Plant–microbe interactions range from symbiotic to pathogenic; in the symbiotic relationship, microbes are called ‘endophytes’. Endophytes are conventionally known as microbes existing in all plant endospheric tissues (roots, shoots, fruits, leaves, flowers, seeds, etc.) without causing harmful consequences to the host plant. These microorganisms are usually more abundant in roots and they can be transferred horizontally and vertically. Particularly, endophytic fungi constitute an extremely large community, reaching up to three million species worldwide. These eukaryotic organisms are known to harbor a large variety of secondary metabolites valuable to mankind, plants and the environment. They constitute an excellent substitute for exploring whole plants, thereby gaining time, facilitating the process of isolation and protecting the ecosystem. The scientific community has approved the excellent roles of the fungal bioactive compounds in several vital fields including medicine, pharmacy, agriculture, industry and bioremediation.
- fungal endophytes
- secondary metabolites
- extracellular enzymes
- biotechnological applications
1. History of Fungal Production of Secondary Metabolites
2. Processes of Fungal Secondary Metabolite Production
3. Biotechnological Applications of Secondary Metabolites Produced by Endophytic Fungi
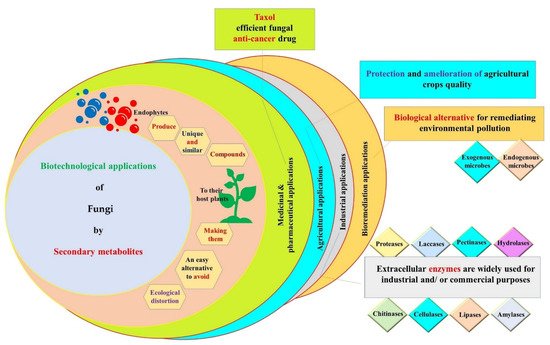
3.1. Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Applications
3.2. Agricultural Applications
3.3. Industrial Applications
3.4. Bioremediation Applications
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/f12121784
