We review the progress in metal phosphate structural chemistry focused on proton conductivity properties. Attention is paid to structure–property relationships, which ultimately determine the potential use of metal phosphates and derivatives in devices relying on proton conduction. The origin of their conducting properties, including both intrinsic and extrinsic conductivity, is rationalized in terms of distinctive structural features and the presence of specific proton carriers or the factors involved in the formation of extended hydrogen-bond networks.
- metal phosphate
- proton conductivity
- H-bond network
- proton carriers
- super protonic
- metal pyrophosphate
1. Introduction.
Metal phosphates (MPs) comprise an ample class of structurally versatile acidic sol-ids, with outstanding performances in a wide variety of applications, such as catalysts [1][2][3], fuel cells [4][5][6], batteries [7], biomedical [8], etc. Depending on the metal/phosphate combinations and the synthetic methodologies, MP solids can be prepared in a vast diver-sity of crystalline forms, from 3D open-frameworks, through layered networks, to 1D polymeric structures. The advantages of these solids are, among others, their low cost and easy prepara-tion, hydrophilic and thermally stability and structural designability to a certain extent. Additionally, their structures are amenable to post-synthesis modifications, including the incorporation of ionic or neutral species that significantly affect their functionality and other important properties, such as the formation of hydrogen bonding networks or inser-tion of proton carriers.
Determining proton conduction mechanisms is key to designing proton conductor materials (Figure 1). Thus, if a vehicle-type mechanism is needed, proton-containing counter ions, such as hydronium ions, NH4+, protonated amine groups, and protonated organic molecules in general, should be incorporated into the structure. Additionally, the immobilization of specific functional groups and the corresponding counter ions onto the framework could be required. On the other hand, solids exhibiting proton transport by a Grotthuss-type mecha-nism basically consist of continuous H-bond networks that favour H+ conduction with low activation energy (Ea). A main drawback for the latter materials is that, above certain temperatures, breaking of the H-bond networks can result, accompanied by the release of water molecules, which makes the construction of permanent H-bonding networks with hydrophilic channels or exploring new alternative conductive media necessary [9].
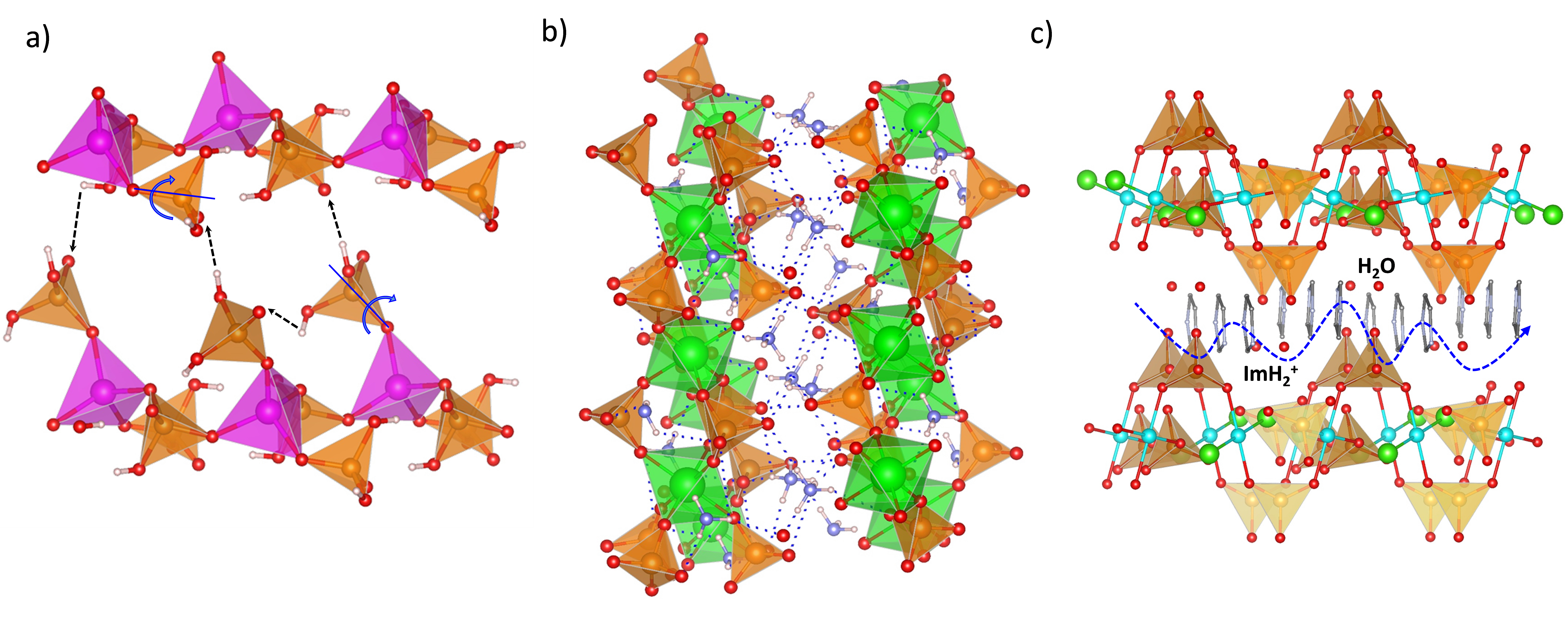
Figure 1. Examples of proton transport in phosphate-containing materials: (a) structural reorientation-mediated proton transfer. Zn (magenta), P (orange), O (red) and H (pale pink). (b) hopping through H-bond networks, and (c) carrier-mediated proton conduction. Zn (magenta), Zr (green), Cu (cyan), Cl (light green), P (orange), O (red), N (blue) and H (pale pink) atoms.
Additionally, an extrinsic proton conduction, associated with surface proton transport, can also result from specific chemical modification and/or induced morphological changes, e.g., with formation of nanoplatelets or nanorods particles [10][11]. Water molecules act both in the formation H-bonding networks inside the framework and as proton carriers. Moreover, other guest species, including organic moieties, can be inserted in their structure following different strategies, such as intercalation [12][13][14], template [15][16], and post-synthesis adsorption [17][18][19]. Accordingly, proton transport in MPs results from the interplay between water/guest molecules and the hydrophilic network/framework walls in specific ways. Thus, in metal phosphates, such as CsH2PO4 [20] or CaHPO4·2H2O [21] the proton-transfer mechanism involves not only the jump of H+ but also the free rotation of the phosphate groups. In other cases, such as for KH2PO4 the proton-transfer mechanism behavior is by defects [22].
2. Super Protonic Metal(I) Phosphates.
Solid acid proton conductors, with stoichiometry MIHyXO4 (MI = Cs, Rb; X = S, P, Se; y = 1, 2), have received much attention because they exhibit exceptional proton transport properties and can be used as electrolytes in fuel cells operated at intermediate temperatures (120−300 °C). The fundamental characteristics of these materials are the phase transition that occurs in response to heating, cooling or application of pressure [6][23], accompanied by an increase in proton conductivity of several orders of magnitude—referred to as super protonic conductivity (Figure 3).
