Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the most widely used non-invasive technique in the primary diagnosis of glioblastoma. Although MRI provides very powerful anatomical information, it has proven to be of limited value for diagnosing glioblastomas in some situations. The final diagnosis requires a brain biopsy that may not depict the high intratumoral heterogeneity present in this tumor type. The gold standard tracer for most PET cancer imaging is 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose ([18F]FDG), a fluorine-18 glucose analog, being the most widely used in clinical radiopharmaceutical practice, and accounting for more than 90% of total PET scans. [18F]FDG is ineffective for diagnosing gliomas due to the high glucose metabolism in the normal brain, which results in suboptimal tumor detection and delineation, especially upon treatment. An innovative option for biomarker identification in vivo is termed “immunotargeted imaging”. By merging the high target specificity of antibodies with the high spatial resolution, sensitivity, and quantitative capabilities of positron emission tomography (PET), “Immuno-PET” allows us to conduct the non-invasive diagnosis and monitoring of patients over time using antibody-based probes as an in vivo, integrated, quantifiable, 3D, full-body “immunohistochemistry” in patients.
- diagnostic imaging
- immuno-PET
- glioblastoma
- neuroimaging
- molecular imaging
- antibody
- nanobody
- theragnostic probes
1. Introduction
2. Current Status of Glioblastoma Classification and Diagnosis
3. Neuroimaging
4. Elements of Immuno-PET: Target, Antibody and Radionuclide
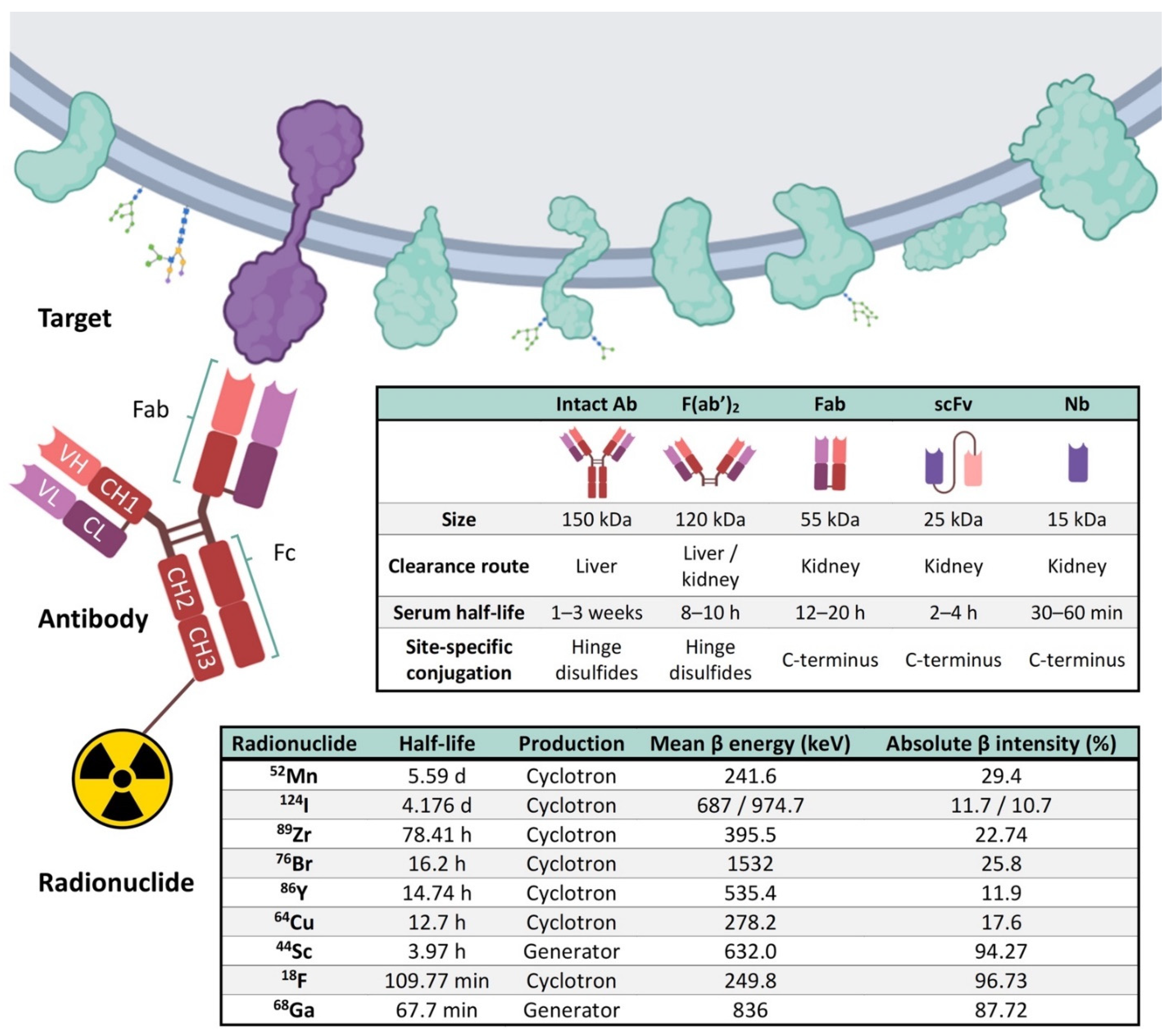
5. Current Perspectives of Immuno-PET for Glioblastoma
|
PET Imaging Probes |
Conjugation Strategy |
Targets |
Application |
Models |
References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
[18F]AlF-NOTA/NODAGA-PODS-Z-EGFR:03115 (EGFR-targeting affibody molecule) |
Cysteine-based random |
EGFR |
Many EGFR gene alterations have been identified in gliomas, especially glioblastomas. |
Subcutaneous xenograft mouse model with U-87 MG vIII cells |
[25] |
|
[124I]I-PEG4-tptddYddtpt-ch806 (tptddYddtpt is a peptide ‘‘clicked″ onto dibenzyl- clooctyne(DBCO)-derivatized ch806) |
Click chemistry |
EGFR |
ch806, an anti-EGFR mAb, can distinguish tumor cells with an amplified/overexpressed EGFR phenotype from normal cells having wild-type levels of EGFR expression. |
Subcutaneous xenograft mouse model with U-87 MG.de2-7 cells |
[26] |
|
[44Sc]Sc−CHX-A″-DTPA−Cetuximab-Fab |
Lysine-based random |
EGFR |
Radiolabeling and preclinical evaluation of 44Sc-labeled protein molecules. |
Subcutaneous xenograft mouse model with U-87 MG |
[27] |
|
[89Zr]Zr-DFO-cetuximab |
Lysine-based random |
EGFR |
89Zr-cetuximab was used to assess transient BBB disruption in vivo permeability induced by the combination of injected microbubbles with low intensity focused ultrasound. |
Orthotopic murine glioma with GL261 cells |
[28] |
|
