Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Biochemistry & Molecular Biology
Liver fibrosis is an intractable disease with high morbidity by advancing into liver cirrhosis that often causes organ failure, where the parenchymal cells are replaced with collagen species and other matrix proteins. Integrins are receptors for matrix proteins that essentially consist of fibrosis tissues, and some integrins activate latent-TGFβ a central driver of fibrosis.
- fibrosis
- integrin
- TGFβ
- therapeutic target
- Hepatic stellate cells
- Culture activation
- Preclinical examination
- myofibroblast
- RGD sequence
1. Introduction
Liver fibrosis is an intractable disease with high morbidity by advancing into liver cirrhosis that often causes organ failure, where the parenchymal cells are replaced with collagen species and other matrix proteins. There are currently no approved drugs to treat fibrosis, despite increasing incidence of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)-associated liver fibrosis that now causes 2 million deaths per year in the world [1,2,3]. Currently, most drugs in clinical trials target the early steps of steatosis/hepatitis and few target fibrogenesis, itself, especially after simtuzumab (anti-LOXL2) [4] and seronsertive (ASK-1 inhibitor) [5] failed in phase II and III, respectively. In this situation, integrin inhibitors have an emerging therapeutic opportunity in fibrosis [6]. Integrins are receptors for matrix proteins that essentially consist of fibrosis tissues, and some integrins activate latent-TGFβ a central driver of fibrosis [7]. In fact, antagonists for avb1 [8] and avb6 [9,10] showed considerable inhibition in experimental animal models for liver, lung, and kidney fibrosis. Encouraged by the discovery of the TGFβ activation in 1999, pharmacological enthusiasm appears to converge into αv-containing integrins.
2. Leading Three Players in Fibrosis Are Each Related to Integrins
Tissue fibrosis is substantially characterized by deposition of excessive extracellular matrix proteins [13]. The matrix proteins are secreted from activated fibroblasts/myofibroblasts [14]. The fibroblast activation and differentiation to myofibroblast are regulated by TGFβ [15]. Matrix proteins, fibroblasts, and TGFβ, these 3 diverse players in fibrosis, are each functionally dependent on integrins to play their role in development of fibrosis. Integrins are committed as a sensor for the cell-matrix environment [16,17], a signaling receptor of fibroblasts [18,19], and an activator of the latent TGFβ complex [18].
Integrins are a family of cell surface α and β heterodimeric receptors for various extracellular matrix proteins. There are 18 α and 8 β subunits that form 24 heterodimers. The classical role of integrins is cell adhesion through binding to matrix proteins or cell surface immunoglobulin superfamily members, including ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 [19], counter-receptors that hematopoietic integrins use to adhere to vascular endothelial cells [20]. As signaling receptors, integrins mediate fundamental cellular behaviors such as cell migration, proliferation, and survival [21]. There are many matrix proteins which are recognized by multiple integrins. Most integrins can bind multiple matrix proteins and one matrix protein often interacts with multiple integrins. Ligand repertoires of each integrin thus overlap with one another but, of note, the repertoire of most of the 24-integrins is unique. Tissues resident cells, such as epithelial and mesenchymal cells, recognize their matrix environment through integrin receptors and integrins are thus sensors for perturbations in the cellular environment including tissue injury. In healthy tissues, integrins contribute to tissue homeostasis by maintaining tissue integrity, for example, epithelial cells know their position on the basement membrane through integrin signals induced by binding to basement membrane ligands such as laminins and collagen type IV (Figure 1).
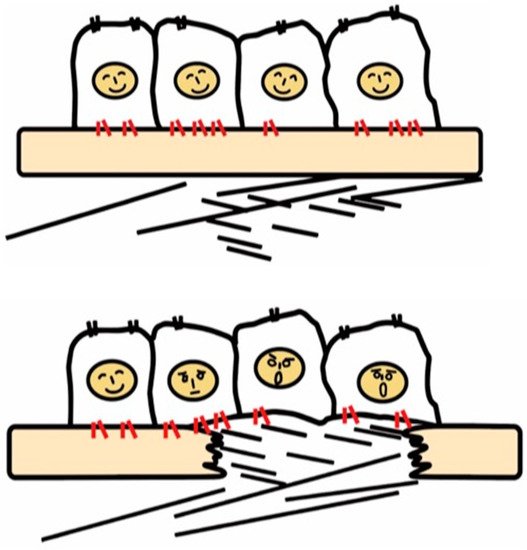
Figure 1. Recognition of tissue injury by epithelial cells via integrin receptors. In the healthy tissue (upper panel), epithelial cells know their peaceful circumstance recognizing components of the basement membrane such as laminin via integrins (red). Upon tissue injury, cells recognize contact with unusual matrix proteins such as collagen type I and fibronectin, which are normally in sub epithelium, and notice the emergent condition.
