One-carbon metabolism (OCM) is a network of biochemical reactions delivering one-carbon units to various biosynthetic pathways. The folate cycle and methionine cycle are the two key modules of this network that regulate purine and thymidine synthesis, amino acid homeostasis, and epigenetic mechanisms. Intersection with the transsulfuration pathway supports glutathione production and regulation of the cellular redox state. Dietary intake of micronutrients, such as folates and amino acids, directly contributes to OCM, thereby adapting the cellular metabolic state to environmental inputs. The contribution of OCM to cellular proliferation during development and in adult proliferative tissues is well established. Nevertheless, accumulating evidence reveals the pivotal role of OCM in cellular homeostasis of non-proliferative tissues and in coordination of signaling cascades that regulate energy homeostasis and longevity.
- aging
- Alzheimer’s disease
- diet
- folate
- metabolism
- methionine
- mitochondria
- neurodegeneration
- one-carbon vitamins
- Parkinson disease
1. Introduction
2. One-Carbon Metabolic Pathways
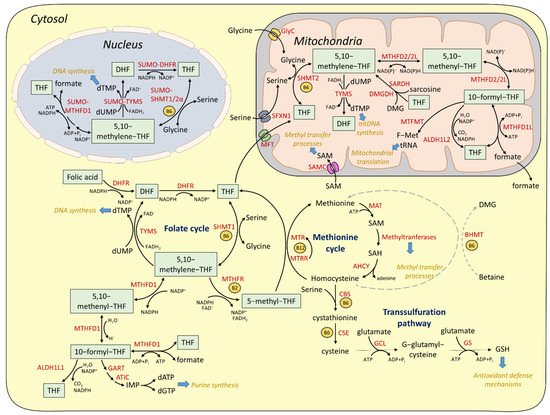
2.1. Cytosolic and Nuclear Pathways of One-Carbon Metabolism
2.2. Mitochondrial One-Carbon Metabolism
3. One-Carbon Metabolism in Aging
| Genetic Manipulation | Environmental Manipulation | Effect on Lifespan | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yeast | |||
| Methionine restriction | CLS extension | [54][55] | |
| met2 deletion | CLS extension | [56][57] | |
| met15 deletion | CLS extension | [56][57] | |
| met3 deletion | RLS extension | [58] | |
| sam1 deletion | RLS extension | [58] | |
| cys4 deletion | CLS extension | [59] | |
| H2S | CLS extension | [60] | |
| gsh1 deletion | 10% glucose | CLS shortening | [61] |
| Nematodes | |||
| sulfamethoxazole | Extension | [62] | |
| dhfr-1 RNAi | extension | [63] | |
| tyms-1 RNAi | extension | [63][64] | |
| daf-2(e1370) | MTHF5 supplementation | Reverses longevity of daf-2 mutants |
[63] |
| mel-32 RNAi | extension | [65] | |
| sams-1 RNAi | extension | [66][67] | |
| sams-5 RNAi | extension | [67] | |
| Glycine supplementation | extension | [65][68] | |
| Serine supplementation | extension | [65][68] | |
| Metformin | extension | [69] | |
| sams-1 mutant | Metformin | Reverse of metformin’s benefits | [69] |
| metr-1 mutant | Metformin | Reverse of metformin’s benefits | [69] |
| H2S | extension | [70][71] | |
| cbs-1 overexpression | extension | [60] | |
| NAC from day 3 | extension | [72] | |
| NAC from L4 | shortening | [73] | |
| taurine | extension | [68] | |
| Acivicin (GSH restriction) | extension | [73] | |
| Flies | |||
| GNMT overexpression | extension | [74] | |
| Methionine restriction | extension | [75][76] | |
| Sams depletion | extension | [74] | |
| Cbs overexpression | extension | [77] | |
| Cbs depletion | Caloric restriction | Reversed CR-driven longevity | [78] |
| Gclc overexpression | extension | [79] | |
| Gclm overexpression | extension | [79] | |
| dAhcyL1/dAhcyL2 suppression | Extension | [80] | |
| Mammals | |||
| Transgenic growth hormone mice | Supplementation of several forms of folate | Extension | [81] |
| wt | Supplementation of several forms of folate | Extension | [81] |
| Female SHR mice | metformin | Extension | [82] |
| Rats, mice | Dietary Methionine restriction | Extension | [83][84][85] |
| Tissue-specific taurine transporter depleted mice | Shortening | [86] | |
| Humans | |||
| C667T MTHFR | Associates with decrease in all-cause mortality | [87][88] | |
3.1. Folate Cycle in Aging
3.2. Methionine Cycle in Aging
3.3. Homocysteine in Aging
3.4. Transsulfuration Pathway in Aging
3.5. Glutathione in Aging
4. One-Carbon Metabolism and Neurodegeneration
4.1. One-Carbon Metabolism in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease
4.2. One-Carbon Metabolism in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/cells11020214
References
- Ducker, G.S.; Rabinowitz, J.D. One-carbon metabolism in health and disease. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 27–42.
- Cossins, E.A.; Chen, L. Folates and one-carbon metabolism in plants and fungi. Phytochemistry 1997, 45, 437–452.
- Bermingham, A.; Derrick, J.P. The folic acid biosynthesis pathway in bacteria: Evaluation of potential for antibacterial drug discovery. Bioessays 2002, 24, 637–648.
- Hanson, A.D.; Gregory, J.F., 3rd. Folate biosynthesis, turnover, and transport in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant. Biol. 2011, 62, 105–125.
- Garratt, L.C.; Ortori, C.A.; Tucker, G.A.; Sablitzky, F.; Bennett, M.J.; Barrett, D.A. Comprehensive metabolic profiling of mono- and polyglutamated folates and their precursors in plant and animal tissue using liquid chromatography/negative ion electrospray ionisation tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 2390–2398.
- Hou, Z.; Matherly, L.H. Biology of the major facilitative folate transporters slc19a1 and slc46a1. Curr. Top. Membr. 2014, 73, 175–204.
- Zhao, R.; Diop-Bove, N.; Visentin, M.; Goldman, I.D. Mechanisms of membrane transport of folates into cells and across epithelia. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2011, 31, 177–201.
- Qiu, A.; Jansen, M.; Sakaris, A.; Min, S.H.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Tsai, E.; Sandoval, C.; Zhao, R.; Akabas, M.H.; Goldman, I.D. Identification of an intestinal folate transporter and the molecular basis for hereditary folate malabsorption. Cell 2006, 127, 917–928.
- Matherly, L.H.; Hou, Z.; Gangjee, A. The promise and challenges of exploiting the proton-coupled folate transporter for selective therapeutic targeting of cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2018, 81, 1–15.
- Matherly, L.H.; Hou, Z. Structure and function of the reduced folate carrier a paradigm of a major facilitator superfamily mammalian nutrient transporter. Vitam. Horm. 2008, 79, 145–184.
- Alam, C.; Kondo, M.; O’Connor, D.L.; Bendayan, R. Clinical implications of folate transport in the central nervous system. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2020, 41, 349–361.
- Ormazabal, A.; Casado, M.; Molero-Luis, M.; Montoya, J.; Rahman, S.; Aylett, S.B.; Hargreaves, I.; Heales, S.; Artuch, R. Can folic acid have a role in mitochondrial disorders? Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 1349–1354.
- Serrano, M.; Pérez-Dueñas, B.; Montoya, J.; Ormazabal, A.; Artuch, R. Genetic causes of cerebral folate deficiency: Clinical, biochemical and therapeutic aspects. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 1299–1306.
- McCord, E.; Pawar, S.; Koneru, T.; Tatiparti, K.; Sau, S.; Iyer, A.K. Folate receptors’ expression in gliomas may possess potential nanoparticle-based drug delivery opportunities. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 4111–4118.
- Tian, Y.; Wu, G.; Xing, J.C.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.M.; Jia, Z.C.; Zhao, R.; Tian, Z.Q.; Wang, S.F.; et al. A novel splice variant of folate receptor 4 predominantly expressed in regulatory t cells. BMC Immunol. 2012, 13, 1471–2172.
- Tibbetts, A.S.; Appling, D.R. Compartmentalization of mammalian folate-mediated one-carbon metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2010, 30, 57–81.
- Anderson, D.D.; Quintero, C.M.; Stover, P.J. Identification of a de novo thymidylate biosynthesis pathway in mammalian mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15163–15168.
- Chon, J.; Stover, P.J.; Field, M.S. Targeting nuclear thymidylate biosynthesis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2017, 53, 48–56.
- Bottiglieri, T. S-adenosyl-l-methionine (same): From the bench to the bedside--molecular basis of a pleiotrophic molecule. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76.
