Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Archaeology
The increasingly entrepreneurial intent of universities implies the commercialization of knowledge and innovation through the triple helix of interactions between universities, industry and government. However, there remains a lack of clarity concerning best practice partnerships for innovation.
- triple helix
- innovation
- partnership development
- sustainable development
1. Introduction
Since the 1940s, there has been a push to encourage universities and industry to increase their engagement to commercialize research [1]. This started with the use of government procurement to encourage research and the development of innovative products [2] initially in the space, defense and energy sectors [3]. The 1950s and 1960s saw the development of science and/or technology parks to commercialize research [4] in America, which was followed, during the 1980s, in the UK [5].
During the 1980s, universities developed an increasing focus on technology transfer [6] to facilitate engagement with business. However, it was only from the 1990s that universities became directly involved in the world of business, actively seeking to commercialize their knowledge and research [3].
The benefits of collaboration range from the local (commercialization of research and innovation [7]) to the regional (revitalization of regions [8][9]) or national (catalyst for techno-economic development [10]) levels. Collaboration is a key part of modern innovation [11], which in turn is an important part of a well-developed entrepreneurial industrial sector [12].
The triple helix model [13] highlights the importance of a partnership between universities, industry and government to create innovation that meets business objectives in developing and commercializing universities’ research outcomes. Including government within the partnership creates outcomes that are socially and economically beneficial [14][15]. Others [16] have proposed the addition of a fourth helix (the quadruple helix) to promote a democratic approach to innovation, where society can provide feedback to create socially acceptable policies and practices. However, this model does not include the explicit consideration of non-market parameters, such as the natural environment [17]. The quintuple helix [18] seeks to address this shortcoming.
However, universities, industry and government struggle to effectively partner—particularly at scale—to deliver economic benefits from the commercialization of research outputs [19][20][21].
2. Discussion and Analysis of the Data
2.1. Articulated Data
2.1.1. Innovation at the University–Industry–Government Nexus
Economies have become increasingly dependent on the exploitation of knowledge for continued economic growth [1][4] and the role of the university is widely debated [22][23][24][25]. Universities play a key role in furthering future economic development, due to their missions to educate, carry out research and engage [26][27]. It is the third mission (engagement) that gets the most attention in terms of how universities can most effectively use the knowledge they create to further economic development [28][29] and do so in a manner that is in the economic interest of society [30][31]. To efficiently utilize their expertise in knowledge creation for the economic benefit of society, there is a need to interact, or partner, with other organizations [32]. There is limited discussion about how universities themselves might use innovation to improve their offerings under missions one and two (see, for example [33][34]).
There is an ongoing conversation about the triple helix, where universities, government and industry interact to help drive knowledge-based economic development, particularly in an industrialized economy [25][35]. The triple helix model is largely accepted as a useful starting point to understand the changing roles of universities, industry and government to partner in innovation to drive economic development.
2.1.2. Intermediaries for Innovation at the University–Industry–Government Nexus
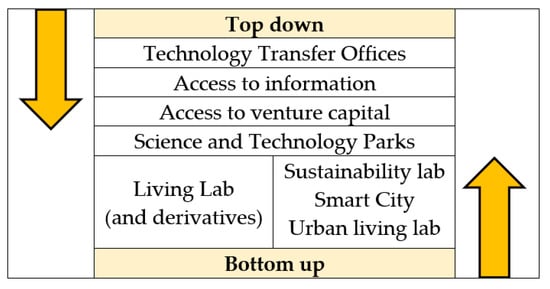
The SLR reveals that the innovation intermediaries created by university, industry and government are created through an internal dynamic, and these are either management led (top-down) or led by an entrepreneurial individual or group (bottom-up) [28][35]. These types of intermediaries for innovation, as identified in the literature, are shown in Figure 1.
Whilst there is a focus on economic development, it is clear from the literature that the deepening knowledge-based economy is affecting not only how industry, government and universities interact, but also how consumers and citizens [32] interact with other partners in the innovation ecosystem. The pace of change affects all sectors of society (university, industry, government as well as people), and this dynamic relationship is rapidly changing, which is leading to new forms of intermediaries that are highly individualized [36]. This, in turn, leads to the opportunity for innovation at different scales and under differing dynamics and delivering different outcomes [37][38].
Various forms of intermediaries are being created as a result of internal dynamics, but also being facilitated by external opportunities and stimuli (exogenous factors). It is this overlay of changing dynamics that has led to new forms of intermediaries for emerging innovation [39] and that are being led by, or include, different actors [40] or different power dynamics and approaches [37][41]. Additionally, new models for innovation are being adopted by different sectors—including the public sector [42] or cities [43]. It is this change in dynamics, structure and power relationships that is leading to the nascent creation of innovation that is seeking to deliver economic, social and environmental enhancements at the same time [19].
2.1.3. Evolution of Intermediaries for Innovation
This SLR reveals an evolution in the ecosystem of intermediaries for innovation. Intermediaries for innovation are individuals or organizations whose role it is to span the boundaries between organizations to facilitate innovation [44]. Innovation intermediaries are evolving from a simple partnership model of a technology transfer officer, through to the development of science and technology parks (STPs) and through to living labs and smart cities. This is a non-linear pathway [35], partly due to the rapid change in the nature of the knowledge-based economy—where knowledge is increasingly shared rather than owned [42], partly as a reflection of a change in knowledge production [16] and partly due to an increased focus (particularly in industrial economies) on the importance of the service-based economy, where service (experiential or simply more tailored [45]) is seen as another key to unlock economic development.