[64Cu]Cu-NOTA-Bs-F(ab)2 (bispecific immunoconjugate by linking two antibody Fab……fragments, an anti-EGFR and an anti-CD105) |
Lysine-based random |
EGFR and CD105 |
EGFR has been extensively studied as a target for anticancer therapy, and its activation stimulates tumor proliferation and angiogenesis. Similarly, CD105 (also called endoglin) is abundantly expressed on activated endothelial cells, and such over-expression is an adverse prognostic factor in many malignant tumor types. |
Subcutaneous xenograft mouse model with U-87 MG |
[29] |
|
[64Cu]Cu-NOTA-EphA2-4B3 (human anti-EphA2 mAb) |
Lysine-based random |
EphA2 |
EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase is overexpressed in several tumors, including glioblastoma. |
Orthotopic brain glioblastoma murine models (two patient-derived cell lines and U-87 MG cells) |
[30] |
|
[89Zr]Zr-DFO-mCD47 |
Lysine-based random |
CD47 |
CD47 is a membrane protein overexpressed on the surface of most cancer cells. It is involved in the increase in intracellular [Ca2+] that occurs upon cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix and is also a receptor for the C-terminal cell-binding domain of thrombospondin. |
Orthotopic murine glioma with GL261 cells |
[31] |
|
[64Cu]Cu-NOTA-AC133 (anti-AC133 mAb) |
Lysine-based random |
AC133 |
AC133 is an N-glycosylation-dependent epitope of the second extracellular loop of CD133/prominin-1, a cholesterol-binding protein of unknown function that locates to plasma membrane protrusions. AC133+ tumor stem cells have been described for glioblastoma multiforme. |
Orthotopic and subcutaneous xenograft mouse models with NCH421k and U-251 MG cells |
[32] |
|
[89Zr]Zr-DFO-bevacizumab (humanized anti-VEGF) |
Lysine-based random |
VEGF |
89Zr-labeled bevacizumab was used to assess BBB opening with mannitol. |
C3HeB/FeJ mice without tumors |
[33] |
|
[68Ga]Ga-DOTA-bevacizumab (humanized anti-VEGF) |
Lysine-based random |
VEGF |
68Ga-labeled bevacizumab was used to assess BBB opening with focused ultrasound exposure in the presence of microbubbles. |
Orthotopic murine glioma with U-87 MG cells |
[34] |
|
[89Zr]Zr-DFO-YY146 (anti-CD146 mAb) |
Lysine-based random |
CD146 |
CD146 plays an important role in several processes involved in tumor angiogenesis, progression, and metastasis. Its expression has been correlated with aggressiveness in high-grade gliomas. |
Subcutaneous xenograft mouse model with U-87 MG and U251 cells |
[35] |
|
[64Cu]Cu-NOTA-YY146 (anti-CD146 mAb) |
Lysine-based random |
CD146 |
CD146 plays an important role in several processes involved in tumor angiogenesis, progression, and metastasis. Its expression has been correlated with aggressiveness in high-grade gliomas. |
Orthotopic and subcutaneous xenograft mouse models with U-87 MG and U-251 MG cells |
[36] |
|
[64Cu]Cu-NOTA-61B (human anti-Dll4 mAb) |
Lysine-based random |
DII4 |
DII4 plays a key role to promote the tumor growth of numerous cancer types. |
Subcutaneous xenograft mouse model with U-87 MG |
[37] |
|
[89Zr]Zr-DFO-LEM2/15 (anti-MM1-MMP mAb) |
Lysine-based random |
