Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Biofilms embrace the capability to resist and survive harsh environmental conditions and defeat the host immune system, so there is a desire for exploring new antibiofilm agents. Antibiofilm agents that can abet the process of dismantling the biofilm has provided research strategies for designing new biofilm dispersal inducers.
- biofilms
- infection
- inhibitors
- extracellular polymeric substances
- antimicrobials
1. Mode of Action of Antibiofilm Agents
1.1. Bacterial Surface Attachment Inhibition
Bacterial appendages like flagella or fimbriae aid their attachment to surfaces, so inhibition of these appendages can be an approach to avert adhesion. Surface coating or surface modification with agents having antibacterial properties is an emerging technique to hostile microbial adhesion and proliferation [102,103,104,105,106]. Inhibition of bacterial adhesion can be achieved by surface coating with biocidal agents or specific polymers having an ability to inhibit the cells impending the surface. Indeed, novel polysaccharides from Antarctic sponge-associated bacteria and lake macroalgae have recently been used to hinder the adhesion of bacteria [107,108]. Surface topography using nanotechnology has recently been explored to generate antibacterial surfaces [109,110,111,112].
1.2. Interfering with Quorum-Sensing
Microbial cell-to-cell communication at the molecular level, which enables the microbes to reciprocate to surrounding changes, is permitted by a mechanism called quorum-sensing (QS). QS is reliant on the binding of an autoinducer to an analogous gene regulator, which activates the ensuing transcriptions [113,114,115,116,117]. QS systems are associated with upregulation of gene expression through the accessory gene regulator (agr) system, forming virulence factors such as adhesins, toxins, hemolysin and autolysins in Gram-positive staphylococcal infections or siderophores, exoproteases, rhamnolipids and exotoxins in P. aeruginosa [121,122,123,124]. The formation of biofilms and related virulence factors by infective microbes requires cell-cell communication, hence agents acting as QS inhibitors and specifically targeting the AHL-QS system in bacteria have been widely explored for their efficacy using in vitro and in vivo models [125,126,127].
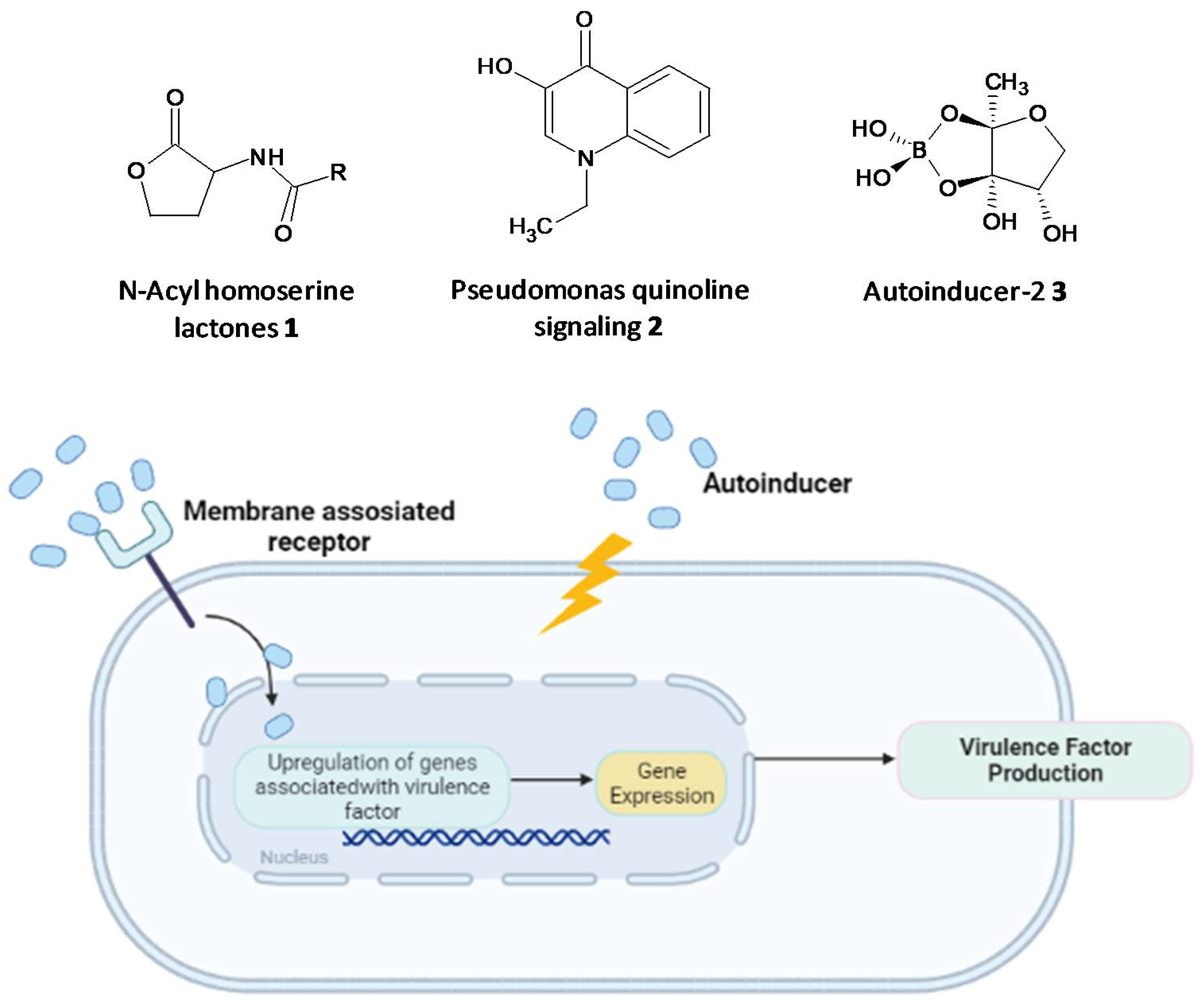
Figure 1. Chemical structures of some autoinducers (top) and production of virulence factors (bottom).
1.3. Nucleotide Second Messenger Signaling Modulating Molecules
The second messenger cyclic di-guanosine monophosphate (c-di-GMP) has emerged as a signaling molecule in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria governing the process of biofilm formation, biosynthesis of EPS, virulence and suppression of cell motility. The enzyme diguanylate cyclase is essential for synthesis of c-di-GMP, inhibition of which has proven to terminate biofilm formation, alluding to the significance of c-di-GMP in the bacterial signaling process [128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135].
1.4. Bacterial Genetic Biodiversification Inhibitors
Genetic biodiversification in bacteria leads to emergence of newer subpopulations, which have been ascribed to be resistant to antibiotic therapies and environmental stressors. Horizontal gene transfer with conjugation plays a crucial role in the outspread of resistance in biofilm colonies [136,137,138]. The social evolution theory anticipates that inhibiting shared traits among the subpopulations could be a viable solution for eradicating the biofilm. The fact that the organism in a subpopulation relies on a shared EPS makes it an interesting target to combat genetic diversification. The spatial structure and heterogeneity provided by biofilms lead to increased genetic diversity [139].
