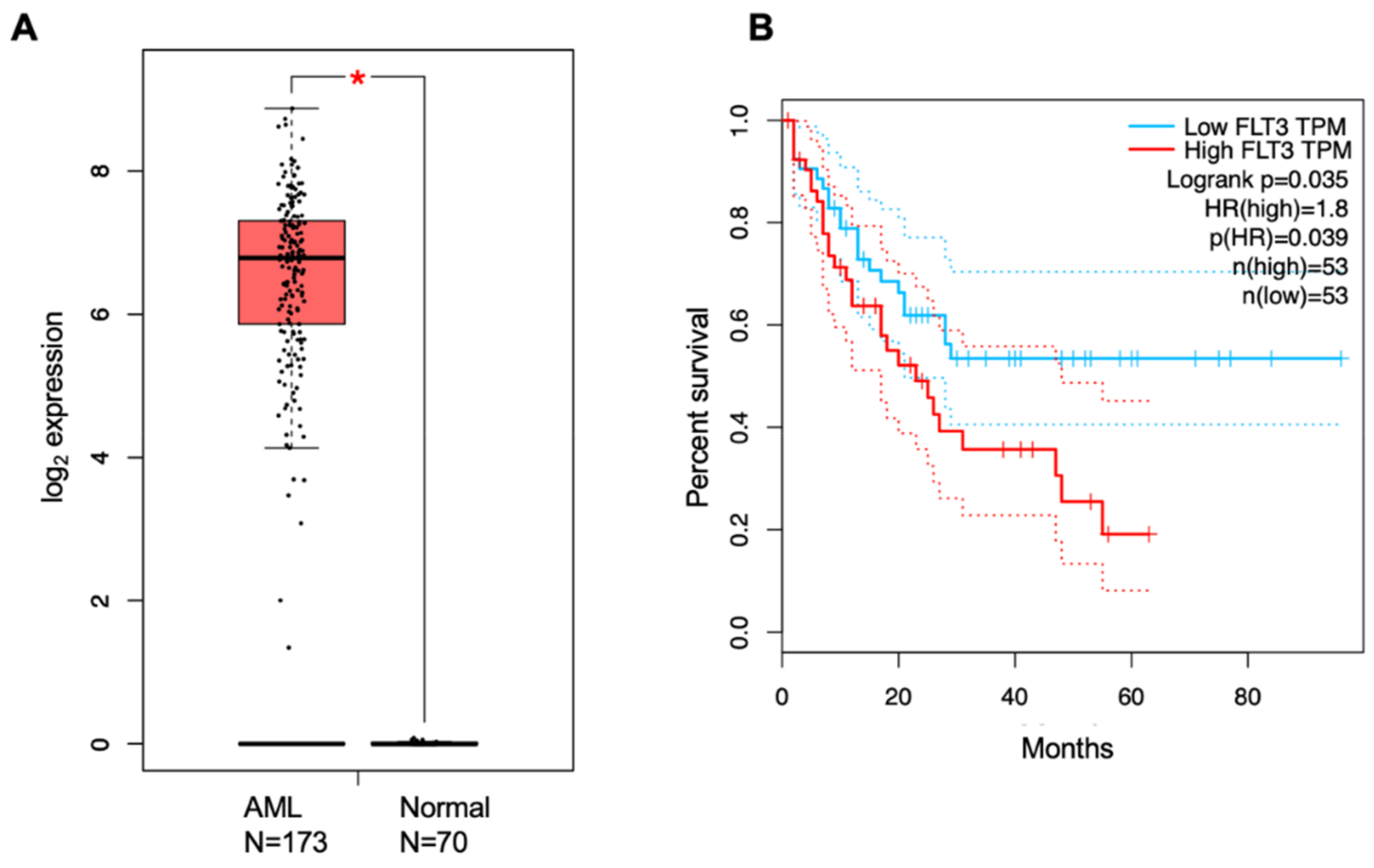
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a disease characterized by uncontrolled proliferation of clonal myeloid blast cells that are incapable of maturation to leukocytes. AML is the most common leukemia in adults and remains a highly fatal disease with a five-year survival rate of 24%. More than 50% of AML patients have mutations in the FLT3 gene, rendering FLT3 an attractive target for small-molecule inhibition. Currently, there are several FLT3 inhibitors in the clinic, and others remain in clinical trials. However, these inhibitors face challenges due to lack of efficacy against several FLT3 mutants. Therefore, the identification of biomarkers is vital to stratify AML patients and target AML patient population with a particular FLT3 mutation.