MT1-MMP/ MMP14 |
MMP14 is a metalloprotease frequently overexpressed in many tumors, and it is associated with tumor growth, invasion, metastasis, and poor prognosis. |
Xenograft mice bearing human U251 cells and two orthotopic brain glioblastoma murine models (patient-derived TS-543 neurospheres and U-251 MG cells) |
[38] |
|
[89Zr]Zr-DFO-fresolimumab (human IgG4 mAb, 1D11) |
Lysine-based random |
TGFβ |
TGFβ mediates extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling, angiogenesis, and immunosuppression, and regulates tumor cell motility and invasion. |
Orthotopic murine glioma with GL261 and SB28 cells |
[39] |
|
[89Zr]Zr-DFO-fresolimumab (human IgG4 mAb, 1D11) |
Lysine-based random |
TGFβ |
TGFβ mediates ECM remodeling, angiogenesis, and immunosuppression, and regulates tumor cell motility and invasion. |
Patients with recurrent high-grade glioma |
[40] |
|
[89Zr]Zr-DFO-F19 (anti-FAP monoclonal antibody) |
Lysine-based random |
FAP |
FAP, a 170 kDa type II transmembrane serine protease, is expressed on glioma cells and within the glioma tumor microenvironment. |
Subcutaneous xenograft mouse model with U-87 MG cells |
[41] |
|
[89Zr]Zr-DFO-PD-1 |
Lysine-based random |
PD-1 |
89Zr labeled αPD-1 antibody was used to assess focal BBB permeability induced by high-intensity, focused ultrasound. |
Orthotopic murine glioma with G48a cells |
[42] |
|
[68Ga]Ga-NOTA-Nb109 (anti-PD-L1 nanobody) |
Lysine-based random |
PD-L1 |
Evaluate the specific affinity of 68Ga-NOTA-Nb109 to several cancer cell lines that expressed endogenous PD-L1. |
Subcutaneous xenograft mouse model with U-87 MG cells |
[43] |
|
[89Zr]Zr-DFO-169 cDb (anti-CD8 cys-diabody) |
Lysine-based random |
CD8 |
Proof-of-concept to detect CD8+ T cell immune response to oncolytic herpes simplex virus (oHSV) M002 immunotherapy in a syngeneic glioblastoma model. |
Orthotopic syngeneic murine glioma with GSC005 cells |
[44] |
|
[89Zr]Zr-DFO-CD11b |
Lysine-based random |
CD11b |
The most abundant population of immune cells in glioblastoma is the CD11b+ tumor-associated myeloid cells. |
Mice bearing established orthotopic syngeneic GL261 gliomas |
[45] |
|
[89Zr/177Lu]Zr/Lu-Lumi804-CD11b |
Lysine-based random |
CD11b |
Theragnostic approach for monitoring and reducing tumor-associated myeloid cells in gliomas to improve immunotherapy responses. |
Mice bearing established orthotopic syngeneic GL261 gliomas |
[46] |
|
[89Zr]Zr-DFO-OX40 |
Lysine-based random |
CD134 |
CD134 (or OX40) is an activated T-cell surface marker, known to be a costimulatory transmembrane molecule of TNF superfamily, primarily expressed on activated effector T cells and regulatory T cells. |
Mice bearing established orthotopic GL261 gliomas |
[47] |
6. Novel Nanobody-Based Immuno-PET Imaging Methods for Glioblastoma
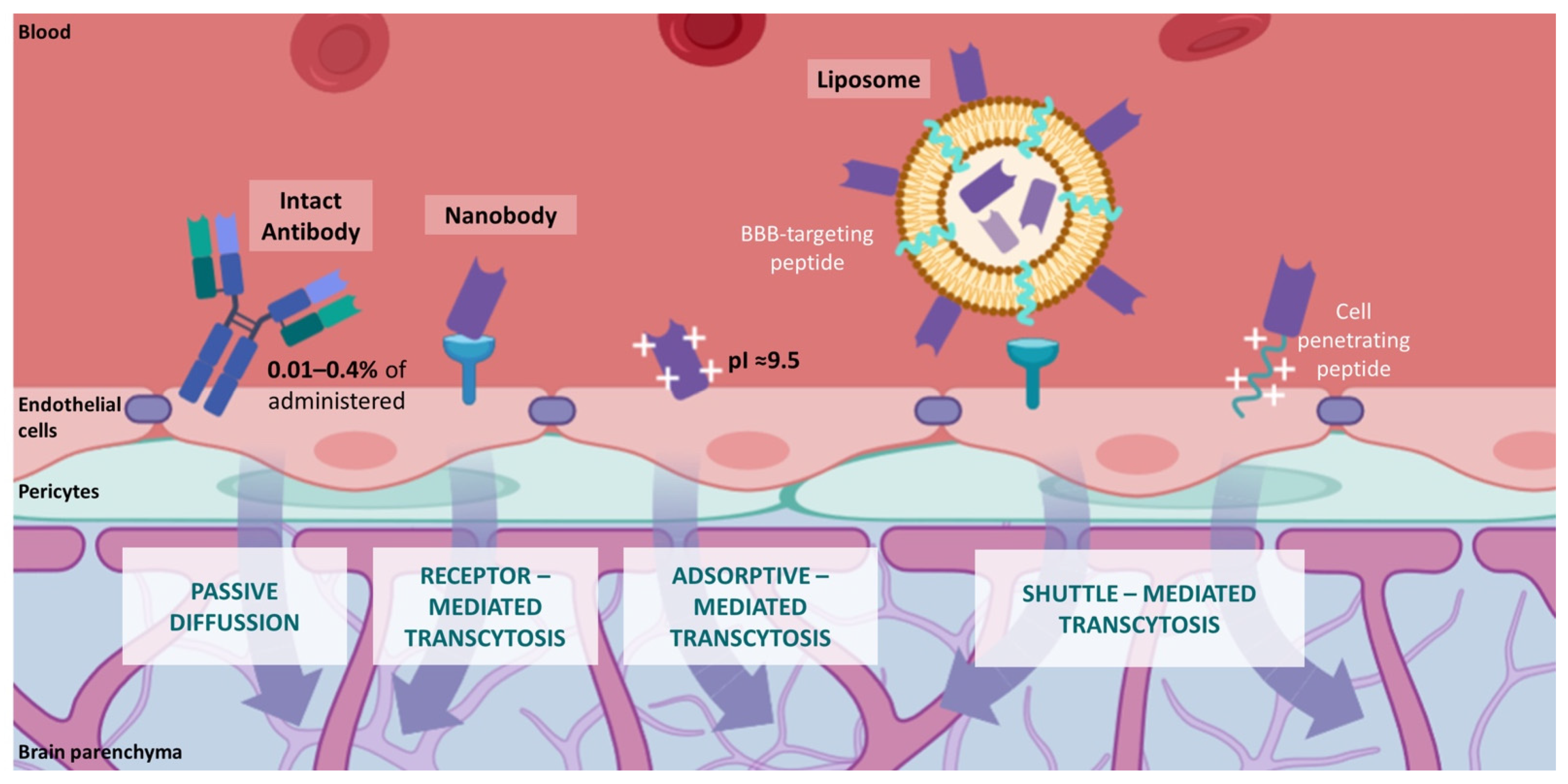
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/cancers14010074
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2014–2018. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, iii1–iii105.
