Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Immunology
The immune response, both innate and adaptive, is a key player in cancer development and progression. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) are a subset of dendritic cells that play one of the central roles in the immune system. They are known mostly as the major IFN type I-producing cells upon stimulation of Toll-like receptors 7 and 9.
- plasmacytoid dendritic cells
- cancer
1. Introduction
The tumor microenvironment is a complicated system of cells that creates an extensive network of interactions. Immune cells form a crucial part of this network and have a huge impact on the development and progression of the disease. Most of the studies concerning cancer immunology have focused on T cell-mediated immune responses, and the positive prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells has been established in many oncologic diseases. In addition, the success of immune checkpoint inhibitors, namely, anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibodies, in clinical trials has produced a new dose of optimism for immunooncology. However, in most malignancies, a significant proportion of patients remain unresponsive to T cell-targeted approaches, and further research on the tumor microenvironment is needed.
In addition to T cells, dendritic cells (DCs) have long been one of the main targets in cancer research. Generally, DCs are one of the central components of the immune system responsible for the initiation of adaptive immune responses. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), a less explored subgroup of DCs, are mostly examined in relation to viral infections and autoimmune diseases, and have been rather disregarded in immunooncology thus far. Primarily, pDCs are known as the most potent producers of interferon α (IFNα) from all of the peripheral blood cells [1]. The main stimuli for secretion were found to be viral nucleic acids or self-derived DNA [2]. Nucleic acids interact with the most important pDC sensing receptors, namely, Toll-like receptors 7 and 9 (TLR7, TRL9), resting in endosomes. After TLRs are triggered, the pDC-derived IFN type I production is dependent on a complex containing MyD88 and IRF7. Within the complex IRAK1 and/or IKKα phosphorylates IRF7, which is translocated into the nucleus and so can regulate the expression of IFNα and other type I IFNs, namely, IFNβ, IFNτ and IFNω [3]. Moreover, the constitutive high expression of IRF7 is a particularity of pDCs that allows them to secrete very rapidly significant amounts of IFNα and β [4] However, type I IFNs are neither the only products of pDCs nor their only possible mechanism of interaction with other players in the tumor microenvironment. Indeed, the MyD88-IRAK4-TRAF6 complex drives NF-κB-dependent inflammatory cytokine induction. The secretion of IL-6, IL-10, TNFα and IFNγ has been reported [5,6]. In addition, the production of chemokines CCL3, CCL4, CCL5, CXCL9, and CXCL10 has been observed as these substances play a role in migration of pDCs themselves and also attract other innate immune cells, such as NK cells and macrophages [7,8]. Furthermore, other functions have been assigned to pDCs, such as antigen presenting function, T regulatory lymphocytes (Tregs) induction, cell-to-cell contact-dependent cytotoxicity, and interactions with NK cells and B cells [5,9,10,11].
2. Overview of pDC Biology
Plasmacytoid DCs count for less than 1% of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in healthy individuals. They can be generated from both common myeloid and common lymphoid progenitors, including substream pathways with various potential to give a rise to pDCs [12]. Plasmacytoid DCs are fully developed in bone marrow, released into peripheral blood as immature (non-activated) cells, and then enter secondary lymphoid organs and peripheral tissues, including pathologic conditions such as tumors, inflammatory and autoinflammatory lesions. In general, the major growth factor for DC development is the fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 ligand (FLT3-L) [13,14]. The FLT3 receptor is expressed on pDC progenitors, and as shown in mouse models with FLT3 deletion, the pDC population is far more dependent on this pathway than the conventional DC (cDC) population [15]. The main transcription factor, both in mice and humans, for differentiating progenitors into the pDC branch and in maintaining the pDC phenotype, is E2-2 [16]. E2-2 is activated through the FLT3 receptor via the STAT 3-dependent mechanism [17]. The interruption of E2-2 expression in mature pDCs leads into their spontaneous differentiation into cDC-like cells [18].