- Sanderson, S.M.; Gao, X.; Dai, Z.; Locasale, J.W. Methionine metabolism in health and cancer: A nexus of diet and precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 625–637.
- Pajares, M.A.; Pérez-Sala, D. Betaine homocysteine s-methyltransferase: Just a regulator of homocysteine metabolism? Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 2792–2803.
- Sbodio, J.I.; Snyder, S.H.; Paul, B.D. Regulators of the transsulfuration pathway. Br. J. Pharm. 2019, 176, 583–593.
- Kutzbach, C.; Stokstad, E.L. Mammalian methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. Partial purification, properties, and inhibition by s-adenosylmethionine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1971, 250, 459–477.
- Finkelstein, J.D. Metabolic regulatory properties of s-adenosylmethionine and s-adenosylhomocysteine. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2007, 45, 1694–1699.
- MacFarlane, A.J.; Perry, C.A.; McEntee, M.F.; Lin, D.M.; Stover, P.J. Mthfd1 is a modifier of chemically induced intestinal carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2010, 32, 427–433.
- Pietzke, M.; Meiser, J.; Vazquez, A. Formate metabolism in health and disease. Mol. Metab. 2020, 33, 23–37.
- Ghannad-Zadeh, K.; Das, S. One-carbon metabolism associated vulnerabilities in glioblastoma: A review. Cancers 2021, 13, 3067.
- Krupenko, N.I.; Holmes, R.S.; Tsybovsky, Y.; Krupenko, S.A. Aldehyde dehydrogenase homologous folate enzymes: Evolutionary switch between cytoplasmic and mitochondrial localization. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 234, 12–17.
- Anderson, D.D.; Stover, P.J. Shmt1 and shmt2 are functionally redundant in nuclear de novo thymidylate biosynthesis. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5839.
- Anderson, D.D.; Woeller, C.F.; Chiang, E.-P.; Shane, B.; Stover, P.J. Serine hydroxymethyltransferase anchors de novo thymidylate synthesis pathway to nuclear lamina for DNA synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 7051–7062.
- Field, M.S.; Kamynina, E.; Agunloye, O.C.; Liebenthal, R.P.; Lamarre, S.G.; Brosnan, M.E.; Brosnan, J.T.; Stover, P.J. Nuclear enrichment of folate cofactors and methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 1 (mthfd1) protect de novo thymidylate biosynthesis during folate deficiency. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 29642–29650.
- Woeller, C.F.; Anderson, D.D.; Szebenyi, D.M.; Stover, P.J. Evidence for small ubiquitin-like modifier-dependent nuclear import of the thymidylate biosynthesis pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 17623–17631.
- Kamynina, E.; Lachenauer, E.R.; DiRisio, A.C.; Liebenthal, R.P.; Field, M.S.; Stover, P.J. Arsenic trioxide targets mthfd1 and sumo-dependent nuclear de novo thymidylate biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2319–E2326.
- Wang, F.K.; Koch, J.; Stokstad, E.L. Folate coenzyme pattern, folate linked enzymes and methionine biosynthesis in rat liver mitochondria. Biochem. Z. 1967, 346, 458–466.
- Titus, S.A.; Moran, R.G. Retrovirally mediated complementation of the glyb phenotype. Cloning of a human gene encoding the carrier for entry of folates into mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 36811–36817.
- Lin, B.F.; Huang, R.F.; Shane, B. Regulation of folate and one-carbon metabolism in mammalian cells. Iii. Role of mitochondrial folylpoly-gamma-glutamate synthetase. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 21674–21679.
- Kory, N.; Wyant, G.A.; Prakash, G.; Uit de Bos, J.; Bottanelli, F.; Pacold, M.E.; Chan, S.H.; Lewis, C.A.; Wang, T.; Keys, H.R.; et al. Sfxn1 is a mitochondrial serine transporter required for one-carbon metabolism. Science 2018, 362.
- Lunetti, P.; Damiano, F.; De Benedetto, G.; Siculella, L.; Pennetta, A.; Muto, L.; Paradies, E.; Marobbio, C.M.T.; Dolce, V.; Capobianco, L. Characterization of human and yeast mitochondrial glycine carriers with implications for heme biosynthesis and anemia*. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 19746–19759.
- Tan, Y.-L.; Sou, N.-L.; Tang, F.-Y.; Ko, H.-A.; Yeh, W.-T.; Peng, J.-H.; Chiang, E.-P.I. Tracing metabolic fate of mitochondrial glycine cleavage system derived formate in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8808.
- Porter, D.H.; Cook, R.J.; Wagner, C. Enzymatic properties of dimethylglycine dehydrogenase and sarcosine dehydrogenase from rat liver. Arch. BioChem. Biophys. 1985, 243, 396–407.
- Zhu, Z.; Leung, G.K.K. More than a metabolic enzyme: Mthfd2 as a novel target for anticancer therapy? Front. Oncol. 2020, 10.
- Ben-Sahra, I.; Hoxhaj, G.; Ricoult, S.J.H.; Asara, J.M.; Manning, B.D. Mtorc1 induces purine synthesis through control of the mitochondrial tetrahydrofolate cycle. Science 2016, 351, 728–733.
- Yang, L.; Garcia Canaveras, J.C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Liang, L.; Jang, C.; Mayr, J.A.; Zhang, Z.; Ghergurovich, J.M.; Zhan, L.; et al. Serine catabolism feeds nadh when respiration is impaired. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 809–821.e806.
- Maynard, A.G.; Kanarek, N. Nadh ties one-carbon metabolism to cellular respiration. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 660–662.
- Nicholls, P. Formate as an inhibitor of cytochrome c oxidase. BioChem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1975, 67, 610–616.
- Minton, D.R.; Nam, M.; McLaughlin, D.J.; Shin, J.; Bayraktar, E.C.; Alvarez, S.W.; Sviderskiy, V.O.; Papagiannakopoulos, T.; Sabatini, D.M.; Birsoy, K.; et al. Serine catabolism by shmt2 is required for proper mitochondrial translation initiation and maintenance of formylmethionyl-trnas. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 610–621.
- Esch, B.M.; Limar, S.; Bogdanowski, A.; Gournas, C.; More, T.; Sundag, C.; Walter, S.; Heinisch, J.J.; Ejsing, C.S.; André, B.; et al. Uptake of exogenous serine is important to maintain sphingolipid homeostasis in saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLOS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008745.
- Horne, D.W.; Holloway, R.S.; Wagner, C. Transport of s-adenosylmethionine in isolated rat liver mitochondria. Arch. BioChem. Biophys. 1997, 343, 201–206.
- Agrimi, G.; Di Noia, M.A.; Marobbio, C.M.; Fiermonte, G.; Lasorsa, F.M.; Palmieri, F. Identification of the human mitochondrial s-adenosylmethionine transporter: Bacterial expression, reconstitution, functional characterization and tissue distribution. BioChem. J. 2004, 379, 183–190.
- Schober, F.A.; Moore, D.; Atanassov, I.; Moedas, M.F.; Clemente, P.; Végvári, Á.; Fissi, N.E.; Filograna, R.; Bucher, A.L.; Hinze, Y.; et al. The one-carbon pool controls mitochondrial energy metabolism via complex i and iron-sulfur clusters. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7.
- Zheng, Y.; Lin, T.Y.; Lee, G.; Paddock, M.N.; Momb, J.; Cheng, Z.; Li, Q.; Fei, D.L.; Stein, B.D.; Ramsamooj, S.; et al. Mitochondrial one-carbon pathway supports cytosolic folate integrity in cancer cells. Cell 2018, 175, 1546–1560.
- De Vitto, H.; Arachchige, D.B.; Richardson, B.C.; French, J.B. The intersection of purine and mitochondrial metabolism in cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 2603.
- French, J.B.; Jones, S.A.; Deng, H.; Pedley, A.M.; Kim, D.; Chan, C.Y.; Hu, H.; Pugh, R.J.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Spatial colocalization and functional link of purinosomes with mitochondria. Science 2016, 351, 733–737.
- Plummer, J.D.; Johnson, J.E. Extension of cellular lifespan by methionine restriction involves alterations in central carbon metabolism and is mitophagy-dependent. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7.
- Fabrizio, P.; Longo, V.D. The chronological life span of saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Mol. Biol. 2007, 371, 89–95.
- Ruckenstuhl, C.; Netzberger, C.; Entfellner, I.; Carmona-Gutierrez, D.; Kickenweiz, T.; Stekovic, S.; Gleixner, C.; Schmid, C.; Klug, L.; Sorgo, A.G.; et al. Lifespan extension by methionine restriction requires autophagy-dependent vacuolar acidification. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10.