- Wen, P.Y.; Santosh, K. Malignant gliomas in adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 492–507.
- Ahmed, R.; Oborski, M.J.; Hwang, M.; Lieberman, F.S.; Mountz, J.M. Malignant gliomas: Current perspectives in diagnosis, treatment, and early response assessment using advanced quantitative imaging methods. Cancer Manag. Res. 2014, 6, 149–170.
- Verhaak, R.G.W.; Hoadley, K.A.; Purdom, E.; Wang, V.; Qi, Y.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Miller, C.R.; Ding, L.; Golub, T.; Mesirov, J.P.; et al. Integrated Genomic Analysis Identifies Clinically Relevant Subtypes of Glioblastoma Characterized by Abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 98–110.
- Deb, P.; Sharma, M.C.; Mahapatra, A.K.; Agarwal, D.; Sarkar, C. Glioblastoma multiforme with long term survival. Neurol. India 2005, 53, 329–332.
- Henriksson, R.; Asklund, T.; Poulsen, H.S. Impact of therapy on quality of life, neurocognitive function and their correlates in glioblastoma multiforme: A review. J. Neurooncol. 2011, 104, 639–646.
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466.
- Esteller, M.; Garcia-Foncillas, J.; Andion, E.; Goodman, S.N.; Hidalgo, O.F.; Vanaclocha, V.; Baylin, S.B.; Herman, J.G. Inactivation of the DNA-Repair Gene MGMT and the Clinical Response of Gliomas to Alkylating Agents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 349, 1350–1354.
- Gilbert, M.R.; Wang, M.; Aldape, K.D.; Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Jaeckle, K.A.; Armstrong, T.S.; Wefel, J.S.; Won, M.; Blumenthal, D.T.; et al. Dose-dense temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma: A randomized phase III clinical trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 4085–4091.
- FDA Approves Expanded Indication for Medical Device to Treat Glioblastoma Multiforme|ESMO. Available online: https://www.esmo.org/oncology-news/archive/fda-approves-expanded-indication-for-medical-device-to-treat-glioblastoma-multiforme (accessed on 11 August 2021).
- Fabian, D.; Eibl, M.d.P.G.P.; Alnahhas, I.; Sebastian, N.; Giglio, P.; Puduvalli, V.; Gonzalez, J.; Palmer, J.D. Treatment of glioblastoma (GBM) with the addition of tumor-treating fields (TTF): A review. Cancers 2019, 11, 174.
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820.
- Reifenberger, G.; Wirsching, H.G.; Knobbe-Thomsen, C.B.; Weller, M. Advances in the molecular genetics of gliomas-implications for classification and therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 434–452.
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1215–1217.
- Capper, D.; Jones, D.T.W.; Sill, M.; Hovestadt, V.; Schrimpf, D.; Sturm, D.; Koelsche, C.; Sahm, F.; Chavez, L.; Reuss, D.E.; et al. DNA methylation-based classification of central nervous system tumours. Nature 2018, 555, 469–474.
- Brat, D.J.; Aldape, K.; Colman, H.; Holland, E.C.; Louis, D.N.; Jenkins, R.B.; Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, B.K.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; Stupp, R.; et al. cIMPACT-NOW update 3: Recommended diagnostic criteria for “Diffuse astrocytic glioma, IDH-wildtype, with molecular features of glioblastoma, WHO grade IV”. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 805–810.
- Tesileanu, C.M.S.; Dirven, L.; Wijnenga, M.M.J.; Koekkoek, J.A.F.; Vincent, A.J.P.E.; Dubbink, H.J.; Atmodimedjo, P.N.; Kros, J.M.; Van Duinen, S.G.; Smits, M.; et al. Survival of diffuse astrocytic glioma, IDH1/2 wildtype, with molecular features of glioblastoma, WHO grade IV: A confirmation of the cIMPACT-NOW criteria. Neuro-Oncology 2020, 22, 515–523.
- Lundy, P.; Domino, J.; Ryken, T.; Fouke, S.; McCracken, D.J.; Ormond, D.R.; Olson, J.J. The role of imaging for the management of newly diagnosed glioblastoma in adults: A systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline update. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 150, 95–120.
- Pandit-Taskar, N.; Postow, M.A.; Hellmann, M.D.; Harding, J.J.; Barker, C.A.; O’Donoghue, J.A.; Ziolkowska, M.; Ruan, S.; Lyashchenko, S.K.; Tsai, F.; et al. First-in-Humans Imaging with 89Zr-Df-IAB22M2C Anti-CD8 Minibody in Patients with Solid Malignancies: Preliminary Pharmacokinetics, Biodistribution, and Lesion Targeting. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 512–519.
- Freise, A.C.; Wu, A.M. In vivo imaging with antibodies and engineered fragments. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 67, 142–152.
- Kerdjoudj, R.; Pniok, M.; Alliot, C.; Kubíček, V.; Havlíčková, J.; Rösch, F.; Hermann, P.; Huclier-Markai, S. Scandium(III) complexes of monophosphorus acid DOTA analogues: A thermodynamic and radiolabelling study with 44Sc from cyclotron and from a 44Ti/44Sc generator. Dalt. Trans. 2016, 45, 1398–1409.
