M. oleifera contains several bioactive phytochemicals including flavonoids and isothiocyanates; polyphenols, carotenoids, alkaloids, and terpenoids; and triterpenoids, moringyne, monopalmitic, di-oleic triglyceride, campesterol, stigmasterol, β-sitosterol, avenasterol, and vitamin A. These bioactive phytochemicals are found in M. oleifera roots, fruits, and seeds. These phytochemicals have medicinal properties which have been shown to be effective antioxidant, antimicrobial, inflammatory, and anti-carcinogenic agents. More studies are required to explore the role of bioactive phytochemicals specially in kidney diseases. M. oleifera also possesses a variety of pharmacological properties, which are closely associated with the presence of its bioactive compounds. Therefore, in the following section we highlighted the pharmacological potential of M. oleifera. M. oleifera showed pharmacological potential against some plausible factors such as oxidative stress, inflammation, fibrosis, and other pathologies responsible for kidney diseases.
- Moringa oleifera
- antioxidant
- anti-aging
- fibrosis
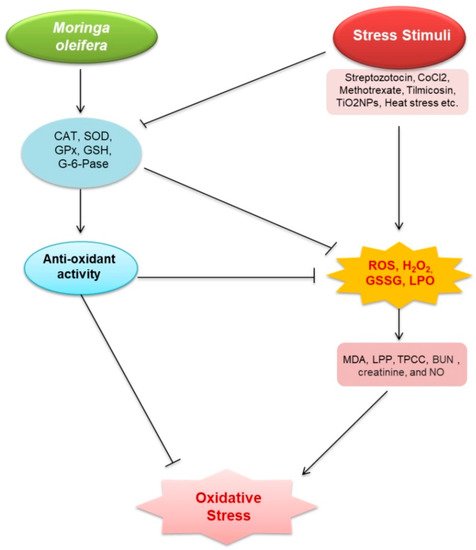
1. Oxidative Stress
| Sl. No. |
Experimental Model | Treatment Dose of Moringa Extract |
Major Research Outcomes | Molecular Markers | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | STZ-induced nephrotoxic male Wister rats | 250 mg/kg b wt for 6 weeks | Amelioration of oxidative stress and inflammation | ↓MDA and ROS ↑CAT, SOD, GSH, and GPx ↓TNF-α and IL-6 |
[8] |
| 2 | db/db mice | 150 mg/kg/day for 5 weeks | Oxidative stress and inflammation | ↓LDL ↓TNF-a, ↓IL-1b, ↓IL-6, ↓COX-2, and ↓iNOS |
[9] |
| 3 | Ischemia-reperfusion induced Wistar rats | 200 mg/kg for 7 days; 400 mg/kg, 7 days by flank incision | Oxidative stress | ↓MDA, ↑PC, ↓AOPP, ↓NO, ↓H2O2, ↓GPx and GST, ↑GSH |
[10] |
| 4 | CoCl2-induced rats | Orally received 400 mg/kg bw/day for 6 weeks | Oxidative stress Inflammation and Apoptosis |
↓MDA, ↓H2O2, ↓8-OHdG, ↓CRP, ↓MPO, ↓TNF-α, and ↓NO ↓TNF-α, and NO↓ |
[11] |
| 5 | Gentamicin (GENT) induced Wistar rats | Orally treated with 100, 200 and 400 mg/kg/day for 28 days | Oxidative stress | ↓K+ level, ↓plasma creatinine, ↑Creatinine clearance, ↓MDA, ↑SOD |
[12] |
| 6 | Nickel-induced Wistar rats | 5% M. oleifera 10% M. oleifera 15% M. oleifera |
Oxidative stress | ↓plasma creatinine, ↓urea, and ↑potassium, ↑plasma level of sodium |
[13] |
| 7 | Methotrexate (MTX)-induced Mice | 300 mg/kg body weight, orally for 7 days | Oxidative stress Inflammation Apoptosis |
↓urea and ↓creatinine, ↓total protein, ↓MDA, ↑SOD and ↑GSH, ↑HO-1, ↑Nrf-2 ↓NF-kB, ↓Caspase-9 |
[14] |
| 8 | Tilmicosin (Til) induced Sprague Dawley rats | 400 or 800 mg/kg bw, by oral gavage for 7 days | Oxidative stress, inflammation |
↓H2O2, ↓MDA, ↑SOD, ↑GPx, mRNA expression ↓TNF-α, ↓IL-1β |
[15] |
| 9 | Hg-induced Male Wistar rats | 1.798 mg/kg p.o three times per week for 21 days | Oxidative stress | ↓MDA level, ↑SOD, and ↑CAT | [16] |
| 10 | TiO2NPs induce male albino rats | Daily oral dose of 400 mg/kg b w for 60 days | Oxidative stress Inflammation |