- acute myeloid leukemia
- FLT3 inhibitors
- FLT3-ITD
- FLT3-TKD
- biomarkers
1. Introduction

2. Biomarkers for FLT3 Inhibition in AML
3. Diagnostic Biomarkers
|
WHO Classification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Recurrent Genetic Abnormalities |
|---|
|
AML with recurrent genetic abnormalities |
|
AML with t(8;21)(q22;q22.1); RUNX1-RUNX1T1 |
|
AML with inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22); CBFB-MYH11 |
|
APL with PML-RARA |
|
AML with t(9;11)(p21.3;q23.3); MLLT3-KMT2A |
|
AML with t(6;9)(p23;q34.1); DEK-NUP214 |
|
AML with inv(3)(q21.3q26.2) or t(3;3)(q21.3;q26.2); GATA2, MECOM |
|
AML (megakaryoblastic) with t(1;22)(p13.3;q13.3); RBM15-MKL1 |
|
Provisional entity: AML with BCR-ABL1 |
|
AML with mutated NPM1 |
|
AML with biallelic mutations of CEBPA |
|
Provisional entity: AML with mutated RUNX1 |
4. Predictive Biomarkers
5. Prognostic Biomarkers
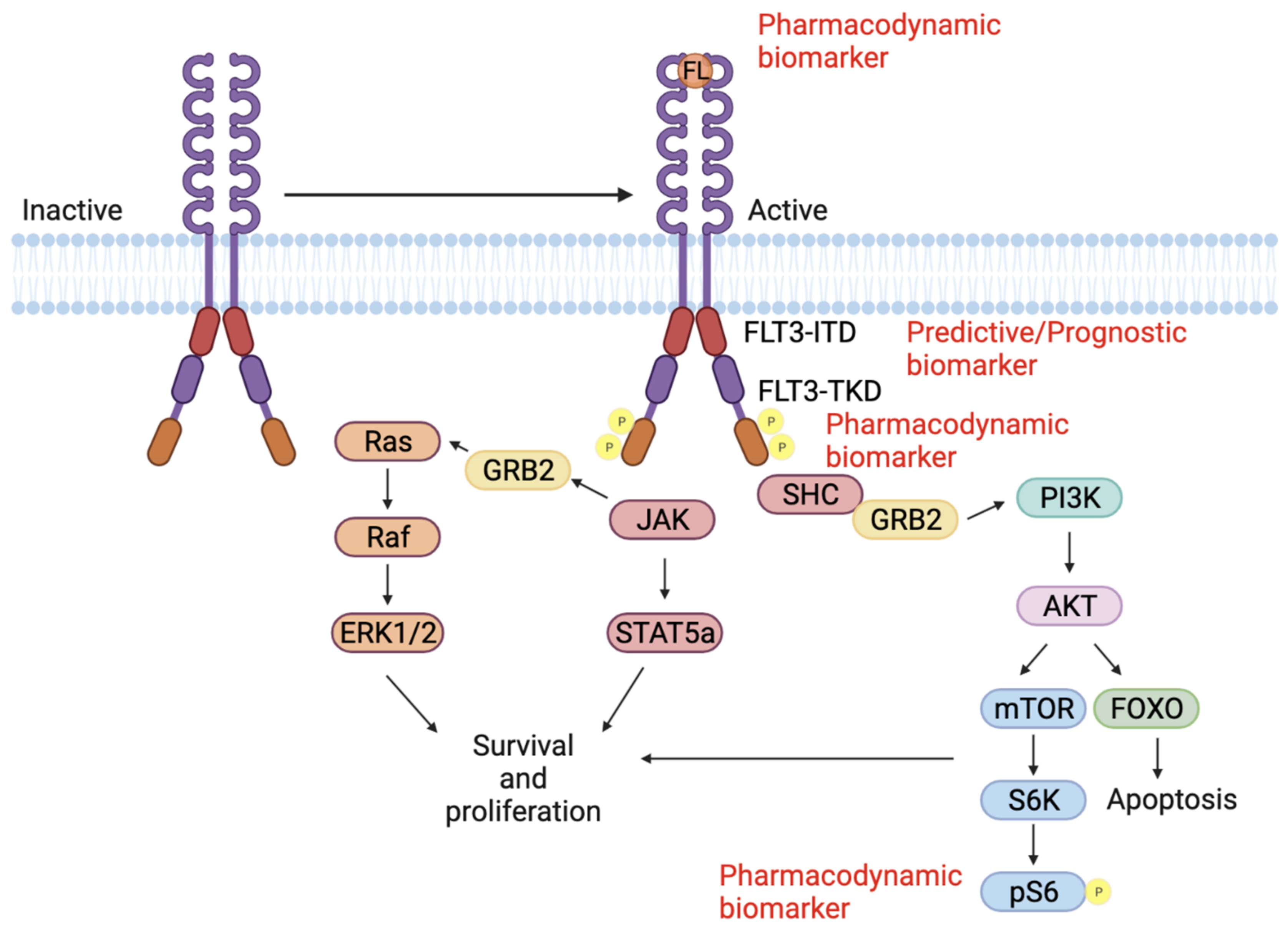
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/cancers14051164
References
- Cancer Stat Facts: Leukemia—Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). 2021. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/amyl.html (accessed on 8 December 2021).
- Shallis, R.M.; Wang, R.; Davidoff, A.; Ma, X.; Zeidan, A.M. Epidemiology of acute myeloid leukemia: Recent progress and enduring challenges. Blood Rev. 2019, 36, 70–87.
- Song, X.; Peng, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Jin, L.; Yang, T.; Qian, M.; Ni, W.; Tong, X.; Lan, J. Incidence, Survival, and Risk Factors for Adults with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Not Otherwise Specified and Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Recurrent Genetic Abnormalities: Analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Database, 2001–2013. Acta Haematol. 2018, 139, 115–127.