1.5. Biofilm Dispersal Inducers
Biofilm dispersal is initiated by the disruption of the EPS matrix to release the microcolonies of planktonic cells that migrate and adhere to new surfaces. Antibiofilm agents that can abet the process of dismantling the biofilm has provided research strategies for designing new biofilm dispersal inducers [140,141,142]. This dispersal process provides an opportunity to target the microorganisms since they now exist in their viable form, a way more susceptible form permitting the attack of standard antimicrobials comparable to cells residing in the biofilm [143,144]. Biofilm dispersal agents have triggered the interest of researchers to design combination treatments along with antibiotics.
2. Emerging Antibiofilm Agents
2.1. Inhibition of Persister Cell Formation by a Synthetic Diterpene
Tkachenko et al. identified a synthetic diterpene derivative as a lead molecule proficient in repressing resistance and annihilating the biofilm formation in Mycobacterium smegmatis. Persister cell formation in Mycobacterium is highly dependent on the alarmone (p)ppGpp and its essential Rel protein. The analogue 4-(4,7-di-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-naphthalene-1-yl)pentanoic acid (DMNP) (4) (Figure 3) was found to inhibit RelMsm activity of (p)ppGpp-synthesis in a concentration-dependent manner [154]. Furthermore, docking studies suggested the interaction of DMNP with RelZ and RelMsm proteins and high affinity with their GTP binding sites, consequently impeding their (p)ppGpp-synthesizing activity [155].
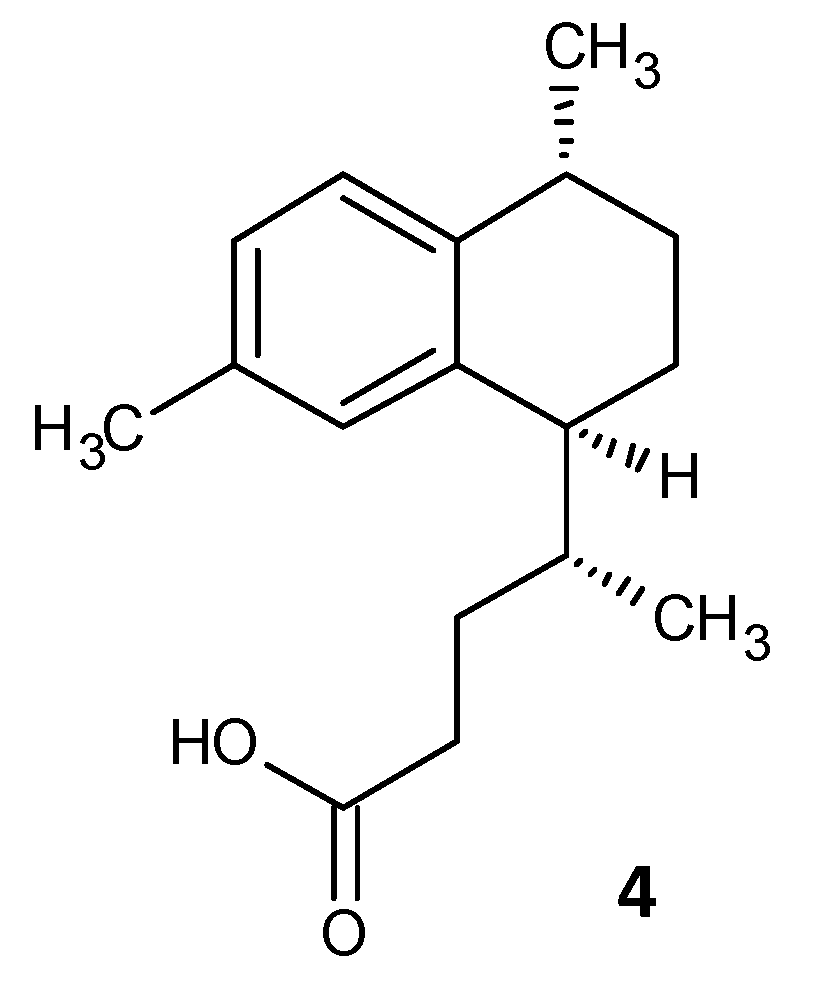
Figure 3. Chemical structure of DMNP.
2.2. Inhibition of Sortase A by 1,2,4-Oxadiazole Topsentin Analogs
A series of seventeen 1,2,4-oxadiazole topsentin analogs was synthesized by Parrino et al. and assessed for their biofilm inhibition, by targeting the membrane enzyme transpeptidase sortase A (SrtA), which attaches surface adhesive molecules to the cell wall in Gram-positive organisms. All these compounds inhibited biofilm formation in S. aureus species with BIC50 values less than 10 μM for the most potent derivatives (5a–c). The potent analogues displayed BIC50 values for S. aureus in the range of 0.7 to 9.7 μM, and additionally showed a superior enzyme inhibition with IC50 values of 2.2 to 10.4 μM. SAR analysis revealed the significance of the presence of the -N=C-O- group in the oxadiazoles for dual antibacterial and biofilm inhibitory activity [156]. In a similar work by Carbone et al., thiazole analogs of nortopsentin were synthesized of which the potent derivatives 6a–b showed BIC50 values against S. aureus of 3.9 and 1.0 µM (Figure 4 and Table 2) [157].