↓MDA, ↑SOD, ↑GSH, ↑GST,↑GPx, ↑Total thiol and ↑HO-1, ↑Nrf2 ↓KIM-1, ↓NF-кB, ↓TNF-α, and ↓HSP-70 |
[17] |
| 11 | NaF induced Oreochromis niloticus | 6.1 mg/L for 8 weeks | Oxidative stress | ↓MDA, ↑SOD, ↑CAT, ↑GSH, ↑GPx, ↑TAC |
[18] |
| 12 | Gentamicin-induced (80 mg/kg) Rabbit | 150 mg/kg body for 10 days, 300 mg/kg wt. for 10 days | Oxidative stress | ↓Serum urea and creatinine levels, ↓LPO |
[19] |
| 13 | Lead treated Male Wistar rats | 500 mg/kg for 7 days | Oxidative stress | ↓ROS, ↓LPP, ↓TPCC, ↓metal content, | [20] |
| 15 | Beryllium-induced rats | 150 mg/kg daily for 5 weeks | Oxidative stress | ↓LPO, ↑GSH, ↑antioxidant enzymes activities, ↑G-6-Pase activity | [21] |
| 16 | Arsenic-induced toxicity in rats | 500 mg/kg, orally, once daily | Oxidative stress | ↑ALAD, ↑GSH,↓ROS, ↑SOD, ↑Catalase, ↓GSSG |
[22] |
| 17 | Heat stress (HS)-induced rabbits | 100, 200, and 300 mg, 6 weeks | Inflammation | ↑cortisol, ↑adrenaline, ↑leptin, ↓IFN-γ, ↓TNF-α, ↓urea, and ↓creatinine, ↓IL-10, ↑NK, and ↑Treg |
[23] |
| 18 | ML-induced male Sprague Dawley rats | Orally 800 mg/kg bw 800 mg/kg bw | Oxidative stress, Inflammation Apoptosis |
↓Total bilirubin, ↓direct bilirubin, ↓indirect bilirubin, ↓urea, and ↓creatinine ↑serum levels of protein, ↑albumin, ↑globulin, ↑GPx, and ↑CAT ↓KIM-1, and ↓TNF-α and ↑Bcl-2, ↓TIMP-1 |
[24] |
| 20 | Seabream (Sparus aurata) | 10% M. oleifera 4 weeks | Inflammation | ↓TGF-β and ↓TNF-α ↑ACH50 and ↑lysozyme activities and ↑IgM level ↑ (lyso and c3), ↑ (occludin and zo-1) |
[25] |
| 21 | APAP-treated mice | 100 mg/kg of bw, 200 mg/kg bw |
Oxidative stress, inflammation |
↑SOD, ↑CAT and ↑GPx, ↓MDA, ↓TNF-α, ↓IL-1β, ↓IL-6, ↓IL-10 |
[26] |
| 22 | Iodide injected Rabbit | 50 mg/kg body weight, orally once daily for 27 sequential days | Oxidative stress | ↓MDA, ↑GSH, ↓NO, ↓lipid peroxidation, ↓ROS | [27] |
| 23 | Glycerol induced rat | 50 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg for 7 days | Oxidative stress Inflammation |
↑SOD, ↑GST, ↑GPX, ↑GSH ↓MPO, ↓Creatinine, ↓BUN, ↓NO ↓H2O2, ↓AOPP, ↓MDA, ↓PC,↑PT, ↑NPT,↓KIM-1 and ↓NF-ҝB |
[28] |
| 24 | Salmonella-induced mice | 14, 42 and 84 mg/kg/day for 28 days | Oxidative stress inflammation |
↑HO-1, ↑SOD-2 ↑Nrf-2 |
[29] |
| 25 | STZ-induced rats | 250 mg/kg and SRC. 42 days | Oxidative stress inflammation |
↓LDL, ↑HDL, ↓CHOL, ↑ORAC ↓IL-6, ↓TNF-α, and ↓MCP-1 |
[30] |
| 26 | TGF-β-treated rat kidney fibroblast cells | 10, 50, and 100 µg/mL | Fibrosis | ↓Type I collagen, fibronectin, and PAI-1 ↓TβRII and Smad4, and phospho-ERK |
[31] |
| 27 | Gentamicin-induced Wistar rats | 28 days at graded doses of 100, 200 and 400 mg/kg | Nephrotoxicity | ↓Creatinine and MDA ↑SOD |
[12] |
2. Inflammation
3. Fibrosis
4. Other Pathologies Those Are Associated with Kidney Diseases
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/plants10122818
References
- Daenen, K.; Andries, A.; Mekahli, D.; Van Schepdael, A.; Jouret, F.; Bammens, B. Oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 975–991.