- Griffiths, M.; Mason, J.; Rindl, M.; Akiki, S.; McMullan, D.; Stinton, V.; Powell, H.; Curtis, A.; Bown, N.; Craddock, C. Acquired Isodisomy for chromosome 13 is common in AML, and associated with FLT3-itd mutations. Leukemia 2005, 19, 2355–2358.
- Takahashi, S. Downstream molecular pathways of FLT3 in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia: Biology and therapeutic implications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2011, 4, 13.
- Gilliland, D.G.; Griffin, J.D. The roles of FLT3 in hematopoiesis and leukemia. Blood 2002, 100, 1532–1542.
- Grafone, T.; Palmisano, M.; Nicci, C.; Storti, S. An overview on the role of FLT3-tyrosine kinase receptor in acute myeloid leukemia: Biology and treatment. Oncol. Rev. 2012, 6, e8.
- Califf, R.M. Biomarker definitions and their applications. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 213–221.
- Döhner, H.; Estey, E.H.; Amadori, S.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Büchner, T.; Burnett, A.K.; Dombret, H.; Fenaux, P.; Grimwade, D.; Larson, R.A.; et al. Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults: Recommendations from an international expert panel, on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood 2010, 115, 453–474.
- Kim, J.H.; Harada, Y.; Ishikawa, Y.; Kawashima, N.; Nakashima, M.; Ushijima, Y.; Nishiyama, T.; Goto, T.; Fukushima, N.; Kihara, R.; et al. Development of Predictive Biomarker and Optimal Treatment Strategy with FLT3 Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2019, 134, 1418.