- Romero, E.; Martínez, A.; Oteo, M.; Ibañez, M.; Santos, M.; Morcillo, M.Á. Development and long-term evaluation of a new 68Ge/68Ga generator based on nano-SnO2 for PET imaging. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12756.
- González-Gómez, R.; Pazo-Cid, R.A.; Sarría, L.; Morcillo, M.Á.; Schuhmacher, A.J. Diagnosis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma by Immuno-Positron Emission Tomography. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1151.
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674.
- Da Pieve, C.; Makarem, A.; Turnock, S.; Maczynska, J.; Smith, G.; Kramer-Marek, G. Thiol-reactive POds-bearing bifunctional chelators for the development of EGFR-targeting AlF-affibody conjugates. Molecules 2020, 25, 1562.
- Lee, F.T.; Burvenich, I.J.G.; Guo, N.; Kocovski, P.; Tochon-Danguy, H.; Ackermann, U.; O’Keefe, G.J.; Gong, S.; Rigopoulos, A.; Liu, Z.; et al. l-Tyrosine Confers Residualizing Properties to a d-Amino Acid-Rich Residualizing Peptide for Radioiodination of Internalizing Antibodies. Mol. Imaging 2016, 15, 1536012116647535.
- Chakravarty, R.; Goel, S.; Valdovinos, H.F.; Hernandez, R.; Hong, H.; Nickles, R.J.; Cai, W. Matching the decay half-life with the biological half-life: ImmunoPET imaging with44Sc-labeled Cetuximab Fab fragment. Bioconjug. Chem. 2014, 25, 2197–2204.
- Tran, V.L.; Novell, A.; Tournier, N.; Gerstenmayer, M.; Schweitzer-Chaput, A.; Mateos, C.; Jego, B.; Bouleau, A.; Nozach, H.; Winkeler, A.; et al. Impact of blood-brain barrier permeabilization induced by ultrasound associated to microbubbles on the brain delivery and kinetics of cetuximab: An immunoPET study using 89Zr-cetuximab. J. Control. Release 2020, 328, 304–312.
- Luo, H.; Hernandez, R.; Hong, H.; Graves, S.A.; Yang, Y.; England, C.G.; Theuer, C.P.; Nickles, R.J.; Cai, W. Noninvasive brain cancer imaging with a bispecific antibody fragment, generated via click chemistry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12806–12811.
- Puttick, S.; Stringer, B.W.; Day, B.W.; Bruce, Z.C.; Ensbey, K.S.; Mardon, K.; Cowin, G.J.; Thurecht, K.J.; Whittaker, A.K.; Fay, M.; et al. EphA2 as a Diagnostic Imaging Target in Glioblastoma: A Positron Emission Tomography/Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Mol. Imaging 2015, 14, 385–395.
- Sheybani, N.D.; Breza, V.R.; Paul, S.; McCauley, K.S.; Berr, S.S.; Miller, G.W.; Neumann, K.D.; Price, R.J. ImmunoPET-informed sequence for focused ultrasound-targeted mCD47 blockade controls glioma. J. Control. Release 2021, 331, 19–29.
- Gaedicke, S.; Braun, F.; Prasad, S.; Machein, M.; Firat, E.; Hettich, M.; Gudihal, R.; Zhu, X.; Klingner, K.; Schüler, J.; et al. Noninvasive positron emission tomography and fluorescence imaging of CD133+ tumor stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E692–E701.
- Lesniak, W.G.; Chu, C.; Jablonska, A.; Du, Y.; Pomper, M.G.; Walczak, P.; Janowski, M. A distinct advantage to intraarterial delivery of 89Zr-bevacizumab in PET imaging of mice with and without osmotic opening of the blood–brain barrier. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 617–622.
- Liu, H.-L.; Hsu, P.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Huang, C.-W.; Chai, W.-Y.; Chu, P.-C.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chen, P.-Y.; Yang, L.-Y.; Kuo, J.S.; et al. Focused Ultrasound Enhances Central Nervous System Delivery of Bevacizumab for Malignant Glioma Treatment. Radiology 2016, 281, 99–108.
- Hernandez, R.; Sun, H.; England, C.G.; Valdovinos, H.F.; Barnhart, T.E.; Yang, Y.; Cai, W. ImmunoPET imaging of CD146 expression in malignant brain tumors. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 2563–2570.
- Yang, Y.; Hernandez, R.; Rao, J.; Yin, L.; Qu, Y.; Wu, J.; England, C.G.; Graves, S.A.; Lewis, C.M.; Wang, P.; et al. Targeting CD146 with a 64Cu-labeled antibody enables in vivo immunoPET imaging of high-grade gliomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E6525–E6534.
- Zhou, B.; Wang, H.; Liu, R.; Wang, M.; Deng, H.; Giglio, B.C.; Gill, P.S.; Shan, H.; Li, Z. PET Imaging of Dll4 expression in glioblastoma and colorectal cancer xenografts using 64Cu-labeled monoclonal antibody 61B. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 3527–3534.
- De Lucas, A.G.; Schuhmacher, A.J.; Oteo, M.; Romero, E.; Cámara, J.A.; de Martino, A.; Arroyo, A.G.; Morcillo, M.; Squatrito, M.; Martinez-Torrecuadrada, J.L.; et al. Targeting MT1-MMP as an immunoPET-based strategy for imaging gliomas. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158634.
- Gonzalez-Junca, A.; Reiners, O.; Borrero-Garcia, L.D.; Beckford-Vera, D.; Lazar, A.A.; Chou, W.; Braunstein, S.; VanBrocklin, H.; Franc, B.L.; Barcellos-Hoff, M.H. Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Functional Transforming Growth Factor β (TGFβ) Activity and Benefit of TGFβ Inhibition in Irradiated Intracranial Tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 109, 527–539.