-
On Campus Structures
On-campus structures includes the creation of several organizational structures within universities to promote the development of partnerships for innovation. These forms of partnership are the simplest and are an organizational response to facilitate the creation of an increasingly entrepreneurial university [35]. In the initial phases at least, this is conducted on campus.
The structures put in place range from technology transfer offices [44], academic liaison officers [30] to act as an intermediary between the university and business, processes to facilitate access to library information for business [26] and the creation of incubators to help start-ups grow into functioning businesses [46]. The purpose of these mechanisms is to assist the transfer of knowledge from the researcher to the consumer via a business.
There is also some evidence in this SLR of the campus itself being used as an innovation, and these were underpinned by a planning perspective [47], asset management [48], by opening up the campus [49] or using the campus to drive radical innovation through institutionalization [50]. These studies show the potential for the entrepreneurial university to drive all three modes (education, research and commercialization) through the operation or development of the campus.
-
Development of Campus-Adjacent Structures
The second significant phase in the development of intermediaries for innovation is the creation of campus-adjacent structures to further the partnership between universities and business. In this SLR, there were 28 case studies looking at STPs. The impetus for the creation of these off-site structures seems to be university, or government driven, but there are examples of it being driven by the private real estate sector [51]. In this SLR, most papers considering STPs focused on a traditional form of STP, where a university creates spaces for businesses to occupy to deliver innovative goods and services (ideally based on or related to the intellectual output of the university).
These campus-adjacent structures have a complex nomenclature, but in this SLR, they are referred to as science and technology parks (STP). This is a generic term to take in research parks, technology parks, innovation parks and business parks. The key definition issue is that they are developed to create an environment conducive to the co-creation of economic value by business, ideally using university created knowledge. They are geographically proximate to the university and tend to focus on the research strengths of the university.
The value of geographical proximity is much debated [52]. This SLR showed strong informal connections between universities and business [26][53][54][55] based on geography but with less evidence of formal connections that deliver innovation based on university-created knowledge [52][56]. One study found that 92% of the on-park research and technology output was through private industry [57], with others considering the role of private capital to innovation success [24], the role of university finance to spin-off success [58] or the role of management [59], or the network benefit [60]. This does not, in itself, mean that STPs represent a failed policy, but that there is not strong evidence for the successful transference of knowledge from creator to consumer via a business based in the university’s STP. The depth of these relationships depends upon the level of service offered by the university to its tenants—with non-core assistance (for example, human resource management functions) being valued by tenants [54] or the value of social capital to start-up success [23].
There is also a stream of work researching the connection between the university and the STP covering the role of knowledge transfer facilitated by librarians [30], the influence of the university on the STP [61], the impact of doctoral education [62] or a more holistic consideration of the STP compared to a technology transfer officer or other intermediaries (see Section 4.1.3) [44].
Although the usefulness of STPs is still subject to debate, the creation of STPs has been adopted in Europe [7][9][63][46][56][57][64][65][66][67] and North America [1], and STPs are widely emulated in the former Eastern bloc countries [11][68][69], as well as the centralized economies of China [2][29][70], Taiwan [71][72], Malaysia [27] and others in Asia; the creation of STPs is also seen as a pathway for economic development in developing nations [8][73][74][75] as well as being subject to international comparisons [4][32][76][77].
-
Development of Living Labs
The next phase in the evolution of intermediaries for innovation is the creation of living labs. These are partnership structures that are focused on user engagement and open innovation. The partners are varied but generally involve university, business, and government (at some level). Living labs (and derivatives) are driven by a desire to innovate within the partnership and this might be the deepening of research findings [78], creating a product or service to commercialize the research [79] or co-creating a new product or service [80].
The external change that is facilitating the development of living labs is the ability for a range of stakeholders to become freely involved in the process of innovation [81]. The service-dominant logic [22], open innovation [82], user innovation [83], user-centered design [84] or even social (rather than economic) innovation [85] have become possible due to the ability to create communities of interest for almost anyone.
Living labs (and derivatives) are widely debated in the literature and are normally considered a network that incorporates both user engagement and open innovation [86]; they have the characteristics as set out in Table 1. There are several forms of living labs, which are also evolving. Sustainability labs [87] are focused on the delivery of economic, social and environmental outcomes at a geographic location. Smart cities are developed as a higher systems level solution under which living labs enable the demonstration and prototyping of products and services. Urban living labs are a network structure within an urban environment [39].
Table 1. Living lab characteristics [83].
| Characteristic | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Real life environments | Real life experimentation to test, develop, research new products, services, systems, processes |
| Stakeholders | Range of partner involvement to co-create. Stakeholders are key to the outputs of the living lab |
| Activities | What the living lab will focus upon. This is defined by whoever is driving the innovation (and is key to delivery of the output/outcome) |
| Business models | Covers how the living lab will operate (essentially why it exists and how it will continue to exist) |
| Methods and tools | The approach taken to innovation |
| Challenges | Economic, social and/or environmental |
| Output and/or outcomes | What the living lab delivers |
| Sustainability | Emergence of innovation that moves society toward delivery of the sustainable development goals |
However, both the literature and practitioners struggle to define living labs and their derivatives [83][39], or to create business cases to build them [40][87], or even best practice guides to help manage them [88]. They are a rapidly evolving creation that, in many respects, is a direct expression of the partnership that created them [87]. That said, there are structures to suit different desired outcomes, such as wicked issues [89] or radical innovation [50], and they are grouped into a genus containing 4 typologies characterized by open innovation: utilizer driven, enabler driven, provider driven, and user driven [86].