- Ling, X.C.; Kuo, K.-L. Oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease. Renal. Replace. Ther. 2018, 4, 53.
- Uddin, M.J.; Kim, E.H.; Hannan, M.A.; Ha, H. Pharmacotherapy against oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease: Promising small molecule natural products targeting nrf2-ho-1 signaling. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 258.
- Sohn, M.; Kim, K.; Uddin, M.J.; Lee, G.; Hwang, I.; Kang, H.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.H.; Ha, H. Delayed treatment with fenofibrate protects against high-fat diet-induced kidney injury in mice: The possible role of ampk autophagy. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2017, 312, F323–F334.
- Hwang, I.; Uddin, M.J.; Lee, G.; Jiang, S.; Pak, E.S.; Ha, H. Peroxiredoxin 3 deficiency accelerates chronic kidney injury in mice through interactions between macrophages and tubular epithelial cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 131, 162–172.
- Rapa, S.F.; Di Iorio, B.R.; Campiglia, P.; Heidland, A.; Marzocco, S. Inflammation and oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease-potential therapeutic role of minerals, vitamins and plant-derived metabolites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 263.
- Pakade, V.; Cukrowska, E.; Chimuka, L. Comparison of antioxidant activity of Moringa oleifera and selected vegetables in South Africa. S. Af. J. Sci. 2013, 109.
- Omodanisi, E.I.; Aboua, Y.G.; Oguntibeju, O.O. Assessment of the anti-hyperglycaemic, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of the methanol extract of Moringa oleifera in diabetes-induced nephrotoxic male Wistar rats. Molecules 2017, 22, 439.
- Tang, Y.; Choi, E.J.; Han, W.C.; Oh, M.; Kim, J.; Hwang, J.Y.; Park, P.J.; Moon, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, E.K. Moringa oleifera from cambodia ameliorates oxidative stress, hyperglycemia, and kidney dysfunction in type 2 diabetic mice. J. Med. Food 2017, 20, 502–510.
- Akinrinde, A.S.; Oduwole, O.; Akinrinmade, F.J.; Bolaji-Alabi, F.B. Nephroprotective effect of methanol extract of Moringa oleifera leaves on acute kidney injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Afr. Health Sci. 2020, 20, 1382–1396.
- Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Khalil, S.R.; Awad, A.; Abu Zeid, E.H.; El-Aziz, R.A.; El-Serehy, H.A. Ethanolic extract of Moringa oleifera leaves influences NF-κB signaling pathway to restore kidney tissue from cobalt-mediated oxidative injury and inflammation in rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1031.
- Nafiu, A.O.; Akomolafe, R.O.; Alabi, Q.K.; Idowu, C.O.; Odujoko, O.O. Effect of fatty acids from ethanol extract of Moringa oleifera seeds on kidney function impairment and oxidative stress induced by gentamicin in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109154.
- Adeyemi, O.S.; Elebiyo, T.C. Moringa oleifera supplemented diets prevented nickel-induced nephrotoxicity in Wistar Rats. J. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 2014, 958621.
