Research has indicated that zinc plays a consequential mechanistic role in the protection against oxidative stress as zinc is required for the proper functioning of the antioxidant system, the suppression of inflammatory mediators, and the modulation of zinc transporters. Recently, the mechanisms surrounding ZnT8, ZIP7, and metallothionein have shown to be of particular pathogenic importance and are considered as potential therapeutic targets in disease management. The literature has shown that zinc dysregulation is associated with diabetes and may be considered as a leading contributor to the deleterious vascular alterations exhibited by the disease. Although further investigation is required, studies have indicated the favorable use of zinc supplementation in the protection against and prevention of oxidative stress and its consequences over the course of the condition.
- oxidative stress
- ROS
- zinc homeostasis
- zinc transporters
1. Zinc Homeostasis
Zinc Distribution in the β-Cell
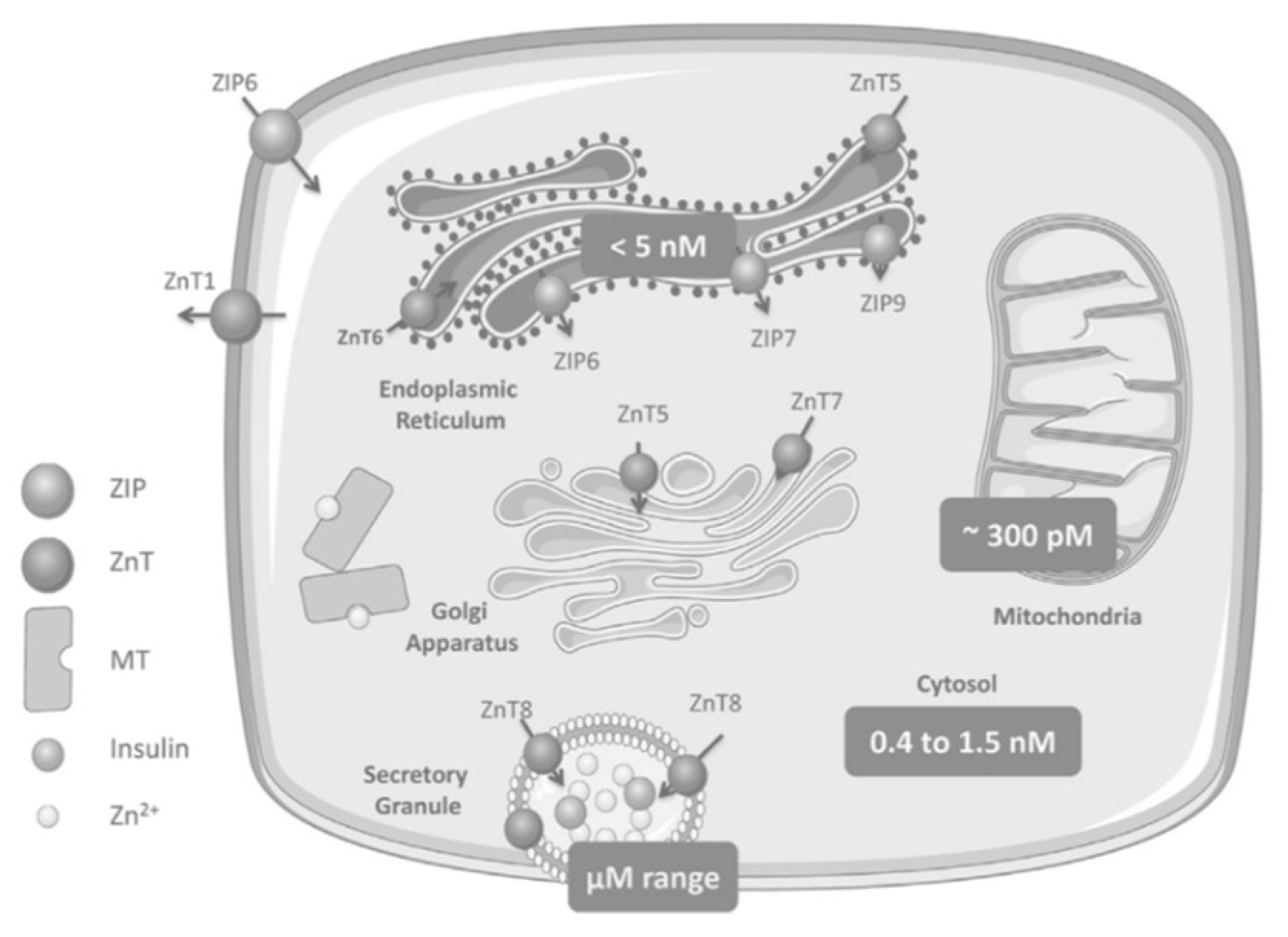
2. Zinc Transporters: Glucose Homeostasis, Insulin Resistance and Immunity
2.1. ZnT8
2.2. ZIP7
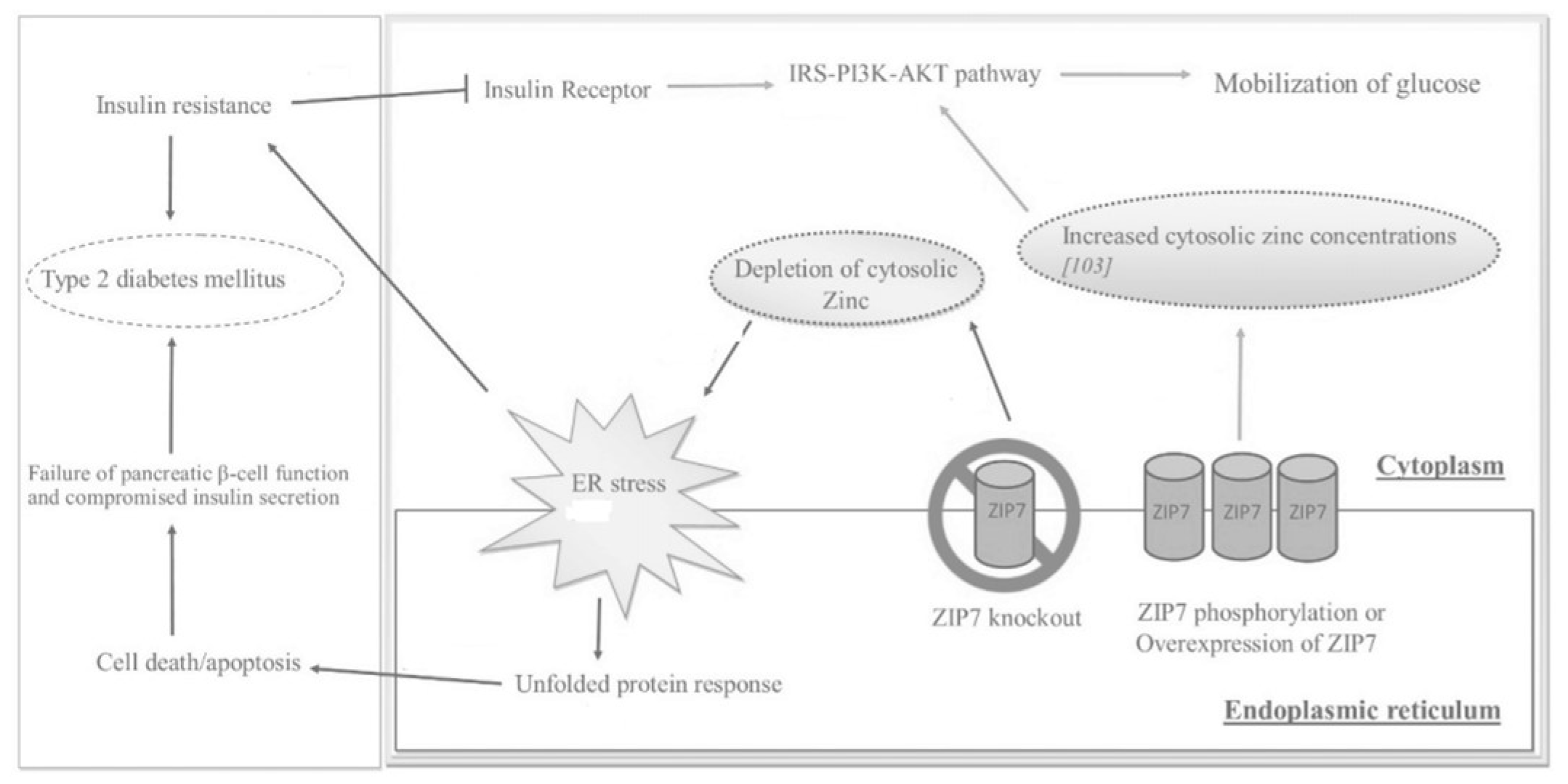
2.3. Metallotionein
2.4. Other ZnT/SLC30A Transporters
2.5. Other ZIP/SLC39A Transporters
| Zinc Transporter | Regulators | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| ZnT1 | Metal-responsive mode of regulation; dietary intake of zinc | Efflux of zinc in smooth muscle cells |
