Influenza viruses pose a significant threat to human health. They are responsible for a large number of deaths annually and have a serious impact on the global economy. There are numerous influenza virus subtypes, antigenic variations occur continuously, and epidemic trends are difficult to predict—all of which lead to poor outcomes of routine vaccination against targeted strain subtypes. Therefore, the development of universal influenza vaccines still constitutes the ideal strategy for controlling influenza. This article reviews the progress in development of universal vaccines directed against the conserved regions of hemagglutinin (HA), neuraminidase (NA), and other structural proteiinfluenza virus; antigenic variation; universal vaccine; cross-protection; cellular immunityns of influenza viruses using new technologies and strategies with the goals of enhancing our understanding of universal influenza vaccines and providing a reference for research into the exploitation of natural immunity against influenza viruses.
1. Introduction
Influenza viruses comprise enveloped RNA viruses with a genome composed of eight single-stranded negative-sense RNA fragments encoding polymerase subunits PA, PB1, and PB2, envelope proteins hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA), nucleoproteins (NP) binding to genomic RNA, matrix protein M1 and ion channel protein M2, nonstructural protein NS1, nuclear export protein NEP, and the more recently discovered PB1-F2, PB1 N40, PA-X, and M42 proteins [1,2,3,4,5]. Annual seasonal outbreaks of influenza occur in winter and spring, which can seriously threaten the life of individuals with increased susceptibility to influenza such as the elderly, children, and those with low immunity. According to the statistics of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 39–56 million people were infected by influenza viruses from October 2019–April 2020, among whom 24,000–62,000 died (https://www.cdc.gov/flu). Moreover, based on statistics from the World Health Organization (WHO), 3–5 million cases of severe respiratory disease induced by influenza virus infection occur every year (https://www.who.int/).
Currently, vaccines are considered as the best choice for the prevention and control of influenza. At present, conventional commercial vaccines include whole inactivated influenza virus vaccines, influenza split vaccines, and attenuated vaccines. For whole inactivated influenza virus vaccines, the virus is inactivated while maintaining antigenicity allowing neutralizing antibodies to be produced following vaccination. However, these vaccines offer weak inter-subtype cross-protection and exhibit high incidence of fever upon use in children. Thus, they are not suitable for children under 12 years of age [6,7,8,9]. For influenza split-virus vaccines, the components of an inactivated virus are segregated using splitting agents, removing nucleic acids and macromolecular proteins while retaining only antigens HA and NA, matrix proteins, and nucleoproteins. Such vaccines are widely used. These vaccines have few side effects and high immunogenicity albeit weak inter-subtype cross-protection [10,11]. In turn, attenuated live vaccines are prepared using HA and NA from the epidemic strains recommended by the WHO in combination with cold-adapted influenza strains as the internal skeleton. These cold-adapted strains can replicate effectively at 25–33 °C although their replication is limited at 37 °C. This type of vaccine can be administered via nasal drops, with the limited replication of viruses in the upper respiratory tract able to stimulate the body to produce high-levels of sIgA and cellular immune response, thereby generating strong cross-protection [12,13,14,15]. However, a risk of gene reassortment exists between this attenuated live vaccine and wild strains. In addition, because of the constant reassortment and mutation of gene fragments in influenza viruses, multi-clade strains also frequently appear (e.g., H5 subtype has multiple clade: clade 2.3.4.4, clade 2.3.2.1, etc.), requiring the development of new targeted vaccines [16]. Thus, numerous challenges exist with regard to controlling the influenza virus using traditional influenza flu vaccines [17,18,19,20,21], highlighting the urgent need for development of universal influenza vaccines to promote influenza prevention and control.
At present, research on universal vaccines is mainly focused on the stem region of HA2, chimeric HA, M2e, NP, and T/B cell epitopes. In this review, the target virus proteins and immune effects of universal vaccines are reviewed in order to analyze the advantages and disadvantages of different universal vaccine strategies and provide a theoretical basis for developing safe, effective, and quality-controllable universal influenza vaccines.