- Johnson, J.E.; Johnson, F.B. Methionine restriction activates the retrograde response and confers both stress tolerance and lifespan extension to yeast, mouse and human cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9.
- McCormick, M.A.; Delaney, J.R.; Tsuchiya, M.; Tsuchiyama, S.; Shemorry, A.; Sim, S.; Chou, A.C.; Ahmed, U.; Carr, D.; Murakami, C.J.; et al. A comprehensive analysis of replicative lifespan in 4,698 single-gene deletion strains uncovers conserved mechanisms of aging. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 895–906.
- Laschober, G.T.; Ruli, D.; Hofer, E.; Muck, C.; Carmona-Gutierrez, D.; Ring, J.; Hutter, E.; Ruckenstuhl, C.; Micutkova, L.; Brunauer, R.; et al. Identification of evolutionarily conserved genetic regulators of cellular aging. Aging Cell 2010, 9, 1084–1097.
- Hine, C.; Harputlugil, E.; Zhang, Y.; Ruckenstuhl, C.; Lee, B.C.; Brace, L.; Longchamp, A.; Treviño-Villarreal, J.H.; Mejia, P.; Ozaki, C.K.; et al. Endogenous hydrogen sulfide production is essential for dietary restriction benefits. Cell 2015, 160, 132–144.
- Tello-Padilla, M.F.; Perez-Gonzalez, A.Y.; Canizal-García, M.; González-Hernández, J.C.; Cortes-Rojo, C.; Olivares-Marin, I.K.; Madrigal-Perez, L.A. Glutathione levels influence chronological life span of saccharomyces cerevisiae in a glucose-dependent manner. Yeast 2018, 35, 387–396.
- Virk, B.; Correia, G.; Dixon, D.P.; Feyst, I.; Jia, J.; Oberleitner, N.; Briggs, Z.; Hodge, E.; Edwards, R.; Ward, J.; et al. Excessive folate synthesis limits lifespan in the c. Elegans: E. Coli aging model. BMC Biol. 2012, 10, 1741–7007.
- Annibal, A.; Tharyan, R.G.; Schonewolff, M.F.; Tam, H.; Latza, C.; Auler, M.M.K.; Grönke, S.; Partridge, L.; Antebi, A. Regulation of the one carbon folate cycle as a shared metabolic signature of longevity. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 021–23856.
- Anderson, E.N.; Corkins, M.E.; Li, J.C.; Singh, K.; Parsons, S.; Tucey, T.M.; Sorkaç, A.; Huang, H.; Dimitriadi, M.; Sinclair, D.A.; et al. C. Elegans lifespan extension by osmotic stress requires fudr, base excision repair, foxo, and sirtuins. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2016, 154, 30–42.
- Liu, Y.J.; Janssens, G.E.; McIntyre, R.L.; Molenaars, M.; Kamble, R.; Gao, A.W.; Jongejan, A.; Weeghel, M.V.; MacInnes, A.W.; Houtkooper, R.H. Glycine promotes longevity in caenorhabditis elegans in a methionine cycle-dependent fashion. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15.
- Hansen, M.; Hsu, A.L.; Dillin, A.; Kenyon, C. New genes tied to endocrine, metabolic, and dietary regulation of lifespan from a caenorhabditis elegans genomic rnai screen. PLoS Genet. 2005, 1, 119–128.
- Chen, C.C.; Lim, C.Y.; Lee, P.J.; Hsu, A.L.; Ching, T.T. S-adenosyl methionine synthetase sams-5 mediates dietary restriction-induced longevity in caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS ONE 2020, 15.
- Edwards, C.; Canfield, J.; Copes, N.; Brito, A.; Rehan, M.; Lipps, D.; Brunquell, J.; Westerheide, S.D.; Bradshaw, P.C. Mechanisms of amino acid-mediated lifespan extension in caenorhabditis elegans. BMC Genet. 2015, 16, 015–0167.
- Cabreiro, F.; Au, C.; Leung, K.Y.; Vergara-Irigaray, N.; Cochemé, H.M.; Noori, T.; Weinkove, D.; Schuster, E.; Greene, N.D.; Gems, D. Metformin retards aging in c. Elegans by altering microbial folate and methionine metabolism. Cell 2013, 153, 228–239.
- Miller, D.L.; Roth, M.B. Hydrogen sulfide increases thermotolerance and lifespan in caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20618–20622.
- Ng, L.T.; Ng, L.F.; Tang, R.M.Y.; Barardo, D.; Halliwell, B.; Moore, P.K.; Gruber, J. Lifespan and healthspan benefits of exogenous h2s in c. Elegans are independent from effects downstream of eat-2 mutation. NPJ Aging Mech. Dis. 2020, 6, 6.
- Oh, S.I.; Park, J.K.; Park, S.K. Lifespan extension and increased resistance to environmental stressors by n-acetyl-l-cysteine in caenorhabditis elegans. Clinics 2015, 70, 380–386.
- Gusarov, I.; Shamovsky, I.; Pani, B.; Gautier, L.; Eremina, S.; Katkova-Zhukotskaya, O.; Mironov, A.; Makarov, A.; Nudler, E. Dietary thiols accelerate aging of c. Elegans. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 021–24634.
- Obata, F.; Miura, M. Enhancing s-adenosyl-methionine catabolism extends drosophila lifespan. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8332.
- Troen, A.M.; French, E.E.; Roberts, J.F.; Selhub, J.; Ordovas, J.M.; Parnell, L.D.; Lai, C.Q. Lifespan modification by glucose and methionine in drosophila melanogaster fed a chemically defined diet. Age 2007, 29, 29–39.
- Lee, B.C.; Kaya, A.; Ma, S.; Kim, G.; Gerashchenko, M.V.; Yim, S.H.; Hu, Z.; Harshman, L.G.; Gladyshev, V.N. Methionine restriction extends lifespan of drosophila melanogaster under conditions of low amino-acid status. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3592.
- Kabil, H.; Kabil, O.; Banerjee, R.; Harshman, L.G.; Pletcher, S.D. Increased transsulfuration mediates longevity and dietary restriction in drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16831–16836.
- Shaposhnikov, M.; Proshkina, E.; Koval, L.; Zemskaya, N.; Zhavoronkov, A.; Moskalev, A. Overexpression of cbs and cse genes affects lifespan, stress resistance and locomotor activity in drosophila melanogaster. Aging 2018, 10, 3260–3272.
- Orr, W.C.; Radyuk, S.N.; Prabhudesai, L.; Toroser, D.; Benes, J.J.; Luchak, J.M.; Mockett, R.J.; Rebrin, I.; Hubbard, J.G.; Sohal, R.S. Overexpression of glutamate-cysteine ligase extends life span in drosophila melanogaster. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 37331–37338.
- Parkhitko, A.A.; Binari, R.; Zhang, N.; Asara, J.M.; Demontis, F.; Perrimon, N. Tissue-specific down-regulation of s-adenosyl-homocysteine via suppression of dahcyl1/dahcyl2 extends health span and life span in drosophila. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1409–1422.
- Lemon, J.A.; Boreham, D.R.; Rollo, C.D. A complex dietary supplement extends longevity of mice. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2005, 60, 275–279.
- Anisimov, V.N.; Berstein, L.M.; Popovich, I.G.; Zabezhinski, M.A.; Egormin, P.A.; Piskunova, T.S.; Semenchenko, A.V.; Tyndyk, M.L.; Yurova, M.N.; Kovalenko, I.G.; et al. If started early in life, metformin treatment increases life span and postpones tumors in female shr mice. Aging 2011, 3, 148–157.
- Miller, R.A.; Buehner, G.; Chang, Y.; Harper, J.M.; Sigler, R.; Smith-Wheelock, M. Methionine-deficient diet extends mouse lifespan, slows immune and lens aging, alters glucose, t4, igf-i and insulin levels, and increases hepatocyte mif levels and stress resistance. Aging Cell 2005, 4, 119–125.
- Orentreich, N.; Matias, J.R.; DeFelice, A.; Zimmerman, J.A. Low methionine ingestion by rats extends life span. J. Nutr. 1993, 123, 269–274.
- Richie, J.P., Jr.; Leutzinger, Y.; Parthasarathy, S.; Malloy, V.; Orentreich, N.; Zimmerman, J.A. Methionine restriction increases blood glutathione and longevity in f344 rats. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 1302–1307.
- Ito, T.; Yoshikawa, N.; Inui, T.; Miyazaki, N.; Schaffer, S.W.; Azuma, J. Tissue depletion of taurine accelerates skeletal muscle senescence and leads to early death in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107409.
