The ongoing SARS-CoV-2 pandemic is a serious threat to public health worldwide and, to date, no effective treatment is available. Thus, we herein review the pharmaceutical approaches to SARS-CoV-2 infection treatment. Numerous candidate medicines that can prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication have been proposed. These medicines include inhibitors of serine protease TMPRSS2 and angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). The S protein of SARS-CoV-2 binds to the receptor in host cells. ACE2 inhibitors block TMPRSS2 and S protein priming, thus preventing SARS-CoV-2 entry to host cells. Moreover, antiviral medicines (including the nucleotide analogue remdesivir, the HIV protease inhibitors lopinavir and ritonavir, and wide-spectrum antiviral antibiotics arbidol and favipiravir) have been shown to reduce the dissemination of SARS-CoV-2 as well as morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19
- therapy
- SARS-CoV-2
- combination therapy
- virus-based therapy
- host-based therapy
- SARS-CoV-2 cell entry inhibitors
1. Introduction
2. SARS-CoV-2 Genetic Structure and Pathogenic Mechanism
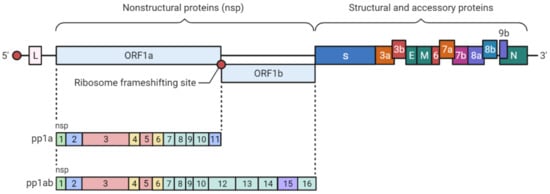
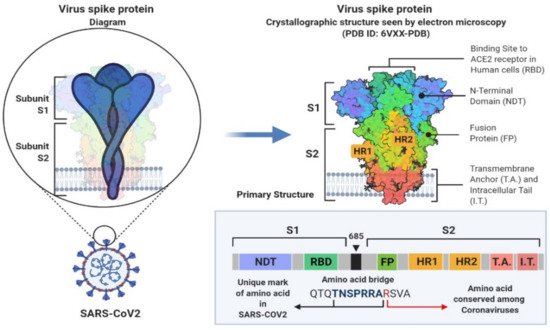
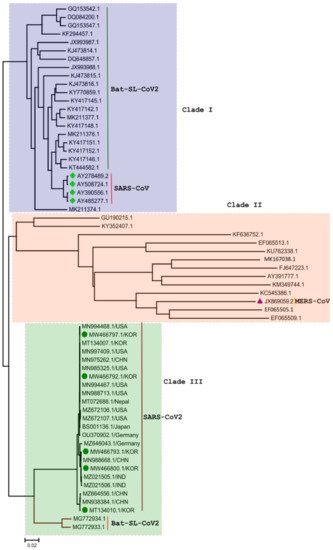
3. Phylogenetic Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Genome
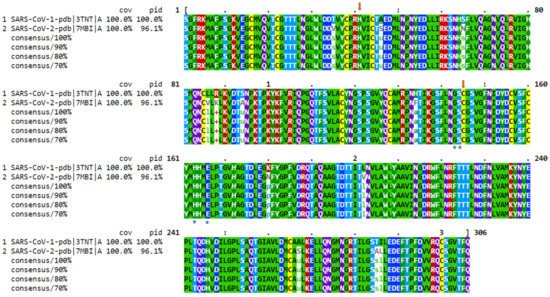
4. Therapeutic Approaches to SAR-COV-2 Infection
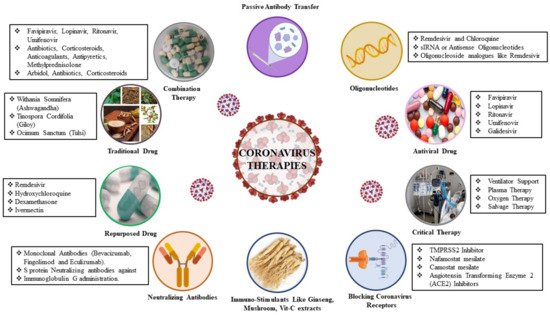
4.1. Virus-Based Therapy
| Antiviral Agent | Drug Target | Mechanism of Action | Infectious Disease | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Remdesivir | RdRp | Terminates the non-obligate chain | SARS-CoV-2, MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV | [20] |
| Favipiravir | RdRp | Inhibits RdRp | SARS-CoV-2, Influenza | [21] |
| siRNA | RdRp | Short chains of dsRNA that interfere | SARS-CoV, MERS-CoVWu | [22] |
| Galidesivir | RdRp | Inhibits viral RNA polymerase function by | Galidesivir SARS-CoV-2, | [23] |
| Ribavirin | RdRp | Inhibits viral RNA synthesis and mRNA capping | SARS-CoV-2, MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, | [24] |
| LJ001 and JL103 | Lipid membrane | Membrane-binding photosensitizers that induce | Enveloped viruses (IAV, filoviruses, poxviruses, arenaviruses, bunyaviruses, paramyxoviruses, flaviviruses and HIV-1) | [25] |
| CR3022 | Spike glycoprotein | Immunogenic antigen against Spike protein | SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV | [26] |
| Griffithsin | Spike glycoprotein | Griffithsin binds to the SARSCoV-2 spike | SARS-CoV-2 | [27] |