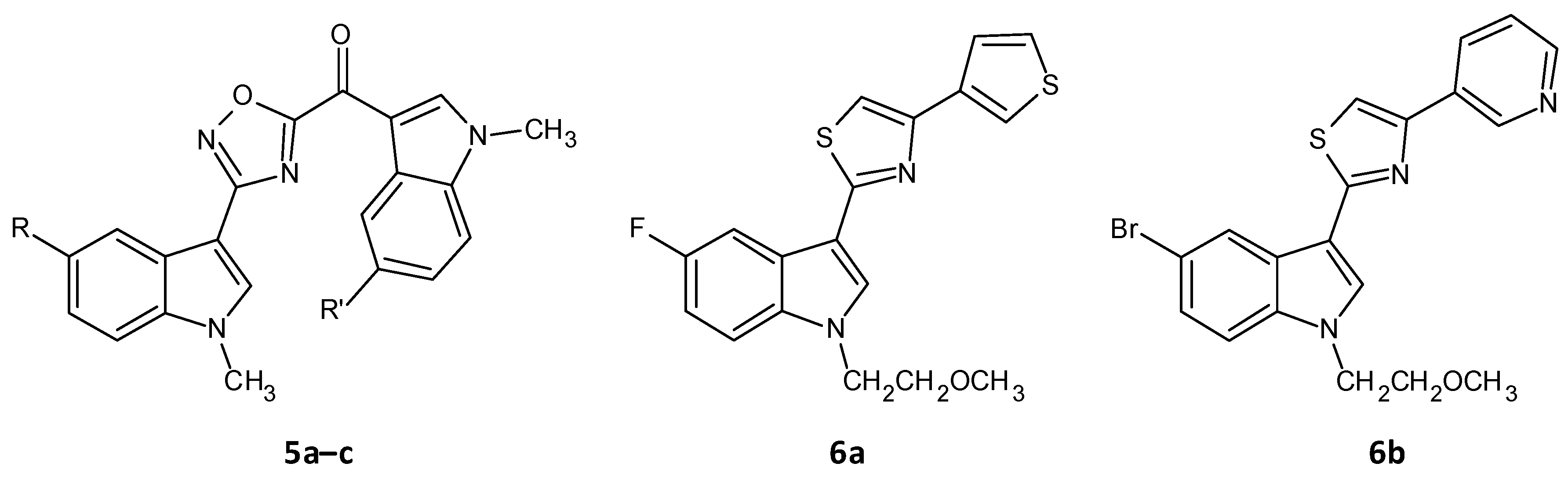 Figure 4. Chemical structures of potent 1,2,4-oxadiazole topsentin analogs.
Figure 4. Chemical structures of potent 1,2,4-oxadiazole topsentin analogs.2.3. Amide Chalcones
El-Messerya et al. synthesised a panel of amide chalcones linked with different secondary amines and assessed them for in vitro antibacterial activity and their antibiofilm activity. A minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) value of 2.0 mg/mL against S. aureus equivalent to the standard ampicillin was shown by compound 7a. Compounds 7a, 7b, and 7c (Figure 5) displayed a significant biofilm inhibition with IC50 values in the range of 2.4 to 8.6 mg/mL against S. aureus, Micrococcus luteus and P. aeuroginosa (Table 3) [158,159].
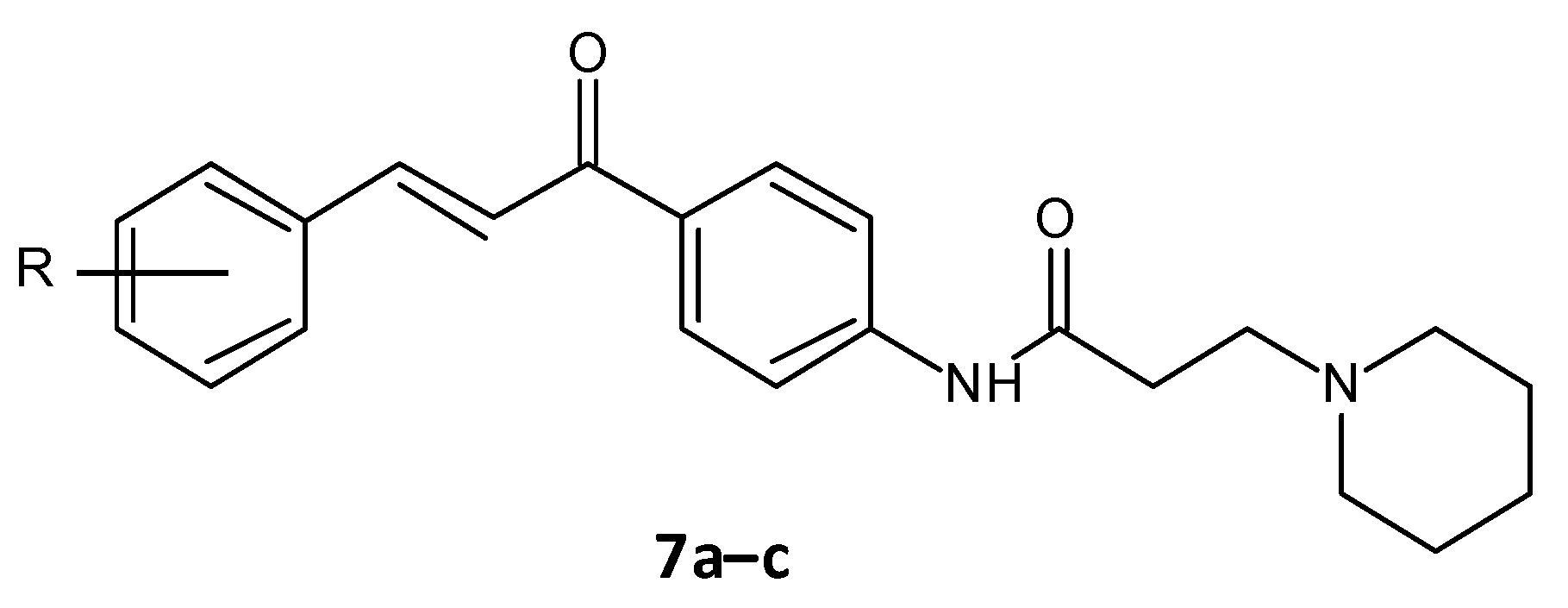
Figure 5. Chemical structure of amide chalcones.
2.4. Cajaninstilbene Acid Derivatives
Chen and co-workers recently developed cajaninstilbene acid derivatives and evaluated their ability to inhibit biofilm formation. Of the synthesized analogues, compounds 8a, 8b and 8c (Figure 6) exhibited promising antibiofilm activity, furthermore 8c displayed potent biofilm inhibition with a ratio of 49.50 ± 1.35% at 50 μM (Table 4). Additionally, compound 8c showed suppression on expression of lasB-lacZ and pqsA-lacZ involved in the QS network pathway in P. aeruginosa. Thereby proving compound 8c as a promising lead with inhibition of QS and associated biofilm formation in P. aeruginosa [160,161].