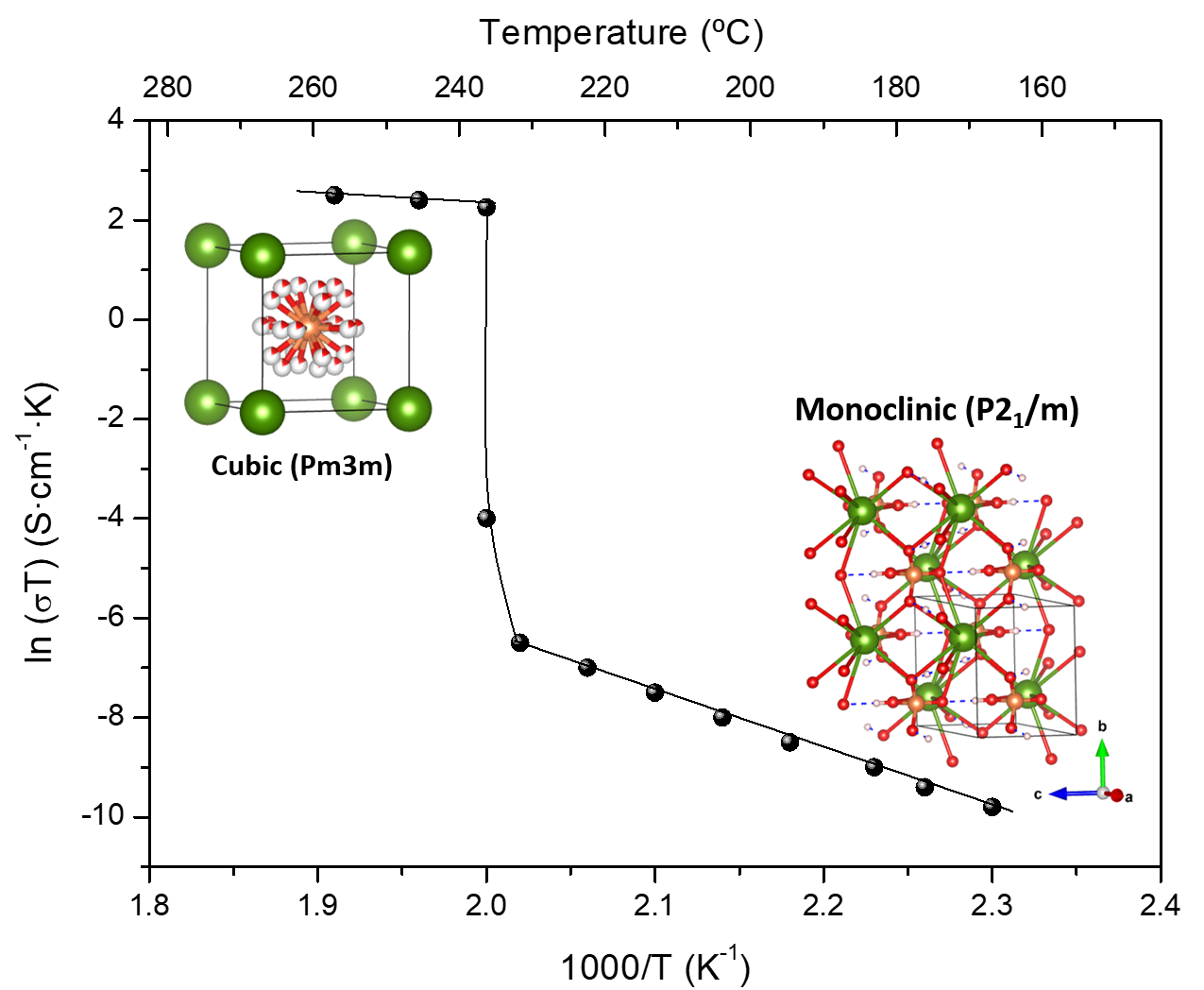
Figure 3. The characteristic high and low temperature proton conductivity and the corresponding structures for CsH2PO4, adapted from [6][24].
This property has been associated with the delocalization of hydrogen bonds [24]. For CsH2PO4, a proton conductivity of 6 × 10−2 S·cm−1 was measured above 230 °C corresponding to the super protonic cubic (Pm−3m) phase [25] while it drastically drops in the low temperature phases. Recently, from an ab initio molecular dynamics simulation study of the solid acids CsHSeO4, CsHSO4 and CsH2PO4, it was concluded that efficient long-range proton transfer in the high temperature (HT) phases is enabled by the interplay of high proton-transfer rates and frequent anion reorientation.
In these compounds, proton conduction follows a Grotthuss mechanism with proton transfer being associated with structural reorientation [26]. The super protonic conductor CsH2PO4 is stable under humidified conditions (PH2O = 0.4 atm) [6], but it dehydrates to CsPO3, via the transient phase Cs2H2P2O7, at 230−260 °C, according to the relationship log(PH2O/atm) = 6.11(±0.82) − 3.63(±0.42) × 1000/(Tdehy/K) [27].
Several studies [6][28][29] have shown that CsH2PO4 can be employed as the electrolyte in fuel cells with good long-term stability. Thus, a continuous, stable power generation for both H2/O2 and direct methanol fuel cells operated at ~240 °C was demonstrated for this electrolyte when stabilized with water partial pressures of ~0.3−0.4 atm. In fact, high performances, corresponding to single cell peak power densities of 415 mW·cm−2, was achieved for a humidified H2/O2 system provided with a CsH2PO4 electrolyte membrane of only 25 µm in thickness [30].
CsH2PO4 composites based on organic additives have been also intensively investigated. Various strategies, including salt modification by cation and anion substitution [31][32][33][34], and mixing with oxide materials [35][36][37][38][39][40][41] or organic additives [25][42][43][44], have been explored to improve the solid acid performance. The preparation of these derivatives and composites involved different synthesis techniques, such as sol-gel, impregnation, thin-casting and electrospinning, depending on the state of the precursor materials and the desired product [6].
3. Divalent Metal Phosphates.
Divalent transition metal phosphates show a great structural versatility, from 1D polymeric topologies through layered framework to 3D open-framework structures. Most of these solids are synthetized in the presence of organic molecules, which are retained as protonated guest species (amines, iminazole derivatives, etc.), thus, compensating the anionic charge of the inorganic framework. This is formed by the metal ion, mainly in octahedral or tetrahedral coordination environments, linked to the phosphate groups with different protonated degrees (HxPO4). The presence of the latter makes possible the formation of effective and extensive hydrogen bond networks with participation of water molecules. In addition, protonated guest species and water itself can act as proton carriers, thus, boosting proton conduction [12][13][14].
A 1D zinc phosphate-based proton conductor, [Zn3(H2PO4)6(H2O)3](BTA) (BTA = 1,2,3-benzotriazole) has been reported [45] that exhibits high proton conductivity, 8 × 10−3 S·cm−1 in anhydrous glassy-state (120 °C). The glassy-state, developed via melt-quenching, was suggested to induce isotropic disordered domains that enhanced H+ dynamics and conductive interfaces. In fact, the capability of the glassy-state material as an electrolyte was found suitable for the rechargeable all-solid-state H+ battery operated in a wide range of temperatures from 25 to 110 °C.
As an example of 2D metal phosphate water-assisted proton conductors, (C2H10N2) [Mn2(HPO4)3](H2O), displayed a proton conductivity of 1.64 × 10−3 S·cm−1 under 99% RH at 20 °C. This proton conductivity was attributed to the formation of dense H-bond networks in the lattice, composed of Mn3O13 units-containing anionic layers [46], which provide efficient proton-transfer pathways for a Grotthuss-type proton transport at high RH.
Several 3D open-framework M(II) phosphates have been reported [14][47], which consist of [CoPO4]∞− or [Zn2(HPO4)2(H2PO4)2]2− anionic frameworks that contain organic charge-compensating ions in their internal cavities. (C2N2H10)0.5CoPO4 exhibited negligible conductivity in anhydrous conditions; however, it displayed a relatively high water-mediated proton conductivity 2.05 × 10−3 S·cm−1 at 56 °C and 98% RH. On the other hand, the solid NMe4·Zn[HPO4][H2PO4] experiences a structural transformation from monoclinic (α) to orthorhombic (β) upon heating at 149 °C. Both polymorphs contain 12-membered rings composed of tetrahedral Zn2+ ions linked to protonated phosphate groups without changing Zn-O-P connectivity (Figure 4).