At the heart of living labs are two key elements: user engagement and open innovation [86]. These two aspects are evident in the case studies in this SLR. It is these two aspects that stand them apart as intermediaries for innovation. Because of this commitment—facilitated by the knowledge economy and technological developments—living labs are footloose. They can be on campus [34][47][49][90][91][92][93], off campus [9], in an STP [22], on a high street [94], local [40][69][78][95][96], precinct scale [97], urban [81][98][99][100][101][102], suburban [103][41], rural [15], regional [82][89], peripheral [104] or city scale [43][80][84][100][105][106][107][108]. They can also be virtual [109].
It is partly this footloose, open and creative element that means that they are potentially difficult to harness at scale: indeed, difficult to harness by policy makers, but also difficult to harness by businesses, universities and the public. These structures are innovative in themselves; each is unique (even with common elements) and each is designed to serve a purpose. Their amorphous shape and shifting nature make them difficult to grasp and initiate at scale. Whilst STPs could be created by policy diktat [53], living labs cannot and as such are more ephemeral and can be a conundrum to universities, business and government. This transformational change of the modus operandii means that a once linear, or apparently linear evolution [35], is now beset by new branches and new forms (such as sustainability labs, urban living labs, and smart cities). These branches and forms are being created at such a pace that the literature is struggling to define them [39], or adequately develop theories to help amortize their existence [110].
-
Living Labs and Sustainable Development
In this SLR, living labs (and derivatives) are the partnership structure that is being used successfully to drive social and economic development [37][111]. It is also the structure that is used in the limited number of studies that are using innovation to drive the delivery of sustainable development [19][83][103][49][75][91][93][99][112][113][114][115][116][117], with the emphasis on both sustainability labs and urban living labs. The literature does not provide guidance for the reasons for this. In a time when the Sustainable Development Goals have been unanimously agreed by the United Nations, it is noteworthy that the literature around developing partnerships for innovation is largely silent on the implications for innovation (an issue also noted by others [83]).
2.2. Attributional Data
Outlined in Table 2, and as defined by Massey (2011), but amended here to meet the needs of an SLR, attributional data relate to comments and discussion about a priori hypotheses or theories that the evaluator brings to the discussion. The data collected are the result of author expertise and assessment, as, in most cases, the theory that underpinned each study went unstated in the study.
Table 2. Categorization and paper breakdown of theories underpinning SLR.
| Theme | Theory | Sub-Theory |
|---|---|---|
| Economic development [1][8][10][31][53] Economic geography [52][75] |
Innovation theory [7][11][15][45][23][27][28][35][37][38][46][55][69][73][94][108][118][119][120][121] | Open innovation theory [3][86][122][123][33][37][39][42][44][78][82][97][102][110][124][125][126][127] |
| Innovation management theory [81][98][117] | ||
| User innovation theory [128][129] | ||
| Collaborative knowledge production [92][102] | ||
| Service or product dominant [22][41][48][50] | ||
| Frugal innovation [118] | ||
| Growth theory [76][59][84] | Knowledge transfer theory [26] | |
| Knowledge spill-over theory of entrepreneurship [58] | ||
| Development economics [130] | ||
| Regional development [28][43][60][71][72][90][93][104][105][131] | Agglomeration economics [29][132] | |
| Management theory [4][133][24][56] | Business design concepts [134] | |
| Business excellence/total quality management [88] | ||
| Construction management [135] | ||
| Corporate real estate management theory [51] | ||
| New public management theory [63] | ||
| Socio-institutional economics [104] | ||
| New institutionalism [68] | ||
| Neo-institutional economics [100] | ||
| Network theories [32][86][77][96][136][137] | Business network theory [84] | |
| Actor network theory [138] | ||
| Systems Theory [11][70][139][140] | Self-organizing systems [47] | |
| Socio technical Systems [49][91] | ||
| Process-based engineering [76] | ||
| Planning [109][110] | Transition theory [141][67][71][101] | Urban sustainability transition [80][106] |
| Transitions theory (sustainability) [142][75][92][101][114][116] | ||
| Transition management [91] | ||
| Value of sustainable development [103][114][116] | ||
| Design theory [87] | Academic capitalism [47][139] | |
| Social theories | Social practice theory [36][87][93] | |
| Social capital theory [103][23] | ||
| Social network analysis [9][57][61][64][65][66] | ||
| Social entrepreneurship [85] | ||
| Social institutionalism [25] | ||
| Theories of learning | Interorganizational learning [62][26] | |
| Experiential learning [30][112] | ||
| Informed learning [109] | ||
| Social learning [79] | ||
| Audit-based learning [34] | ||
| Absorptive capacity [143][54] |
The selected papers in this SLR were underpinned by 28 different theories (as detailed in Table 2). The theories supporting the research reveal three intersecting themes which were categorized as economic development, social theories and a thinner vein on theories of learning.
Most studies have an economic theoretical underpinning (see Table 2 for a detailed disposition of the papers and their theoretical underpinning) developed through theories of innovation, economic geography, planning and transitions.
Aligned with economic development is a suite of papers dealing with social theories. This encapsulates both how society develops, but also how individuals interact with partnerships. To some degree, this is the practical element in the development of the papers, as it focuses the papers on the theory of how individuals in society interact with innovation.
The final theoretical category is around theories of learning. This is a shallower vein of research that links through to economic development and social theories but can be divided into two theoretical strands. One is how, particularly, (though not exclusively) universities can use innovation to help deliver learning to their students. The other strand relates to continuous improvement and considers how organizations (individually and collectively) can retain and improve upon their learning by doing.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/su132413780
References
- Mitchell, G.A. Research parks: Instrument, or harbinger of a new university paradigm? Interchange 1992, 23, 99–104.