Unlike cDCs, pDCs enter T lymphocyte-rich areas of lymphatic organs directly from the blood through high endothelial vessels (HEVs) [19]. The main receptors driving migration into the secondary lymphatic organs are L-selectin CD62L and CCR7. The latter is upregulated upon TLR9 stimulation and interacts with chemokines CCL19 and CCL21 produced by fibroblastic reticular cells, the stromal cells in T cell zones of lymph nodes [19,20]. Additional important pathways that lead pDC migration in homeostatic and pathologic conditions are CXCR4/CXCL12 and CXCR3/CXCL9/CXCL10/CXCL11 [21,22]. CXCL12 and ligands of CXCR3 are expressed in both secondary lymphoid organs and in epithelium inflamed either due to a viral infection or due to a malignant transformation [21,23]. It has been reported that the capability of the chemokine CXCL12 to enhance the recruitment of pDCs was conducted by CXCR3 ligands, induced under inflammatory conditions [23]. At least partial dependency on the CXCR4/CXCL12 pathway was demonstrated in melanoma, ovarian cancer, and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma [21,24,25]. This result implies that other receptors, including CCR6 or CCR7, might play a role in pDC migration to the tumor sites [26,27].
Originally, pDCs were named “plasmacytoid monocytes” and characterized as CD4+ CD123+ cells that were negative for lineage markers of B cells, T cells, NK cells, and monocytes [28]. Since then, specific surface markers that facilitate the analysis and isolation of these cells from blood and peripheral tissues have been described. A C-type lectin blood DC antigen 2 (BDCA-2) is a commonly used marker for pDC identification. Nevertheless, there are drawbacks in its use for pDC enrichment, because engagement of the receptor with an antibody leads to a decrease of pDC functional capacity [29]. Therefore, a blood dendritic cell antigen 4 (BDCA–4) is used for pDC enrichment [30]. BDCA-4 is identical to neuropilin-1 (NP-1), a receptor known to be expressed on other non-hematopoietic cells, such as neurons and some tumor cells. The standard markers used to identify pDC in mice are B220, Ly6C, BST2, Siglec-H and CD11c [31].
Human plasmacytoid DCs can be further divided into minor subpopulations with variability in functional characteristics. The CD2high pDC subpopulation showed expression of lysozyme, secreted more IL12p40, and was more efficient in triggering proliferation of naïve T cells [32]. Moreover, Zhang et al. further diversified CD2high subsets and identified CD2+CD5+CD81+ pDCs in blood, bone marrow, and tonsils [33]. This subset produced little IFNα upon TRL stimulation; however, in addition to T cell proliferation, this subset also promoted plasma cell differentiation. Recently, Alculumbre et al. reported three subsets based on PD-L1 and CD80 expression. Cells with plasmacytoid morphology, specialized in type I IFN production expressed PD-L1 but not CD80. Cells negative for PD-L1 but positive for CD80 showed dendritic morphology and adaptive immune functions. As expected, double positive PD-L1+CD80+ pDCs showed both innate and adaptive functions [34]. Other pDC subpopulations were defined based on CXCL10 expression and/or IFNα secretion, however their specific functions are yet to be explored [35,36].