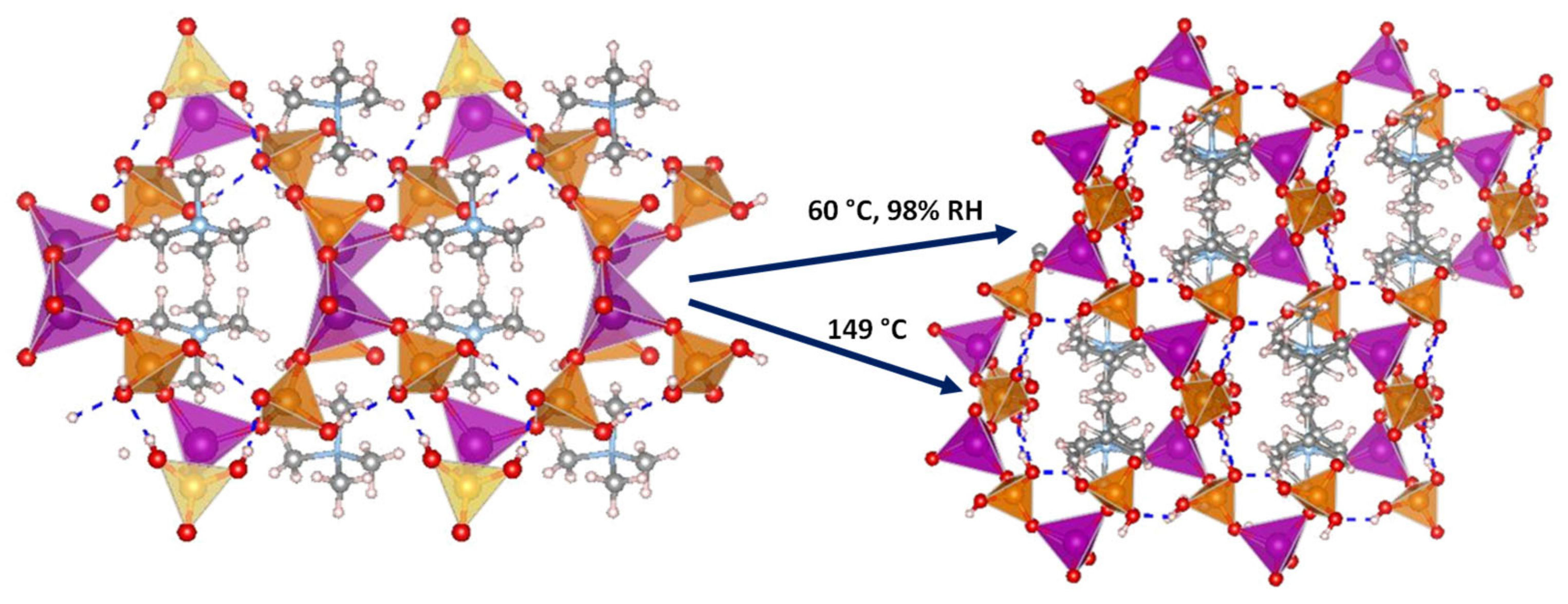
Figure 4. Irreversible structural transformation in NMe4Zn[HPO4][H2PO4]4 adapted from [47]. N (sky-blue), O (red), Zn (magenta), P (orange), C (grey) and H (pale pink) atoms.
The α phase transforms into the β phase at high humidity and temperatures above 60 °C, and then reaches a proton conductivity of 1.30 × 10−2 S·cm−1 at 98% RH, a behaviour that might be attributed to the participation of adsorbed water molecules in creating H-bonding networks with effective pathways for proton conduction. The conductivity drastically decreases at 65 °C. In anhydrous conditions, the α phase exhibited a proton conductivity of ~10−4 S·cm−1 at 160 °C, similar values were found for other reported zinc phosphates at temperatures between 130 and 190 °C [12][48][49].
4. Trivalent Metal Phosphates.
A few examples of phosphate-based proton conductors of other trivalent metals do exist. Among them, two Fe(III) phosphates, 1D (C4H12N2)1.5[Fe2(OH)(H2PO4)(HPO4)2(PO4)]·0.5H2O [13] and 3D open-framework iron(III) phosphate (NH3(CH2)3NH3)2[Fe4(OH)3(HPO4)2(PO4)3]·4H2O [50], have been reported. Both compounds contain Fe4O20 tetramers as a common structural feature. The 1D solid is composed of chains of tetramers bridged by PO43- groups and having terminal H2PO4- and HPO42- groups [51], while piperazinium cations and water molecules are disorderly situated in between chains. This arrangement gives rise to extended hydrogen bonding interactions and hence proton conducting pathways. The proton conductivity measured at 40 °C and 99% RH was 5.14 × 10−4 S·cm−1, and it was maintained upon dispersion of this solid in PVDF [13]. In the case of the 3D solid, infinite chains of interconnected tetramers are interlinked, in turn by phosphate groups that generate large tunnels (Figure 5). The diprotonated 1,3-diaminopropane and water molecules, localized inside tunnels, form an extended hydrogen bond network with the P–OH groups pointing toward cavities. These interactions favour proton hopping, the measured proton conductivity being of 8.0 × 10−4 S·cm−1, at 44 °C and 99% RH, and with an Ea of 0.32 eV [52]. Furthermore, the proton conductivity of this compound increased up to 5 × 10−2 S·cm−1 at 40 °C upon exposure to aqua-ammonia vapors from 1 M NH3·H2O solution. This result confirms this treatment as an effective way of enhancing proton conductivity, which has been elsewhere demonstrated for the case of coordination polymers [53][54].
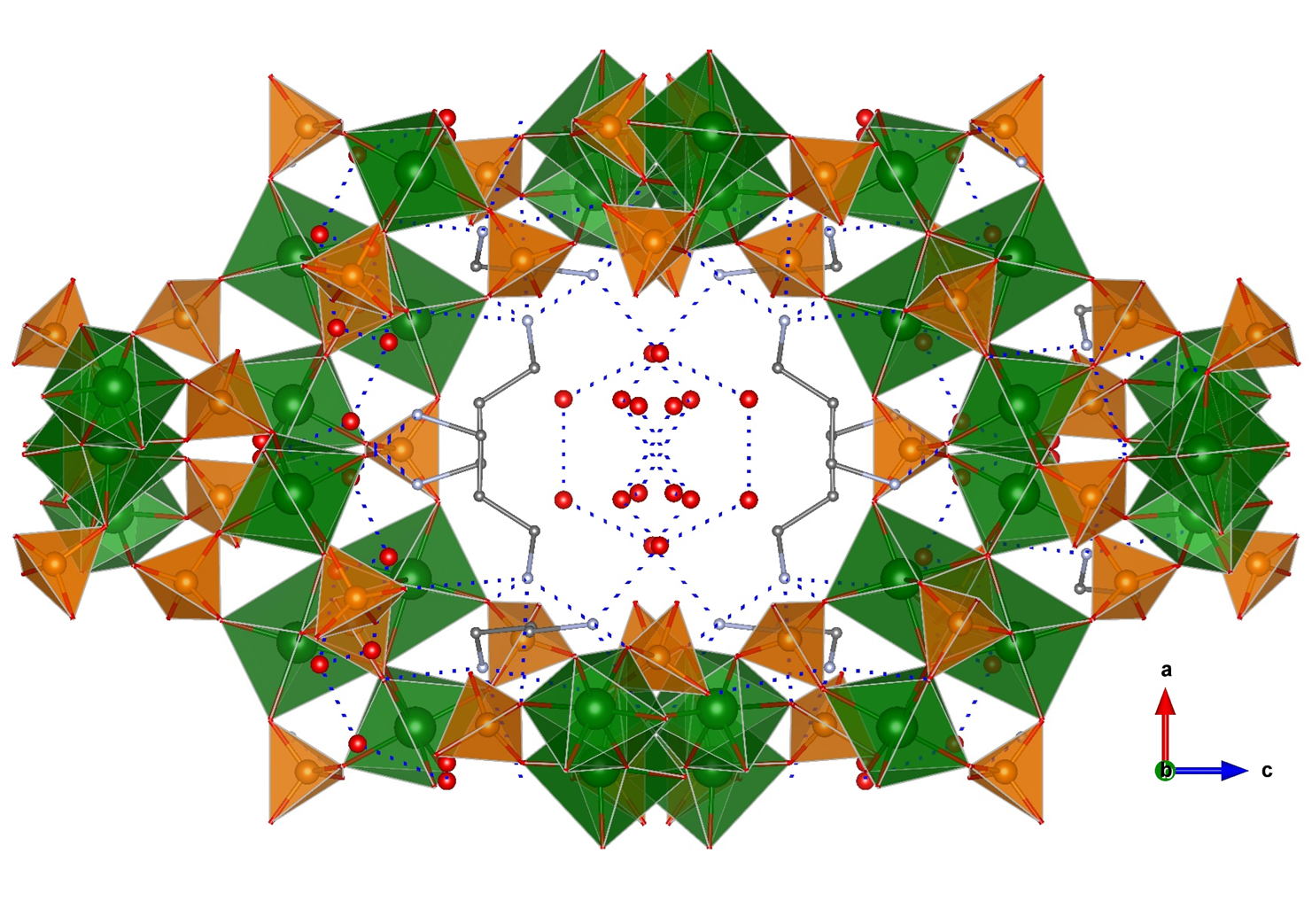

Figure 5. Open-framework structure of (NH3(CH2)3NH3)2[Fe4(OH)3(HPO4)2(PO4)3]·4H2O showing guest species inside channels and H-bond interactions. Fe (green), O (red), P (orange), and C (grey) atoms.