- Zhou, C. Emergence of the entrepreneurial university in evolution of the triple helix: The case of Northeastern University in China. J. Technol. Manag. China 2008, 3, 109–126.
- Van Geenhuizen, M. From Ivory Tower to Living Lab: Accelerating the Use of University Knowledge. Environ. Plan. C Gov. Policy 2013, 31, 1115–1132.
- Olvera, C.; Pique, J.M.; Cortes, U.; Nemirovsky, M. Evaluating the Success of Companies at University Science Parks: Key Performance and Innovation Indicators; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 77–92.
- Quintas, P.D.; Wield, D.; Massey, D. Academic-Industry Links and Innovation: Questioning the Science Park Model. Technovation 1992, 12, 161.
- Berbegal-Mirabent, J.F.; Sabaté, F.; Cañabate, A. Brokering knowledge from universities to the marketplace: The role of knowledge transfer offices. Manag. Decis. 2012, 50, 1285–1307.
- Tschanz, R.; Cristo, S.; Delgado, L.; Hiroz, V.; Jordan, M.; Kalt, R.; Mitchell, M.; Muller, N.; Roeoesli, C.; Tamburello, V.; et al. “No Innovation Without Cooperation”—How Switzerland Innovation Promotes Cooperation between Industry, Research and Startups. Chimia 2020, 74, 755–757.
- Sanni, M.; Egbetokun, A.A.; Siyanbola, W.O. A model for the design and development of a Science and Technology Park in developing countries. Int. J. Manag. Enterp. Dev. 2009, 8, 62–81.
- Van der Sijde, P.; Vogelaar, G.; Hoogeveen, A.; Ligtenberg, H.; van Velzen, M. Attracting high-tech companies: The case of the University of Twente and its region. Ind. High. Educ. 2002, 16, 97–104.
- Wonglimpiyarat, J. The innovation incubator, university business incubator and technology transfer strategy: The case of Thailand. Technol. Soc. 2016, 46, 18–27.
- Bekniyazova, D.S.; Nurgaliyeva, A.; Korabayev, B.; Dyussembekova, G.; Altybassarova, M.; Alkeyev, M. Innovation activity in the Republic of Kazakhstan: State controlling and ways to increase management efficiency. J. Internet Bank. Commer. 2016, S3, 1–14.
- Dhewanto, W.; Lantu, D.C.; Herliana, S.; Permatasari, A. The obstacles for science technology parks in a developing country. Int. J. Technol. Learn. Innov. Dev. 2016, 8, 4–19.
- Etzkowitz, H.; Leydesdorff, L. The Triple Helix—University-Industry-Government Relations: A Laboratory for Knowledge Based Economic Development. EASST Rev. 1995, 14, 14–19.
- Etzkowitz, H.; Leydesdorff, L. The dynamics of innovation: From National Systems and “Mode 2” to a Triple Helix of university–industry–government relations. Res. Policy 2000, 29, 109–123.
- Guzman, J.G.; Schaffers, H.; Bilicki, V.; Merz, C.; Valenzuela, M. Living labs fostering open innovation and rural development: Methodology and results. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Technology Management Conference (ICE 2008), Lisbon, Portugal, 23–28 June 2008.
- Carayannis, E.G.; Campbell, D.F.J. ‘Mode 3’ and ‘Quadruple Helix’: Toward a 21st century fractal innovation ecosystem. Int. J. Technol. Manag. 2009, 46, 201–234.
- Meadows, D.H.; Meadows, D.L.; Randers, J.; Behrens, W.W., III (Eds.) The Limits to Growth: A Report for the Club of Rome’s Project on the Predicament of Mankind; Universe Books: New York, NY, USA, 1972.
- Carayannis, E.G.; Barth, T.D.; Campbell, D.F.J. The Quintuple Helix innovation model: Global warming as a challenge and driver for innovation. J. Innov. Entrep. 2012, 1, 2.
- Burbridge, M. If Living Labs Are the Answer—What’s the Question? A Review of the Literature. In International High-Performance Built Environment Conference—A Sustainable Built Environment Conference 2016 Series; Ding, L., Fiorito, F., Osmond, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 1725–1732.
- Australia Government. National Innovation and Science Agenda; Australia Government: Canberra, Australia, 2015.
- OECD. Collaboration on Innovation. In OECD Science, Technology and Industry Scoreboard 2015: Innovation for Growth and Society; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2015.
- Ådahl, M. Commercial consortia. In Living Labs: Design and Assessment of Sustainable Living; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 385–390.
- Bandera, C.; Thomas, E. The Role of Innovation Ecosystems and Social Capital in Startup Survival. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2019, 66, 542–551.
- Campanella, F.; Peruta, M.R.D.; del Giudice, M. Creating conditions for innovative performance of science parks in europe. How manage the intellectual capital for converting knowledge into organizational action. J. Intellect. Cap. 2014, 15, 576–596.
- Hladchenko, M.; Pinheiro, R. Implementing the Triple Helix model: Means-ends decoupling at the state level? Minerva 2019, 57, 1–22.
- Aportela-Rodriguez, I.M.; Pacios, A.R. University Libraries and Science and Technology Parks: Reasons for Collaboration. Libri 2017, 67, 235–244.
- Malairaja, C.; Zawdie, G. Science parks and university-industry collaboration in Malaysia. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2008, 20, 727–739.
- Etzkowitz, H.; Zhou, C. Innovation incommensurability and the science park. R D Manag. 2017, 48, 73–87.
- Jongwanich, J.; Kohpaiboon, A.; Yang, C.-H. Science park, triple helix, and regional innovative capacity: Province-level evidence from China. J. Asia Pac. Econ. 2014, 19, 333–352.