- Soliman, M.M.; Aldhahrani, A.; Alkhedaide, A.; Nassan, M.A.; Althobaiti, F.; Mohamed, W.A. The ameliorative impacts of Moringa oleifera leaf extract against oxidative stress and methotrexate-induced hepato-renal dysfunction. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110259.
- Abou-Zeid, S.M.; Ahmed, A.I.; Awad, A.; Mohammed, W.A.; Metwally, M.M.M.; Almeer, R.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Khalil, S.R. Moringa oleifera ethanolic extract attenuates tilmicosin-induced renal damage in male rats via suppression of oxidative stress, inflammatory injury, and intermediate filament proteins mRNA expression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110997.
- Abarikwu, S.O.; Benjamin, S.; Ebah, S.G.; Obilor, G.; Agbam, G. Protective effect of Moringa oleifera oil against HgCl2-induced hepato- and nephro-toxicity in rats. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 28, 337–345.
- Abdou, K.H.; Moselhy, W.A.; Mohamed, H.M.; El-Nahass, E.S.; Khalifa, A.G. Moringa oleifera leaves extract protects titanium dioxide nanoparticles-induced nephrotoxicity via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling and amelioration of oxidative stress. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 2019, 187, 181–191.
- Ahmed, N.F.; Sadek, K.M.; Soliman, M.K.; Khalil, R.H.; Khafaga, A.F.; Ajarem, J.S.; Maodaa, S.N.; Allam, A.A. Moringa oleifera leaf extract repairs the oxidative misbalance following Sub-chronic exposure to sodium fluoride in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Animals 2020, 10, 626.
- Ouédraogo, M.; Lamien-Sanou, A.; Ramdé, N.; Ouédraogo, A.S.; Ouédraogo, M.; Zongo, S.P.; Goumbri, O.; Duez, P.; Guissou, P.I. Protective effect of Moringa oleifera leaves against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rabbits. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 65, 335–339.
- Velaga, M.K.; Daughtry, L.K.; Jones, A.C.; Yallapragada, P.R.; Rajanna, S.; Rajanna, B. Attenuation of lead-induced oxidative stress in rat brain, liver, kidney and blood of male Wistar rats by Moringa oleifera seed powder. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2014, 33, 323–337.
- Agrawal, N.D.; Nirala, S.K.; Shukla, S.; Mathur, R. Co-administration of adjuvants along with Moringa oleifera attenuates beryllium-induced oxidative stress and histopathological alterations in rats. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 1465–1473.
- Gupta, R.; Kannan, G.M.; Sharma, M.; SJ, S.F. Therapeutic effects of Moringa oleifera on arsenic-induced toxicity in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 20, 456–464.
- Abdel-Latif, M.; Sakran, T.; Badawi, Y.K.; Abdel-Hady, D.S. Influence of Moringa oleifera extract, vitamin C, and sodium bicarbonate on heat stress-induced HSP70 expression and cellular immune response in rabbits. Cell Stress Chaperones 2018, 23, 975–984.
- Abd-Elhakim, Y.M.; Mohamed, W.A.M.; El Bohi, K.M.; Ali, H.A.; Mahmoud, F.A.; Saber, T.M. Prevention of melamine-induced hepatorenal impairment by an ethanolic extract of Moringa oleifera: changes in KIM-1, TIMP-1, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and inflammation-related genes. Gene 2021, 764, 145083.
- Mansour, A.T.; Miao, L.; Espinosa, C.; García-Beltrán, J.M.; Ceballos Francisco, D.C.; Esteban, M. Effects of dietary inclusion of Moringa oleifera leaves on growth and some systemic and mucosal immune parameters of seabream. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 44, 1223–1240.
- Karthivashan, G.; Kura, A.U.; Arulselvan, P.; Md Isa, N.; Fakurazi, S. The modulatory effect of Moringa oleifera leaf extract on endogenous antioxidant systems and inflammatory markers in an acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxic mice model. Peer J. 2016, 4, e2127.
- Altaee, R.A.; Fadheel, Q.J. The nephroprotective effects of moringa oleifera extract against contrast induced nephrotoxicity. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2021, 33, 63–70.
