Gymnema inodorum (GI) is an indigenous medicinal plant and functional food in Thailand
that has recently helped to reduce plasma glucose levels in healthy humans. It is renowned for the
medicinal properties of gymnemic acid and its ability to suppress glucose absorption. However,
the effects of gymnemic acids on adipogenesis that contribute to the accumulation of adipose
tissues associated with obesity remain unknown. The present study aimed to determine the
effects of gymnemic acids derived from GI tea on adipogenesis. We purified and identified GiA-7
and stephanosides C and B from GI tea that inhibited adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells.
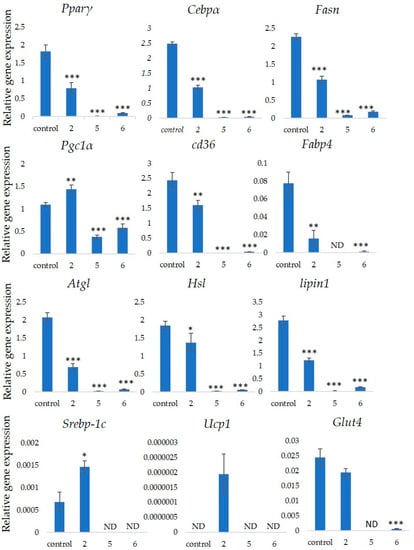
These compounds also suppressed the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
(Pparγ)-dependent genes, indicating that they inhibit lipid accumulation and the early stage of 3T3-L1
preadipocyte differentiation. Only GiA-7 induced the expression of uncoupling protein 1 (Ucp1) and
pparγ coactivator 1 alpha (Pgc1α), suggesting that GiA-7 induces mitochondrial activity and beige-like
adipocytes. This is the first finding of stephanosides C and B in Gymnema inodorum. Our results
suggested that GiA-7 and stephanosides C and B from GI tea could help to prevent obesity.
- Gymnema inodorum
- adipogenesis
- gymnemic acid
- obesity
Note:All the information in this draft can be edited by authors. And the entry will be online only after authors edit and submit it.
Definition:Gymnema inodorum (GI) is an indigenous medicinal plant and functional food in Thailand that has recently helped to reduce plasma glucose levels in healthy humans. It is renowned for the medicinal properties of gymnemic acid and its ability to suppress glucose absorption.
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
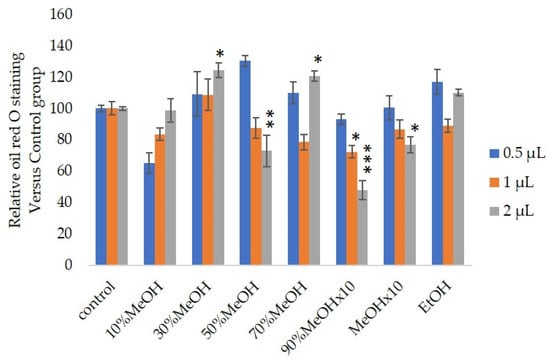
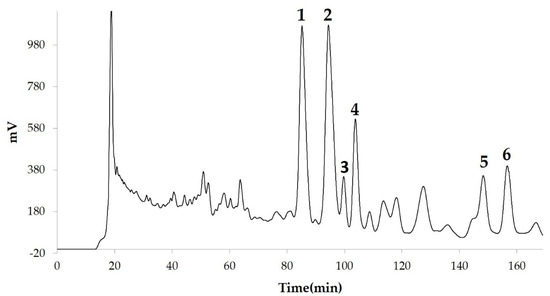
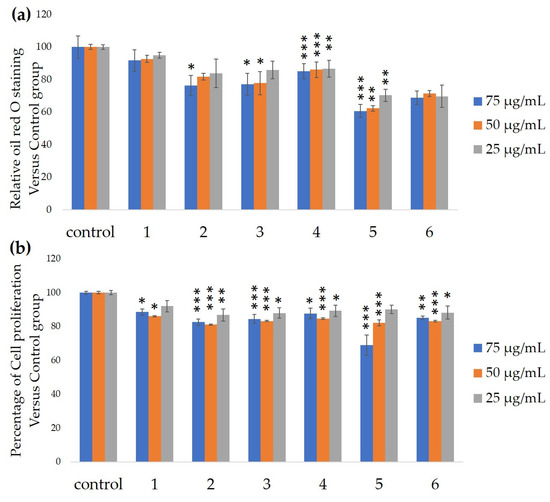
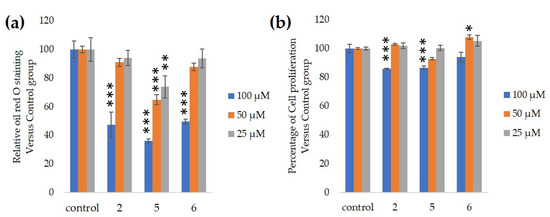
3. Discussions and Conclusions
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/nu12092851