Other trivalent metal phosphates have been reported, e.g., BPOx [55] and CePO4 [56]. The former exhibited a proton conductivity of 7.9 × 10−2 S·cm−1 as self-supported electrolyte and 4.5 × 10−2 S·cm−1 as (PBI)−4BPOx composite membrane, measured at 150 °C and 5% RH, but structure/conductivity correlations were not established because of its amorphous nature.
There are only a few examples of metal(III) pyrophosphates displaying proton conductivity. Among them is the open framework magnesium aluminophosphate MgAlP2O7(OH)(H2O)2 (JU102) [57]. Its structure is composed of tetrahedral Al3+ and octahedral Mg2+ ions coordinated by pyrophosphate ions. This connectivity results in an open framework with unidirectional 8-ring channels. The proton conduction properties originate from the existence of an H-bond network in which coordinated water molecules participate. Thus, the proton conductivity measured at 55 °C on water-immersed samples was 3.86 × 10−4 S·cm−1, which raised to 1.19 × 10−3 S·cm−1 when calcined at 250 °C and measured at the same conditions, while the Ea value hardly changed from 0.16 to 0.2 eV. This behaviour was explained as being due to a dehydration–rehydration process that enhances proton conductivity by altering the H-bonding network and the pathway of proton transfer.
Another example of 3D open framework metal(III) pyrophosphate is the compound NH4TiP2O7 [58]. The structure of this solid is composed of negatively charged [TiP4O12]− layers, forming one-dimensional six-membered ring channels, where the NH4+ ions are located. Its proton conductivity increased from 10−6 S·cm−1 under anhydrous conditions to 10−3 S·cm−1 at full-hydration conditions and 84 °C. The low Ea value, 0.17 eV, characteristic of a Grotthuss-type proton-transfer mechanism, was associated with the role played by the NH4+ ions in the channels as proton donors and promoters of proton migration. A drop in proton conductivity was observed when the triclinic TiP2O7 phase formed by thermal decomposition of NH4TiP2O7 [58].
5. Tetravalent Metal Phosphates and Pyrophosphates
5.1. Zirconium Phosphates
The prototype of layered metal(IV) phosphates is zirconium hydrogen phosphate, which presents mainly three topologies, known as the forms α: Zr(HPO4)2·H2O (α-ZrP), γ: Zr(PO4)(O2P(OH)2) 2H2O (γ-ZrP), and λ: (Zr(PO4)XY, X= halides, OH-, HSO4-, and Y=DMTHUS, H2O, etc.) (λ-ZrP). α-ZrP is the most thermal and hydrolytically stable phase and, thus, the most studied compound following the pioneering works by Giulio Alberti and Abraham Clearfield groups [59][60][61].
In the structure of α-ZrP, planar Zr atoms are coordinated by the three oxygen atoms of HO-PO3- groups, while the P-OH bond points toward the interlayer space giving rise to small cavities, where the lattice water is located. Although this water forms hydrogen bonds with P-OH groups, an extended interlayer hydrogen bond network is absent in this structure [60]. On the other hand, the structure of γ-ZrP consists of a biplanar Zr atomic system connected through bridge PO43− groups, while the externally located H2PO4- groups complete the octahedral coordination of the Zr atoms.
Due to the higher stability of the α form, proton conductivity studies have been conducted mainly with this phase. Typical values of 10−6–10−4 S·cm−1 have been determined at RT and 90% RH with activation energy (Ea) ranging between 0.26 (90% RH) and 0.52 eV (5% RH). This conductivity originates from surface transport and is dominated by surface hydration since the long distance between adjacent P-OH groups hinders proton diffusion along the internal layer surface [62].
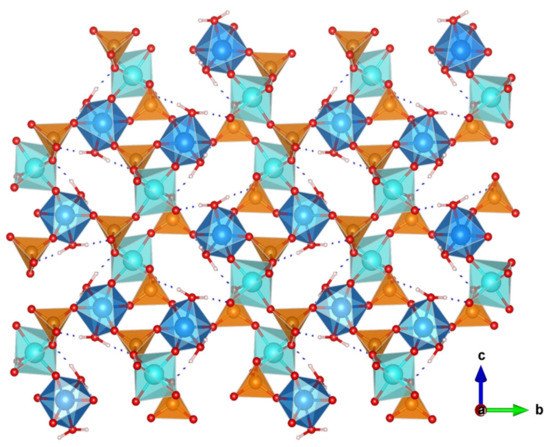
The great versatility of zirconium phosphate preparation under numerous experimental conditions, has been exploited to synthesize various novel derivatives, which displayed remarkable proton conductivity properties. Two examples are layered (NH4)2[ZrF2(HPO4)2] [63] and the 3D open framework zirconium phosphate (NH4)5[Zr3(OH)3F6(PO4)2(HPO4)] [64]. In both structures, the participation of NH4+ ions in the formation of extended hydrogen-bond networks (Figure 6) resulted in proton conductivities of 1.45 × 10−2 S·cm−1 (at 90 °C and 95% RH) and 4.41 × 10−2 S·cm−1 (at 60 °C and 98% RH), respectively. From the Ea values found, 0.19 and 0.33 eV, respectively, a Grotthuss-type proton-transfer mechanism was inferred for these materials.

Figure 6. Layered structure of compound (NH4)2[ZrF2(HPO4)2] and possible proton-transfer pathways (adapted from [63]).