2. Novel Universal Influenza Vaccines
2.1. Universal Influenza Vaccines Targeting T/B Cell Epitopes
Epitope vaccines comprise a novel type of vaccine in which T/B cell epitopes are predicted using bioinformatics. The epitope peptides that stimulate the response of T/B cells are screened and obtained, and epitope vaccines are developed through viral vectors, fusion protein, or tandem expression. However, for influenza viruses, the sequence differences among different subtypes are so large that it is difficult to produce extensive protection through use of individual subtype strains. Therefore, the exploration of conservative or differential dominant T/B cell epitopes among different subtypes and their subsequent use to develop universal vaccines by means of expressing all the dominant T/B cell peptides may serve to produce excellent protection. Numerous attempts have been made to develop such influenza epitope vaccines. For example, the overlapping MHC class II restricted B cell epitopes and MHC class I restricted T cell epitopes have been screened out from the HA proteins of H1, H2, H3, H5, H7, and H9 subtypes and connected with other epitopes in series to construct plasmid DNA and virus vector vaccines. However, studies in animals found that the epitope vaccine group could produce extensive specific cell response but could not provide complete protection [
62,
63,
64].
In addition, researchers have engineered conserved T cell epitopes of M1, NS1, PB1, and PA proteins, or M2e, HA fusion peptide, NP T cell epitopes, and the HA α-helical region into vaccinia virus vector-based vaccines for immunizing animals, which were challenged with A/WSN/33, A/PR/8/34 or A/California/07/09 strains of influenza virus [
48]. However, the vaccine only delayed death and did not provide protection [
48]. Hassan et al. [
64] generated human adenovirus replication defective vectors to express multi-epitopes—M2e, HA fusion domain (HFD), T-cell epitope of nucleoprotein (TNP), and HA α-helix domain (HαD)—of an H5N1 avian influenza virus and evaluated its immunogenicity and protective efficacy in a mouse model. Immunized animals were then challenged with H5N2, H7N9, or H9N2 influenza virus. The epitope vaccine induced humoral and cell-mediated immune response and significantly reduced the viral load in mouse lung. Compared with the single HA subunit vaccine group, the viral load of each organ in the epitope vaccine group was lower and the protection was more extensive; however, the vaccine’s ability to protect animals was not mentioned [
64]. In turn, Eickhoff et al. [
63] used state-of-the-art immunoinformatic tools to identify putative pan-HLA-DR and HLA-A2 supertype-restricted T cell epitopes highly conserved among >50 widely diverse influenza A strains—representing hemagglutinin types 1, 2, 3, 5, 7 and 9–and constructed these epitopes into eukaryotic expression plasmids. The results showed that pan-HLA-DR epitope and HLA-A2 epitope vaccines all protected 50% of immunized animals from A/H3N2 or A/PR8/H1N1 influenza infection and significantly reduced the viral load of H3N2 infection [
63].
Overall, these results suggest that current epitope vaccines are only capable of producing partial protection for immunized animals rather than serving as universal vaccines. Nevertheless, epitope vaccines offer unique advantages as they stimulate the wide range of the body’s immune response, are safe, and afford simple and rapid mass production, in accordance with the preferred direction of future universal influenza vaccine development. Notably, several epitope vaccines are undergoing clinical review. Multimmer-001 (M-001)—developed by BiondVax Pharmaceuticals Ltd. (Israel)—is a single recombinant protein containing nine conserved epitopes from the HA (four B and one Th epitopes), NP (two CTL and one Th epitope), and M1 (one peptide that contains both B and CTL epitopes) proteins of both influenza type A and type B strains (Victoria and Yamagata lineages) that are known to induce both humoral and cellular immunity. Currently, the M-001 vaccine is in phase IIb clinical trials to evaluate its safety and immunogenicity as a standalone vaccine or as a primer to an H5N1 influenza vaccine product (Fluart Innovative Vaccines Ltd., Hungary) in healthy adults (aged 18–60 years) [
65,
66,
67,
68]. In turn, FLU-v, developed by PepTcell (SEEK), is a peptide vaccine comprised of four synthetic peptides with conserved epitopes from influenza A and B strains designed to provide a broadly protective cellular immune response against influenza A and B. Results from phase IIb clinical trials showed that adjuvanted FLU-v recipients (
n = 40) were significantly less likely to develop mild to moderate influenza disease (MMID) following intranasal challenge of A/CA04/H1N1 vs. placebo (
n = 42) (32.5 vs. 54.8%
p = 0.035) [
69,
70,
71]. Nevertheless, overall the vaccine protection effect was poor. It is thus expected that considerable time will be required to develop a peptide vaccine. In addition, the diverse alleles of HLA-I and HLA-II in the population should be carefully considered in the development of universal influenza epitope vaccines.