Once the basement membrane is injured, however, cells detect damage-associated matrix proteins such as collagen type I and fibronectin. The recognition of tissue injury by integrins also applies to interstitial cells including fibroblasts. Important roles of otherwise resting fibroblasts are to detect perturbations, migrate, and repair tissue injury through secretion of matrix proteins [22]. In these contexts, integrins have long been predicted to play a vital role in the development of fibrosis.
3. Activation of Latent TGFβ by Integrins
The discovery that integrins control the activity of TGFβ, the master regulator of fibrosis [23], provided the strongest evidence for contributions of integrins to fibrosis. In 1999, integrin β6 subunit knockout mice (lacking integrin αvβ6 heterodimer) were found to be protected against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis [24]. These mice were previously found to have exaggerated lung inflammation and so were predicted to have worse fibrosis in response to tissue injury [25]. This seemingly contradictory result was resolved by the discovery of αvβ6 mediated-TGFβ activation. Due to the anti-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic bilateral nature of TGFβ, the lack of TGFβ activation in the β6-knockout leads to both exaggerated inflammation and protection from fibrosis. TGFβ is stored in the matrix milieu encapsulated with pro-domain of the TGFβ gene product (the so-called latency-associated peptide (LAP)) as an inactive homodimer (Figure 2). This manner of storage allows TGFβ to be rapidly activated and act at once on demand without de novo protein synthesis. The mechanisms underlying the TGFβ release from pro-TGFβ was a long-standing controversy, and the discovery of a regulatory system was a big innovation in understanding mechanisms underlying tissue fibrosis.
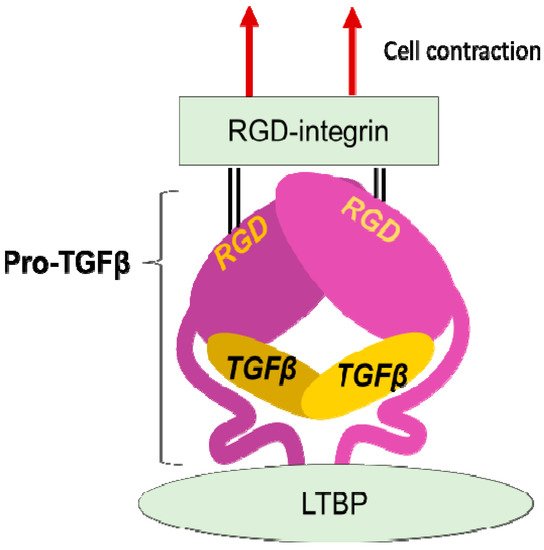
Figure 2. Integrin mediated TGFβ activation. TGFβ is stored in the extracellular milieu anchoring to LTBP that is fixed to matrix proteins, as a pro-protein, also termed as LAP. The pro-TGFβ protein forms homodimer holding TGFβ by the pro-domains. There is an RGD sequence in the pro-domain. To release TGFβ, RGD-recognizing integrins binds to the RGD sequences and pro-domains are removed from the matured TGFβ by cellular tensile force initiated by contraction of the cell expressing the integrins.
LAP contains an RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp) tripeptide that αv-containing and other integrins preferentially bind (Figure 2). Binding of cell surface αvβ6 to the RGD in the pro-TGFβ complex, together with contraction of the αvβ6-expressing cell was found to change the conformation of the latent complex, since the other end of the complex is anchored to latent transforming growth factor β binding protein (LTBP) cross-linked to the extracellular matrix [26]. Following release from the complex, TGFβ can bind to its receptors. This is the process called "TGFβ activation". This discovery owes much to a bioassay, where luciferase TGFβ signal reporter cells and β6-transfected cells are co-cultured.