- Daver, N.; Schlenk, R.F.; Russell, N.H.; Levis, M.J. Targeting FLT3 mutations in AML: Review of current knowledge and evidence. Leukemia 2019, 33, 299–312.
- Kaito, Y.; Hirano, M.; Futami, M.; Nojima, M.; Tamura, H.; Tojo, A.; Imai, Y. CD155 and CD112 as possible therapeutic targets of FLT3 inhibitors for acute myeloid leukemia. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 23, 51.
- Levis, M.; Brown, P.; Smith, B.D.; Stine, A.; Pham, R.; Stone, R.; De Angelo, D.; Galinsky, I.; Giles, F.; Estey, E.; et al. Plasma inhibitory activity (PIA): A pharmacodynamic assay reveals insights into the basis for cytotoxic response to FLT3 inhibitors. Blood 2006, 108, 3477–3483.
- Prada-Arismendy, J.; Arroyave, J.C.; Röthlisberger, S. Molecular biomarkers in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Rev. 2016, 31, 63–76.
- Percival, M.-E.; Lai, C.; Estey, E.; Hourigan, C.S. Bone marrow evaluation for diagnosis and monitoring of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Rev. 2017, 31, 185–192.
- Bain, B.J.; Barnett, D.; Linch, D.; Matutes, E.; Reilly, J.T. General Haematology Task Force of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology Revised guideline on immunophenotyping in acute leukaemias and chronic lymphoproliferative disorders. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2002, 24, 1–13.
- Geller, R.B.; Zahurak, M.; Hurwitz, C.A.; Burke, P.J.; Karp, J.E.; Piantadosi, S.; Civin, C.I. Prognostic importance of immunophenotyping in adults with acute myelocytic leukaemia: The significance of the stem-cell glycoprotein CD34 (My 10). Br. J. Haematol. 1990, 76, 340–347.
- Craig, F.E.; Foon, K.A. Flow cytometric immunophenotyping for hematologic neoplasms. Blood 2008, 111, 3941–3967.
- Bene, M.C.; Castoldi, G.; Knapp, W.; Ludwig, W.D.; Matutes, E.; Orfao, A.; van’t Veer, M.B. Proposals for the immunological classification of acute leukemias. European Group for the Immunological Characterization of Leukemias (EGIL). Leukemia 1995, 9, 1783–1786.
- Mrózek, K.; Heerema, N.A.; Bloomfield, C.D. Cytogenetics in acute leukemia. Blood Rev. 2004, 18, 115–136.
- Grimwade, D. The clinical significance of cytogenetic abnormalities in acute myeloid leukaemia. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2001, 14, 497–529.
- Kumar, C.C. Genetic Abnormalities and Challenges in the Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 95–107.
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.; Thiele, J.; Borowitz, M.J.; Le Beau, M.M.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Cazzola, M.; Vardiman, J.W. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 2391–2405.
- Arber, D.A.; Brunning, R.D.; Le Beau, M.M.; Falini, B.; Vardiman, J.W.; Porwit, A.; Thiele, J.; Foucar, K.; Dohner, H.; Bloomfield, C. Acute myeloid leukaemia and related precursor neoplasms. In WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; Swerdlow, S.H., Campo, E., Harris, N.L., Jaffe, E.S., Pileri, S.A., Stein, H., Thiele, J., Vardiman, J.W., Eds.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2017.
- Fröhling, S.; Skelin, S.; Liebisch, C.; Scholl, C.; Schlenk, R.F.; Döhner, H.; Döhner, K. Comparison of Cytogenetic and Molecular Cytogenetic Detection of Chromosome Abnormalities in 240 Consecutive Adult Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 2480–2485.
- van Dongen, J.J.M.; Macintyre, E.A.; Gabert, J.A.; Delabesse, E.; Rossi, V.; Saglio, G.; Gottardi, E.; Rambaldi, A.; Dotti, G.; Griesinger, F.; et al. Standardized RT-PCR analysis of fusion gene transcripts from chromosome aberrations in acute leukemia for detection of minimal residual disease. Leukemia 1999, 13, 1901–1928.