- Husemoen, L.L.; Skaaby, T.; Jørgensen, T.; Thuesen, B.H.; Fenger, M.; Grarup, N.; Sandholt, C.H.; Hansen, T.; Pedersen, O.; Linneberg, A. Mthfr c677t genotype and cardiovascular risk in a general population without mandatory folic acid fortification. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 1549–1559.
- Yang, Q.; Bailey, L.; Clarke, R.; Flanders, W.D.; Liu, T.; Yesupriya, A.; Khoury, M.J.; Friedman, J.M. Prospective study of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (mthfr) variant c677t and risk of all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality among 6000 us adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 1245–1253.
- Varela-Moreiras, G.; Pérez-Olleros, L.; García-Cuevas, M.; Ruiz-Roso, B. Effects of ageing on folate metabolism in rats fed a long-term folate deficient diet. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 1994, 64, 294–299.
- Challet, E.; Dumont, S.; Mehdi, M.K.; Allemann, C.; Bousser, T.; Gourmelen, S.; Sage-Ciocca, D.; Hicks, D.; Pévet, P.; Claustrat, B. Aging-like circadian disturbances in folate-deficient mice. NeuroBiol. Aging 2013, 34, 1589–1598.
- Bahous, R.H.; Cosín-Tomás, M.; Deng, L.; Leclerc, D.; Malysheva, O.; Ho, M.K.; Pallàs, M.; Kaliman, P.; Bedell, B.J.; Caudill, M.A.; et al. Early manifestations of brain aging in mice due to low dietary folate and mild mthfr deficiency. Mol. NeuroBiol. 2019, 56, 4175–4191.
- Ukraintseva, S.; Yashin, A.; Arbeev, K.; Kulminski, A.; Akushevich, I.; Wu, D.; Joshi, G.; Land, K.C.; Stallard, E. Puzzling role of genetic risk factors in human longevity: "Risk alleles" as pro-longevity variants. Biogerontology 2016, 17, 109–127.
- Hall, H.; Cooper, B.R.; Qi, G.; Wijeratne, A.B.; Mosley, A.L.; Weake, V.M. Quantitative proteomic and metabolomic profiling reveals altered mitochondrial metabolism and folate biosynthesis pathways in the aging drosophila eye. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2021, 20, 100127.
- Virk, B.; Jia, J.; Maynard, C.A.; Raimundo, A.; Lefebvre, J.; Richards, S.A.; Chetina, N.; Liang, Y.; Helliwell, N.; Cipinska, M.; et al. Folate acts in e. coli to accelerate c. elegans aging independently of bacterial biosynthesis. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 1611–1620.
- Onken, B.; Driscoll, M. Metformin induces a dietary restriction-like state and the oxidative stress response to extend c. Elegans healthspan via ampk, lkb1, and skn-1. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, 0008758.
- Blount, B.C.; Mack, M.M.; Wehr, C.M.; MacGregor, J.T.; Hiatt, R.A.; Wang, G.; Wickramasinghe, S.N.; Everson, R.B.; Ames, B.N. Folate deficiency causes uracil misincorporation into human DNA and chromosome breakage: Implications for cancer and neuronal damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3290–3295.
- Chow, H.M.; Herrup, K. Genomic integrity and the ageing brain. Nat. Rev. NeuroSci. 2015, 16, 672–684.
- Steinberg, S.E.; Fonda, S.; Campbell, C.L.; Hillman, R.S. Cellular abnormalities of folate deficiency. Br. J. Haematol. 1983, 54, 605–612.
- Kesavan, V.; Pote, M.S.; Batra, V.; Viswanathan, G. Increased folate catabolism following total body gamma-irradiation in mice. J. Radiat. Res. 2003, 44, 141–144.
- Batra, V.; Kesavan, V.; Mishra, K.P. Modulation of enzymes involved in folate dependent one-carbon metabolism by gamma-radiation stress in mice. J. Radiat. Res. 2004, 45, 527–533.
- Choi, S.W.; Kim, Y.I.; Weitzel, J.N.; Mason, J.B. Folate depletion impairs DNA excision repair in the colon of the rat. Gut 1998, 43, 93–99.
- Simon, K.W.; Ma, H.; Dombkowski, A.A.; Cabelof, D.C. Aging alters folate homeostasis and DNA damage response in colon. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2012, 133, 75–82.
- Dorling, J.L.; Martin, C.K.; Redman, L.M. Calorie restriction for enhanced longevity: The role of novel dietary strategies in the present obesogenic environment. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 64, 25.
- Lee, B.C.; Kaya, A.; Gladyshev, V.N. Methionine restriction and life-span control. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2016, 10.
- Parkhitko, A.A.; Jouandin, P.; Mohr, S.E.; Perrimon, N. Methionine metabolism and methyltransferases in the regulation of aging and lifespan extension across species. Aging Cell 2019, 18, 28.
- Mota-Martorell, N.; Jové, M.; Berdún, R.; Pamplona, R. Plasma methionine metabolic profile is associated with longevity in mammals. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 725.
- Sanz, A.; Caro, P.; Ayala, V.; Portero-Otin, M.; Pamplona, R.; Barja, G. Methionine restriction decreases mitochondrial oxygen radical generation and leak as well as oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA and proteins. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 1064–1073.
- Lees, E.K.; Król, E.; Grant, L.; Shearer, K.; Wyse, C.; Moncur, E.; Bykowska, A.S.; Mody, N.; Gettys, T.W.; Delibegovic, M. Methionine restriction restores a younger metabolic phenotype in adult mice with alterations in fibroblast growth factor 21. Aging Cell 2014, 13, 817–827.
- Stone, K.P.; Wanders, D.; Orgeron, M.; Cortez, C.C.; Gettys, T.W. Mechanisms of increased in vivo insulin sensitivity by dietary methionine restriction in mice. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3721–3733.
- Wanders, D.; Forney, L.A.; Stone, K.P.; Burk, D.H.; Pierse, A.; Gettys, T.W. Fgf21 mediates the thermogenic and insulin-sensitizing effects of dietary methionine restriction but not its effects on hepatic lipid metabolism. Diabetes 2017, 66, 858–867.
- Wanders, D.; Stone, K.P.; Forney, L.A.; Cortez, C.C.; Dille, K.N.; Simon, J.; Xu, M.; Hotard, E.C.; Nikonorova, I.A.; Pettit, A.P.; et al. Role of gcn2-independent signaling through a noncanonical perk/nrf2 pathway in the physiological responses to dietary methionine restriction. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1499–1510.
- Gu, X.; Orozco, J.M.; Saxton, R.A.; Condon, K.J.; Liu, G.Y.; Krawczyk, P.A.; Scaria, S.M.; Harper, J.W.; Gygi, S.P.; Sabatini, D.M. Samtor is an s-adenosylmethionine sensor for the mtorc1 pathway. Science 2017, 358, 813–818.
- Stone, K.P.; Ghosh, S.; Kovalik, J.P.; Orgeron, M.; Wanders, D.; Sims, L.C.; Gettys, T.W. The acute transcriptional responses to dietary methionine restriction are triggered by inhibition of ternary complex formation and linked to erk1/2, mtor, and atf4. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 021–83380.
- Aissa, A.F.; Gomes, T.D.; Almeida, M.R.; Hernandes, L.C.; Darin, J.D.; Bianchi, M.L.; Antunes, L.M. Methionine concentration in the diet has a tissue-specific effect on chromosomal stability in female mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 456–462.
- Bárcena, C.; López-Otín, C.; Kroemer, G. Methionine restriction for improving progeria: Another autophagy-inducing anti-aging strategy? Autophagy 2019, 15, 558–559.
- Zou, K.; Rouskin, S.; Dervishi, K.; McCormick, M.A.; Sasikumar, A.; Deng, C.; Chen, Z.; Kaeberlein, M.; Brem, R.B.; Polymenis, M.; et al. Life span extension by glucose restriction is abrogated by methionine supplementation: Cross-talk between glucose and methionine and implication of methionine as a key regulator of life span. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6.
- Tain, L.S.; Jain, C.; Nespital, T.; Froehlich, J.; Hinze, Y.; Grönke, S.; Partridge, L. Longevity in response to lowered insulin signaling requires glycine n-methyltransferase-dependent spermidine production. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13043.
- Brown-Borg, H.M.; Rakoczy, S.; Wonderlich, J.A.; Borg, K.E.; Rojanathammanee, L. Metabolic adaptation of short-living growth hormone transgenic mice to methionine restriction and supplementation. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2018, 1418, 118–136.