3. Negative Role of pDCs in Solid Tumors
3.1. Dysregulation of pDC Functions in the Tumor Microenvironment
A decreased capacity to produce IFNα is considered as the main indicator of pDC dysfunction. Hartman et al. reported a diminished capacity of pDCs derived from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) to produce IFNα upon CpG stimulation compared to blood-derived pDCs [49]. A possible mechanism of this phenomenon was suggested to be a decrease in TLR9 expression [49]. The same author group later elucidated the underlying mechanism of impaired IFNα secretion, identifying prostaglandin E2 and TGFβ from HNSCC culture supernatants as the most important negative regulators of pDC functions [50]. Other research teams reported similar effects on IFNα secretion in the setting of HNSCC when blood-derived human pDCs were incubated with tumor supernatants [51,52]. Bruchhage et al. also analyzed cytokines in HNSCC supernatants and tested their effect on pDCs. In this study, IL-10 was identified as one of the major actors that impaired IFNα secretion [51]. Similarly, tumor-associated pDCs showed decreased IFNα secretion upon TLR7 and TLR9 stimulation in breast and ovarian cancers [52,53]. However, in comparison to HNSCC, different mechanisms explaining this phenomenon were observed, as the most important soluble factors in the tumor microenvironment responsible for the impaired function were designated TNFα and TGFβ, but not IL-10 [54]. Indeed, TGFβ and TNFα in a synergistic manner negatively affected IRF-7 expression and thus inhibited the IFNα secretion pathway. Moreover, to support the significance of this IFN-regulating pathway in breast cancer, higher expression of IRF-7-regulated genes in primary tumors of breast cancer patients positively correlated with prolonged bone metastasis-free survival [55]. The important role of TGFβ was also demonstrated by Terra et al. In TC1 and B16-OVA mouse models, TGFβ was identified as the main cytokine suppressing IFNα production by tumor-associated pDCs [56].
Additionally, immunoglobulin-like transcript 7 (ILT-7) signaling was shown to play a role in the negative regulation of type I IFN production by pDCs [57]. However, the phenomenon was demonstrated by the interaction of CpG-stimulated blood-derived pDCs with ILT-7 ligands-expressing human cancer cell lines and not in patient tumor tissue. In human melanoma invaded lymph nodes and skin metastases, higher infiltration of the LAG3+ pDC subpopulation compared to blood was reported. Moreover, LAG3-mediated activation of pDCs led to low production of IFNα but high secretion of IL-6, suggesting an important role for this alternative activation pathway in establishing the immunosuppressive microenvironment [58]. Functionally impaired pDCs were also identified in preneoplastic lesions of the uterine cervix [59]. Based on in vitro experiments, Demoulin et al. showed low IFNα secretion by pDCs upon cocultivation with cervical cancer cell lines infected by human papillomavirus 16 (HPV16) [60]. In this study, high mobility group B1 protein (HMGB-1) produced by neoplastic keratinocytes was identified as an important negative regulator of IFNα secretion. In contrast, HIV1-stimulated blood-derived pDCs from healthy donors secreted HMGB-1, which increased IFNα production in an autologous loop [61]. In view of the fact that pre/malignant lesions of the cervix are associated with chronic infection with high-risk HPV, it is worth noting that blood circulating pDCs were also shown to react by IFNα secretion upon stimulation with HPV16 capsid-derived virus-like particles, although the amount of IFNα was lower than upon CpG 2216 stimulation [59]. This demonstrates a possible “fight” between the immunomodulatory capacity of the tumor cells and the stimulatory effect of viral antigens on pDCs. Therefore, the pDC phenotype and function might differ in virus-associated tumors and tumors of other etiologies.
3.2. Pro-Tumorigenic Effects of pDC
The many times reported mechanism by which pDCs augment the immunosuppressive environment is the induction of Tregs through the ICOS/ICOS-L pathway or indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) expression [45]. Interestingly, unlike tolerogenic DCs, immunosuppresive pDCs do not have to show an immature phenotype, but can even be stimulated by TLR9 agonists. Tumor-infiltrating Tregs produce IL-10 and TGFβ, which further support tumor progression. As described above, IL-10 and TGFβ could impair the capacity of pDCs to produce IFNα and potentially create a vicious cycle intensifying the immunosuppressive effect of the tumor. The importance of ICOS-L+ pDCs in the induction of Tregs was reported in human melanoma, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and liver tumors [53,62,63,64]. Furthermore, in a human ovarian cancer study, high densities of pDCs and ICOS+ Foxp3+ Tregs were found to be strong predictors of disease progression [62]. A positive correlation between the proportions of tumor-infiltrating pDCs and Tregs was also found in glioma, thyroid gland cancer, and gastric cancer [65,66,67]. In contrast, the only study which is in a discrepancy with these reports and concerns tumor-infiltrating cells is focused on colorectal cancer (CRC) [68]. In CRC high densities of Tregs were shown to be rather a positive prognostic marker [69,70]. Thus, Tregs in CRC are supposed to have anti-tumorigenic effect helping to suppress undesirable chronic inflammation in the tumor tissue. Positive correlation of functionally impaired pDC and Tregs may therefore occur in tumors, where a suppressive microenvironment prevails and Tregs support these protumoral conditions.