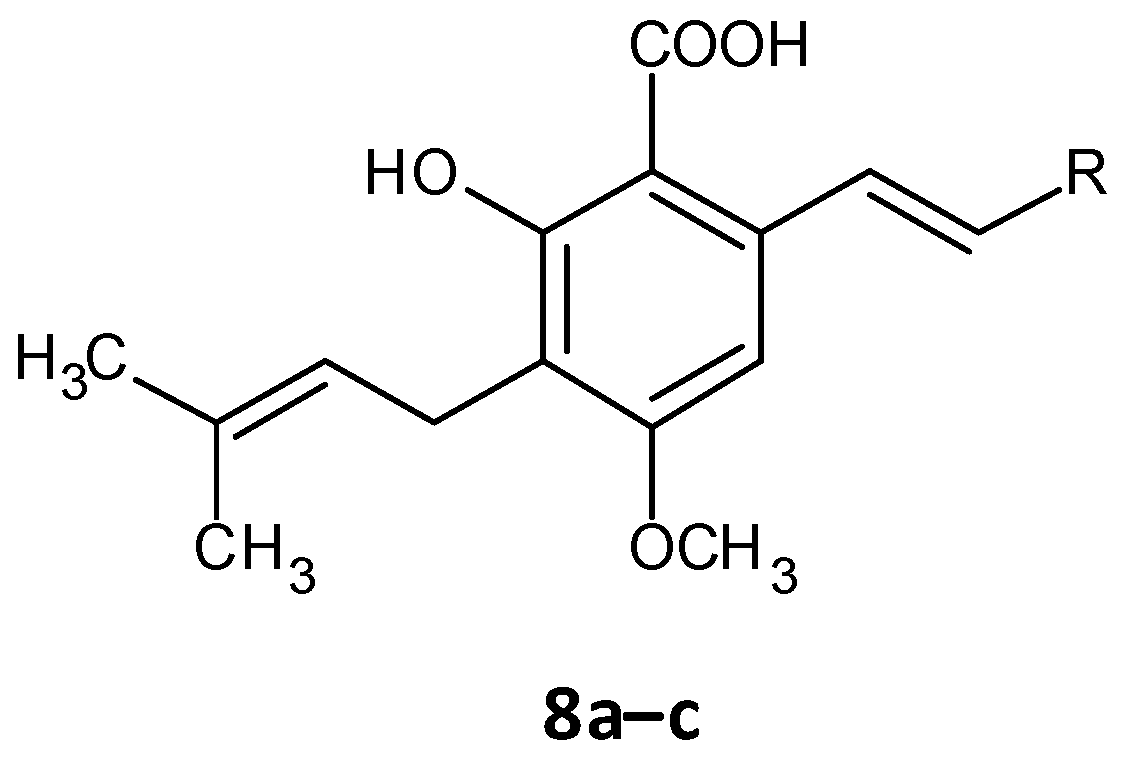
Figure 6. Chemical structure of cajaninstilbene acid derivatives.
2.5. Quorum Quenching Agents
The persister cells have the ability to communicate amongst themselves leading to virulence and the generation of resistance. Different quorum quenching agents have been explored in order to find adjuvant therapy. The bacterial QS inhibitory effect of subtilosin (9), a cyclic lantibiotic formed by B. subtilis KATMIRA1933, was assessed by Algburi et al. [162]. Subtilosin shows its effect by targeting the surface receptor and binding to the bacterial cell membrane by electrostatic forces. The study revealed that at a concentration of 15.1 μg/mL an inhibition of 80% of L. monocytogenes and about 60% of E. coli biofilms was seen. Moreover, subtilosin decreased the autoinducer-2 formation in Gardnerella vaginalis at a concentration of 3–4 μg/mL [152]. Zhou et al. evaluated the QS inhibitory potential of hordenine (10) isolated from sprouting barley towards P. aeruginosa. It was found to inhibit the autoinducer AHLs at concentrations of 0.5 to 1.0 mg/ mL. Additionally, it also remarkably suppressed the QS associated genes lasR, rhlR, rhlI and lasI [163]. In another work by Zhao et al. the QS inhibitory effect of falcarindiol (11) against P. aeruginosa infestation was assessed. Biofilm formation and associated virulance factors were significantly inhibited at subinhibitory concentrations. Also, there was appreciable downregulation of the mRNA expression of QS associated genes lasI, lasB, rhlA, pqsA, rhlR, phzH and rhl I [164]. QS and biofilm inhibitory effects of a few hordenine derivatives towards P. aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens was recently analysed by Liu et al. Derivatives 12a–g exhibited superior QS inhibitory activity and biofilm inhibition towards P. aeruginosa. Additionally, analogues 12a–c and 12g displayed remarkable QS inhibition against S. marcescens. SAR studies revealed essential factors involved in activity like alkyl chain length, presence or absence of amino or hydroxyl groups and unsaturation in the aromatic benzene ring [165]. A thiolactone analog of AHL covalently linked to ciprofloxacin (QS0108) (13) was developed by Ganguly et al. to assess them as inhibitors of AHL-2 in P. aeruginosa. This system effectively disrupted dormant and mature biofilms compared to antibiotic treatment alone (Figure 7) [166].
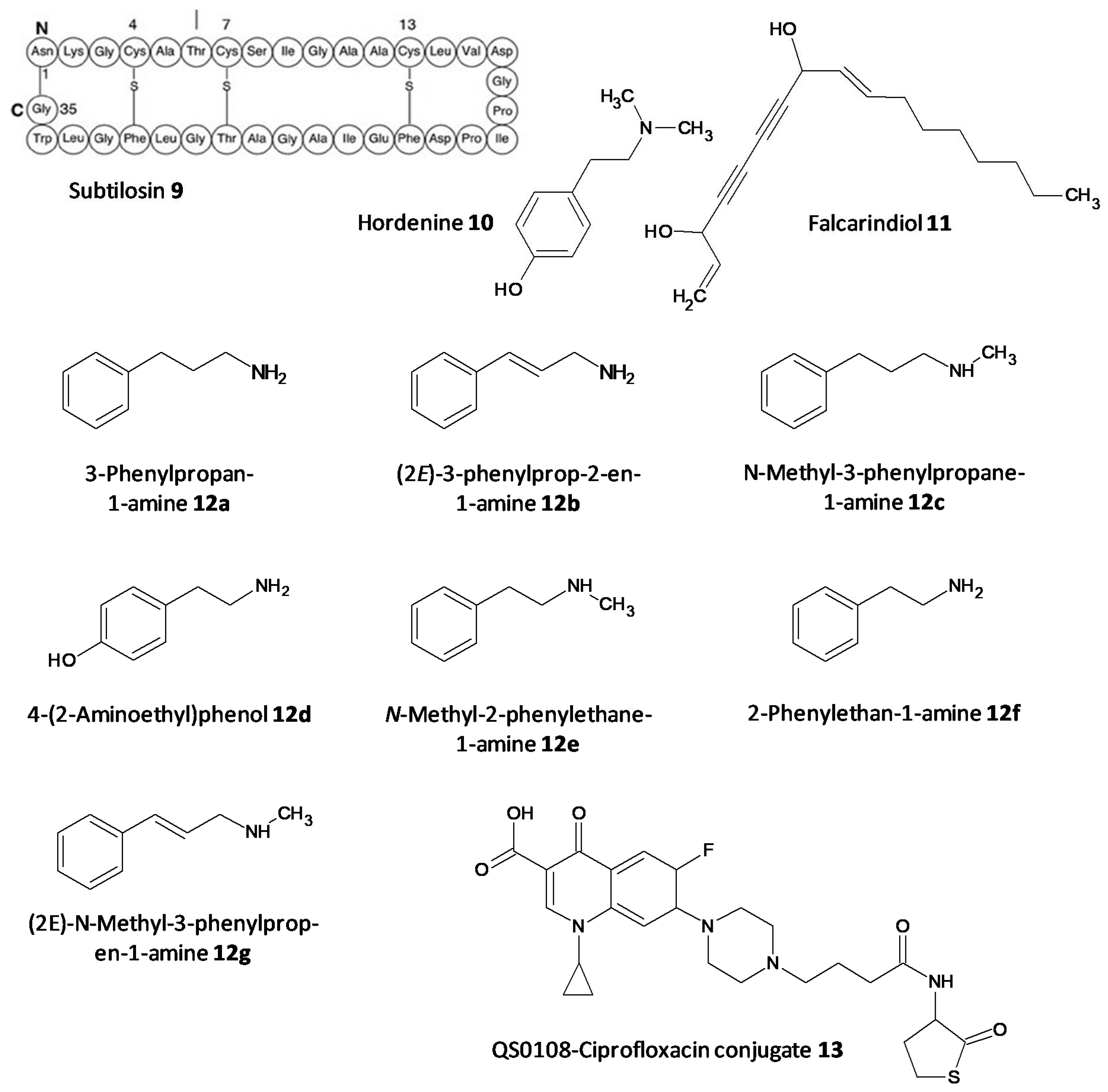
Figure 7. Chemical structures of various quorum sensing inhibitors.