- Bakouros, Y.L.; Samara, E.T. Academic Liaison Offices vs. technology transfer units: Could they form a new joint mechanism towards the exploration of Academic/Research results? Int. J. Innov. Sci. 2010, 2, 145–157.
- Parry, M. Science and Technology Parks and Universities—Facing the Next Industrial Revolution; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 109–140.
- Schoonmaker, M.G.; Carayannis, E.G. Mode 3: A Proposed Classification Scheme for the Knowledge Economy and Society. J. Knowl. Econ. 2013, 4, 556–577.
- Kantola, T.; Hirvikoski, T.; Lehto, P.; Aholaakko, T.-J.; Kukkonen, M.-L.; Partamies, S. Towards Co-Creation of eHealth Services. Interdiscip. Stud. J. 2014, 3, 192.
- Emblen-Perry, K. Auditing the University: Promoting Business Education for Sustainability through Audit-Based Learning; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 303–322.
- Etzkowitz, H. The new visible hand: An assisted linear model of science and innovation policy. Sci. Public Policy 2006, 33, 310–320.
- Ståhlbröst, A.; Holst, M. Reflecting on Actions in Living Lab Research. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2017, 7, 27–34.
- De Silva, M.; Wright, M. Entrepreneurial co-creation: Societal impact through open innovation. R D Manag. 2019, 49, 318–342.
- Seppä, M. From Business Administration to Business Creation: The Case of the Kalevala Global Business Creation School. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2012, 2, 6–11.
- Steen, K.Y.G.; Van Bueren, E.M. The Defining Characteristics of Urban Living Labs. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2017, 7, 21–33.
- Schaffers, H.; Turkama, P. Living Labs for Cross-Border Systemic Innovation. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2012, 2, 25–30.
- Ayvari, A.; Jyrama, A. Rethinking value proposition tools for living labs. J. Serv. Theory Pract. 2017, 27, 1024–1039.
- Gasco, M. Living labs: Implementing open innovation in the public sector. Gov. Inf. Q. 2017, 34, 90–98.
- Lukkari, O.; Mustonen, J.; Tuikka, T. City of Oulu as an innovative service platform. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Technology Management Conference (ICE 2008), Lisbon, Portugal, 23 June–25 June 2008; pp. 1–4.
- Fernández-Esquinas, M.; Merchán-Hernández, C.; Valmaseda-Andía, O. How effective are interface organizations in the promotion of university-industry links? Evidence from a regional innovation system. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2016, 19, 424–442.
- Almirall, E.; Lee, M.; Wareham, J. Mapping Living Labs in the Landscape of Innovation Methodologies. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2012, 2, 12–18.
- McAdam, M.; McAdam, R. The networked incubator: The role and operation of entrepreneurial networking with the university science park incubator (USI). Int. J. Entrep. Innov. 2006, 7, 87–98.
- Bergquist, D.; Hempel, C.A.; Green, J.L. Bridging the Gap between Theory and Design: A Proposal for Regenerative Campus Development at the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2019, 20, 548–567.
- Ahlava, A.; Suominen, J.; Rossi, S. Controlling Risks Through Flexibility and Urban Integration: The Regeneration of Otaniemi Campus in Finland. In Handbook of Theory and Practice of Sustainable Development in Higher Education; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 21–35.
- Bracco, S.; Delfino, F.; Laiolo, P.; Morini, A. Planning & open-air demonstrating smart city sustainable districts. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4636.
- Ventura, R.; Quero, M.J.; Díaz-Méndez, M. The role of institutions in achieving radical innovation. Mark. Intell. Plan. 2019, 38, 310–324.
- Magdaniel, F.C.C.; de Jonge, H.; den Heijer, A. Campus development as catalyst for innovation. J. Corp. Real Estate 2018, 20, 84–102.
- Vedovello, C. Science parks and university -Industry interaction: Geographical proximity between the agents as a driving force. Technovation 1997, 17, 491–502.
- Motohashi, K. The role of the science park in innovation performance of start-up firms: An empirical analysis of Tsinghua Science Park in Beijing. Asia Pac. Bus. Rev. 2013, 19, 578–599.
- van Oostrom, M.; Pedraza-Rodríguez, J.A.; Fernández-Esquinas, M. Does the Location in a Science and Technology Park Influence University—Industry Relationships?: Evidence From a Peripheral Region. Int. J. Knowl. Manag. 2019, 15, 66–82.
- Hung, W.C. Measuring the use of public research in firm R&D in the Hsinchu Science Park. Scientometrics 2012, 92, 63–73.
- Ramírez-Alesón, M.; Fernández-Olmos, M. Unravelling the effects of Science Parks on the innovation performance of NTBFs. J. Technol. Transf. 2018, 43, 482–505.
- Minguillo, D.; Thelwall, M. Research excellence and university–industry collaboration in UK science parks. Res. Eval. 2015, 24, 181–196.
- Corsi, C.; Prencipe, A. Improving innovation in University Spin-offs. The fostering role of university and region. J. Technol. Manag. Innov. 2016, 11, 13–21.
- Feldman, J.M. The Managerial Equation and Innovation Platforms: The Case of Linkoand Berzelius Science Park. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2007, 15, 1027–1045.
- Latorre-Martínez, M.P.; Navarro, E.; Pastor, T.; Iniguez-Berrozpe, T. Analysis of the network of relations of organizations set up at walqa technology park. In Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 1335–1346.
- Farre-Perdiguer, M.; Sala-Rios, M.; Torres-Sole, T. Network analysis for the study of technological collaboration in spaces for innovation. Science and technology parks and their relationship with the university. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2016, 13, 8.