- Yamazaki, H.; Suzuki, M.; Otsuki, A.; Shimizu, R.; Bresnick, E.H.; Engel, J.D.; Yamamoto, M. A Remote GATA2 Hematopoietic Enhancer Drives Leukemogenesis in inv(3)(q21;q26) by Activating EVI1 Expression. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 415–427.
- Lugthart, S.; Van Drunen, E.; Van Norden, Y.; Van Hoven, A.; Erpelinck, C.A.J.; Valk, P.J.M.; Beverloo, H.B.; Löwenberg, B.; Delwel, R. High EVI1 levels predict adverse outcome in acute myeloid leukemia: Prevalence of EVI1 overexpression and chromosome 3q26 abnormalities underestimated. Blood 2008, 111, 4329–4337.
- Yamamoto, Y. Activating mutation of D835 within the activation loop of FLT3 in human hematologic malignancies. Blood 2001, 97, 2434–2439.
- Falini, B.; Mecucci, C.; Tiacci, E.; Alcalay, M.; Rosati, R.; Pasqualucci, L.; La Starza, R.; Diverio, D.; Colombo, E.; Santucci, A.; et al. Cytoplasmic Nucleophosmin in Acute Myelogenous Leukemia with a Normal Karyotype. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 254–266.
- Pabst, T.; Mueller, B.U.; Zhang, P.; Radomska, H.S.; Narravula, S.; Schnittger, S.; Behre, G.; Hiddemann, W.; Tenen, D. Dominant-negative mutations of CEBPA, encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-α (C/EBPα), in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 263–270.
- Mardis, E.R.; Ding, L.; Dooling, D.J.; Larson, D.E.; McLellan, M.D.; Chen, K.; Koboldt, D.C.; Fulton, R.S.; Delehaunty, K.D.; McGrath, S.D.; et al. Recurring Mutations Found by Sequencing an Acute Myeloid Leukemia Genome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1058–1066.
- Osato, M.; Asou, N.; Abdalla, E.; Hoshino, K.; Yamasaki, H.; Okubo, T.; Suzushima, H.; Takatsuki, K.; Kanno, T.; Shigesada, K.; et al. Biallelic and heterozygous point mutations in the runt domain of the AML1/PEBP2alphaB gene associated with myeloblastic leukemias. Blood 1999, 93, 1817–1824.
- Gari, M.; Goodeve, A.; Wilson, G.; Winship, P.; Langabeer, S.; Linch, D.; Vandenberghe, E.; Peake, I.; Reilly, J. c-kit proto-oncogene exon 8 in-frame deletion plus insertion mutations in acute myeloid leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 1999, 105, 894–900.
- King-Underwood, L.; Renshaw, J.; Pritchard-Jones, K. Mutations in the Wilms’ tumor gene WT1 in leukemias. Blood 1996, 87, 2171–2179.
- Bos, J.L.; Toksoz, D.; Marshall, C.J.; Vries, M.V.-D.; Veeneman, G.H.; Van Der Eb, A.J.; Van Boom, J.H.; Janssen, J.W.G.; Steenvoorden, A.C.M. Amino-acid substitutions at codon 13 of the N-ras oncogene in human acute myeloid leukaemia. Nature 1985, 315, 726–730.
- Caligiuri, M.A.; Schichman, S.A.; Strout, M.P.; Mrózek, K.; Baer, M.R.; Frankel, S.R.; Barcos, M.; Herzig, G.P.; Croce, C.M.; Bloomfield, C.D. Molecular rearrangement of the ALL-1 gene in acute myeloid leukemia without cytogenetic evidence of 11q23 chromosomal translocations. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 370–373.
- Buhagiar, A.; Borg, J.; Ayers, D. Overview of current microRNA biomarker signatures as potential diagnostic tools for leukaemic conditions. Non-Coding RNA Res. 2020, 5, 22–26.
- Zhi, F.; Cao, X.; Xie, X.; Wang, B.; Dong, W.; Gu, W.; Ling, Y.; Wang, R.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y. Identification of Circulating MicroRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Detecting Acute Myeloid Leukemia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56718.