2.6. Antimicrobial Peptides
AMPs are emerging as attractive antibiofilm agents owing to various properties that they display, such as a broad-spectrum of antimicrobial activity, decreased resistance and synergistic effects shown with few antibiotics. Indeed, these properties mean that AMPs could become the next generation of antimicrobials to curb the biofilm related resistance shown by current antibiotics.
Festa et al. a worked on the AMP 1018-K6 as an antibiofilm agent against MRSA and enterotoxigenic S. aureus isolated from cheese. This peptide exhibited remarkable eradication of preformed Staphylococcal biofilms within 15 min. Moreover, it prevented further formation of biofilms and displayed bactericidal action against the planktonic cells [172]. In a continuation of the work on 1018-K6, Colagiorgi et al. worked on the antibiofilm ability of the food pathogen Salmonella enterica. Of the 42 strains included in the study, 1018-K6 profoundly decreased the biofilm formation in several S. enterica strains at subinhibitory concentrations [173].
2.7. Antibiotics Affecting Bacterial Cell Permeability
Antibiotics affecting cell permeability target several components of the cell wall and its synthesis. The peptidoglycan class of antibiotic vancomycin inhibits the cell wall synthesis by complex formation with the D-Ala-D-Ala subunit at the carboxyl terminal in a peptidoglycan chain [174,175,176]. AMPs like polymyxin B pile up in the outer membrane by binding to lipid A and eventually invade the inner membrane making its way into the cytoplasm. The resistance to this antibiotic is seen by either mutations in the governing systems PmrAB and PhoP/PhoQ or modification of the phosphate functional groups of lipid A [177,178].
5.8. Enzymatic Cleavage Inhibitors
On being exposed to an antibiotic the bacterial cells inturn release enzymes which act in a defensive way in the extracellular space, cleaving and deactivating the antibiotic. The resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics has been associated to the enzyme beta-lactamase. A combination of ceftazidime and a beta-lactamase inhibitor avibactam has been explored for its antibiofilm activity towards carbapenemase-producing K. pneumoniae. Avibactum (14) was also proven to irreversibly curb the β-lactamase enzyme from Mycobacterium tuberculosis [179,180,181,182]. 7-Hydroxytropolone (15) acts as an inhibitor of the enzyme aminoglycoside-2”-O-adenylyltransferase and was active against bacterial strains resistant to amioglycosides. The structure of 7-hydroxytropolone, exhibits an eccentric vicinal positioning of the oxygens which aids in the enzyme inhibition [183]. Plazomicin (ACHN-490) (16) a neamine derivative was designed by modifying the sites that displayed affinity to the resistance caused by aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes allowing it to preserve the antimicrobial activity towards pathogens that possess aminoglycoside resistance genes [184,185] (Figure 8).
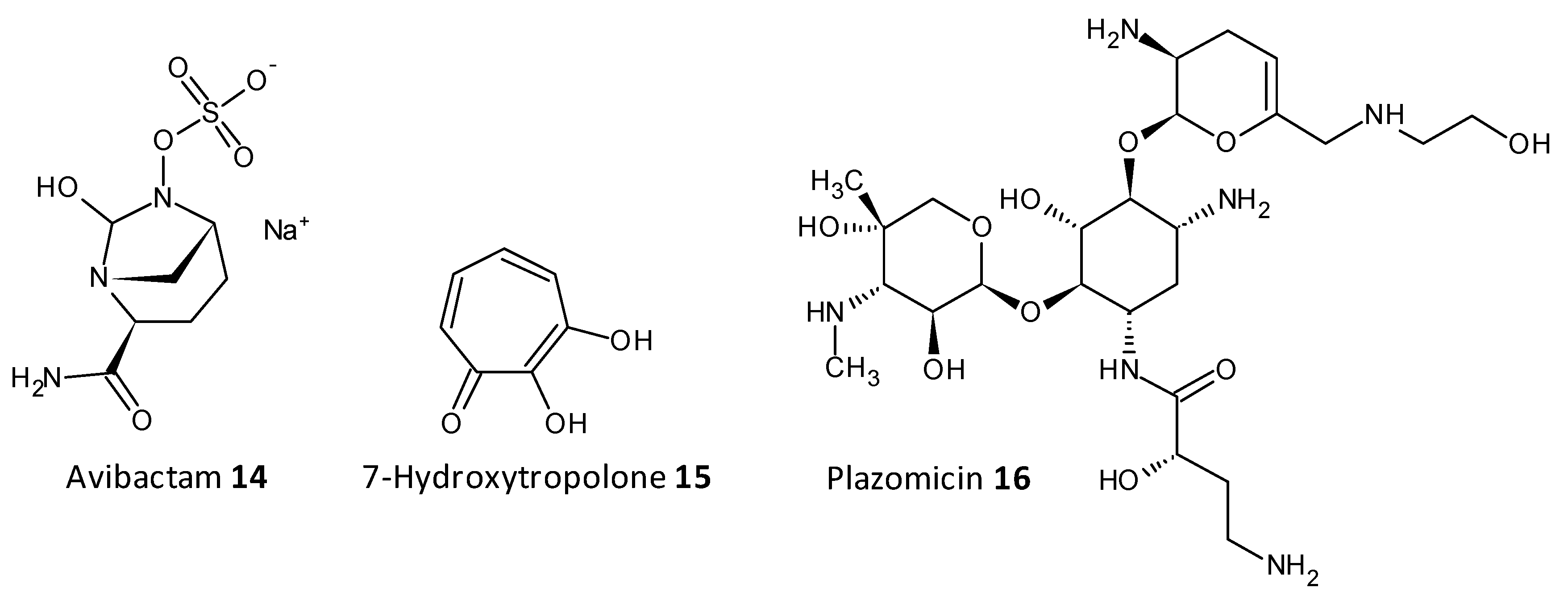
Figure 8. Chemical structures of some enzymatic cleavage inhibitors.
