In the search of animal stroke models providing translational advantages for biomedical research, pigs are large mammals with interesting brain characteristics and wide social acceptance. Compared to rodents, pigs have human-like highly gyrencephalic brains. In addition, increasingly through phylogeny, animals have more sophisticated white matter connectivity; thus, ratios of white-to-gray matter in humans and pigs are higher than in rodents. Swine models provide the opportunity to study the effect of stroke with emphasis on white matter damage and neuroanatomical changes in connectivity, and their pathophysiological correlate.
- stroke, swine, gyrencephalic brain, white matter
Note:All the information in this draft can be edited by authors. And the entry will be online only after authors edit and submit it.
1. Introduction
Stroke is a life-threatening disease that causes neuronal loss and subsequent high rates of mortality or permanent disability. Around 17 million stroke cases occur each year worldwide, causing 6 million fatalities and leaving around 6 million patients with serious disabilities. There are two major types of strokes: The ischemic type, which is associated with the occlusion of a cerebral artery and accounts for 85% of all strokes, and the hemorrhagic stroke, which results from blood spill because of an arterial wall rupture. Clinically, stroke treatment is limited to interventions that restore blood flow in the ischemic stroke type, either pharmacologically or via mechanical thrombectomy, and only a small 15% of all stroke patients might benefit from these therapies. Many of the pathophysiological mechanisms of stroke (e.g., excitotoxicity, the core and penumbra concepts, cortical spreading depolarization, excess of free radical production, or inflammation) have been primarily identified as drivers of neuronal death in rodent models with gray matter (GM)-rich brains before being confirmed in human stroke. In contrast, the pathways that contribute to the complex pathology of neuronal soma-devoid areas of white matter (WM) following a stroke event are relatively understudied, and mostly use rodent models or perinatal hypoxic models of cerebral palsy. However, damage to the WM areas is increasingly recognized as a cause of long-term cognitive and motor disabilities in most stroke survivors. This is why research, development, and characterization of swine models of stroke, which combine both the mechanistic knowledge gained in rodent research and a greater degree of neuroanatomical and connectivity similarities with humans, may play a key role to bridge the gap from pre-clinical findings to clinical implementation.
2. Pig Brain to Model Human Stroke Pathophysiology
Pigs are big mammals with interesting characteristics for their use in biomedical translational research as compared to dogs and non-human primates (NHPs) [1]. There are ethical challenges associated with the fact that NHPs are highly close to humans, and canine models are not as socially accepted as other models due to their setting as companion animals in western cultures [1,2]. Conversely, due to their generalized use in the meat industry, pigs are higher-order animals that do not arise the same ethical issues as other animals do in a vast majority of the population [3].
In contrast with lissencephalic brains of rodents—and some commonly used NHPs like the marmoset [1,4]—pigs have human-like highly gyrencephalic brains (Figure 1), resembling lobes, gyri, and sulci/fissures of the human brain anatomy [5,6,7] with a comparable organization of motor and somatosensory areas to other mammals [8]. This resemblance with humans has also been found in several brain structures such as the limbic system, the brainstem, as well as other subcortical and diencephalic nuclei [5]. Swine brain mass is comparable to or greater than that of commonly used NHP models [5,9] with a well-developed prefrontal cortex in terms of cytoarchitecture and connectivity [10]. The development of the brain is remarkably similar to that in humans, including the myelination process [6,10,11,12], showing remarkable similarities in the resting-state networks and connectivity [13]. Due to fibrous dura mater, the increase in intracranial pressure (ICP) in large animal models of stroke is similar to that observed in humans suffering stroke [14]. Importantly, swine models allow a trustworthy tracking of brain damage evolution using the same non-invasive multimodal imaging sequences and instruments used in clinical practice [15,16] (Figure 1). Pigs also display complex individual behaviors and social interactions that can be analyzed using a number of validated tests [17,18]. Additionally, pigs have some neurovascular characteristics [19,20], including the diameter of their cerebrals vessels, which make them suitable for pre-first-in-human validation of endovascular devices or new neurosurgical techniques [15].