- Marcucci, G.; Mrózek, K.; Radmacher, M.D.; Garzon, R.; Bloomfield, C.D. The prognostic and functional role of microRNAs in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2011, 117, 1121–1129.
- Faraoni, I.; Laterza, S.; Ardiri, D.; Ciardi, C.; Fazi, F.; Lo-Coco, F. MiR-424 and miR-155 deregulated expression in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukaemia: Correlation with NPM1 and FLT3 mutation status. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2012, 5, 26.
- Orgueira, A.M.; Raíndo, A.P.; López, M.C.; Rodríguez, B.A.; Arias, J.D.; Ferro, R.F.; Vence, N.A.; López, B.; Blanco, A.A.; Pérez, L.B.; et al. Gene expression profiling identifies FLT3 mutation-like cases in wild-type FLT3 acute myeloid leukemia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247093.
- FDA. List of Cleared or Approved Companion Diagnostic Devices (In Vitro and Imaging Tools). Available online: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics (accessed on 1 November 2019).
- Olsen, D.; Jã¸rgensen, J.T.; Jørgensen, J.T. Companion Diagnostics for Targeted Cancer Drugs – Clinical and Regulatory Aspects. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 105.
- Invivoscribe. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gtr/tests/562156/ (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Short, N.; Kantarjian, H.; Ravandi, F.; Daver, N. Emerging treatment paradigms with FLT3 inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2019, 10.
- Tallman, M.S.; Wang, E.S.; Altman, J.K.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Bhatt, V.R.; Bixby, D.; Coutre, S.E.; De Lima, M.; Fathi, A.T.; Fiorella, M.; et al. Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Version 3.2019, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019, 17, 721–749.
- NCCN Clinical Oncology Guidelines. Acute Myeloid Leukemia Accessed (version 2.2018). 2018. Available online: www.nccn.org (accessed on 17 December 2021).
- Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wan, D.; Jiang, Z. Clinical implications of recurrent gene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 9, 4–11.
- Patel, J.P.; Gönen, M.; Figueroa, M.E.; Fernandez, H.; Sun, Z.; Racevskis, J.; Van Vlierberghe, P.; Dolgalev, I.; Thomas, S.; Aminova, O.; et al. Prognostic Relevance of Integrated Genetic Profiling in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1079–1089.
- Sahoo, S.S.; Kozyra, E.; Wlodarski, M.W. Germline predisposition in myeloid neoplasms: Unique genetic and clinical features of GATA2 deficiency and SAMD9/SAMD9L syndromes. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2020, 33, 101197.
- Babushok, D.V.; Bessler, M.; Olson, T.S. Genetic predisposition to myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia in children and young adults. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 57, 520–536.
- Kantarjian, H.; Kadia, T.; DiNardo, C.; Daver, N.; Borthakur, G.; Jabbour, E.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Konopleva, M.; Ravandi, F. Acute myeloid leukemia: Current progress and future directions. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 1–25.
- McMahon, C.M.; Perl, A.E. Gilteritinib for the treatment of relapsed and/or refractory FLT3-mutated acute myeloid leukemia. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 841–849.
- Müller, J.P.; Schmidt-Arras, D. Novel Approaches to Target Mutant FLT3 Leukaemia. Cancers 2020, 12, 2806.
- Bhat, A.A.; Younes, S.N.; Raza, S.S.; Zarif, L.; Nisar, S.; Ahmed, I.; Mir, R.; Kumar, S.; Sharawat, S.K.; Hashem, S.; et al. Role of non-coding RNA networks in leukemia progression, metastasis and drug resistance. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 57.
- Swords, R.; Freeman, C.; Giles, F.J. Targeting the FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2176–2185.
- Tang, Z.; Li, C.; Kang, B.; Gao, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W98–W102.