2.2. Universal Mosaic Influenza Vaccines
Mosaic vaccines are a new vaccine strategy developed mainly for viruses with easily mutated genes and numerous subtypes. In these vaccines, the most conservative T cell epitopes are selected from viral gene sequences using bioinformatics to calculate and synthesize a chimeric gene sequence, and a Mosaic protein sequence covering potential T/B cell epitopes is then obtained using a specific genetic algorithm. Currently, Mosaic vaccines for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) prevention have entered phase III clinical trials [
72,
73,
74]. Similarly, Mosaic vaccines offer good prospects for the prevention of influenza. In particular, studies of Mosaic H5 HA in animals show that this vaccine can elicit full protection against clade 0, 1, and 2 avian influenza viruses of H5N1 and also protect against seasonal H1N1 virus (A/Puerto Rico/8/34) [
75,
76,
77]. In addition, Corder et al. [
78] designed Mosaic H1 HA vaccines according to human H1 influenza HA sequences isolated from 1918 to 2018. Mice immunized with a prime or prime-boost strategy using recombinant adenovirus Ad5-mosaic were completely protected against A/Nanchang/1/99, A/FM/1/47, and A/PR/8/34 viruses. However, the study did not evaluate the vaccine’s protective effects against heterologous virus [
78]. Nevertheless, because of the large sequence differences among different subtypes and the challenges associated with exploiting the huge sequence information base, it is expected that Mosaic vaccines will likely be limited to being designed using HAs of the same subtype, for which they produce good protective effects [
78,
79,
80]. Accordingly, current Mosaic vaccines are based on the prediction of T/B cell epitopes as the main core technology in combination with a specific algorithm to screen out sequences with high T/B epitope coverage rate in the sequence database [
75,
79,
80]. However, as variations are always present, it is difficult to obtain epitope sequences covering all subtypes while maintaining the correct HA protein conformation. Thus, current Mosaic vaccine strategies appear in direct contrast to those needed to develop a universal influenza vaccine that produces protection against heterogeneous virus. In the future, it may be warranted to develop Mosaic vaccines rather by continuously optimizing the algorithm based on different target proteins and producing sequences with a higher epitope coverage rate based on the principle of seeking common ground while preserving differences.
2.3. Nanoparticle Universal Influenza Vaccines
Nano-vaccine technology can package virus particles or effective antigens into virus-like nanoparticles. The resultant nanoparticle vaccine display antigens on the surface of particles or enclose antigens in the particles in order to increase the antigenicity and immunogenicity of the vaccine. At present, research on nanoparticle universal influenza vaccines is mainly focused on virus-targeted proteins—e.g., HA, HA stem, M2e, NP, NA, and mosaic—which are synthesized into nanoparticles to increase the immune effect of the vaccine [
81,
82,
83,
84,
85,
86,
87].
In general, two strategies exist to increase the antigenicity of nanoparticle vaccines. The first is to display antigens on the surface of particles such as nano gold or silver, polymers, and other inorganic matter or on self-assembled ferritin, VLPs, chitosan, and other organic matter to improve the ability of immune cells to recognize the antigen. Single or multiple antigens are loaded onto the surface of the nanoparticles or fused and expressed with self-assembled proteins to form nanoparticles [
83,
85,
88,
89,
90]. Kanekiyo et al. [
91] combined the expression of the HA receptor binding domain (RBD) of the H1N1 subtype of two viruses fused with a ferritin nanoparticle scaffold sequence to assemble double-loaded nanoparticle vaccines. The immunization results showed that the double-load assembled nanoparticle vaccine could induce extensive humoral immunity, with levels of neutralizing antibodies that were higher than those of a single-assembly nanoparticle vaccine [
91]. Nevertheless, this study did not provide vaccine protection data against homologous or heterologous virus in animals. Bernasconi et al. [
92] loaded an HA trimer (A/Puerto Rico/8/34 H1N1) and 3M2e-3Eα (A/Victoria/3/75 H3N2) fusion protein onto the surface of nanoparticles to immunize animals using polysaccharides and palmitate liposomes as the core of the nanoparticles. The vaccine could induce immune protection, which was mediated by enhancing the level of CD4
+ T cells in the lung and serum IgG and local IgA antibodies against HA and M2e. Notably, double-load M2e-HA nanoparticles produced complete protection against PR8 virus and high dose of single 3M2e-3Eα nanoparticles could produce complete protection against mouse-adapted X47 virus—a reassortant between A/Victoria/3/75 (H3N2) and A/Puerto Rico/8/34 (H1N1) [
92]. However, this study also did not demonstrate vaccine protection data against heterologous virus in animals. Overall, these results suggest that nanoparticles are advantageous for small immunogenic proteins or small-molecule epitopes to enhance immunogenicity as well as for loading multiple proteins.