- Adedapo, A.; Ue, E.; Falayi, O.; Ogunpolu, B.; Omobowale, T.; Oyagbemi, A.; Oguntibeju, O. Methanol stem extract of Moringa oleifera mitigates glycerol-induced acute kidney damage in rats through modulation of KIM-1 and NF-kB signaling pathways. Sci. Afr. 2020, 9, e00493.
- Widodo, N.; Widjajanto, E.; Jatmiko, Y.; Rifa’i, M. Red Moringa oleifera leaf fermentation extract protecting Hepatotoxicity in Balb/C mice injected with Salmonella typhi through Nrf-2, HO-1, and SOD-2 signaling pathways. R. J. Pharm. Technol. 2020, 13, 5947–5952.
- Omodanisi, E.I.; Aboua, Y.G.; Chegou, N.N.; Oguntibeju, O.O. Hepatoprotective, antihyperlipidemic, and anti-inflammatory Activity of Moringa oleifera in diabetic-induced damage in male Wistar Rats. Pharmacogn. Res. 2017, 9, 182–187.
- Park, S.-H.; Chang, Y.-C. Anti-fibrotic effects by Moringa root extract in rat kidney fibroblast. J. Life Sci. 2012, 22, 1371–1377.
- Valavanidis, A.; Vlachogianni, T.; Fiotakis, C. 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG): A critical biomarker of oxidative stress and carcinogenesis. J. Environ. Sci. Health C. Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2009, 27, 120–139.
- Oyagbemi, A.A.; Omobowale, T.O.; Azeez, I.O.; Abiola, J.O.; Adedokun, R.A.; Nottidge, H.O. Toxicological evaluations of methanolic extract of Moringa oleifera leaves in liver and kidney of male Wistar rats. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2013, 24, 307–312.
- Anders, H.J.; Schaefer, L. Beyond tissue injury-damage-associated molecular patterns, toll-like receptors, and inflammasomes also drive regeneration and fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 1387–1400.
- Uddin, M.J.; Pak, E.S.; Ha, H. Carbon monoxide releasing molecule-2 protects mice against acute kidney injury through inhibition of ER stress. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 22, 567–575.
- Uddin, M.J.; Jeong, J.; Pak, E.S.; Ha, H. Co-releasing molecule-2 prevents acute kidney Injury through suppression of ROS-Fyn-ER stress signaling in mouse model. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9947772.
- Mackensen-Haen, S.; Bader, R.; Grund, K.E.; Bohle, A. Correlations between renal cortical interstitial fibrosis, atrophy of the proximal tubules and impairment of the glomerular filtration rate. Clin. Nephrol. 1981, 15, 167–171.
- Akcay, A.; Nguyen, Q.; Edelstein, C.L. Mediators of inflammation in acute kidney injury. Mediators Inflamm. 2009, 2009, 137072.
- Akchurin, O.M.; Kaskel, F. Update on inflammation in chronic kidney disease. Blood Purif. 2015, 39, 84–92.
- Elhelaly, A.E.; AlBasher, G.; Alfarraj, S.; Almeer, R.; Bahbah, E.I.; Fouda, M.M.A.; Bungău, S.G.; Aleya, L.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Protective effects of hesperidin and diosmin against acrylamide-induced liver, kidney, and brain oxidative damage in rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 35151–35162.
- Behl, T.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, L.; Sehgal, A.; Zengin, G.; Brata, R.; Fratila, O.; Bungau, S. Exploring the multifaceted therapeutic potential of withaferin a and its derivatives. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 571.
- Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Abushouk, A.I.; Bahbah, E.I.; Bungău, S.G.; Alyousif, M.S.; Aleya, L.; Alkahtani, S. Fucoidan protects against subacute diazinon-induced oxidative damage in cardiac, hepatic, and renal tissues. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 11554–11564.
- Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Abo El-Ela, F.I.; Alshahrani, F.K.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Al-Zharani, M.; Almutairi, B.; Alyousif, M.S.; Bungau, S.; Aleya, L.; Alkahtani, S. Protective effects of thymoquinone against acrylamide-induced liver, kidney and brain oxidative damage in rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 37709–37717.
- Jaja-Chimedza, A.; Graf, B.L.; Simmler, C.; Kim, Y.; Kuhn, P.; Pauli, G.F.; Raskin, I. Biochemical characterization and anti-inflammatory properties of an isothiocyanate-enriched moringa (Moringa oleifera) seed extract. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182658.