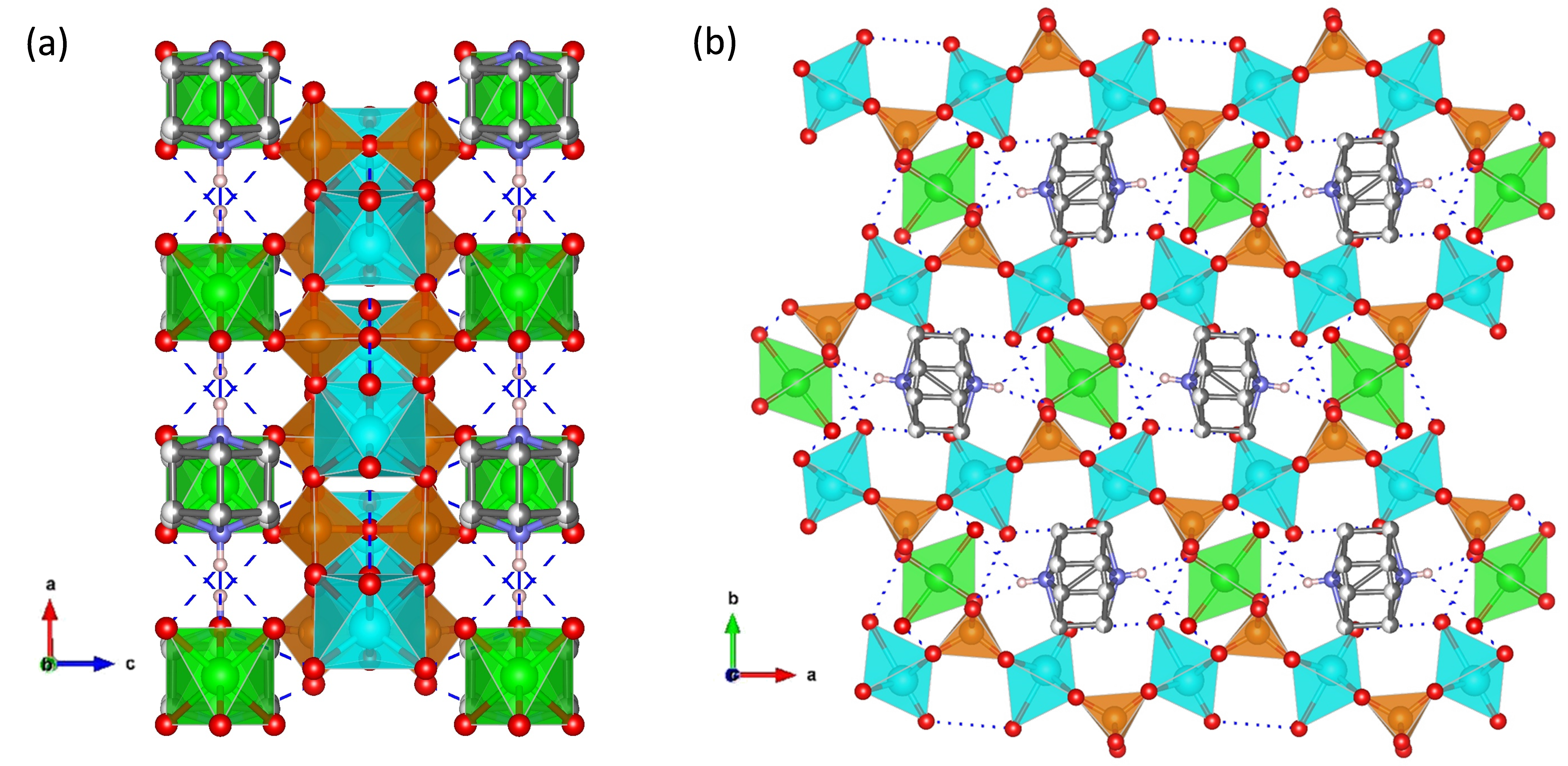
A one-dimensional zirconium phosphate, (NH4)3Zr(H2/3PO4)3, consisting of anionic [Zr(H2/3PO4)3]n3n− chains bonded to charge-compensating NH4+ ions was reported [65]. In this structure, the phosphates groups are disorderly protonated, while NH4+ ions occupy ordered positions in between adjacent chains (Figure 7). This arrangement generates H-bonding infinite chains of acid–base pairs (N-H···O-P) that lead to a high proton conductivity in anhydrous state of 1.45 × 10−3 S·cm−1, at 180 °C. This material also showed a remarkable high performance in PEMFC and DMFC under operation conditions.

5.2. Titanium and Tin(IV) Phosphates.
Structurally, titanium(IV) phosphates are more diverse than ZrP, given that structures containing an oxo/hydroxyl ligand or mixed-valence (TiIII/TiIV) titanium ions have been reported. In addition to the zirconium phosphate analogues, α- [66] and γ-TiP [67], two more other layered titanium phosphates, TiO(OH)(H2PO4)·2H2O [68] and Ti2O3(H2PO4)2·2H2O are known [69]. Furthermore, the mixed-valence titanium phosphate TiIIITiIV(HPO4)4·C2N2H9·H2O contains microporous channels [70], where monoprotonated ethylenediamine and lattice water are accommodated, which favours its transformation into a porous phase, Ti2(HPO4)4, at 600 °C with a 3D structure similar to that of τ-Zr(HPO4)2 [71].
The crystal structure of two other open-frameworks Ti2O(PO4)2·2H2O polymorphs (ρ-TiP and π-TiP) has been reported [72][73]. Fibrous ρ-TiP and π-TiP crystallize in triclinic and monoclinic unit cells, respectively, and are composed of TiO6 and TiO4(H2O)2 octahedra bridged through the orthophosphate groups (Figure 8). This type of connectivity creates two types of 1D channels running parallel to the direction of the fibre growth [72][73][74]. 31P MAS-NMR spectroscopy studies revealed that π-TiP has capability of adsorbing superficially protonated phosphate species (H3PO4/H2PO4-/HPO42-), which affects the proton conductivity properties as confirmed by AC impedance measurements.
The isomorphous series of layered α-metal(IV) phosphates [M(IV) = Zr, Ti, Sn) showed appreciable differences in the hydrogen bond interaction of the lattice water with the layers, associated with a variable layer corrugation degree along the series; α-TiP and α-SnP displaying H-bonds stronger than the prototype α-ZrP [75], which, in turn, might have significant implications in making internal surfaces accessible to proton conduction paths.
Recent studies carried out on a nanolayered γ-type tin phosphate, Sn(HPO4)2·3H2O, have revealed that this solid could be obtained in a water-delaminated form, which showed a high proton conductivity of ~1 × 10−2 S·cm−1 at 100 °C and 95% RH. This high value was attributed to strong H-bonds between water and the SnP layers, in combination with a high surface area of 223 m2·g−1 [76].
Other tetravalent phosphates such as silicophosphates with POH groups have received attention as proton-conducting electrolytes [77] but its solid-state structural characterization is elusive, at least, under conditions similar to those used in operating fuel cells [78].
5.3. Tetravalent Pyrophosphates.
Tetravalent metal pyrophosphates (MP2O7; M = Sn, Ce, Ti, Zr), in particular tin(IV) derivatives, combine high thermal stability (T ³ 400 °C) with conductivities of 10−3–10−2 S·cm−1 in the temperature range of 100–300 °C, under anhydrous or low humidity conditions [79][80][81][82][83]. The origin of this proton conductivity was initially explained because of protons being incorporated into the framework, formed by metal(IV) octahedra and corner-sharing phosphate tetrahedral, after interaction with water vapor.
Defect sites, such as electron holes [84] and oxygen vacancies are believed to favour proton generation [85]. These protons may occupy hydrogen-bonding interstitial sites on either the M−O−P or the P−O−P bonds, thus, generating a hopping proton transport between these sites [86][87]. In support of this, 1H NMR studies revealed two signals corresponding to hydrogen-bonded interstitial protons at phosphate tetrahedral and metal octahedral sites in In3+-doped SnP2O7. Furthermore, indium doping seemed not to affect the proton conduction occurring by a hopping mechanism between octahedral and tetrahedral sites.
Thus, the increased proton conductivity is instead attributable to increased proton concentration [88]. The strategy of dopant insertion into the M(IV) pyrophosphate has been further extended to include other dopant divalent and trivalent metal ions, such as Mg2+, Al3+, Sb3+, Sc3+, and Ga3+, with a maximum conductivity of 0.195 S·cm−1 being reported for In0.1Sn0.9P2O7 [89]. However, recent studies on metal doped and undoped SnP2O7 suggested that it is in co-precipitated phosphorous-rich amorphous phases where the proton conductivity mostly resides, while the crystalline phase exhibit a very low conductivity (~10−8 S·cm−1 at 150−300 °C) [90].
