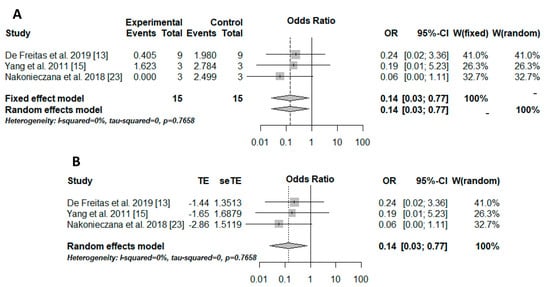
Figure 1. Ilustration of the results of the quantitative analysis. The experimental group (positive events) included microorganisms that received the association therapy (aPDT + AMP), while the control group included microorganisms that received only aPDT. (A) results of the meta-analysis illustrated in a forest plot. OR: odds ratio; CI: confidence interval; W: weight, [12][14][22]. (B) trim-and-fill method results illustrated in a forest plot. TE: estimated mean; seTE: estimated standard deviation; OR: odds ratio; CI: confidence interval; W: weight, [12][14][22].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms23063226
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