| ZnT2 | Metal-responsive mode of regulation; dietary intake of zinc | Zinc transport in vesicles and lysosomes of pancreas, kidney, testis, epithelial cells, small intestine |
| ZnT3 | Glucose status | Transport of zinc to synaptic vesicles |
| ZnT4 | Unaffected by changes in dietary zinc uptake; regulated by extracellular zinc concentrations | Transport of zinc in the trans-Golgi network and in the cytoplasmic vesicular compartment |
| ZnT5 | Glucose status; zinc-responsive elements | Transport of zinc into Golgi lumen for storage |
| ZnT7 | Glucose status | Transport of zinc to Golgi apparatus in retina, liver, epithelial cells, small intestine; may play a redundant role of ZnT8 |
| ZnT8 | Glucose status | Regulation of zinc in the secretory vesicles of pancreatic β-cells |
| ZnT9 | Expressed in low levels in response to dietary intake of zinc | Export of zinc out of myocytes; efflux of zinc in smooth muscle cells |
| ZIP1 | Testosterone and prolactin | Uptake of zinc into cells |
| ZIP6 | Estrogen stimulation, glucose status | Down-regulation leads to poor insulin secretion |
| ZIP7 | Glucose status | Increases cytosolic zinc concentrations that participate in glucose mobilization and metabolism |
| ZIP8 | Glucose status, TNF-∝ in lung epithelial cells | Increases intracellular zinc levels |