| Peptide (P9) | Spike glycoprotein | Inhibits spike protein-mediated cell-cell entry or | Broad-spectrum (SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, influenza) | [28] |
| Nafamostat | Spike glycoprotein | Inhibits spike-mediated membrane fusion A | SARS-CoV-2, MERS-CoV | [29] |
| Ritonavir | 3CLpro | Inhibits 3CLpro | SARS-CoV-2, MERS-CoV | [30] |
| Lopinavir | 3CLpro | Inhibits 3CLpro | SARS-CoV-2, MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, HCoV-229E, HIV, HPV | [31] |
| Darunavir and cobicistat | 3CLpro | Inhibits 3CLpro | SARS-CoV-2 | [32] |
4.2. Host-Based Therapy
| Antiviral Agent | Drug Target | Mechanism of Action | Infectious Disease | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baricitinib | Clathrin-mediated endocytosis | Baricitinib | Clathrin-mediated endocytosis | [34] |
| Chloroquine | Endosomal acidification |
A lysosomatropic base that appears to disrupt intracellular trafficking and viral fusion events | SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV | [33] |
| Convalescent plasma | - | Inhibits virus entry to the target cells | SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, Influenza | [35,36] |
| Camostat Mesylate | Surface protease | Potent serine protease inhibitor | SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, HcoV-229E | [33] |
| Corticosteroids | Pulsed methylprednisolone | Patients with severe MERS who were treated with systemic corticosteroid with or without antivirals and interferons had no favorable response | SARS-CoV, MERS-CoVL | [35] |
| Nitazoxanide | Interferon response | Induces the host innate immune response | Coronaviruses, SARS-CoV-2 | [19] |
| Recombinant interferons | Interferon response | Exogenous interferons | SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV | [37] |
4.2.1. Neutralizing Antibodies
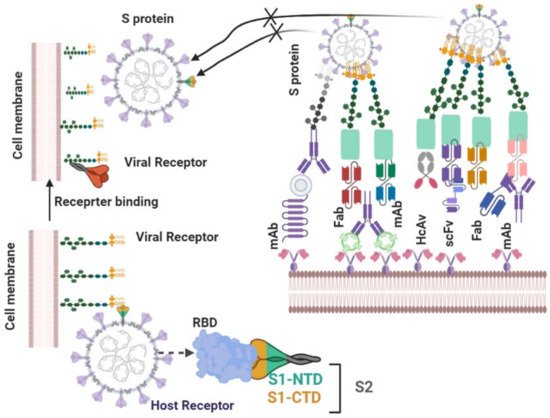
| S.N. | Antibody Name | Antibody Type | Origin | PDB ID | Epitopes | Neutralizing Mechanism | Cross Neutralizing Activity | Protective Efficacy | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CV30 | Human IgG | Infected COVID-19 patients | 6XE1 | D420-Y421, Y453, L455-N460, Y473-S477, F486-N487, Y489, Q493, T500, G502, Y505 | Block hACE2-RBD interaction | no | IC50 value of 0.03 µg/mL | [35] |
| 2 | REGN10933 Recombinant | full-human antibodies | Humanized mice and COVID-19-convalescent patients | 6XDG | R403, K417, Y421, Y453, L455-F456, A475-G476, E484-Y489, Q493 | Block hACE2-RBD interaction, ADCC & ADCP | no | IC50 value of 37.4 pM | |
| 3 | B38 | Human IgG | COVID-19-convalescent patient | 7BZ5 | R403, D405-E406, Q409, D420-Y421, Y452, L454-N460, Y473-S477, F486-N487, Y489-F490, Q493-G496, Q498, T500-V503, Y505 | Block hACE2-RBD interaction | no | A single dose of B38 (25 mg/kg) | [35] |