- Jang, H.S.; Shin, W.J.; Lee, J.E.; Do, J.T. Cpg and non-cpg methylation in epigenetic gene regulation and brain function. Genes 2017, 8, 148.
- Greenberg, M.V.C.; Bourc’his, D. The diverse roles of DNA methylation in mammalian development and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 590–607.
- Bollati, V.; Schwartz, J.; Wright, R.; Litonjua, A.; Tarantini, L.; Suh, H.; Sparrow, D.; Vokonas, P.; Baccarelli, A. Decline in genomic DNA methylation through aging in a cohort of elderly subjects. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2009, 130, 234–239.
- Horvath, S.; Zhang, Y.; Langfelder, P.; Kahn, R.S.; Boks, M.P.M.; van Eijk, K.; van den Berg, L.H.; Ophoff, R.A. Aging effects on DNA methylation modules in human brain and blood tissue. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R97.
- Horvath, S.; Gurven, M.; Levine, M.E.; Trumble, B.C.; Kaplan, H.; Allayee, H.; Ritz, B.R.; Chen, B.; Lu, A.T.; Rickabaugh, T.M.; et al. An epigenetic clock analysis of race/ethnicity, sex, and coronary heart disease. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 171.
- Singhal, R.P.; Mays-Hoopes, L.L.; Eichhorn, G.L. DNA methylation in aging of mice. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1987, 41, 199–210.
- Vanyushin, B.F.; Nemirovsky, L.E.; Klimenko, V.V.; Vasiliev, V.K.; Belozersky, A.N. The 5-methylcytosine in DNA of rats. Tissue and age specificity and the changes induced by hydrocortisone and other agents. Gerontologia 1973, 19, 138–152.
- Cole, J.J.; Robertson, N.A.; Rather, M.I.; Thomson, J.P.; McBryan, T.; Sproul, D.; Wang, T.; Brock, C.; Clark, W.; Ideker, T.; et al. Diverse interventions that extend mouse lifespan suppress shared age-associated epigenetic changes at critical gene regulatory regions. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 58.
- Wilkinson, G.S.; Adams, D.M.; Haghani, A.; Lu, A.T.; Zoller, J.; Breeze, C.E.; Arnold, B.D.; Ball, H.C.; Carter, G.G.; Cooper, L.N.; et al. DNA methylation predicts age and provides insight into exceptional longevity of bats. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1615.
- Lozoya, O.A.; Martinez-Reyes, I.; Wang, T.; Grenet, D.; Bushel, P.; Li, J.; Chandel, N.; Woychik, R.P.; Santos, J.H. Mitochondrial nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced (nadh) oxidation links the tricarboxylic acid (tca) cycle with methionine metabolism and nuclear DNA methylation. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16.
- Han, S.; Brunet, A. Histone methylation makes its mark on longevity. Trends Cell Biol. 2012, 22, 42–49.
- Kumar, A.; Palfrey, H.A.; Pathak, R.; Kadowitz, P.J.; Gettys, T.W.; Murthy, S.N. The metabolism and significance of homocysteine in nutrition and health. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 14, 017–0233.
- Ostrakhovitch, E.A.; Tabibzadeh, S. Homocysteine and age-associated disorders. Ageing Res. Rev. 2019, 49, 144–164.
- Perna, A.F.; Ingrosso, D. Homocysteine and Chronic Kidney Disease: An Ongoing Narrative. J Nephrol. 2019, 32, 673–675.
- van Ede, A.E.; Laan, R.F.; Blom, H.J.; Boers, G.H.; Haagsma, C.J.; Thomas, C.M.; De Boo, T.M.; van de Putte, L.B. Homocysteine and folate status in methotrexate-treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2002, 41, 658–665.
- Schwaninger, M.; Ringleb, P.; Winter, R.; Kohl, B.; Fiehn, W.; Rieser, P.A.; Walter-Sack, I. Elevated plasma concentrations of homocysteine in antiepileptic drug treatment. Epilepsia 1999, 40, 345–350.
- Konstantinova, S.V.; Tell, G.S.; Vollset, S.E.; Nygård, O.; Bleie, Ø.; Ueland, P.M. Divergent associations of plasma choline and betaine with components of metabolic syndrome in middle age and elderly men and women. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 914–920.
- Huang, B.X.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Tan, X.Y.; Lan, Q.Y.; Li, C.L.; Chen, Y.M.; Zhu, H.L. Serum betaine is inversely associated with low lean mass mainly in men in a chinese middle-aged and elderly community-dwelling population. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 2181–2188.
- Lee, H.J.; Noormohammadi, A.; Koyuncu, S.; Calculli, G.; Simic, M.S.; Herholz, M.; Trifunovic, A.; Vilchez, D. Prostaglandin signals from adult germ stem cells delay somatic aging of caenorhabditis elegans. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 790–810.
- Mota-Martorell, N.; Jové, M.; Borrás, C.; Berdún, R.; Obis, È.; Sol, J.; Cabré, R.; Pradas, I.; Galo-Licona, J.D.; Puig, J.; et al. Methionine transsulfuration pathway is upregulated in long-lived humans. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 162, 38–52.
- Sokolov, A.S.; Nekrasov, P.V.; Shaposhnikov, M.V.; Moskalev, A.A. Hydrogen sulfide in longevity and pathologies: Inconsistency is malodorous. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 67, 28.
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, Z.H.; Ren, Z.; Qu, S.L.; Liu, M.H.; Liu, L.S.; Jiang, Z.S. Hydrogen sulfide, the next potent preventive and therapeutic agent in aging and age-associated diseases. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 33, 1104–1113.
- Dziegelewska, M.; Holtze, S.; Vole, C.; Wachter, U.; Menzel, U.; Morhart, M.; Groth, M.; Szafranski, K.; Sahm, A.; Sponholz, C.; et al. Low sulfide levels and a high degree of cystathionine β-synthase (cbs) activation by s-adenosylmethionine (sam) in the long-lived naked mole-rat. Redox Biol. 2016, 8, 192–198.
- Wei, Y.; Kenyon, C. Roles for ros and hydrogen sulfide in the longevity response to germline loss in caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E2832–E2841.
- Bithi, N.; Link, C.; Henderson, Y.O.; Kim, S.; Yang, J.; Li, L.; Wang, R.; Willard, B.; Hine, C. Dietary restriction transforms the mammalian protein persulfidome in a tissue-specific and cystathionine γ-lyase-dependent manner. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–20.
- Pow, D.V.; Sullivan, R.; Reye, P.; Hermanussen, S. Localization of taurine transporters, taurine, and (3)h taurine accumulation in the rat retina, pituitary, and brain. Glia 2002, 37, 153–168.
- Ames, B.N. Prolonging healthy aging: Longevity vitamins and proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 10836–10844.
- Du, G.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhuo, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, H. Taurine represses age-associated gut hyperplasia in drosophila via counteracting endoplasmic reticulum stress. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13319.
- Liu, Y.; Hyde, A.S.; Simpson, M.A.; Barycki, J.J. Emerging regulatory paradigms in glutathione metabolism. Adv. Cancer Res. 2014, 122, 69–101.
- Go, Y.M.; Jones, D.P. Redox theory of aging: Implications for health and disease. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1669–1688.
- Schulz, T.J.; Zarse, K.; Voigt, A.; Urban, N.; Birringer, M.; Ristow, M. Glucose restriction extends caenorhabditis elegans life span by inducing mitochondrial respiration and increasing oxidative stress. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 280–293.
- Elshorbagy, A.K.; Jernerén, F.; Scudamore, C.L.; McMurray, F.; Cater, H.; Hough, T.; Cox, R.; Refsum, H. Exploring the lean phenotype of glutathione-depleted mice: Thiol, amino acid and fatty acid profiles. PLoS ONE 2016, 11.
- Kumar, P.; Liu, C.; Hsu, J.W.; Chacko, S.; Minard, C.; Jahoor, F.; Sekhar, R.V. Glycine and n-acetylcysteine (glynac) supplementation in older adults improves glutathione deficiency, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, insulin resistance, endothelial dysfunction, genotoxicity, muscle strength, and cognition: Results of a pilot clinical trial. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, 372.
- El-Hafidi, M.; Franco, M.; Ramírez, A.R.; Sosa, J.S.; Flores, J.A.P.; Acosta, O.L.; Salgado, M.C.; Cardoso-Saldaña, G. Glycine increases insulin sensitivity and glutathione biosynthesis and protects against oxidative stress in a model of sucrose-induced insulin resistance. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 21.