The second method is to encapsulate single or multiple antigens in particles using liposomes and then transport them into cells via the endocytosis mechanism of cells using a double-layer structure of lipids as a carrier, thereby enhancing the efficiency of cell processing and antigen presentation. Toward this end, researchers immunized animals with M2e of multiple influenza viruses encapsulated by liposome nanoparticles, which produced 90–100% survival following lethal challenge with H1N1 (A/PR/8/34) [
93]. Dhakal et al. [
94] selected ten highly conserved and well-characterized influenza A virus chemically synthesized peptides (from M2e, HA, NP, PB1, NA, PA) and encapsulated these in liposomes. Following immunization, the peptide flu vaccine partially protected pigs from flu-induced fever and pneumonic lesions and reduced nasal virus shedding and viral load in the lungs [
94]. In turn, Wang et al. [
95] used pulmonary surfactant-biomimetic nanoparticles to package cGAMP as an adjuvant to mix with inactivated H1N1 influenza vaccine and then administered the immunization through the respiratory tract, resulting in extensive protection against H1NI, H3N2, H5N1, and H7N9 virus infection. As research on the protective mechanism of vaccines has demonstrated that lipid bilayer nanoparticles with a negative charge can effectively mediate endocytosis after binding with pulmonary surfactant protein in the alveoli, cGAMP could effectively activate the downstream STING pathway and stimulate the pulmonary epithelial cells to secrete cytokines, thereby enhancing the immune response of the body to T/B cells produced by vaccines. Notably, CD8
+ T cells were found to play a key role in the cross-immunoprotection mediated by the vaccine [
95]. Therefore, for some adjuvants or antigens that play a direct role in cells, lipid encapsulation might support effective transmission into cells through the endocytosis mechanism in order to enhance the immune effect of the vaccine.
Multiple key target proteins for universal vaccines have been identified in preliminary research (). Together, the findings indicate that nanoparticles are suitable as carriers to transfer these antigens into cells or to be recognized and processed by the body, thereby effectively stimulating immune response to produce extensive immune protection.
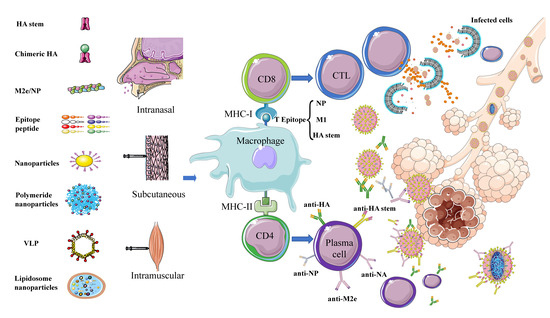
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of immune responses activated by different types of potential universal influenza vaccines. Universal influenza vaccines developed using different strategies involving different target proteins are administered by subcutaneous, intranasal, and intramuscular routes. The antigen is phagocytosed and processed by macrophages and other APC cells. Subsequently, B cell epitopes form a complex with MHC-II and are presented to the cell surface. Under the combined action of CD4 cells, B cells are activated to differentiate into plasma cells and secrete antibodies—e.g., anti-HA, anti-NA, anti-NP, anti-M2e, and anti-HA stem–to neutralize the virus. T cell epitopes—mainly, NP, M1, and HA stem—form a complex with MHC-I and are presented to the cell surface, under the action of CD8 cells and activate T cells to differentiate into CTLs to kill virus-infected cells.
3. Adjuvants
Adjuvants are key components in the study of universal influenza vaccines because of their potential to increase the titer and/or breadth of the antibody repertoire and enhance T cell immune responses, particularly subunit and inactivated vaccines. Adjuvants are injected into the body together with antigens to enhance the immune response ability of the body to antigens. The mechanism of action of adjuvants may rely upon a combination of various mechanisms including formation of a depot, induction of cytokines and chemokines, recruitment of immune cells, enhancement of antigen uptake and presentation, and promotion of antigen transport to draining lymph nodes [
96,
97]. Adjuvants include interferon pathway activators Poly I:C and cGAMP, cytokines including interferon and interleukin, and bacterial structural components flagellin and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) along with immunoregulatory oligonucleotide sCPG and synthetic chemical substances that play a role in immunological enhancement [
51,
95,
98,
99,
100,
101,
102,
103,
104]. However, as universal influenza vaccines have been developed into multiple vaccine types—e.g., viral vectors, DNA, and subunit—to express influenza cocktail proteins such as HA stem, chimeric HA, M1, M2e, NP and epitope peptide (), suitable adjuvants should be selected according to the vaccine strategy and type of desired immune response activation. For example, for universal influenza vaccines that mainly activate T cell response, such as HA stem, M1, NP protein, and T epitope vaccines, an adjuvant that activates the T cell response should be selected—e.g., Poly I:C, CAF01, CD1d ligands, AS01, or CpG-ODN. For vaccines that mainly activate humoral immune responses, such as those based on chimeric HA and M2e proteins, an adjuvant that activates antibody responses should be selected—e.g., aluminum adjuvant, MF59, or AS30 [
105]. In summary, the scale and breadth of the antibody immune response and T cell immune response determine the ability of the vaccine to protect against heterologous strains. Choosing the right adjuvant can greatly improve the efficacy of the vaccine.