- Germain-Alamartine, E.; Moghadam-Saman, S. Aligning doctoral education with local industrial employers’ needs: A comparative case study. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2020, 28, 234–254.
- Nielsen, C. Getting value for money from your science park. Public Money Manag. 2016, 36, 539.
- Minguillo, D.; Thelwall, M. Mapping the network structure of science parks An exploratory study of cross-sectoral interactions reflected on the web. Aslib Proc. 2012, 64, 332–357.
- Minguillo, D.; Thelwall, M. Which are the best innovation support infrastructures for universities? Evidence from R&D output and commercial activities. Scientometrics 2015, 102, 1057–1081.
- Minguillo, D.; Tijssen, R.; Thelwall, M. Do science parks promote research and technology? A scientometric analysis of the UK. Scientometrics 2015, 102, 701–725.
- Steinthorsson, R.S.; Hilmarsson, E.; Janusson, H.B. Towards openness and inclusiveness: The evolution of a science park. Ind. High. Educ. 2017, 31, 388–398.
- Karpińska, A. Innovation and science dilemmas. Unintended consequences of innovation policy for science. Polish experience. Cogent Soc. Sci. 2020, 6, 1718055.
- Prepelita-Raileanu, B.; Pastae, O.M. Bridging the gap between higher education, academic research and Romanian business community. In Proceedings of the 9th WSEAS Conference on Education and Education Technology, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 4 October 2010; pp. 4–6.
- Yan, M.-R.; Yan, H.; Zhan, L.; Yan, X.; Xu, M. Evaluation of Technological Innovations and the Industrial Ecosystem of Science Parks in Shanghai: An Empirical Study. Sci. Technol. Soc. 2020, 25, 482–504.
- Tsai, C.-L.; Chang, H.-C. Evaluation of critical factors for the regional innovation system within the HsinChu science-based park. Kybernetes 2016, 45, 699–716.
- Wang, W.-B.; Hung, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-C. University-Industry Research Collaboration in Taiwan. J. Inf. Optim. Sci. 2012, 33, 665–683.
- Widiawan, K. Identifying the most suitable university-industry partnership model in developing countries. In Proceedings of the 2008 4th IEEE International Conference on Management of Innovation and Technology, Bangkok, Thailand, 21–24 September 2008; pp. 128–133.
- Melo, P.; Maravilhas, S. Are interaction linkages based on geographic proximity focused on development of firms innovation activities still relevant? Empirical study of the ICT firms located in the city of Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. RISUS Rev. Inovação E Sustentabilidade 2019, 10, 12–19.
- Benltoufa, A.N.H.S.; Noureddine, H.; Jaafar, F.; Maraoul, M.; Said, L.; Zili, M.; Hedfi, H.; Labidi, M.; Bouzidi, A.; Jrad, B.B.; et al. From smart campus to smart city: Monastir living lab. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Engineering and Technology (ICET), Antalya, Turkey, 21–23 August 2017.
- Aslani, A.; Eftekhari, H.; Didari, M. Comparative Analysis of the Science and Technology Parks of the US Universities and a Selected Developing Country. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Innovation and Management, Vaasa, Finland, 17–19 November 2014; pp. 1–7.
- Yun, S.; Lee, J. An innovation network analysis of science clusters in South Korea and Taiwan. Asian J. Technol. Innov. 2013, 21, 277–289.
- Martinez, S.; Bjerkas, S.; Ludvigsen, A.E.; Fensli, R. Agder Living Lab: From Ideas to Large-Scale Deployment and Long-Term User Adoption of Inclusive Health Solutions; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 391–399.
- Hakkarainen, L.; Hyysalo, S. How Do We Keep the Living Laboratory Alive? Learning and Conflicts in Living Lab Collaboration. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2013, 3, 16–22.
- Chronéer, D.; Ståhlbröst, A.; Habibipour, A. Urban Living Labs: Towards an Integrated Understanding of their Key Components. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2019, 9, 50–62.
- Baccarne, B.; Mechant, P.; Schuurma, D.; De Marez, L.; Colpaert, P. Urban Socio-technical Innovations with and by Citizens. Interdiscip. Stud. J. 2014, 3, 143.
- Dhakal, S.; Mahmood, M.; Wiewora, A.; Brown, K.; Keast, R. The Innovation Potential of Living-Labs to Strengthen Small and Medium Enterprises in Regional Australia. Australas. J. Reg. Stud. 2013, 19, 456–474.
- Hossain, M.; Leminen, S.; Westerlund, M. A systematic review of living lab literature. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 976–988.
- Artto, K.; Kyro, R.; Ahola, T.; Peltokorpi, A.; Sandqvist, K. The Cuckoo’s Nest Approach for Co-Creating Business Ecosystems in Smart Cities. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2016, 6, 26–37.
- Lundström, A.; Zhou, C. Promoting innovation based on social sciences and technologies: The prospect of a social innovation park. Innovation 2011, 24, 133–149.
- Leminen, S.; Westerlund, M.; Nyström, A.-G. Living Labs as Open-Innovation Networks. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2012, 2, 6–11.
- Burbridge, M.; Morrison, G.M.; van Rijn, M.; Silvester, S.; Keyson, D.V.; Baedeker, C.; Liedtke, C. Business models for sustainability in living labs. In Living Labs: Design and Assessment of Sustainable Living; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 391–403.
- Katzy, B. Designing Viable Business Models for Living Labs. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2012, 2, 19–24.