- Sekhar, R.V.; McKay, S.V.; Patel, S.G.; Guthikonda, A.P.; Reddy, V.T.; Balasubramanyam, A.; Jahoor, F. Glutathione synthesis is diminished in patients with uncontrolled diabetes and restored by dietary supplementation with cysteine and glycine. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 162–167.
- Dekhne, A.S.; Hou, Z.; Gangjee, A.; Matherly, L.H. Therapeutic targeting of mitochondrial one-carbon metabolism in cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 2245–2255.
- Korsmo, H.W.; Jiang, X. One carbon metabolism and early development: A diet-dependent destiny. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 32, 579–593.
- Reina-Campos, M.; Diaz-Meco, M.T.; Moscat, J. The complexity of the serine glycine one-carbon pathway in cancer. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 219.
- Yang, M.; Vousden, K.H. Serine and one-carbon metabolism in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 650–662.
- Imbard, A.; Benoist, J.-F.; Blom, H.J. Neural tube defects, folic acid and methylation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 4352–4389.
- Naninck, E.F.G.; Stijger, P.C.; Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M. The importance of maternal folate status for brain development and function of offspring. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 502–519.
- Troen, A.M. Folate and vitamin b12: Function and importance in cognitive development. Nestle Nutr. Inst. Workshop Ser. 2012, 70, 161–171.
- Kronenberg, G.; Colla, M.; Endres, M. Folic acid, neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disease. Curr. Mol. Med. 2009, 9, 315–323.
- Coppedè, F. One-carbon epigenetics and redox biology of neurodegeneration. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 170, 19–33.
- Knopman, D.S.; Amieva, H.; Petersen, R.C.; Chételat, G.; Holtzman, D.M.; Hyman, B.T.; Nixon, R.A.; Jones, D.T. Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 33.
- Otaegui-Arrazola, A.; Amiano, P.; Elbusto, A.; Urdaneta, E.; Martínez-Lage, P. Diet, cognition, and alzheimer’s disease: Food for thought. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 1–23.
- Corrada, M.M.; Kawas, C.H.; Hallfrisch, J.; Muller, D.; Brookmeyer, R. Reduced risk of alzheimer’s disease with high folate intake: The baltimore longitudinal study of aging. Alzheimers Dement. 2005, 1, 11–18.
- Luchsinger, J.A.; Tang, M.-X.; Miller, J.; Green, R.; Mayeux, R. Relation of higher folate intake to lower risk of alzheimer disease in the elderly. Arch. Neurol. 2007, 64, 86–92.
- Ma, F.; Wu, T.; Zhao, J.; Song, A.; Liu, H.; Xu, W.; Huang, G. Folic acid supplementation improves cognitive function by reducing the levels of peripheral inflammatory cytokines in elderly chinese subjects with mci. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37486.
- Sofi, F.; Cesari, F.; Abbate, R.; Gensini, G.F.; Casini, A. Adherence to mediterranean diet and health status: Meta-analysis. BMJ 2008, 337, a1344.
- Ravaglia, G.; Forti, P.; Maioli, F.; Martelli, M.; Servadei, L.; Brunetti, N.; Porcellini, E.; Licastro, F. Homocysteine and folate as risk factors for dementia and alzheimer disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 636–643.
- Robinson, N.; Grabowski, P.; Rehman, I. Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis: Is there a role for folate? Mech. Ageing Dev. 2018, 174, 86–94.
- Smith, A.D.; Refsum, H.; Bottiglieri, T.; Fenech, M.; Hooshmand, B.; McCaddon, A.; Miller, J.W.; Rosenberg, I.H.; Obeid, R. Homocysteine and dementia: An international consensus statement. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 62, 561–570.
- Kennedy, B.P.; Bottiglieri, T.; Arning, E.; Ziegler, M.G.; Hansen, L.A.; Masliah, E. Elevated s-adenosylhomocysteine in alzheimer brain: Influence on methyltransferases and cognitive function. J. Neural. Transm. 2004, 111, 547–567.
- Fuso, A.; Seminara, L.; Cavallaro, R.A.; D’Anselmi, F.; Scarpa, S. S-adenosylmethionine/homocysteine cycle alterations modify DNA methylation status with consequent deregulation of ps1 and bace and beta-amyloid production. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2005, 28, 195–204.
- O’Brien, R.J.; Wong, P.C. Amyloid precursor protein processing and alzheimer’s disease. Annu. Rev. NeuroSci. 2011, 34, 185–204.
- Fuso, A.; Nicolia, V.; Cavallaro, R.A.; Ricceri, L.; D’Anselmi, F.; Coluccia, P.; Calamandrei, G.; Scarpa, S. B-vitamin deprivation induces hyperhomocysteinemia and brain s-adenosylhomocysteine, depletes brain s-adenosylmethionine, and enhances ps1 and bace expression and amyloid-β deposition in mice. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2008, 37, 731–746.
- Do Carmo, S.; Hanzel, C.E.; Jacobs, M.L.; Machnes, Z.; Iulita, M.F.; Yang, J.; Yu, L.; Ducatenzeiler, A.; Danik, M.; Breuillaud, L.S.; et al. Rescue of early bace-1 and global DNA demethylation by s-adenosylmethionine reduces amyloid pathology and improves cognition in an alzheimer’s model. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6.
- Wang, S.C.; Oelze, B.; Schumacher, A. Age-specific epigenetic drift in late-onset alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, 0002698.
- Iwata, A.; Nagata, K.; Hatsuta, H.; Takuma, H.; Bundo, M.; Iwamoto, K.; Tamaoka, A.; Murayama, S.; Saido, T.; Tsuji, S. Altered cpg methylation in spoRadic. alzheimer’s disease is associated with app and mapt dysregulation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 23, 648–656.
- Fuso, A.; Nicolia, V.; Pasqualato, A.; Fiorenza, M.T.; Cavallaro, R.A.; Scarpa, S. Changes in presenilin 1 gene methylation pattern in diet-induced b vitamin deficiency. NeuroBiol. Aging 2011, 32, 187–199.
- Fuso, A.; Nicolia, V.; Ricceri, L.; Cavallaro, R.A.; Isopi, E.; Mangia, F.; Fiorenza, M.T.; Scarpa, S. S-adenosylmethionine reduces the progress of the alzheimer-like features induced by b-vitamin deficiency in mice. NeuroBiol. Aging 2012, 33, 4.
- Monti, N.; Cavallaro, R.A.; Stoccoro, A.; Nicolia, V.; Scarpa, S.; Kovacs, G.G.; Fiorenza, M.T.; Lucarelli, M.; Aronica, E.; Ferrer, I.; et al. Cpg and non-cpg presenilin1 methylation pattern in course of neurodevelopment and neurodegeneration is associated with gene expression in human and murine brain. Epigenetics 2020, 15, 781–799.
- Tian, T.; Bai, D.; Li, W.; Huang, G.-W.; Liu, H. Effects of folic acid on secretases involved in aβ deposition in app/ps1 mice. Nutrients 2016, 8, 556.
- Fuso, A.; Nicolia, V.; Cavallaro, R.A.; Scarpa, S. DNA methylase and demethylase activities are modulated by one-carbon metabolism in alzheimer’s disease models. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2011, 22, 242–251.
- Li, W.; Liu, H.; Yu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Wilson, J.X.; Huang, G. Folic acid administration inhibits amyloid β-peptide accumulation in app/ps1 transgenic mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 883–891.
- Barrachina, M.; Ferrer, I. DNA methylation of alzheimer disease and tauopathy-related genes in postmortem brain. J. NeuroPathol. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 68, 880–891.
- Stoccoro, A.; Tannorella, P.; Migliore, L.; Coppedè, F. Polymorphisms of genes required for methionine synthesis and DNA methylation influence mitochondrial DNA methylation. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 1003–1012.
- Blanch, M.; Mosquera, J.L.; Ansoleaga, B.; Ferrer, I.; Barrachina, M. Altered mitochondrial DNA methylation pattern in alzheimer disease-related pathology and in parkinson disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 385–397.
- Janssens, V.; Longin, S.; Goris, J. Pp2a holoenzyme assembly: In cauda venenum (the sting is in the tail). Trends BioChem. Sci. 2008, 33, 113–121.
- Sontag, E.; Hladik, C.; Montgomery, L.; Luangpirom, A.; Mudrak, I.; Ogris, E.; White, C.L., 3rd. Downregulation of protein phosphatase 2a carboxyl methylation and methyltransferase may contribute to alzheimer disease pathogenesis. J. NeuroPathol. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 63, 1080–1091.