| ZIP13 | Gene mutation leads to loss of function | Inhibition of adipocyte browning |
| ZIP14 | Acute phase response during inflammation; IL-6 | Rapid intake of plasma zinc into the organs |
3. Conclusions
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/biomedicines10010139
References
- Myers, S.A.; Nield, A.; Myers, M. Zinc transporters, mechanisms of action and therapeutic utility: Implications for type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 2012, 173712.
- Woodruff, G.; Bouwkamp, C.G.; de Vrij, F.M.; Lovenberg, T.; Bonaventure, P.; Kushner, S.A.; Harrington, A.W. The Zinc Transporter SLC39A7 (ZIP7) Is Essential for Regulation of Cytosolic Zinc Levels. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 94, 1092–1100.
- Chabosseau, P.; Rutter, G.A. Zinc and diabetes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016, 611, 79–85.
- Zalewski, P.D.; Beltrame, J.F.; Wawer, A.A.; Abdo, A.I.; Murgia, C. Roles for endothelial zinc homeostasis in vascular physiology and coronary artery disease. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3511–3525.
- Adulcikas, J.; Sonda, S.; Norouzi, S.; Sohal, S.S.; Myers, S. Targeting the Zinc Transporter ZIP7 in the Treatment of Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 408.
- Fukunaka, A.; Fujitani, Y. Role of Zinc Homeostasis in the Pathogenesis of Diabetes and Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 476.