| 4 | CC12.1 | Human IgG | COVID-19-convalescent patient | 6XC3 | R403, D405-E406, R408-Q409, D420-Y421, Y453, L455-N460, Y473-S477, F486-N487, Y489, Q493-G496, Q498, T500-V503, Y505 | Block hACE2-RBD interaction | no | IC50 value of 0.019 µg/mL | [36] |
| 5 | CB6 | Human IgG | COVID-19-convalescent patient | 7C01 | R403, D405-E406, R408-Q409, D420-Y421, L455-N460, Y473-S477, F486-N487, Y489, Q493, Y495, N501-G502, G504-Y505 | Block hACE2-RBD interaction | no | A single dose of CB6-LALA (50 mg/kg) | [37] |
| 6 | C105 | Human IgG | COVID-19-convalescent patient | 6XCN, 6XCM | R403, D405, R408, D420-Y421, Y453, L455-N460, Y473, A475-G476, F486-N487, G502, Y505 | Block hACE2-RBD interaction | no | IC50 value of 26.1 ng/mL | [41] |
| 7 | CC12.3 | Human IgG | COVID-19-convalescent patient | 6XC7 | R403, D405, D420-Y421, Y453, L455-N460, Y473-S477, F486-N487, Y489, Q493, G496, N501, Y505 | Block hACE2-RBD interaction | no | IC50 value of 0.018 µg/mL | [42] |
| 8 | CR3022 | Human IgG | SARS-convalescent patient | 6YOR, 6 W41 | Y369-N370, F374-K386, L390, F392, D428, T430, F515-L517 | Trapping RBD in the less stable up conformation while leading to destabilization of S | SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2 | ND50 value of 0.114 µg/mL | [19] |
| 9 | EY6A | Human IgG | Late-stage COVID-19 patient | 6ZDH, 6ZER, 6ZCZ | Y369, F374-S375, F377-K386, N388, L390, P412-G413, D427-F429, L517 | destabilization of S | SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2 | ND50 value of ~10.8 µg/mL | [26] |
| 10 | VHH-72 | Llama single domain antibody | llama immunized with prefusionstabilized betacoronavirus spikes | 6WAQ | Y356-T359, F361-C366, A371-T372, G391-D392, R395, N424, I489, Y494 | Trapping RBD in the less stable up conformation while leading to destabilization of S, Block hACE2_RBD interaction | SARS-CoV, SARS-Co-V-2 | IC50 values of 0.14 µg/mL and 0.2 mg/mL. | [19] |
| 11 | BD23 | Human IgG | COVID-19-convalescent patient | 7BYR | G446, Y449, L452, T470, E484-F486, Y489-F490, L492-S494, G496, Q498, T500-N501, Y505 | Block hACE-RBD2 interaction | no | IC50 value of 8.5 µg/mL | [26] |
| 12 | Fab 2–4 | Human IgG | Infected COVID-19 patients | 6XEY | Y449, Y453, L455-F456, E484-F486, Y489-F490, L492-S494, G496 | Locking RBD in the down conformation while occluding access to ACE2 | no | Neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 live virus with IC50 value of 0.057 µg/mL | [41] |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/biomedicines9111620