- Zhou, X.W.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Tanila, H.; Bjorkdahl, C.; Liu, R.; Winblad, B.; Pei, J.J. Tau hyperphosphorylation correlates with reduced methylation of protein phosphatase 2a. NeuroBiol. Dis. 2008, 31, 386–394.
- Sontag, J.M.; Nunbhakdi-Craig, V.; Montgomery, L.; Arning, E.; Bottiglieri, T.; Sontag, E. Folate deficiency induces in vitro and mouse brain region-specific downregulation of leucine carboxyl methyltransferase-1 and protein phosphatase 2a b(alpha) subunit expression that correlate with enhanced tau phosphorylation. J. NeuroSci. 2008, 28, 11477–11487.
- Zheng, M.; Zou, C.; Li, M.; Huang, G.; Gao, Y.; Liu, H. Folic acid reduces tau phosphorylation by regulating pp2a methylation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 861.
- Park, H.J.; Lee, K.W.; Oh, S.; Yan, R.; Zhang, J.; Beach, T.G.; Adler, C.H.; Voronkov, M.; Braithwaite, S.P.; Stock, J.B.; et al. Protein phosphatase 2a and its methylation modulating enzymes lcmt-1 and pme-1 are dysregulated in tauopathies of progressive supranuclear palsy and alzheimer disease. J. NeuroPathol. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 77, 139–148.
- Nasa, I.; Kettenbach, A.N. Effects of carboxyl-terminal methylation on holoenzyme function of the pp2a subfamily. BioChem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 2015–2027.
- Li, W.; Jiang, M.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cui, S.; Huang, G. Folic acid inhibits tau phosphorylation through regulation of pp2a methylation in sh-sy5y cells. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2015, 19, 123–129.
- Sontag, E.; Nunbhakdi-Craig, V.; Sontag, J.M.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Ogris, E.; Dayal, S.; Lentz, S.R.; Arning, E.; Bottiglieri, T. Protein phosphatase 2a methyltransferase links homocysteine metabolism with tau and amyloid precursor protein regulation. J. NeuroSci. 2007, 27, 2751–2759.
- Taleski, G.; Schuhmacher, D.; Su, H.; Sontag, J.-M.; Sontag, E. Disturbances in pp2a methylation and one-carbon metabolism compromise fyn distribution, neuritogenesis, and app regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296.
- Sontag, J.-M.; Wasek, B.; Taleski, G.; Smith, J.; Arning, E.; Sontag, E.; Bottiglieri, T. Altered protein phosphatase 2a methylation and tau phosphorylation in the young and aged brain of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (mthfr) deficient mice. Front. Aging NeuroSci. 2014, 6, 214.
- Zhang, C.E.; Tian, Q.; Wei, W.; Peng, J.H.; Liu, G.P.; Zhou, X.W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, D.W.; Wang, J.Z. Homocysteine induces tau phosphorylation by inactivating protein phosphatase 2a in rat hippocampus. NeuroBiol. Aging 2008, 29, 1654–1665.
- Ho, P.I.; Collins, S.C.; Dhitavat, S.; Ortiz, D.; Ashline, D.; Rogers, E.; Shea, T.B. Homocysteine potentiates beta-amyloid neurotoxicity: Role of oxidative stress. J. NeuroChem. 2001, 78, 249–253.
- McCaddon, A.; Hudson, P.; Hill, D.; Barber, J.; Lloyd, A.; Davies, G.; Regland, B.j. Alzheimer’s disease and total plasma aminothiols. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 53, 254–260.
- Zafrilla, P.; Mulero, J.; Xandri, M.J.; Santo, E.; Caravaca, G.; Morillas, M.J. Oxidative stress in alzheimer patients in different stages of the disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 1075–1083.
- Resende, R.; Moreira, P.I.; Proença, T.; Deshpande, A.; Busciglio, J.; Pereira, C.; Oliveira, C.R. Brain oxidative stress in a triple-transgenic mouse model of alzheimer disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 2051–2057.
- Cankurtaran, M.; Yesil, Y.; Kuyumcu, M.E.; Oztürk, Z.A.; Yavuz, B.B.; Halil, M.; Ulger, Z.; Cankurtaran, E.S.; Arıoğul, S. Altered levels of homocysteine and serum natural antioxidants links oxidative damage to alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2013, 33, 1051–1058.
- Ghodake, S.R.; Suryakar, A.N.; Kulhalli, P.M.; Shaikh, A.K. The study of homocysteine and its relationship with oxidative stress biomarkers in alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Med. Sci. Clin. Invent. 2016.
- Hama, Y.; Hamano, T.; Shirafuji, N.; Hayashi, K.; Ueno, A.; Enomoto, S.; Nagata, M.; Kimura, H.; Matsunaga, A.; Ikawa, M.; et al. Influences of folate supplementation on homocysteine and cognition in patients with folate deficiency and cognitive impairment. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3138.
- Román, G.C. Mthfr gene mutations: A potential marker of late-onset alzheimer’s disease? J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 47, 323–327.
- Beyer, K.; Lao, J.I.; Carrato, C.; Rodriguez-Vila, A.; Latorre, P.; Mataró, M.; Llopis, M.A.; Mate, J.L.; Ariza, A. Cystathionine beta synthase as a risk factor for alzheimer disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2004, 1, 127–133.
- The role of cystathionine β-synthase in homocysteine metabolism. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2005, 7, 813–822.
- Paul, B.D. Neuroprotective roles of the reverse transsulfuration pathway in alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging NeuroSci. 2021, 13.
- Tjiattas, L.; Ortiz, D.O.; Dhivant, S.; Mitton, K.; Rogers, E.; Shea, T.B. Folate deficiency and homocysteine induce toxicity in cultured dorsal root ganglion neurons via cytosolic calcium accumulation. Aging Cell 2004, 3, 71–76.
- Poddar, R.; Paul, S. Homocysteine-nmda receptor-mediated activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase leads to neuronal cell death. J. NeuroChem. 2009, 110, 1095–1106.
- Danysz, W.; Parsons, C.G. Alzheimer’s disease, β-amyloid, glutamate, nmda receptors and memantine–Searching for the connections. Br. J. Pharm. 2012, 167, 324–352.
- Övey, İ.S.; Naziroğlu, M. Homocysteine and cytosolic gsh depletion induce apoptosis and oxidative toxicity through cytosolic calcium overload in the hippocampus of aged mice: Involvement of trpm2 and trpv1 channels. Neuroscience 2015, 284, 225–233.
- Kruman, I.I.; Culmsee, C.; Chan, S.L.; Kruman, Y.; Guo, Z.; Penix, L.; Mattson, M.P. Homocysteine elicits a DNA damage response in neurons that promotes apoptosis and hypersensitivity to excitotoxicity. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 6920–6926.
- Vanzin, C.S.; Manfredini, V.; Marinho, A.E.; Biancini, G.B.; Ribas, G.S.; Deon, M.; Wyse, A.T.; Wajner, M.; Vargas, C.R. Homocysteine contribution to DNA damage in cystathionine β-synthase-deficient patients. Gene 2014, 539, 270–274.
- Andra, A.; Tanigawa, S.; Bito, T.; Ishihara, A.; Watanabe, F.; Yabuta, Y. Effects of vitamin b(12) deficiency on amyloid-β toxicity in caenorhabditis elegans. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 962.
- Lam, A.B.; Kervin, K.; Tanis, J.E. Vitamin b12 impacts amyloid beta-induced proteotoxicity by regulating the methionine/s-adenosylmethionine cycle. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109753.
- Leiteritz, A.; Dilberger, B.; Wenzel, U.; Fitzenberger, E. Betaine reduces β-amyloid-induced paralysis through activation of cystathionine-β-synthase in an alzheimer model of caenorhabditis elegans. Genes Nutr. 2018, 13, 018–0611.
- Bermejo, P.; Martín-Aragón, S.; Benedí, J.; Susín, C.; Felici, E.; Gil, P.; Ribera, J.M.; Villar, A.M. Peripheral levels of glutathione and protein oxidation as markers in the development of alzheimer’s disease from mild cognitive impairment. Free Radic. Res. 2008, 42, 162–170.
- Mandal, P.K.; Saharan, S.; Tripathi, M.; Murari, G. Brain glutathione levels--a novel biomarker for mild cognitive impairment and alzheimer’s disease. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 78, 702–710.
- Ansari, M.A.; Scheff, S.W. Oxidative stress in the progression of alzheimer disease in the frontal cortex. J. NeuroPathol. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 69, 155–167.
- Saharan, S.; Mandal, P.K. The emerging role of glutathione in alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 40, 519–529.
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schrag, A.-E.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17013.