2.9. Efflux Pump Inhibitors
Efflux of antibiotics, by overexpression of efflux pumps, leads to their extrusion out of the cell, making them inactive. EPIs are a recent class of compounds which specifically aim to prevent the efflux of antibiotics out of the cell, which is a determinant of the resistance shown toward antibiotics. A peptidomimetic efflux pump inhibitor MC-207,110 (17a), also known as phenylalanyl arginyl β-naphthylamide, and its analogue MC-04124 (17b) (Figure 9) enhanced the antimicrobial activity of erythromycin and levofloxacin against clinical strains of P. aeruginosa overexpressing MexAB-OprM [186,187]. A synthetic small molecule IITR08027 (18) (Figure 9) showed reversal of resistance towards fluoroquinolones in clinical strains of A. baumannii overexpressing multidrug and toxic compound extrusion (MATE) efflux pumps and the recombinant strains of E. coli. IITR08027 disrupts the proton gradient important for activating the efflux pump [188]. MBX2319 (19) a pyrazolopyridine analogue displayed inhibition of AcrAB-TolC-overexpressing in E. coli and potentiated the efficacy of antibiotics like levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and piperacillin [189] (Figure 9).
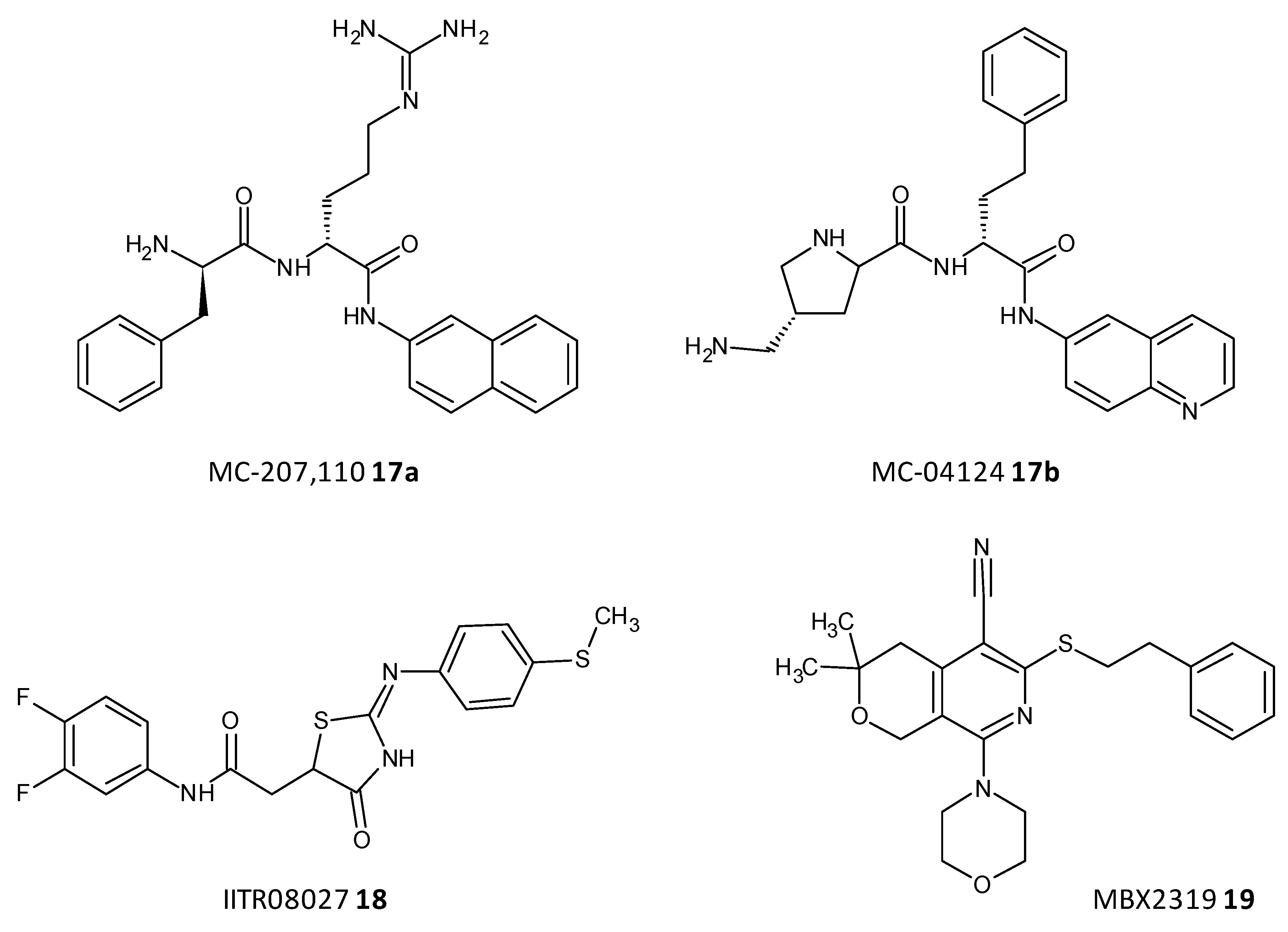
Figure 9. Chemical structures of some efflux pumps inhibitors.
2.10. Quaternary Ammonium Compounds
QACs represent a class of broad-spectrum antimicrobials possessing a central amphiphilic core and a lipophilic alkyl side chain linked to a hydrophilic quaternary ammonium framework. Although QACs imitate the action of the AMPs they have a comparatively simplified structure. The mode of action of these agents as antimicrobials is by cleavage of the cell membrane, which consequently leads to nutrient leakage followed by cell lysis and death. Although, this class of compounds have already been established as disinfectants, antiseptics and preservatives their role as antibiofilm agents has only recently been recognised.