Low crystallinity titanium pyrophosphates also exhibit high proton conductivity [91]. Values of 0.0019–0.0044 S·cm−1, at 100 °C and 100% RH were reported for these compounds. The proton conduction is attributable to the presence of H2PO4- and HPO42− species, demonstrated by 31P MAS NMR and FTIR, and it occurs through a water-facilitated Grotthuss-type proton transport mechanism. Titanium phosphates are also prone to be functionalized with phosphonates groups. Thus, mixed titanium phosphate/phosphonates, Ti(HPO4)1.00(O3PC6H4SO3H)0.85(OH)0.30·nH2O [92], displayed an exceptional proton conductivity of 0.1 S·cm−1 at 100 °C.
A structurally different proton-conductor metal pyrophosphate is the mixed template-containing vanadium nickel pyrophosphate, (C6H14N2)[NiV2O6H8(P2O7)2]·2H2O (Figure 9). Its crystal structure is composed of octahedrally coordinated V(IV) and Ni(II) interconnected through bridging pyrophosphate groups, thus creating a 3D framework of [NiV2O6H8(P2O7)2]2− unit charged-compensated by protonated DABCO molecules. Hydrogen-bonding networks inside 3D channels facilitate the proton transport, and thus this material exhibits a remarkable proton conductivity of 2.0 × 10−2 S·cm−1 at 60 °C and 100% RH through a Grotthuss-type proton-transfer mechanism (Ea = 0.38 eV) [93].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ma15041292
References
- Shivhare, A.; Kumara, A.; Srivastava, R. Metal phosphate catalysts to upgrade ligno-cellulose biomass into value-added chemicals and biofuels. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 3818–3841.
- Zhao, H.; Yuan, Z.-Y. Insights into Transition Metal Phosphate Materials for Efficient Electrocatalysis. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 3797–3810.
- Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, D.; Wei, X.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y. New Versatile Synthetic Route for the Preparation of Metal Phosphate Decorated Hydrogen Evolution Photocatalysts. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 1566–1575.
- Goñi-Urtiaga, A.; Presvytes, D.; Scott, K. Solid acids as electrolyte materials for proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolysis: Review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 3358–3372.
- Paschos, O.; Kunze, J.; Stimming, U.; Maglia, F. A review on phosphate based, solid state, protonic conductors for intermediate temperature fuel cells. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2011, 23, 234110.
- Haile, S.M.; Chisholm, C.R.I.; Sasaki, K.; Boysen, D.A.; Uda, T. Solid acid proton conductors: From laboratory curiosities to fuel cell electrolytes. Faraday Discuss. 2007, 134, 17–39.
- Cheng, Q.; Zhao, X.; Yang, G.; Mao, L.; Liao, F.; Chen, F.; He, P.; Pan, D.; Chen, S. Recent advances of metal phosphates-based electrodes for high-performance metal ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 41, 842–882.
- Habraken, W.; Habibovic, P.; Epple, M.; Bohner, M. Calcium phosphates in biomedical applications: Materials for the future? Mater. Today 2015, 19, 69–87.
- Li, J.; Yi, M.; Zhang, L.; You, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, B. Energy related ion transports in coordination polymers. Nano Select. 2021, 1–19.
- Pica, M.; Donnadio, A.; Casciola, M. From microcrystalline to nanosized α-zirconium phosphate: Synthetic approaches and applications of an old material with a bright future. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 374, 218–235.
- Wong, N.E.; Ramaswamy, P.; Lee, A.S.; Gelfand, B.S.; Bladek, K.J.; Taylor, J.M.; Spasyuk, D.M.; Shimizu, G.K.H. Tuning Intrinsic and Extrinsic Proton Conduction in Metal−Organic Frameworks by the Lanthanide Contraction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 14676–14683.
- Horike, S.; Umeyama, D.; Inukai, M.; Itakura, T.; Kitagawa, S. Coordination-network-based ionic plastic crystal for anhydrous proton conductivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7612–7615.
- Zhang, K.-M.; Lou, Y.-L.; He, F.-Y.; Duan, H.-B.; Huang, X.-Q.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, H.-R. The water-mediated proton conductivity of a 1D open framework inorganic-organic hybrid iron phosphate and its composite membranes. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 134, 109032.
- Yu, J.-W.; Yu, H.-J.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zou, Y., Luo, H.-B.; Wang, L.; Ren, X.-M. Humidity-sensitive irreversible phase transformation of open-framework zinc phosphate and its water-assisted high proton conduction properties. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 8070–8075.
- Su, X.; Yao, Z.; Ye, Y.; Zeng, H.; Xu, G.; Wu, L.; Ma, X.; Chen, Q.-H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; et al. 40-Fold Enhanced Intrinsic Proton Conductivity in Coordination Polymers with the Same Proton-Conducting Pathway by Tuning Metal Cation Nodes. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 983–986.
- Shi, J.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, Z. Exploration of new water stable proton-conducting materials in an amino acid-templated metal phosphate system. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 654–658.
- Zhang, K.-M.; He, F.-Y.; Duan, H.-B.; Zhao, H.-R. An alkali metal ion-exchanged metal-phosphate (C2H10N2)xNa1−x[Mn2(PO4)2] with high proton conductivity of 10−2 S·cm−1. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 6639–6646.
- Zhang, K.-M.; Jia, Y.; Gu, Y., He, F.-Y.; Zhao, H.-R. A facile and efficient method to improve the proton conductivity of open framework metal phosphates under aqueous condition. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 120, 108128.
- Umeyama, D.; Horike, S.; Inukai, M.; Kitagawa, S. Integration of Intrinsic Proton Conduction and Guest-Accessible Nanospace into a Coordination Polymer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 11345–11350.
- Baranov, A.I.; Khiznichenko, V.P.; Sandler, V.A.; Shuvalov, L.A. Frequency dielectric dispersion in the ferroelectric and superionic phases of CsH2PO4. Ferroelectrics 1988, 81, 183–186.
- Colomban, P. Chemistry of Solid-State Materials. In Proton Conductors: Solid, Membranes and Gels-Materials and Devices; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992.
- Fragua, D.M.; Castillo, J.; Castillo, R.; Vargas, R.A. New amorphous phase KnH2PnO3n+1(n>>1) in KH2PO4. Rev. Latin Am. Metal. Mat. 2009, 2, 491–497.
- Botez, C.E.; Tackett, R.J.; Hermosillo, J.D.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L. High pressure synchrotron x-ray diffraction studies of superprotonic transitions in phosphate solid acids. Solid State Ion. 2012, 213, 58–62.
- Baranov, A.I. Crystals with disordered hydrogen-bond networks and superprotonic conductivity. Review. Crystallogr. Rep. 2003, 48, 1012–1037.
- Bagryantseva, I.N.; Gaydamaka, A.A.; Ponomareva, V.G. Intermediate temperature proton electrolytes based on cesium dihydrogen phosphate and Butyral polymer. Ionics 2020, 26, 1813–1818.
- Dreßler, C.; Sebastiani, D. Effect of anion reorientation on proton mobility in the solid acids family CsHyXO4 (X = S, P, Se, y = 1, 2) from ab initio molecular dynamics simulations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 10738–10752.
- Taninouchi, Y.K.; Uda, T.; Awakura, Y.; Ikeda, A.; Haile, S.M. Dehydration behavior of the superprotonic conductor CsH2PO4 at moderate temperatures: 230 to 260 °C. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 3182–3189.
- Mathur, L.; Kim, I.-H.; Bhardwaj, A.; Singh, B.; Park, J.-Y.; Song, S.-J. Structural and electrical properties of novel phosphate based composite electrolyte for low-temperature fuel cells. Composites Part B 2020, 202, 108405.
- Otomo, J.; Tamaki, T.; Nishida, S.; Wang, S.; Ogura, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Wen, C.-J.; Nagamoto, H.; Takahashi, H. Effect of water vapor on proton conduction of cesium dihydrogen phosphate and application to intermediate temperature fuel cells. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2005, 35, 865–870.