- Day, J.O.; Mullin, S. The genetics of parkinson’s disease and implications for clinical practice. Genes 2021, 12, 1006.
- Murray, L.K.; Jadavji, N.M. The role of one-carbon metabolism and homocysteine in parkinson’s disease onset, pathology and mechanisms. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2019, 32, 218–230.
- Fan, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Chen, G.; Qi, G.; Ma, X.; Jin, Y. Role of homocysteine in the development and progression of parkinson’s disease. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 2332–2338.
- Paul, R.; Borah, A. L-dopa-induced hyperhomocysteinemia in parkinson’s disease: Elephant in the room. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2016, 1860, 1989–1997.
- van der Steen, W.; den Heijer, T.; Groen, J. Vitamin b6 deficiency caused by the use of levodopa. Ned. Tijdschr. Geneeskd. 2018, 23, 162.
- Rojo-Sebastián, A.; González-Robles, C.; García de Yébenes, J. Vitamin b6 deficiency in patients with parkinson disease treated with levodopa/carbidopa. Clin. Neuropharmacol 2020, 43, 151–157.
- Miller, J.W.; Selhub, J.; Nadeau, M.R.; Thomas, C.A.; Feldman, R.G.; Wolf, P.A. Effect of l-dopa on plasma homocysteine in pd patients: Relationship to b-vitamin status. Neurology 2003, 60, 1125–1129.
- dos Santos, E.F.; Busanello, E.N.; Miglioranza, A.; Zanatta, A.; Barchak, A.G.; Vargas, C.R.; Saute, J.; Rosa, C.; Carrion, M.J.; Camargo, D.; et al. Evidence that folic acid deficiency is a major determinant of hyperhomocysteinemia in parkinson’s disease. Metab. Brain Dis. 2009, 24, 257–269.
- Murakami, K.; Miyake, Y.; Sasaki, S.; Tanaka, K.; Fukushima, W.; Kiyohara, C.; Tsuboi, Y.; Yamada, T.; Oeda, T.; Miki, T.; et al. Dietary intake of folate, vitamin b6, vitamin b12 and riboflavin and risk of parkinson’s disease: A case-control study in japan. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 757–764.
- Shen, L. Associations between b vitamins and parkinson’s disease. Nutrients 2015, 7, 7197–7208.
- Christine, C.W.; Auinger, P.; Joslin, A.; Yelpaala, Y.; Green, R. Vitamin b12 and homocysteine levels predict different outcomes in early parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 762–770.
- Luthra, N.S.; Marcus, A.H.; Hills, N.K.; Christine, C.W. Vitamin b12 measurements across neurodegenerative disorders. J. Clin. Mov. Disord. 2020, 7, 3.
- Ibrahimagic, O.C.; Smajlovic, D.; Dostovic, Z.; Pasic, Z.; Kunic, S.; Iljazovic, A.; Hajdarevic, D.S. Hyperhomocysteinemia and its treatment in patients with parkinson’s disease. Mater. Sociomed 2016, 28, 303–306.
- Chen, H.; Zhang, S.M.; Schwarzschild, M.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Logroscino, G.; Willett, W.C.; Ascherio, A. Folate intake and risk of parkinson’s disease. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 160, 368–375.
- de Lau, L.M.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Witteman, J.C.; Hofman, A.; Breteler, M.M. Dietary folate, vitamin b12, and vitamin b6 and the risk of parkinson disease. Neurology 2006, 67, 315–318.
- Diao, H.-M.; Song, Z.-F.; Xu, H.-D. Association between mthfr genetic polymorphism and parkinson’s disease susceptibility: A meta-analysis. Open Med. 2019, 14, 613–624.
- Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Guo, L.; Yu, Q.; Li, H.; Teng, J.; Xie, A. Mthfr c677t and a1298c polymorphisms may contribute to the risk of parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis of 19 studies. NeuroSci. Lett. 2018, 662, 339–345.
- Fong, C.S.; Shyu, H.Y.; Shieh, J.C.; Fu, Y.P.; Chin, T.Y.; Wang, H.W.; Cheng, C.W. Association of mthfr, mtr, and mtrr polymorphisms with parkinson’s disease among ethnic chinese in taiwan. Clin. Chim Acta 2011, 412, 332–338.
- Miranda-Morales, E.; Meier, K.; Sandoval-Carrillo, A.; Salas-Pacheco, J.; Vázquez-Cárdenas, P.; Arias-Carrión, O. Implications of DNA methylation in parkinson’s disease. Front. Mol. NeuroSci. 2017, 10.
- Henderson, A.R.; Wang, Q.; Meechoovet, B.; Siniard, A.L.; Naymik, M.; De Both, M.; Huentelman, M.J.; Caselli, R.J.; Driver-Dunckley, E.; Dunckley, T. DNA methylation and expression profiles of whole blood in parkinson’s disease. Front. Genet. 2021, 12.
- Jowaed, A.; Schmitt, I.; Kaut, O.; Wüllner, U. Methylation regulates alpha-synuclein expression and is decreased in parkinson’s disease patients’ brains. J. NeuroSci. 2010, 30, 6355–6359.
- Matsumoto, L.; Takuma, H.; Tamaoka, A.; Kurisaki, H.; Date, H.; Tsuji, S.; Iwata, A. Cpg demethylation enhances alpha-synuclein expression and affects the pathogenesis of parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, 0015522.
- Ai, S.X.; Xu, Q.; Hu, Y.C.; Song, C.Y.; Guo, J.F.; Shen, L.; Wang, C.R.; Yu, R.L.; Yan, X.X.; Tang, B.S. Hypomethylation of snca in blood of patients with spoRadic. parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 337, 123–128.
- Guhathakurta, S.; Evangelista, B.A.; Ghosh, S.; Basu, S.; Kim, Y.-S. Hypomethylation of intron1 of α-synuclein gene does not correlate with parkinson’s disease. Mol. Brain 2017, 10, 6.
- Gu, J.; Barrera, J.; Yun, Y.; Murphy, S.K.; Beach, T.G.; Woltjer, R.L.; Serrano, G.E.; Kantor, B.; Chiba-Falek, O. Cell-type specific changes in DNA methylation of snca intron 1 in synucleinopathy brains. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15.
- Obeid, R.; Schadt, A.; Dillmann, U.; Kostopoulos, P.; Fassbender, K.; Herrmann, W. Methylation status and neurodegenerative markers in parkinson disease. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 1852–1860.
- Desplats, P.; Spencer, B.; Coffee, E.; Patel, P.; Michael, S.; Patrick, C.; Adame, A.; Rockenstein, E.; Masliah, E. Alpha-synuclein sequesters dnmt1 from the nucleus: A novel mechanism for epigenetic alterations in lewy body diseases. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 9031–9037.
- Lüth, T.; Wasner, K.; Klein, C.; Schaake, S.; Tse, R.; Pereira, S.L.; Laß, J.; Sinkkonen, L.; Grünewald, A.; Trinh, J. Nanopore single-molecule sequencing for mitochondrial DNA methylation analysis: Investigating parkin-associated parkinsonism as a proof of concept. Front. Aging NeuroSci. 2021, 13.
- Malpartida, A.B.; Williamson, M.; Narendra, D.P.; Wade-Martins, R.; Ryan, B.J. Mitochondrial dysfunction and mitophagy in parkinson’s disease: From mechanism to therapy. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2021, 46, 329–343.
- Guo, J.D.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Li, G.R.; Liu, X.L. Damage to dopaminergic neurons by oxidative stress in parkinson’s disease (review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1817–1825.
- Bjørklund, G.; Peana, M.; Maes, M.; Dadar, M.; Severin, B. The glutathione system in parkinson’s disease and its progression. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 120, 470–478.
- Chinta, S.J.; Kumar, M.J.; Hsu, M.; Rajagopalan, S.; Kaur, D.; Rane, A.; Nicholls, D.G.; Choi, J.; Andersen, J.K. Inducible alterations of glutathione levels in adult dopaminergic midbrain neurons result in nigrostriatal degeneration. J. NeuroSci. 2007, 27, 13997–14006.
- Srivastav, S.; Singh, S.K.; Yadav, A.K.; Srikrishna, S. Folic acid supplementation ameliorates oxidative stress, metabolic functions and developmental anomalies in a novel fly model of parkinson’s disease. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 1350–1359.
- Meiser, J.; Delcambre, S.; Wegner, A.; Jäger, C.; Ghelfi, J.; d’Herouel, A.F.; Dong, X.; Weindl, D.; Stautner, C.; Nonnenmacher, Y.; et al. Loss of dj-1 impairs antioxidant response by altered glutamine and serine metabolism. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 89, 112–125.