- Oblak, M.; Randic, M.; Solmajer, T. Quantitative structure-activity relationship of flavonoid analogues. 3. Inhibition of p56lck protein tyrosine kinase. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2000, 40, 994–1001.
- Olszanecki, R.; Gebska, A.; Kozlovski, V.I.; Gryglewski, R.J. Flavonoids and nitric oxide synthase. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2002, 53, 571–584.
- Sulaiman, M.R.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Bujarimin, A.S.; Somchit, M.N.; Israf, D.A.; Moin, S. Evaluation of Moringa oleifera aqueous extract for antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities in animal models. Pharm. Biol. 2008, 46, 838–845.
- García-Mediavilla, V.; Crespo, I.; Collado, P.S.; Esteller, A.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; Tuñón, M.J.; González-Gallego, J. The anti-inflammatory flavones quercetin and kaempferol cause inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase-2 and reactive C-protein, and down-regulation of the nuclear factor kappaB pathway in Chang Liver cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 557, 221–229.
- Hämäläinen, M.; Nieminen, R.; Vuorela, P.; Heinonen, M.; Moilanen, E. Anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids: Genistein, kaempferol, quercetin, and daidzein inhibit STAT-1 and NF-kappaB activations, whereas flavone, isorhamnetin, naringenin, and pelargonidin inhibit only NF-kappaB activation along with their inhibitory effect on iNOS expression and NO production in activated macrophages. Mediators. Inflamm. 2007, 2007, 45673.
- Tan, W.S.; Arulselvan, P.; Karthivashan, G.; Fakurazi, S. Moringa oleifera flower extract suppresses the activation of inflammatory mediators in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated raw 264.7 macrophages via NF-κB Pathway. Mediators. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 720171.
- Park, E.J.; Cheenpracha, S.; Chang, L.C.; Kondratyuk, T.P.; Pezzuto, J.M. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by 4- isothiocyanate from Moringa oleifera. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 971–982.
- Fard, M.T.; Arulselvan, P.; Karthivashan, G.; Adam, S.K.; Fakurazi, S. Bioactive extract from Moringa oleifera inhibits the pro-inflammatory mediators in lipopolysaccharide stimulated macrophages. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2015, 11, S556.
- Efstratiadis, G.; Divani, M.; Katsioulis, E.; Vergoulas, G. Renal fibrosis. Hippokratia 2009, 13, 224–229.
- Hamza, A.A. Ameliorative effects of Moringa oleifera Lam seed extract on liver fibrosis in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 345–355.
- Lin, T.A.; Wu, V.C.; Wang, C.Y. Autophagy in chronic kidney diseases. Cells 2019, 8, 61.
- Kimura, T.; Takabatake, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Kaimori, J.Y.; Matsui, I.; Namba, T.; Kitamura, H.; Niimura, F.; Matsusaka, T.; Soga, T.; et al. Autophagy protects the proximal tubule from degeneration and acute ischemic injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 902–913.
- Takahashi, A.; Kimura, T.; Takabatake, Y.; Namba, T.; Kaimori, J.; Kitamura, H.; Matsui, I.; Niimura, F.; Matsusaka, T.; Fujita, N.; et al. Autophagy guards against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 517–525.
- Liu, S.; Hartleben, B.; Kretz, O.; Wiech, T.; Igarashi, P.; Mizushima, N.; Walz, G.; Huber, T.B. Autophagy plays a critical role in kidney tubule maintenance, aging and ischemia-reperfusion injury. Autophagy 2012, 8, 826–837.
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516.
- Bonegio, R.; Lieberthal, W. Role of apoptosis in the pathogenesis of acute renal failure. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2002, 11, 301–308.
- Molitoris, B.A. Acute renal failure. Drugs Today (Barc) 1999, 35, 659–666.
- Havasi, A.; Borkan, S.C. Apoptosis and acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 29–40.
- Feldenberg, L.R.; Thevananther, S.; del Rio, M.; de Leon, M.; Devarajan, P. Partial ATP depletion induces Fas- and caspase-mediated apoptosis in MDCK cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, F837–F846.