- Den Hollander, M.W.; Bensch, F.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Oude Munnink, T.H.; Enting, R.H.; Den Dunnen, W.F.A.; Heesters, M.A.A.M.; Kruyt, F.A.E.; Lub-De Hooge, M.N.; De Groot, J.C.; et al. TGF-β antibody uptake in recurrent high-grade glioma imaged with 89Zr-fresolimumab PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 1310–1314.
- Pandya, D.N.; Sinha, A.; Yuan, H.; Mutkus, L.; Stumpf, K.; Marini, F.C.; Wadas, T.J. Imaging of fibroblast activation protein alpha expression in a preclinical mouse model of glioma using positron emission tomography. Molecules 2020, 25, 3672.
- Molotkov, A.; Doubrovin, M.; Bhatt, N.; Hsu, F.C.; Beserra, A.; Chopra, R.; Mintz, A. 3D optical/CT as a preclinical companion imaging platform for glioblastoma drug development. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 1686–1694.
- Liu, Q.; Jiang, L.; Li, K.; Li, H.; Lv, G.; Lin, J.; Qiu, L. Immuno-PET imaging of 68Ga-labeled nanobody Nb109 for dynamic monitoring the PD-L1 expression in cancers. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 1721–1733.
- Kasten, B.B.; Houson, H.A.; Coleman, J.M.; Leavenworth, J.W.; Markert, J.M.; Wu, A.M.; Salazar, F.; Tavaré, R.; Massicano, A.V.F.; Gillespie, G.Y.; et al. Positron emission tomography imaging with 89 Zr—Labeled anti—CD8 cys—Diabody reveals—Infiltration during oncolytic virus therapy in a glioma murine model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15384.
- Nigam, S.; McCarl, L.; Kumar, R.; Edinger, R.S.; Kurland, B.F.; Anderson, C.J.; Panigrahy, A.; Kohanbash, G.; Edwards, W.B. Preclinical ImmunoPET Imaging of Glioblastoma-Infiltrating Myeloid Cells Using Zirconium-89 Labeled Anti-CD11b Antibody. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2020, 22, 685–694.
- Foster, A.; Nigam, S.; Tatum, D.S.; Raphael, I.; Xu, J.; Kumar, R.; Plakseychuk, E.; Latoche, J.D.; Vincze, S.; Li, B.; et al. Novel theranostic agent for PET imaging and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy of tumour-infiltrating immune cells in glioma. EBioMedicine 2021, 71, 103571.
- Nobashi, T.W.; Mayer, A.T.; Xiao, Z.; Chan, C.T.; Chaney, A.M.; James, M.L.; Gambhir, S.S. Whole-body PET imaging of T cell response to Glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 6445–6456.
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. The Microenvironmental Landscape of Brain Tumors. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 326–341.
- Pyonteck, S.M.; Akkari, L.; Schuhmacher, A.J.; Bowman, R.L.; Sevenich, L.; Quail, D.F.; Olson, O.C.; Quick, M.L.; Huse, J.T.; Teijeiro, V.; et al. CSF-1R inhibition alters macrophage polarization and blocks glioma progression. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1264–1272.
- Quail, D.F.; Bowman, R.L.; Akkari, L.; Quick, M.L.; Schuhmacher, A.J.; Huse, J.T.; Holland, E.C.; Sutton, J.C.; Joyce, J.A. The tumor microenvironment underlies acquired resistance to CSF-1R inhibition in gliomas. Science 2016, 352, aad3018.
- Bouleau, A.; Lebon, V.; Truillet, C. PET imaging of immune checkpoint proteins in oncology. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 222, 107786.
- Lu, C.T.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Wong, H.L.; Cai, J.; Peng, L.; Tian, X.Q. Current approaches to enhance CNS delivery of drugs across the brain barriers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 2241–2257.
- Pardridge, W.M. Drug targeting to the brain. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1733–1744.
- Dong, X. Current strategies for brain drug delivery. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1481–1493.
- Brasnjevic, I.; Steinbusch, H.W.M.; Schmitz, C.; Martinez-Martinez, P. Delivery of peptide and protein drugs over the blood-brain barrier. Prog. Neurobiol. 2009, 87, 212–251.
- Levites, Y.; Smithson, L.A.; Price, R.W.; Dakin, R.S.; Yuan, B.; Sierks, M.R.; Kim, J.; McGowan, E.; Kim Reed, D.; Rosenberry, T.L.; et al. Insights into the mechanisms of action of anti-Aβ antibodies in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 2576–2578.
- Pepinsky, R.B.; Shao, Z.; Ji, B.; Wang, Q.; Meng, G.; Walus, L.; Lee, X.; Hu, Y.; Graff, C.; Garber, E.; et al. Exposure levels of anti-LINGO-1 Li81 antibody in the central nervous system and dose-efficacy relationships in rat spinal cord remyelination models after systemic administration. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 339, 519–529.
- Zhang, Y.; Pardridge, W.M. Rapid transferrin efflux from brain to blood across the blood-brain barrier. J. Neurochem. 2001, 76, 1597–1600.
- Siegelman, J.; Fleit, H.B.; Peress, N.S. Characterization of immunoglobulin G-Fe receptor activity in the outflow system of the cerebrospinal fluid. Cell Tissue Res. 1987, 248, 599–605.
- Cooper, P.R.; Ciambrone, G.J.; Kliwinski, C.M.; Maze, E.; Johnson, L.; Li, Q.; Feng, Y.; Hornby, P.J. Efflux of monoclonal antibodies from rat brain by neonatal Fc receptor, FcRn. Brain Res. 2013, 1534, 13–21.
- Ruano-Salguero, J.S.; Lee, K.H. Antibody transcytosis across brain endothelial-like cells occurs nonspecifically and independent of FcRn. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3685.
- Salvador, J.P.; Vilaplana, L.; Marco, M.P. Nanobody: Outstanding features for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 1703–1713.