- Zivkovic, S. Systemic innovation labs: A lab for wicked problems. Soc. Enterp. J. 2018, 14, 348–366.
- Mohamad, Z.F.; Kadir, S.N.A.; Nasaruddin, A.; Sakai, N.; Mohamed Zuki, F.; Hussein, H.; Sulaiman, A.-H.; Mohammad, S.A. Heartware as a driver for campus sustainability: Insights from an action-oriented exploratory case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 1086–1096.
- Berker, T.; Woods, R. Identifying and addressing reverse salients in infrastructural change. The case of a small zero emission campus in Southern Norway. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2020, 21, 1625–1640.
- Cooper, L.; Gorman, D. A Holistic Approach to Embedding Social Responsibility and Sustainability in a University—Fostering Collaboration between Researchers, Students and Operations; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 177–192.
- Fabregà, M.B. How Entrepreneurship in Higher Education Helps to Sustainable Development at the Local Level: The Case of Tecnocampus; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 587–604.
- van Winden, W.; Hagemans, I.; van Hemert, P. The Street-Wise University: The Amsterdam Knowledge Mile as an Intermediary and Place-Making Concept. Soc. Sci. 2019, 8, 229.
- Callaghan, R.; Herselman, M. Applying a Living Lab methodology to support innovation in education at a university in South Africa. J. Transdiscipl. Res. South. Afr. 2015, 11, e1–e18.
- Mulvenna, M.D.; Bergvall-Kareborn, B.; Galbraith, B.; Wallace, J.; Martin, S. Living Labs Are Innovation Catalyst. In Innovation through Knowledge Transfer 2010; Howlett, R.J., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 253–264.
- Punt, E.; Afrooz, A.; Pettit, C. Precinct scale living laboratories: Case study of Randwick living lab. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, VI-4/W2-2020, 127–134.
- Baccarne, B.; Logghe, S.; Schuurman, D.; De Marez, L. Governing Quintuple Helix Innovation: Urban Living Labs and Socio-Ecological Entrepreneurship. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2016, 6, 22–30.
- Boeri, A.; Longo, D.; Gianfrate, V.; Lorenzo, V. Resilient communities. Social infrastructures for sustainable growth of urban areas. A case study. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2017, 12, 227–237.
- Canzler, W.; Engels, F.; Rogge, J.C.; Simon, D.; Wentland, A. From “living lab” to strategic action field: Bringing together energy, mobility, and Information Technology in Germany. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2017, 27, 25–35.
- Frantzeskaki, N.; van Steenbergen, F.; Stedman, R.C. Sense of place and experimentation in urban sustainability transitions: The Resilience Lab in Carnisse, Rotterdam, The Netherlands. Sustain. Sci. 2018, 13, 1045–1059.
- Tukiainen, T.; Leminen, S.; Westerlund, M. Cities as Collaborative Innovation Platforms. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2015, 5, 16–23.
- Buhr, K.; Federley, M.; Karlsson, A. Urban Living Labs for Sustainability in Suburbs in Need of Modernization and Social Uplift. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2016, 6, 27–34.
- Antonopoulos, C.N.; Papadakis, V.G.; Stylios, C.D.; Efstathiou, M.P.; Groumpos, P.P. Mainstreaming innovation policy in less favoured regions: The case of Patras Science Park, Greece. Sci. Public Policy 2009, 36, 511–521.
- Vallance, P.; Tewdwr-Jones, M.; Kempton, L. Building collaborative platforms for urban innovation: Newcastle City Futures as a quadruple helix intermediary. Eur. Urban Reg. Stud. 2020, 27, 325–341.
- Bartelt, V.L.; Urbaczewski, A.; Mueller, A.G.; Sarker, S. Enabling collaboration and innovation in Denver’s smart city through a living lab: A social capital perspective. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2020, 29, 369–387.
- Coenen, T.; Robijt, S. Heading for a FALL: A Framework for Agile Living Lab Projects. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2017, 7, 37–43.
- Lindberg, M.; Segerstedt, E.; Hidman, E.; Nilsson, K.; Karlberg, H.; Balogh, J. Co-Creative Place Innovation in an Arctic Town. J. Place Manag. Dev. 2020, 13, 447.
- Hughes, H.; Wolf, R.; Foth, M. Informed digital learning through social living labs as participatory methodology: The case of Food Rescue Townsville. Inf. Learn. Sci. 2017, 118, 518–534.
- Leminen, S.; Rajahonka, M.; Westerlund, M. Towards Third-Generation Living Lab Networks in Cities. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2017, 7, 21–35.
- Dekker, R.; Contreras, J.F.; Meijer, A. The Living Lab as a Methodology for Public Administration Research: A Systematic Literature Review of its Applications in the Social Sciences. Int. J. Public Adm. 2020, 43, 1207–1217.
- Jernsand, E.M. Student living labs as innovation arenas for sustainable tourism. Tour. Recreat. Res. 2019, 44, 337–347.
- Verhoef, L.A.; Bossert, M.; Newman, J.; Ferraz, F.; Robinson, Z.P.; Agarwala, Y.; Wolff, P.J.; Jiranek, P.; Hellinga, C. Towards a Learning System for University Campuses as Living Labs for Sustainability; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 135–149.
- Zen, I.S. Exploring the living learning laboratory: An approach to strengthen campus sustainability initiatives by using sustainability science approach. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2017, 18, 939–955.
- Nifa, F.A.A.; Rahim, S.A.; Rani, W.N.M.; Ismail, M.N. Collaborative Procurement for Developing a Sustainable Campus; American Institute of Physics: Melville, NY, USA, 2016.