- Uda, T.; Haile, S.M. Thin-membrane solid-acid fuel cell. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 2005, 8, A245–A246.
- Navarrete, L.; Andrio, A.; Escolástico, S.; Moya, S.; Compañ, V.; Serra, J.M. Protonic Conduction of Partially-Substituted CsH2PO4 and the Applicability in Electrochemical Devices. Membranes 2019, 9, 49.
- Ponomareva, V.G.; Bagryantseva, I.N.; Gaydamaka, A.A. Study of the Phase Composition and Electrotransport Properties of the Systems Based on Mono- and Disubstituted Phosphates of Cesium and Rubidium. Chem. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 27, 238–245.
- Martsinkevich, V.V.; Ponomareva, V.G. Double salts Cs1-xMxH2PO4 (M = Na, K, Rb) as proton conductors. Solid State Ion. 2012, 225, 236–240.
- Ponomareva, V.G.; Bagryantseva, I.N. Superprotonic CsH2PO4-CsHSO4 solid solutions. Inorg. Mater. 2012, 48, 187–194.
- Ponomareva, V.G.; Uvarov, N.F.; Lavrova, G.V.; Hairetdinov, E.F. Composite protonic solid electrolytes in the CsHSO4-SiO2 system. Solid State Ion. 1996, 90, 161–166.
- Ponomareva, V.G.; Shutova, E.S.; Matvienko, A.A. Conductivity of Proton Electrolytes Based on Cesium Hydrogen Sulfate Phosphate. Inorg. Mater. 2004, 40, 721–728.
- Otomo, J.; Minagawa, N.; Wen, C.-J.; Eguchi, K.; Takahashi, H. Protonic conduction of CsH2PO4 and its composite with silica in dry and humid atmospheres. Solid State Ion. 2003, 156, 357–369.
- Ponomareva, V.G.; Shutova, E.S. High-temperature behavior of CsH2PO4 and CsH2PO4-SiO2 composites. Solid State Ion. 2007, 178, 729–734.
- Singh, D.; Singh, J.; Kumar, P.; Veer, D.; Kumar, D.; Katiyar, R.S.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, A. The Influence of TiO2 on the Proton Conduction and Thermal Stability of CsH2PO4 Composite Electrolytes. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 37, 227–236.
- Singh, D.; Kumar, P.; Singh, J.; Veer, D.; Kumar, A.; Katiyar, R.S. Structural, thermal and electrical properties of composites electrolytes (1−x) CsH2PO4/x ZrO2 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.4) for fuel cell with advanced electrode. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 46.
- Veer, D.; Kumar, P.; Singh, D.; Kumar, D.; Katiyar, R.S. A synergistic approach to achieving high conduction and stability of CsH2PO4/NaH2PO4/ZrO2 composites for fuel cells. Mater. Adv. 2021, 3, 409–417.
- Aili, D.; Gao, Y.; Han, J.; Li, Q. Acid-base chemistry and proton conductivity of CsHSO4, CsH2PO4 and their mixtures with N-heterocycles. Solid State Ion. 2017, 306, 13–19.
- Bagryantseva, I.N.; Ponomareva, V.G.; Khusnutdinov, V.R. Intermediate temperature proton electrolytes based on cesium dihydrogen phosphate and poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene). J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 14196–14206.
- Ponomareva, V.G.; Bagryantseva, I.N.; Shutova, E.S. Hybrid systems based on nanodiamond and cesium dihydrogen phosphate. Mater. Today 2020, 25, 521–524.
- Ma, N.; Kosasang, S.; Yoshida, A.; Horike, S. Proton-conductive coordination polymer glass for solid-state anhydrous proton batteries. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 5818–5824.
- Zhao, H.-R.; Xue, C.; Li, C.-P.; Zhang, K.-M.; Luo, H.-B.; Liu, S.-X.; Ren, X.-M. A Two-Dimensional inorganic−organic hybrid solid of manganese(II) hydrogenophosphate showing high proton conductivity at room temperature. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 8971–8975.
- Wang, M.; Luo, H.-B.; Liu, S.-X.; Zou, Y.; Tian, Z.-F.; Li, L.; Liu, J.-L.; Ren, X.-M. Water assisted high proton conductance in a highly thermally stable and superior water-stable open-framework cobalt phosphate. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 19466–19472.
- Umeyama, D.; Horike, S.; Inukai, M.; Itakura, T.; Kitagawa, S. Inherent Proton Conduction in a 2D Coordination Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 12780–12785.
- Inukai, M.; Horike, S.; Chen, W.; Umeyama, D.; Itakurad, T.; Kitagawa, S. Template-directed proton conduction pathways in a coordination framework. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2014, 2, 10404–10409.
- Zhao, H.R.; Jia, Y.; Gu, V.; He, F.Y.; Zhang, K.M.; Tian, Z.F.; Liu, J.L. A 3D open-framework iron hydrogenophosphate showing high proton conductance under water and aqua-ammonia vapor. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 9046–9051.
- Zima, V.; Lii, K.-H. Synthesis and characterization of a novel one-dimensional iron phosphate: [C4H12N2]1.5[Fe2(OH)(H2PO4)(HPO4)2(PO4)]·0.5H2O. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1998, 24, 4109–4112.
- Lii, K.-H.; Huang, Y.-F. Large tunnels in the hydrothermally synthesized open-framework iron phosphate (NH3(CH2)3NH3)2[Fe4(OH)3(HPO4)2(PO4)3]·xH2O. Chem. Commun. 1997, 9, 839–840.
- Bazaga-García, M.; Colodrero, R.M.P.; Papadaki, M.; Garczarek, P.; Zon, J.; Olivera-Pastor, P.; Losilla, E.R.; Reina, L.L.; Aranda, M.A.; Choquesillo-Lazarte, D.; et al. Guest Molecule-Responsive Functional Calcium Phosphonate Frameworks for Tuned Proton Conductivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5731–5739.
- Lim, D.-W.; Kitagawa, H. Proton Transport in Metal−Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 8416–8467.
- Mamlouk, M.; Scott, K. A boron phosphate-phosphoric acid composite membrane for medium temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2015, 286, 290–298.
- Pusztai, P.; Haspel, H.; Tóth, I.Y.; Tombácz, E.; László, K.; Kukovecz, Á.; Kónya, Z. Structure-Independent Proton Transport in Cerium(III) Phosphate Nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 9947–9956.
- Mu, Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.Y.; Yu, J.H. Organotemplate-free synthesis of an open-framework magnesium aluminophosphate with proton conduction properties. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2149–2151.
- Petersen, H.; Stefmann, N.; Fischer, M.; Zibrowius, I.R.; Philippi, W.; Schmidt, W.; Weidenthaler, C. Crystal structures of two titanium phosphate-based proton conductors: Ab initio structure solution and materials properties. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 2379–2390.
- Clearfield, A.; Smith, S.D. The crystal structure of zirconium phosphate and the mechanism of its ion exchange behavior. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 28, 325–330.
- Clearfield, A.; Smith, G.D. Crystallography and structure of alpha-zirconium bis(monohydrogen orthophosphate) monohydrate. Inorg. Chem. 1969, 8, 431–436.
- Troup, J.M.; Clearfield, A. Mechanism of ion exchange in zirconium phosphates. 20. Refinement of the crystal structure of .alpha.-zirconium phosphate. Inorg. Chem. 1977, 16, 3311–3314.
- Casciola, M. From layered zirconium phosphates and phosphonates to nanofillers for ionomeric membranes. Solid State Ion. 2019, 336, 1–10.
- Gui, D.; Zheng, T.; Xie, J.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Diwu, J.; Chai, Z.; Wang, S. Significantly dense two-dimensional hydrogen-bond network in a layered zirconium phosphate leading to high proton conductivities in both water-assisted low-temperature and anhydrous intermediate-temperature regions. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 12508–12511.