- Krasniqi, A.; D’Huyvetter, M.; Devoogdt, N.; Frejd, F.Y.; Sörensen, J.; Orlova, A.; Keyaerts, M.; Tolmachev, V. Same-day imaging using small proteins: Clinical experience and translational prospects in oncology. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 885–891.
- Širochmanová, I.; Čomor, Ľ.; Káňová, E.; Jiménez-Munguía, I.; Tkáčová, Z.; Bhide, M. Permeability of the Blood-Brain Barrier and Transport of Nanobodies Across the Blood-Brain Barrier. Folia Vet. 2018, 62, 59–66.
- Muyldermans, S.; Baral, T.N.; Retamozzo, V.C.; De Baetselier, P.; De Genst, E.; Kinne, J.; Leonhardt, H.; Magez, S.; Nguyen, V.K.; Revets, H.; et al. Camelid immunoglobulins and nanobody technology. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 128, 178–183.
- Hamers-Casterman, C.; Atarhouch, T.; Muyldermans, S.; Robinson, G.; Hammers, C.; Songa, E.B.; Bendahman, N.; Hammers, R. Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains. Nature 1993, 363, 446–448.
- Muyldermans, S. Nanobodies: Natural single-domain antibodies. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 775–797.
- Jovčevska, I.; Muyldermans, S. The Therapeutic Potential of Nanobodies. BioDrugs 2020, 34, 11–26.
- Steeland, S.; Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Libert, C. Nanobodies as therapeutics: Big opportunities for small antibodies. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 1076–1113.
- Jovčevska, I.; Zupanec, N.; Kočevar, N.; Cesselli, D.; Podergajs, N.; Stokin, C.L.; Myers, M.P.; Muyldermans, S.; Ghassabeh, G.H.; Motaln, H.; et al. TRIM28 and β-actin identified via nanobody-based reverse proteomics approach as possible human glioblastoma biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113688.
- Jovčevska, I.; Zupanec, N.; Urlep, Ž.; Vranic, A.; Matos, B.; Stokin, C.L.; Muyldermans, S.; Myers, M.P.; Buzdin, A.A.; Petrov, I.; et al. Differentially expressed proteins in glioblastoma multiforme identified with a nanobody-based anti-proteome approach and confirmed by OncoFinder as possible tumor-class predictive biomarker candidates. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 44141–44158.
- Van De Water, J.A.J.M.; Bagci-Onder, T.; Agarwal, A.S.; Wakimoto, H.; Roovers, R.C.; Zhu, Y.; Kasmieh, R.; Bhere, D.; Van Bergen En Henegouwen, P.M.P.; Shah, K. Therapeutic stem cells expressing variants of EGFR-specific nanobodies have antitumor effects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16642–16647.
- Samec, N.; Jovcevska, I.; Stojan, J.; Zottel, A.; Liovic, M.; Myers, M.P.; Muyldermans, S.; Šribar, J.; Križaj, I.; Komel, R. Glioblastoma-specific anti-TUFM nanobody for in-vitro immunoimaging and cancer stem cell targeting. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 17282–17299.
- Zottel, A.; Jovčevska, I.; Šamec, N.; Mlakar, J.; Šribar, J.; Križaj, I.; Skoblar Vidmar, M.; Komel, R. Anti-vimentin, anti-TUFM, anti-NAP1L1 and anti-DPYSL2 nanobodies display cytotoxic effect and reduce glioblastoma cell migration. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12.
- Ruiz-López, E.; Schuhmacher, A.J. Transportation of Single-Domain Antibodies through the Blood-Brain Barrier. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1131.
- Gao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Lu, H. Single domain antibody-based vectors in the delivery of biologics across the blood–brain barrier: A review. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 11, 1818–1828.
- Pothin, E.; Lesuisse, D.; Lafaye, P. Brain delivery of single-domain antibodies: A focus on VHH and VNAR. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 937.
- Bélanger, K.; Iqbal, U.; Tanha, J.; MacKenzie, R.; Moreno, M.; Stanimirovic, D. Single-Domain Antibodies as Therapeutic and Imaging Agents for the Treatment of CNS Diseases. Antibodies 2019, 8, 27.
- Fishman, J.B.; Rubin, J.B.; Handrahan, J.V.; Connor, J.R.; Fine, R.E. Receptor-mediated transcytosis of transferrin across the blood-brain barrier. J. Neurosci. Res. 1987, 18, 299–304.
- Fillebeen, C.; Descamps, L.; Dehouck, M.P.; Fenart, L.; Benaïssa, M.; Spik, G.; Cecchelli, R.; Pierce, A. Receptor-mediated transcytosis of lactoferrin through the blood-brain barrier. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 7011–7017.
- Muruganandam, A.; Tanha, J.; Narang, S.; Stanimirovic, D. Selection of phage-displayed llama single-domain antibodies that transmigrate across human blood-brain barrier endothelium. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 240–242.
- Abulrob, A.; Sprong, H.; Van Bergen En Henegouwen, P.; Stanimirovic, D. The blood-brain barrier transmigrating single domain antibody: Mechanisms of transport and antigenic epitopes in human brain endothelial cells. J. Neurochem. 2005, 95, 1201–1214.
- Farrington, G.K.; Caram-Salas, N.; Haqqani, A.S.; Brunette, E.; Eldredge, J.; Pepinsky, B.; Antognetti, G.; Baumann, E.; Ding, W.; Garber, E.; et al. A novel platform for engineering blood-brain barrier-crossing bispecific biologics. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 4764–4778.
- Tamai, I.; Sai, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Kamata, M.; Wakamiya, T.; Tsuji, A. Structure-internalization relationship for adsorptive-mediated endocytosis of basic peptides at the blood-brain barrier. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 280, 410–415.