- da Silva, L.C.P.; Wright, M. Sustainable Campus Model at the University of Campinas—Brazil: An Integrated Living Lab for Renewable Generation, Electric Mobility, Energy Efficiency, Monitoring and Energy Demand Management; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 457–472.
- Cigir, K. Creating a living lab model for tourism and hospitality businesses to stimulate CSR and sustainability innovations. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2018, 217, 569–583.
- Pisoni, A.; Michelini, L.; Martignoni, G. Frugal approach to innovation: State of the art and future perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 107–126.
- Steruska, J.; Simkova, N.; Pitner, T. Do science and technology parks improve technology transfer? Technol. Soc. 2019, 59, 101127.
- Van Dierdonck, R.; Debackere, K.; Engelen, B. University-industry relationships: How does the Belgian academic community feel about it? Res. Policy 1990, 19, 551–566.
- Verloo, H.; Lorette, A.; Gomes da Rocha, C.; Amoussou, J.-R.; Gillès de Pélichy, E.; Matos Queiros, A.; Mendez Rubio, M.; von Gunten, A. A Comprehensive Scoping Review Protocol of Using Living Labs to Explore Needs and Solutions for Older Adults with Dementia. Smart Homecare Technol. TeleHealth 2020, 7, 19–27.
- Leminen, S. Coordination and Participation in Living Lab Networks. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2013, 3, 5–14.
- Leminen, S.; Nyström, A.-G.; Westerlund, M.; Kortelainen, M.J. The effect of network structure on radical innovation in living labs. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2016, 31, 743–757.
- Hagy, S.; Morrison, G.; Elfstrand, P. Co-Creation in Living Labs; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016.
- Logghe, S.; Schuurman, D. Action Research as a Framework to Evaluate the Operations of a Living Lab. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2017, 7, 35–41.
- Marasso, L.; Giangreco, E.; Storelli, D.; Chetta, V.; Camillò, A. Turrisi, G. Antonucci, G.; Barile, M.; Centrone, B.; Papadia, D.; Simone, F. Idea Management System for Smart City Planning. Interdiscip. Stud. J. 2014, 3, 227.
- Schuurman, D.; de Marez, L.; Ballon, P. Open Innovation Processes in Living Lab Innovation Systems: Insights from the LeYLab. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2013, 3, 28–36.
- Veeckman, C.; van der Graaf, S. The City as Living Laboratory: Empowering Citizens with the Citadel Toolkit. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2015, 5, 6–17.
- Westerlund, M.; Leminen, S.; Habib, C. Key Constructs and a Definition of Living Labs as Innovation Platforms. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2018, 8, 51–62.
- Kimatu, J.N. Evolution of strategic interactions from the triple to quad helix innovation models for sustainable development in the era of globalization. J. Innov. Entrep. 2016, 5, 16.
- Charles, D. The rural university campus and support for rural innovation. Sci. Public Policy 2016, 43, 763–773.
- Kuo-Feng, H.; Chwo-Ming, Y.; Dah-Hsian, S. R&D Collaborations in a Cluster: An Empirical Study for the Taiwan’s Hsinchu Science Park. Tai Da Guan Li Lun Cong 2010, 21, 47.
- Veeckman, C.; Schuurman, D.; Leminen, S.; Westerlund, M. Linking Living Lab Characteristics and Their Outcomes: Towards a Conceptual Framework. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2013, 3, 6–15.
- Schaffers, H.; Cordoba, M.G.; Hongisto, P.; Kallai, T.; Merz, C.; Van Rensburg, J. Exploring Business Models for Open Innovation in Rural Living Labs. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Technology Management Conference (ICE), Sophia Antipolis, France, 4–6 June 2007; pp. 1–8. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7458702 (accessed on 9 December 2021).
- Hartkopf, V.; Loftness, V.; Mahdavi, A.; Lee, S.; Shankavaram, J. An integrated approach to design and engineering of intelligent buildings—The Intelligent Workplace at Carnegie Mellon University. Autom. Constr. 1997, 6, 401–415.
- Wehrmann, C.; van de Sanden, M.C.A. Universities as living labs for science communication. J. Sci. Commun. 2017, 16, C03.
- Yan, M.-R.; Chien, K.-M.; Hong, L.-Y.; Yang, T.-N. Evaluating the collaborative ecosystem for an innovation-driven economy: A systems analysis and case study of science parks. Sustainability 2018, 10, 887.
- Sandrine, R.; Guillaume, G.; Philippe, V. Citizen Involvement in Local Environmental Governance: A Methodology Combining Human-Centred Design and Living lab Approaches. Electron. J. E-Gov. 2014, 12, 108.
- Hladchenko, M. Knowledge Valorisation: A Route of Knowledge That Ends In Surplus Value (An Example of The Netherlands). Int. J. Educ. Manag. 2016, 30, 668–678.
- Carayannis, E.G. Mode 3 Knowledge Production in Quadruple Helix Innovation Systems: 21st-Century Democracy, Innovation, and Entrepreneurship for Development; Elias, G.C., David, F.J.C., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012.
- Purcell, W.M.; Henriksen, H.; Spengler, J.D. Universities as the Engine of Transformational Sustainability toward Delivering the Sustainable Development Goals: “Living Labs” for Sustainability. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2019, 20, 1343–1357.
- Voytenko, Y.; McCormick, K.; Evans, J.; Schliwa, G. Urban living labs for sustainability and low carbon cities in Europe: Towards a research agenda. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 123, 45–54.
- Martins, J.T. Relational capabilities to leverage new knowledge: Managing directors’ perceptions in UK and Portugal old industrial regions. Learn. Organ. 2016, 23, 398–414.
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!