In a study by Kumar Tiwari et al. two quaternary ammonium methacrylate (QAM) derivatives, dimethylaminododecyl methacrylate (DMADDM) (20) and dimethylaminohexadecyl methacrylate (DMAHDM) (21), were designed and evaluated for their efficacy as antibiofilm agents against E. faecalis, Streptococcus gordonii, Actinomyces naeslundii, and Lactobacillus acidophilus using chlorhexidine and sodium hypochlorite as standards. In particular, the minimal biofilm inhibitory concentration (MBIC) for DMADDM and DMAHDM against a combination of four endodontic bacteria was 25 μg/mL and 6.25 μg/mL, respectively [190]. Daood et al. investigated quaternary ammonium silanes (QASs) (22) as biofilm disruptors by exposing them to S. mutans and L. acidophilus preformed biofilms over dentine disks, at different concentrations. Inhibition of enzyme SrtA, responsible for the adhesion of proteins onto the cell membrane and connecting the proteins to form pili, was studied at a concentration of 2% QAS dilution and exhibited significant reduction with an IC50 value of 3.3 ± 2.7 μM, a more potent value as compared to polyhexamethylene biguanide taken as positive control, IC50 = 24.5 ± 4.1 μM [191].
In a study conducted by Ooi et al., two distinct QACs having a dicationic porphyrin core, XF-70 (23a) and XF-73 (23b), were evaluated for their disruption of S. aureus biofilms. Both analogues entirely disrupted preformed S. aureus biofilms at a concentration of 2.6 μM [192,193]. The analogue XF-73 is currently being developed as a topical preparation by Destiny Pharma (Brighton, UK) and has started with a phase-II trial to assess its effect on patients with post surgical Staphylococcal nasal infestation. A phase–I trial of XF-73 has shown noteworthy positive results [194]. Murakami et al. evaluated the effectiveness of 4,4′-(α,ω-hexamethylenedithio) bis (1-octylpyridinium bromide) (4DTBP-6,8) commonly known as gemini QACs a seventh generation BisQACs as an antibacterial and antibiofilm agent towards P. aeruginosa. A susceptibility assay for biofilm cells was performed which showed the numbers of surviving cells with cetylpyridinium chloride and benzalkonium chloride used as reference was 984- and 186- fold higher compared to cells treated with 4DTBP-6,8 (24) (Figure 10) [195].
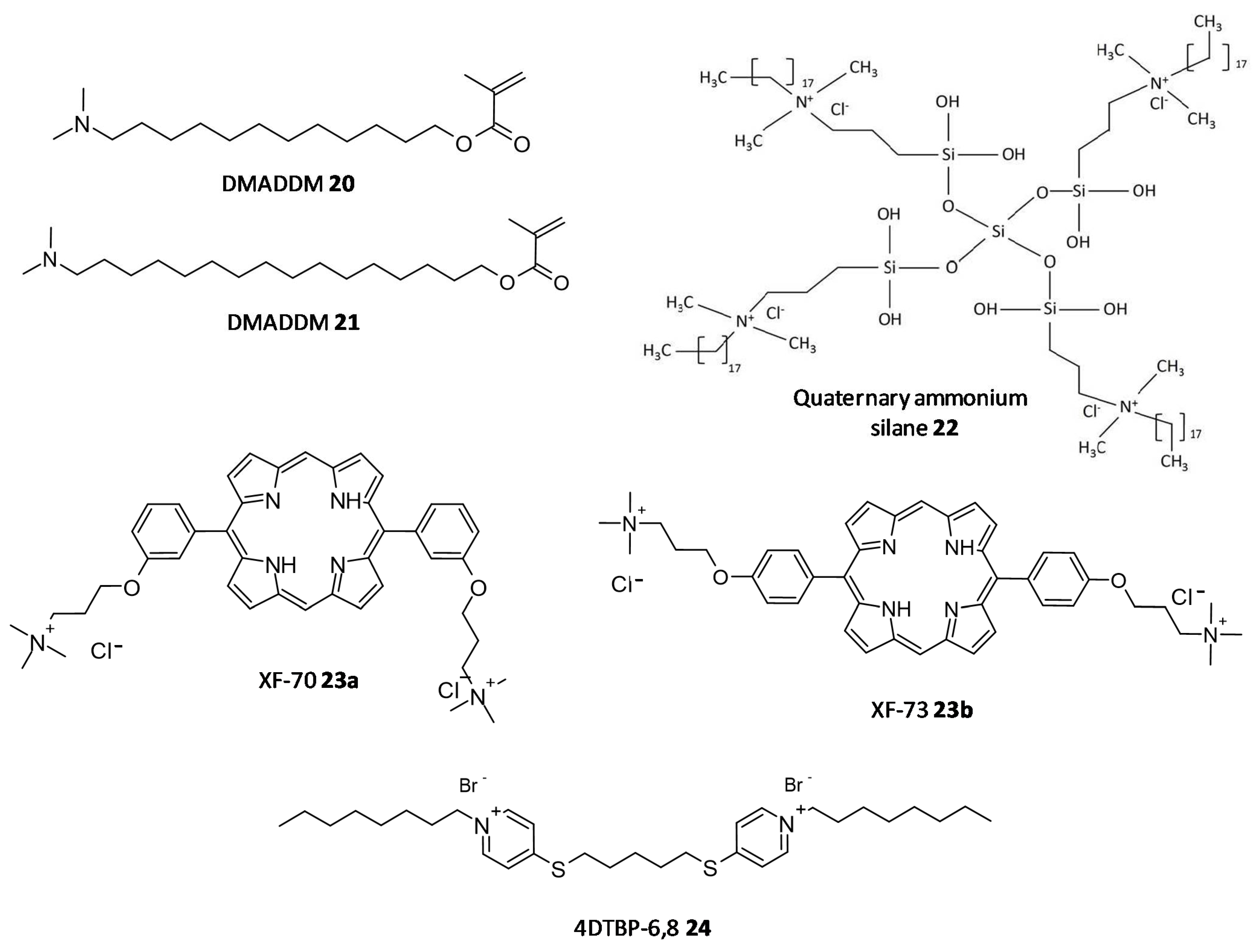
Figure 10. Chemical structures of some quaternary ammonium compounds.
2.11. Natural Compounds
Dong et al. evaluated resveratrol as a biofilm inhibitor against Aeromonas hydrophila. The significant reduction in biofilm formation using resveratrol (25) was noted at concentrations higher than 0.25 μg/mL and a 49.11% reduction in biofilm biogenesis was observed with 4 μg/mL [196]. Oh et al. investigated Raffinose (26), which is a α-galactosyl derivatives of sucrose, and their isolate from ginger extract and evaluated for their ability to prevent biofouling in membrane bioreactors involved in membrane filtration and treatment of waste water. It was observed that the extract significantly reduced 25–52% of the P. aeruginosa and S. aureus co-culture biofilms at a concentration range of 0–1000 μM. In addition, Raffinose also decreased the transmembrane pressure in lab-scale membrane bioreactors compared to furanone C-30 used as control [197].