- Hervé, F.; Ghinea, N.; Scherrmann, J.M. CNS delivery via adsorptive transcytosis. AAPS J. 2008, 10, 455–472.
- Li, T.; Bourgeois, J.P.; Celli, S.; Glacial, F.; Le Sourd, A.M.; Mecheri, S.; Weksler, B.; Romero, I.; Couraud, P.O.; Rougeon, F.; et al. Cell-penetrating anti-GFAP VHH and corresponding fluorescent fusion protein VHH-GFP spontaneously cross the blood-brain barrier and specifically recognize astrocytes: Application to brain imaging. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 3969–3979.
- Li, T.; Vandesquille, M.; Koukouli, F.; Dudeffant, C.; Youssef, I.; Lenormand, P.; Ganneau, C.; Maskos, U.; Czech, C.; Grueninger, F.; et al. Camelid single-domain antibodies: A versatile tool for in vivo imaging of extracellular and intracellular brain targets. J. Control. Release 2016, 243, 1–10.
- Rotman, M.; Welling, M.M.; Bunschoten, A.; De Backer, M.E.; Rip, J.; Nabuurs, R.J.A.; Gaillard, P.J.; Van Buchem, M.A.; Van Der Maarel, S.M.; Van Der Weerd, L. Enhanced glutathione PEGylated liposomal brain delivery of an anti-amyloid single domain antibody fragment in a mouse model for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Control. Release 2015, 203, 40–50.
- van Lith, S.A.M.; van den Brand, D.; Wallbrecher, R.; van Duijnhoven, S.M.J.; Brock, R.; Leenders, W.P.J. A Conjugate of an Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) VHH and a Cell-Penetrating Peptide Drives Receptor Internalization and Blocks EGFR Activation. ChemBioChem 2017, 18, 2390–2394.
- Yin, W.; Zhao, Y.; Kang, X.; Zhao, P.; Fu, X.; Mo, X.; Wan, Y.; Huang, Y. BBB-penetrating codelivery liposomes treat brain metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer with EGFRT790M mutation. Theranostics 2020, 10, 6122–6135.
- Chakravarty, R.; Goel, S.; Cai, W. Nanobody: The “magic bullet” for molecular imaging? Theranostics 2014, 4, 386–398.
- Iqbal, U.; Trojahn, U.; Albaghdadi, H.; Zhang, J.; O’Connor-Mccourt, M.; Stanimirovic, D.; Tomanek, B.; Sutherland, G.; Abulrob, A. Kinetic analysis of novel mono- and multivalent VHH-fragments and their application for molecular imaging of brain tumours: RESEARCH PAPER. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1016–1028.
- Fatehi, D.; Baral, T.N.; Abulrob, A. In vivo imaging of brain cancer using epidermal growth factor single domain antibody bioconjugated to near-infrared quantum dots. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 5355–5362.
- Iqbal, U.; Albaghdadi, H.; Luo, Y.; Arbabi, M.; Desvaux, C.; Veres, T.; Stanimirovic, D.; Abulrob, A. Molecular imaging of glioblastoma multiforme using anti-insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-7 single-domain antibodies. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 1606–1616.
- Iqbal, U.; Albaghdadi, H.; Nieh, M.P.; Tuor, U.I.; Mester, Z.; Stanimirovic, D.; Katsaras, J.; Abulrob, A. Small unilamellar vesicles: A platform technology for molecular imaging of brain tumors. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 195102.
- Vosjan, M.J.W.D.; Vercammen, J.; Kolkman, J.A.; Stigter-Van Walsum, M.; Revets, H.; Van Dongen, G.A.M.S. Nanobodies targeting the hepatocyte growth factor: Potential new drugs for molecular cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 1017–1025.
- Vandesquille, M.; Li, T.; Po, C.; Ganneau, C.; Lenormand, P.; Dudeffant, C.; Czech, C.; Grueninger, F.; Duyckaerts, C.; Delatour, B.; et al. Chemically-defined camelid antibody bioconjugate for the magnetic resonance imaging of Alzheimer’s disease. mAbs 2017, 9, 1016–1027.
- Rotman, M.; Welling, M.M.; van den Boogaard, M.L.; Moursel, L.G.; van der Graaf, L.M.; van Buchem, M.A.; van der Maarel, S.M.; van der Weerd, L. Fusion of hIgG1-Fc to 111In-anti-amyloid single domain antibody fragment VHH-pa2H prolongs blood residential time in APP/PS1 mice but does not increase brain uptake. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2015, 42, 695–702.
- Debie, P.; Devoogdt, N.; Hernot, S. Targeted Nanobody-Based Molecular Tracers for Nuclear Imaging and Image-Guided Surgery. Antibodies 2019, 8, 12.
- Duggan, S. Caplacizumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2018, 78, 1639–1642.
- Scully, M.; Cataland, S.R.; Peyvandi, F.; Coppo, P.; Knöbl, P.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Metjian, A.; de la Rubia, J.; Pavenski, K.; Callewaert, F.; et al. Caplacizumab Treatment for Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 335–346.
- Keyaerts, M.; Xavier, C.; Heemskerk, J.; Devoogdt, N.; Everaert, H.; Ackaert, C.; Vanhoeij, M.; Duhoux, F.P.; Gevaert, T.; Simon, P.; et al. Phase I study of 68Ga-HER2-Nanobody for PET/CT assessment of HER2 expression in breast carcinoma. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 27–33.
- Xing, Y.; Chand, G.; Liu, C.; Cook, G.J.R.; O’Doherty, J.; Zhao, L.; Wong, N.C.L.; Meszaros, L.K.; Ting, H.H.; Zhao, J. Early phase I study of a 99mTc-labeled anti-programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) single-domain antibody in SPECT/CT assessment of PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1213–1220.