4. Trends of Target-Integrins for Fibrosis
An RGD-tripeptide is the first amino acid sequence found as a motif that integrins recognize [27] and is present in many matrix proteins such as fibronectin, vitronectin, and tenascin-C. It is an RGD-peptide that helped the discovery of the first heterodimer by eluting a fibronectin affinity column in 1985 [28]. As many as 8 of 24 members of the integrin family recognize RGD (Figure 3) including all of 5 αv-integrins. This simple linear RGD sequence has played a central role in current thinking about integrin-mediated matrix biology. It seems, therefore, natural that RGD-based pharmacophores have been extensively studied as integrin inhibitors. High hopes for inhibitors of αvβ3 [29] and αvβ5 [16,21,30,31] as anticancer agents due to their proposed anti-angiogenic potential boosted the pharmacological enthusiasm for RGD-based drugs.
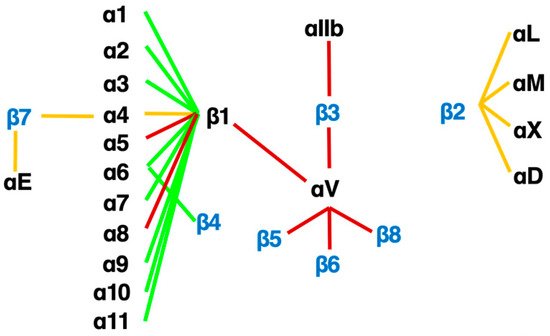
Figure 3. The integrin family. Twenty-four heterodimers and the combinations of 18 α and 8 β subunits are indicated. Eight RGD-recognizing integrins are paired with red lines. Orange lines indicate leukocyte integrins. An alternative name for αIIbβ3 is GPIIb/IIIa, and for αLβ2 are LFA1 and CD11a/18.
Currently, there are three therapeutics venture companies in the US that focus on targeting the integrin family and have developed drugs now in clinical trials [6]. Two of these companies have been well-funded by venture capital and partnerships with pharmaceutical companies. Morphic Therapeutics has a small molecule inhibitor of the α4β7 integrin in clinical trials and Pliant Therapeutics developed a dual inhibitor of αvβ1/αvβ6 for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis [32] and a selective inhibitor on αvβ1 for NASH-associated fibrosis. Indalo began a trial of a pan-αv inhibitor that has now been stopped. These concentrated developments on anti-αv-inhibitors are based on many animal experiments and in vitro mechanistic studies, especially αvβ6. A profibrotic role of αvβ6 and an anti-fibrotic effect of the anti-αvβ1 antagonists have been described in lung [9,10], biliary [33], and kidney fibrosis [34,35]. Anti-fibrotic treatment targeting αvβ6 has been effective across organs. However, expression of β6 subunit is restricted to the epithelial cells, not central to fibrosis, and the profibrotic role was found irrelevant to some fibrosis models such as CCl4-induced liver fibrosis [33], where fibrosis develops in distance from epithelium. In addition, the pro-TGFβ activation was found to be performed by any of the other αv-integrins, αvβ1, αvβ3, αvβ5 and αvβ8 [36,37,38,39], depending on conditions. To explore further profibrotic effects of the αv-integrins, first, Itgav was deleted selectively in myofibroblasts in pdgfrb-Cre driven conditional αv-knockout mice [39]. The mice lacking all myofibroblast αv-integrins were protected from liver fibrosis. Next, to determine which integrin was important to fibrosis, individual integrins were deleted for αvβ3, αvβ5, αvβ6 (global) and αvβ8 (HSC selective), but no protection was found. Therefore, either a combinatory effect of the αv-integrins or an independent effect of αvβ1 (not deleted due to technical limitation) was hypothesized to drive fibrosis. Shortly, a specific small molecule blockade against αvβ1, C8, was developed and showed an excellent inhibitory effect on murine fibrosis models in multiple organs [8], despite off-target effects of C8 on α4β1 found later [40]. The above history of the RGD peptide starting from the use in the elution buffer, and the established pharmacophore may explain why general interests in integrin-inhibitors converge on αv-integrins. Inhibitors of integrins αvβ1 and αvβ6 are the leading pack in 2021 [6].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms222312794
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