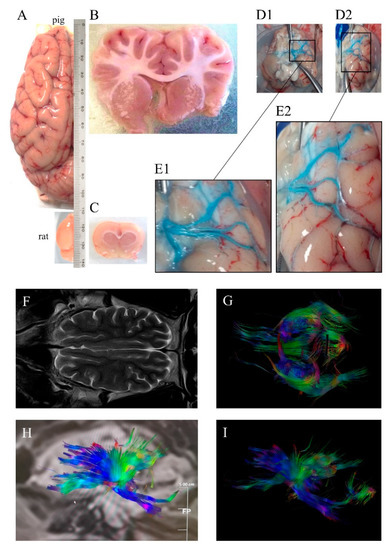
Figure 1. (A) Dorsal view of pig and rat brain hemispheres showing differences in size and gyrencephaly. Coronal (B) pig and (C) rat sections showing differences in white matter. (D1) Ventral view of pig brain (without cerebellum) injected unilaterally i.a. ex vivo a blue dye, (D2) ventrolateral view of the same brain, (E1) and (E2) magnifications of the insets in (D1) and (D2), respectively, showing three main middle cerebral arteries. (F) Horizontal pig brain section obtained by magnetic resonance T2 sequence, (G) tractography using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and (H,I) sagittal pig brain tractography, with colors denoting directionality. Images were obtained at the Comparative Medicine and Bioimage Centre of Catalonia (CMCiB).
As a general rule, larger brains require longer fibers to connect distant cerebral areas. Across species, brain connectivity through white matter increases more rapidly than brain size [1,21]. The ratios of white-to-gray matter in humans and pigs are similar and much higher than those of mice and rats: Rodents have a WM brain composition of 10% compared to the >60% of both humans and swine [1,22,23] (Figure 1). The failure in stroke clinical trials of many neuroprotectants that are beneficial in rodents is thought to be in part due to the fact that the study of treatments with potential protection against ischemic axonal damage in the preclinical phase are seldom considered [24,25]. Hence, using larger gyrencephalic animals with a WM volume similar to that in humans could be pivotal in the preclinical study of stroke pathophysiology and of new clinically effective treatments [26,27].
Another aspect of the swine that should not be disregarded in stroke research is its size (Figure 1), as large animal species offer some advantages compared to smaller species. To begin with, depending on the strain and at sexual maturity, pigs can have a weight similar to that of humans, allowing the use of equipment and procedures specialized for humans in the clinical arena [2,3,28]. Additionally, their size allows repeated sampling of body fluids with minimal physiological disturbance, which eases performing longitudinal studies [3,29]. Moreover, pigs are much closer genetically to humans than mice [30,31], and have the potential to offer a better modeling of human gene regulation and function [32]; also, several models of pathologies and comorbidities usually found in stroke patients, such as obesity or atherosclerosis, have been established in swine [33]. The shorter the phylogenetic distance between the model and the modeled species, the better inference of the results obtained is anticipated [2]; moreover, animal models with comorbidities could potentially improve that inference. In sum, all these features make the pig an excellent research animal to obtain results with more translation to the clinic.
3. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
The pig brain resemblance to the human brain provides a unique opportunity to study structural brain damage by non-invasive imaging techniques used in humans and to compare with acute histological and metabolic measurements not available in human studies unless in fatal cases. In addition, new gene-manipulation procedures and comorbidity models in pigs can provide in the years to come the opportunity to experimentally assess the roles of specific molecules and pathways in the pathophysiology of stroke.
The main limitations of swine brain to model human stroke are: (1) The presence of the rete mirabile, that handicaps endovascular access to intracranial arteries to produce focal brain ischemia; (2) the fact that pig plasminogen has resistance to tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)-mediated activation; (3) the significant contribution of both posterior and anterior cerebral arteries to the circulation through the circle of Willis; and that (4) pigs take longer than rodents to reach sexual maturity, adult animal models are interesting due to the relationship between ageing and the disease, but mature pigs of conventional strains can be difficult to manage considering their size. The size issue can be solved by using adult miniature pigs, which in turn are more stable strains adapted for their use in biomedical research. However, studies using aged animals are still lacking. Stroke incidence is notably affected by age and aged brains are in an enhanced inflammatory and oxidative state that renders them more vulnerable to ischemia. Concerning the rete mirabile, the study of Cui et al. mentioned above reports achieving focal cerebral ischemia by an endovascular embolization of the rete unilaterally. The replication of these results would translate into models in which a much less severe surgery is needed to induce the pathology, thus leading to a refinement of the current techniques according to the 3 Rs principle. Even so, new techniques and/or new stroke-inducing paradigms in swine (adapted from rodent stroke models, for instance clot induction by ferrous chloride or by thrombin or innovative approaches) will foster the role of porcine stroke models to bridge the gap from pre-clinical findings to clinical implementation.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms21186568