- Milne, P.; Wilhelm-Benartzi, C.; Grunwald, M.R.; Bigley, V.; Dillon, R.; Freeman, S.D.; Gallagher, K.; Publicover, A.; Pagan, S.; Marr, H.; et al. Serum Flt3 ligand is a biomarker of progenitor cell mass and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3052–3061.
- Marando, L.; Huntly, B.J.P. Molecular Landscape of Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 22, 61.
- DiNardo, C.D.; Cortes, J. Mutations in AML: Prognostic and therapeutic implications. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2016, 2016, 348–355.
- Kiyoi, H.; Kawashima, N.; Ishikawa, Y. FLT3 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia: Therapeutic paradigm beyond inhibitor development. Cancer Sci. 2019, 111, 312–322.
- Madan, V.; Koeffler, H.P. Differentiation therapy of myeloid leukemia: Four decades of development. Haematologica 2021, 106, 26–38.
- Tsai, H.K.; Brackett, D.G.; Szeto, D.; Frazier, R.; MacLeay, A.; Davineni, P.; Manning, D.K.; Garcia, E.; Lindeman, N.I.; Le, L.P.; et al. Targeted Informatics for Optimal Detection, Characterization, and Quantification of FLT3 Internal Tandem Duplications Across Multiple Next-Generation Sequencing Platforms. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 1162–1178.
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, B.-D.; Wang, C.-C.; Wang, Y.-G.; Wang, H.-F.; Wang, J.-H.; Liu, L.-X.; Lou, F.; Cao, S.-B.; Hu, X.-X.; et al. A novel prognostic scoring model for newly diagnosed FLT3-ITD-positive acute myeloid leukemia. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 4527–4537.
- Boddu, P.C.; Kadia, T.M.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Cortes, J.; Alfayez, M.; Borthakur, G.; Konopleva, M.; Jabbour, E.J.; Daver, N.G.; Dinardo, C.D.; et al. Validation of the 2017 European LeukemiaNet classification for acute myeloid leukemia withNPM1andFLT3-internal tandem duplication genotypes. Cancer 2018, 125, 1091–1100.
- Levis, M. FLT3 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia: What is the best approach in 2013? Hematology 2013, 2013, 220–226.
- Castaño-Bonilla, T.; Alonso-Dominguez, J.M.; Barragán, E.; Rodríguez-Veiga, R.; Sargas, C.; Gil, C.; Chillón, C.; Vidriales, M.B.; García, R.; Martínez-López, J.; et al. Prognostic significance of FLT3-ITD length in AML patients treated with intensive regimens. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20745.
- Port, M.; Böttcher, M.; Thol, F.; Ganser, A.; Schlenk, R.; Wasem, J.; Neumann, A.; Pouryamout, L. Prognostic significance of FLT3 internal tandem duplication, nucleophosmin 1, and CEBPA gene mutations for acute myeloid leukemia patients with normal karyotype and younger than 60 years: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Hematol. 2014, 93, 1279–1286.
- Garg, M.; Nagata, Y.; Kanojia, D.; Mayakonda, A.; Yoshida, K.; Keloth, S.H.; Zang, Z.J.; Okuno, Y.; Shiraishi, Y.; Chiba, K.; et al. Profiling of somatic mutations in acute myeloid leukemia with FLT3-ITD at diagnosis and relapse. Blood 2015, 126, 2491–2501.
- Döhner, K.; Thiede, C.; Jahn, N.; Panina, E.; Gambietz, A.; Larson, R.A.; Prior, T.W.; Marcucci, G.; Jones, D.; Krauter, J.; et al. Impact of NPM1/FLT3-ITD genotypes defined by the 2017 European LeukemiaNet in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2020, 135, 371–380.
- Ravandi, F.; Walter, R.B.; Freeman, S.D. Evaluating measurable residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 1356–1366.
- Bacher, U.; Haferlach, C.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, T.; Schnittger, S. Prognostic relevance of FLT3-TKD mutations in AML: The combination matters—An analysis of 3082 patients. Blood 2008, 111, 2527–2537.
- El Achi, H.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R. Biomarkers in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Leveraging Next Generation Sequencing Data for Optimal Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 3997.