- Yu, J.-W.; Yu, H.-J.; Yao, Z.-Y.; Li, Z.-H.; Ren, Q.; Luo, H.-B.; Zou, Y.; Wang, L.; Ren, X.-M. A water-stable open-framework zirconium(IV) phosphate and its water-assisted high proton conductivity. CrystEngComm 2021, 23, 6093–6097.
- Gui, D.; Dai, X.; Tao, Z.; Zheng, T.; Wang, X.; Silver, M.A.; Shu, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; et al. Unique proton transportation pathway in a robust inorganic coordination polymer leading to intrinsically high and sustainable anhydrous proton conductivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 6146–6155.
- Alberti, G.; Cardini-Galli, P.; Costantino, U.; Torracca, E. Crystalline insoluble salts of polybasic metals—I Ion-exchange properties of crystalline titanium phosphate. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1967, 29, 571–578.
- Christensen, A.N.; Anderson, E.K.; Andersen, I.G.; Alberti, G.; Nielsen, M.; Lehmann, E.K. X-Ray Powder diffraction study of layer compounds. The crystal structure of α-Ti (HPO4)2·H2O and a proposed structure for γ-Ti (H2PO4)(PO4)·2H2O. Acta Chem. Scand. 1990, 44, 865–872.
- Li, Y.J.; Whittingham, M.S. Hydrothermal synthesis of new metastable phases: Preparation and intercalation of a new layered titanium phosphate. Solid State Ion. 1993, 63, 391–395.
- Kőrösi, L.; Papp, S.; Dékány, I. A layered titanium phosphate Ti2O3(H2PO4)2·2H2O with rectangular morphology: Synthesis, structure, and cysteamine intercalation. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 4356–4363.
- Ekambaram, S.; Serre, C.; Férey, G.; Sevov, S.C. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of an ethylenediamine-templatedmixed-valence titanium phosphate. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 444–449.
- Krogh Andersen, A.M.; Norby, P.; Hanson, J.C.; Vogt, T. Preparation and characterization of a new 3-dimensional zirconium hydrogen phosphate, τ-Zr(HPO4)2. Determination of the complete crystal structure combining synchrotron X-ray single-crystal diffraction and neutron powder diffraction. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 876–881.
- Bortun, A.I.; Khainakov, S.A.; Bortun, L.N.; Poojary, D.M.; Rodriguez, J.; Jose, R. Garcia, J.R.; Clearfield, A. Synthesis and characterization of two novel fibrous titanium phosphates Ti2O(PO4)2·2H2O. Chem. Mater. 1997, 9, 1805–1811.
- Salvadó, M.A.; Pertierra, P.; García-Granda, S.; García, J.R.; Fernández-Diaz, M.T.; Dooryhee, E. Crystal structure, including H-atom positions, of Ti2O(PO4)2·(H2O)2 determined from synchrotron X-ray and neutron powder data. Eur. J. Solid State Inorg. Chem. 1997, 34, 1237–1247.
- Babaryk, A.A.; Adawy, A.; García, I. Trobajo, C.; Amghouz, Z.; Colodrero, R.M.P. Cabeza, A.; Olivera-Pastor, P.; Bazaga-García, M.; dos Santos-Gómez, L. Structural and proton conductivity studies of fibrous π-Ti2O(PO4)2·2H2O: Application in chitosan-based composite membranes. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 7667–7677.
- Bruque, S.; Aranda, M.A.G.; R. Losilla, E.; Olivera-Pastor, P.; Maireles-Torres, P. Synthesis optimization and crystal structures of layered metal(IV) hydrogen phosphates, .alpha.-M(HPO4)2.cntdot.H2O (M = Ti, Sn, Pb). Inorg. Chem. 1995, 34, 893–899.
- Huang, W.; Komarneni, S.; Noh,Y.D.; Ma, J.; Chen, K.; Xue, D.; Xuea, X.; Jiang, B. Novel inorganic tin phosphate gel: Multifunctional material. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 2682–2685.
- Zhang, J.; Aili, D.; Lu, S.; Li, Q.; Jiang, S.P. Advancement toward Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells at Elevated Temperatures. AAAS Res. 2020, 2020, 9089405.
- Ansari, Y.; Telpriore, G.; Tucker, C.; Angell, A. A novel, easily synthesized, anhydrous derivative of phosphoric acid for use in electrolyte with phosphoric acid-based fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2013, 237, 47–51.
- Sato, Y.; Shen, Y.; Nishida, M.; Kanematsu, W.; Hibino, T. Proton Conduction in Non-Doped and Acceptor-Doped Metal Pyrophosphate (MP2O7) Composite Ceramics at Intermediate Temperatures. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 3973–3981.
- Singh, B.; Kima, J.-H.; Park, J.-Y.; Song, S.-J. Dense composite electrolytes of Gd3+-doped cerium phosphates for low-temperature proton-conducting ceramic-electrolyte fuel cells. Ceram. Inter. 2015, 41, 4814–4821.
- Nagao, M.; Kamiya, T.; Heo, P.; Tomita, A.; Hibino, T.; Sano, M. Proton conduction in In3+-doped SnP2O7 at intermediate temperatures. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, 1604–1609.
- Nagao, M.; Takeuchi, A.; Heo, P.; Hibino, T.; Sano, M.; Tomita, A. A proton-conducting In3 + -doped SnP2O7 electrolyte for intermediate-temperature fuel cells. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2006, 9, A105.
- Jin, Y.; Fujiwara, K.; Hibino, T. High temperature, low humidity proton exchange membrane based on an inorganic–organic hybrid structure. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2010, 13, B8.
- Jin, Y.; Shen, Y.; Hibino, T. Proton conduction in metal pyrophosphates (MP2O7) at intermediate temperatures. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 6214–6217.
- Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Payzant, E.; Xia, C.; Chu, D. An oxide ion and proton co-ion conducting Sn0.9In0.1P2O7 electrolyte for intermediate-temperature fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, B1264.
- Kreller, C.R.; Pham, H.H.; Wilson, M.S.; Mukundan, R.; Henson, N.; Sykora, M.; Hartl, M.; Daemen, L.; Garzon, F.H. Intragranular phase proton conduction in crystalline Sn1−xInxP2O7 (x = 0 and 0.1). J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 23896–23905.
- Kreller, C.R.; Wilson, M.S.; Mukundan, R.; Brosha, E.L.; Garzon, F.H. Stability and conductivity of In3+-doped SnP2O7 with varying phosphorous to metal ratios. ECS Electrochem. Lett. 2013, 2, F61−F63.
- Foran, G.Y.; Goward, G.R. Site-Specific Proton Dynamics in Indium-Doped Tin Pyrophosphate. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 28407–28416.
- Scott, K.; Xu, C.; Wu, X. Intermediate temperature proton-conducting membrane electrolytes for fuel cells. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Energy Environ. 2014, 3, 24–41.
- Anfimova, T.; Lie-Andersena, T.; Pristed Jensen, E.; C. Brorson Prag, C.; Nielsen, U.G.; Sørensen, D.R.; Skou, E.M.; Christensen, E.; Bjerrum, N.J.;.Li, Q. The effect of preparation method on the proton conductivity of indium doped tin pyrophosphates. Solid State Ion. 2015, 278, 209–216.
- Hogarth, W.H.J.; Muir, S.S.; Whittaker, A.K.; Diniz da Costa, J.C.; Drennan, J.; Lu, G.Q. Proton conduction mechanism and the stability of sol–gel titanium phosphates. Solid State Ion. 2007, 177, 3389–3394.
- Alberti, G.; Costantino, U.; Casciola, M.; Ferroni, S.; Massinelli, L.; Staiti, P. Preparation, characterization and proton conductivity of titanium phosphate sulfophenylphosphonate. Solid State Ion. 2001, 145, 249–255.
- Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Sun, X.; Jian, J.; Li, G.; Yuan, H. Proton conduction in organically templated 3D open-framework vanadium−nickel pyrophosphate. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 4394–4398.