In a study by Husain et al., Pseudomonas species producing metallo-b-lactamase (MbLs) enzymes from camel meat were isolated and evaluated for their ability to form biofilms. Additionally, the effect of the flavone naringin (27) on the biogenesis of biofilm against the isolated Pseudomonas species was assessed by in silico and in vitro studies. A total of 55% isolates were found to produce MbLs. Naringin attenuated up to 57% of the biofilm formation in the isolated Pseudomonas species. Naringin remarkably turned down biofilms EPS and alginate density. Disruption of preformed biofilms from 32–60% was seen at respective 0.50 MICs. Naringin can thus be explored as a promising food preservative against foodborne Pseudomonas species forming biofilms [198].
In a work by Lyu et al. the biofilm inhibition ability of ursolic acid (28) was evaluated towards oral Streptococci species. Ursolic acid being a natural product can be derived from plant parts such as privet leaves, berries, loquat leaf, paulownia leaves and iron holly. It was observed that ursolic acid inhibits multi-species biofilms of S. mutans, S. gordonii and S. sanguinis at a concentration of 7.80 μg/mL. Moreover they inhibited specifically glucosyltransferases the prime cariogenic component of oral biofilms and displayed relatively less cytotoxicity towards human oral cells [199]. Wei et al. and Pun et al. recently investigated the outcome of phloretin (29) on Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation. Phloretin in sub-MIC levels was used at different temperatures of 37 °C and 4 °C to treat the biofilm. It showed maximum inhibition of the biofilm up to 60% with a concentration of 20 μg/mL. Moreover, the amount of biofilm aggregation and adhesion in L. monocytogenes was subsequently diminished. The thickness of the biofilm was lessened by 2 μm at a concentration of 20 μg/mL. The mode of biofilm inhibition study revealed the role of phloretin reducing the QS related gene agr by 50% with 20 μg/mL phloretin [200,201].
Wang et al. investigated Baicalin (30), a natural compound derived from the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis, and evaluated its ability to inhibit biofilm formation in Staphylococcus saprophyticus and its QS by selectively inhibiting the MsrA drug efflux pump. The study displayed promising results with baicalin decreasing biofilm biogenesis, and bacterial aggregation by downstreaming the mRNA transcription proportion of the QS regulators agrA, agrC, sarA and RNAIII [202,203].
Reis et al. evaluated three flavonoids from Brosimum acutifolium, 4′-hydroxy-7,8(2″,2″-dimethylpyran) flavan (31), brosimine b (32) and 4-hydroxy-lonchocarpin (33), as antibiofilm agents. A and B decreased the viability in preformed S. aureus biofilms upto 73% at a concentration of 50 μM. Additionally, B decreased the biofilm biomass upto 48% at a concentration of 100 μM whereas C was unable to reduce the biofilm biomass. B at a concentration of 100 μM curbed 70–98% of planktonic cells in a 24-old MRSA biofilm (Figure 11) [204].
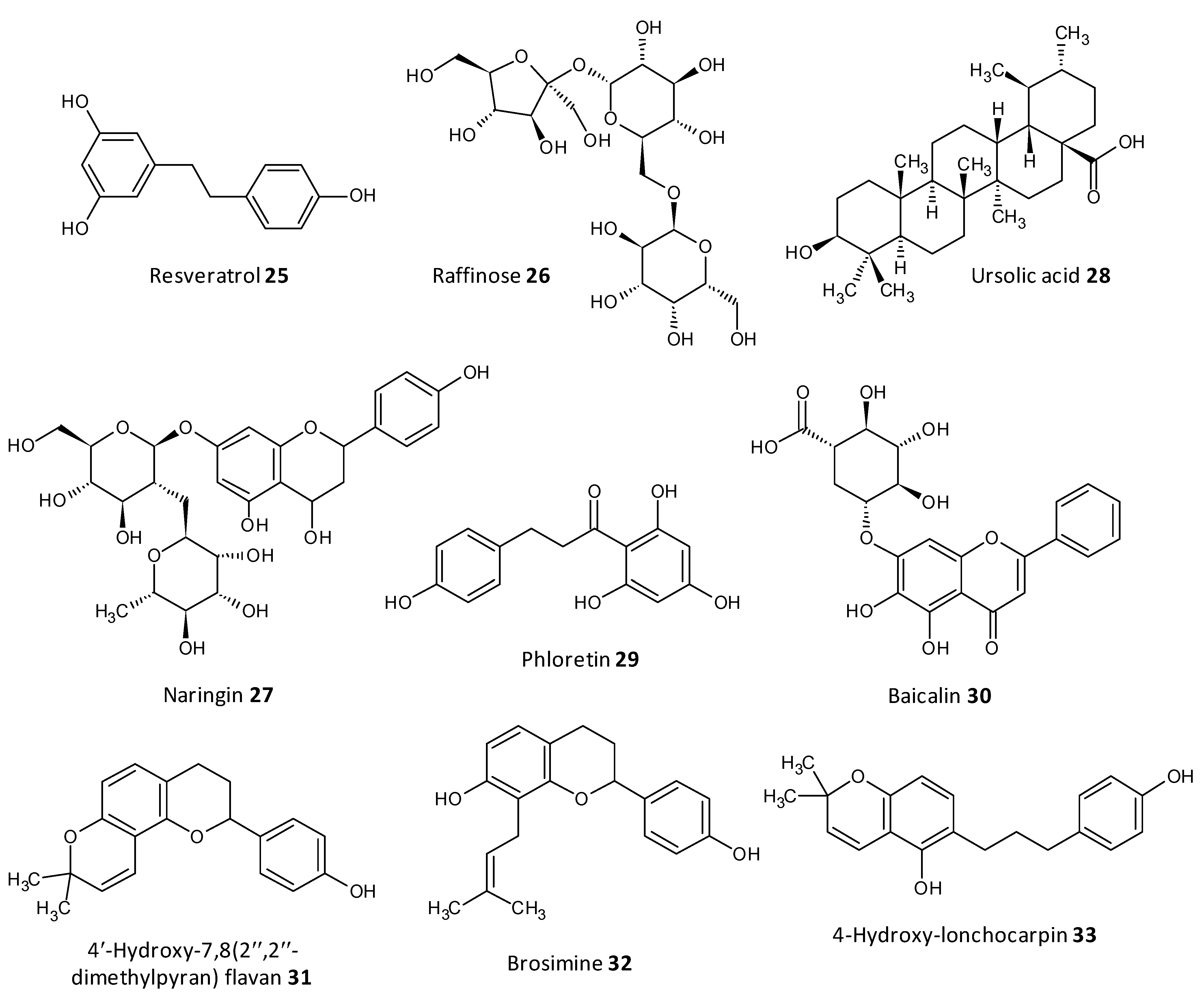
Figure 11. Chemical structures of some natural antibiofilm agents.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/microorganisms10020303
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