In addition to ICOS-L stimulation, costimulation by OX40L expressed on pDCs led to the polarization of the immune response towards the Th2 direction in a melanoma mice model [64]. Consistent with these results, increased levels of OX40L+ pDC and Th2 T cells were detected in the peripheral blood of patients with advanced stages of melanoma [64]. In a mouse model of melanoma, IDO+ pDCs derived from tumor-draining lymph nodes were reported to stimulate CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs. These Tregs subsequently caused upregulation of PD-L1 and PD-L2 on DCs and promoted the immunosuppressive microenvironment [71]. This effect was abrogated when IDO-KO mice were used. This study suggests that the effect of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors may be augmented by targeting the negative action of tumor infiltrating pDCs. To support this hypothesis, Ray et al. showed in multiple myeloma (MM) patients that blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 axis in pDCs and in cocultures with CD8+ and CD4+ T cells caused an increased proliferation rate of T lymphocytes [72]. Moreover, using an anti-PD-L1 antibody in a pDC coculture with autologous NK cells from MM patients restored NK cell cytolytic activity against GFP+ MM.1S cells.
In addition to induction of Tregs, there are sporadic reports about other tumor-promoting functions of pDCs. Curiel et al. described the induction of neoangiogenesis via TNFα and IL-8 production by CD40L-activated pDCs derived from human ovarian tumor ascites [73]. Another partially proangiogenic and proinvasive cytokine, IL-1α, was reported to be produced by pDCs from human non-small cell lung cancer tissue [74]. However, IL-1α is an ambivalent cytokine with both pro- and antitumoral effects. In addition to the above-mentioned mechanisms by which pDCs contribute to the induction and maintenance of the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, granzyme B secreted by IL-3-stimulated pDCs was reported to be able to decrease both CD4+ and CD8+ T cell proliferation [75]. This phenomenon was further enhanced by IL-10 but inhibited by TLR stimulation. Because of the aforementioned negative role of pDCs in many tumors, the possibility of pDC depletion could be a way to release a local immune response. Sawant et al. reported a decrease in tumor burden and metastatic spread after pDC depletion in a breast cancer mouse model using an anti-PDCA-1 antibody [76]. In a glioma mouse model, pDC depletion led to prolonged survival, decreased tumor-infiltrating Treg numbers, and substantially decreased production of IL-10 in the remaining intratumoral Tregs [65].
Plasmacytoid DC contributions to tumor promotion and suppression are summarized in Figure 1.
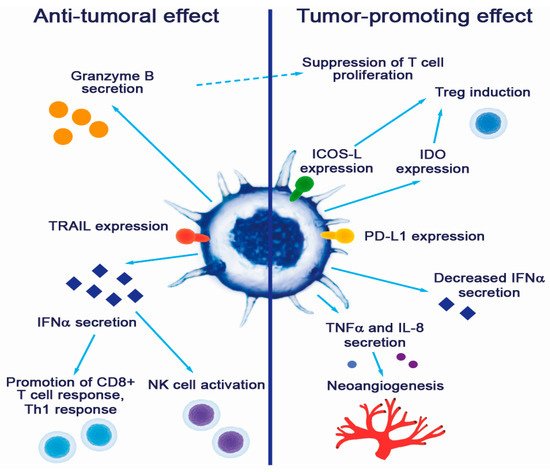
Figure 1. Contribution of pDCs to cancer pathogenesis.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/cancers11040470
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