4. Perspective
The specific segmental gene structure and lack of polymerase proof reading function of influenza viruses are conducive to gene reassortment and mutation during infection of the host. Consequently, the development of vaccines always lags behind the evolution of variation in viruses. However, the development of universal influenza vaccines represents the key to preventing influenza. To date, most studies have focused on humoral and cellular immune responses, which can provide extensive protection after animals are immunized with the stem region of HA, chimeric HA, NA, and M2e, M1, NP, and T/B epitopes, Mosaic, or Nanoparticles (). Nevertheless, although numerous achievements have been made, disadvantages as well as advantages of each method remain (). Accordingly, a universal vaccine should be designed to stimulate both humoral and cellular immunity, with the ability to activate CD8+ T cells being key to generating broad protection. In fact, the protective effects of many universal influenza vaccines have been evaluated only in animals and have not yet entered clinical trials in humans. There are a number of factors that prevent vaccines from being evaluated from animals to humans. The most important factor is that the evaluation of human clinical trials is different from that of animal trials, and there are very complex factors (infants, the elderly, pregnant women, sub-healthy populations and overweight/obese individuals) that often fail to achieve the same immune effects as animal trials. The huge cost of human clinical evaluation of vaccines is also one of the important reasons. Therefore, the prevention and control of influenza viruses is a common problem faced by mankind all over the world, which needs the joint efforts of every researcher.
Table 1. Advantages and disadvantages of universal influenza vaccines.
|
Vaccine Type
|
Protein Expression System
|
Protection Ratio
|
Advantage
|
Disadvantage
|
References
|
|
Homologous
|
Heterologous
|
|
HA stem
|
Eukaryotic expression
|
Complete protection
|
Partial protection; Poor protection for different HA groups
|
Single HA stem can produce extensive protection for the same HA group
|
Protection is limited by group differences
|
[22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33]
|
|
Chimeric HA
|
Eukaryotic expression or rescue chimeric attenuated virus vaccine
|
Complete protection
|
Partial protection; Poor protection for different HA groups
|
Easy production of chimeric attenuated vaccine
|
Protection is limited by the type of chimeric subtype and requires multiple immunizations with different chimeric vaccines
|
[24,33,34,35,36,37,38,39]
|
|
NA
|
Eukaryotic expression
|
Complete protection
|
Partially protected or unprotected
|
Strong ability to protect different HA subtype strains of the same NA type
|
Poor protection against different NA types
|
[40,41,42,43,44,45]
|
|
M1, M2e, NP
|
Viral vectors, plasmids
|
Partial protection
|
Generates different protection according to M1, M2e and NP sequence differences
|
Wide range of protection without being limited by HA group differences
|
Not fully protected; Poor immunogenicity requires tandem or combined expression with other proteins
|
[39,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61]
|
|
Epitope peptide
|
Chemical synthesis, prokaryotic expression, viral vectors, plasmids
|
Partial protection
|
Different protection depending on how much dominant epitope of certain flu covered
|
Simple, stable, easy to synthesize, non-toxic; not restricted by HA group differences
|
Difficult to screen for co-conserved epitopes in large influenza databases; Limited by population MHC diversity; Poor immunogenicity
|
[62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71]
|
|
Mosaic
|
Viral vector, eukaryotic expression
|
Complete protection
|
Different protection based on the subtype on which the Mosaic design is based
|
Strong protection and extensive protection for different clades of the same subtype
|
Difficult to find a sequence that covers all epitopes in the large influenza database
|
[72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80]
|
|
Nanoparticles
|
Gold nanoparticles, polymers, VLPs, liposomes
|
Different protection according to the type of antigen loaded
|
Efficiently improve immunogenicity; Load multiple antigens
|
Complex preparation process
|
[81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95]
|
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/v12091033