- Norouzi, S.; Adulcikas, J.; Sohal, S.S.; Myers, S. Zinc transporters and insulin resistance: Therapeutic implications for type 2 diabetes and metabolic disease. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 87.
- Do Marreiro, D.N.; Cruz, K.J.C.; Morais, J.B.S.; Beserra, J.B.; Severo, J.S.; de Oliveira, A.R.S. Zinc and Oxidative Stress: Current Mechanisms. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 24.
- Olechnowicz, J.; Tinkov, A.; Skalny, A.; Suliburska, J. Zinc status is associated with inflammation, oxidative stress, lipid, and glucose metabolism. J. Physiol. Sci. 2018, 68, 19–31.
- Farooq, M. Zinc Deficiency is Associated with Poor Glycemic Control. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2019, 29, 253–257.
- Zhao, T.; Huang, Q.; Su, Y.; Sun, W.; Huang, Q.; Wei, W. Zinc and its regulators in pancreas. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 27, 453–464.
- Choi, S.; Liu, X.; Pan, Z. Zinc deficiency and cellular oxidative stress: Prognostic implications in cardiovascular diseases. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1120–1132.
- Mondragon, P.; Bergdahl, A. Metallothionein expression in slow- vs. fast-twitch muscle fibers following 4 weeks of streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes. Facets 2018, 3, 315–325.
- Williams, C.L.; Long, A.E. What has zinc transporter 8 autoimmunity taught us about type 1 diabetes? Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1969–1976.
- Huang, Q.; Du, J.; Merriman, C.; Gong, Z. Genetic, Functional, and Immunological Study of ZnT8 in Diabetes. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 2019, 1524905.
- Anzilotti, C.; Swan, D.J.; Boisson, B.; Deobagkar-Lele, M.; Oliveira, C.; Chabosseau, P.; Engelhardt, K.R.; Xu, X.; Chen, R.; Alvarez, L.; et al. An essential role for the Zn2+ transporter ZIP7 in B cell development. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 350–361.
- Miao, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Sun, W.; Tan, Y.; Cai, L.; Zheng, Y.; Su, G.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y. Zinc protects against diabetes-induced pathogenic changes in the aorta: Roles of metallothionein and nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2013, 12, 54.
- Wang, J.; Song, Y.; Elsherif, L.; Song, Z.; Zhou, G.; Prabhu, S.D.; Saari, J.T.; Cai, L. Cardiac metallothionein induction plays the major role in the prevention of diabetic cardiomyopathy by zinc supplementation. Circulation 2006, 113, 544–554.
- Fiorentino, T.V.; Prioletta, A.; Zuo, P.; Folli, F. Hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress and its role in diabetes mellitus related cardiovascular diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 5695–5703.
- Liu, Y.; Batchuluun, B.; Ho, L.; Zhu, D.; Prentice, K.J.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Zhang, M.; Pourasgari, F.; Hardy, A.B.; Taylor, K.M.; et al. Characterization of Zinc Influx Transporters (ZIPs) in Pancreatic β Cells: Roles in regulating cytosolic zinc homeostasis and insulin secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 18757–18769.
- Chabosseau, P.; Woodier, J.; Cheung, R.; Rutter, G.A. Sensors for measuring subcellular zinc pools. Metallomics 2018, 10, 229–239.
- Aydemir, T.B.; Cousins, R.J. The Multiple Faces of the Metal Transporter ZIP14 (SLC39A14). J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 174–184.
- Jarosz, M.; Olbert, M.; Wyszogrodzka, G.; Młyniec, K.; Librowski, T. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of zinc. Zinc-dependent NF-κB signaling. Inflammopharmacology 2017, 25, 11–24.
- Barman, S.; Pradeep, S.R.; Srinivasan, K. Zinc supplementation mitigates its dyshomeostasis in experimental diabetic rats by regulating the expression of zinc transporters and metallothionein. Metallomics 2017, 9, 1765–1777.
