Honey, a natural sweetener has been used universally as a complete food and in complementary medicine since early antiquity. Honey contains over 180 substances, including sugars mainly fructose and glucose, water and a plethora of minor constituents such as vitamins, minerals and phytochemicals. Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease occurring in the inner lining of arterial walls due to the progressive plaque formation. Multiple risk factors are implicated in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, including oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, hypercholesterolemia, hypertension, diabetes and cigarette smoking.
- Honey
- composition
- antioxidants
- atherosclerosis
- inflammation
- oxidative stress
- cholesterol
1. Introduction
2. Honey Composition and Antioxidant Activity
2.1. Honey Composition
|
Proximates (g) |
Minerals (mg) |
Vitamins (mg) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Fructose |
38.2 |
Calcium |
3–31 |
Ascorbic acid |
2.2–2.5 |
|
Glucose |
31.3 |
Potassium |
40.0–3500.0 |
Thiamin |
0.0–0.01 |
|
Sucrose |
0.7 |
Copper |
0.02–0.60 |
Riboflavin |
0.01–0.02 |
|
Other disaccharides |
5.0 |
Iron |
0.03–4.00 |
Niacin |
0.1–0.2 |
|
Water |
17.1 |
Magnesium |
0.7–13.0 |
Pantothenic acid |
0.02–0.11 |
|
Organic acids |
0.5 |
Manganese |
0.02–2.0 |
Pyridoxine (B6) |
0.01–0.32 |
|
Proteins, amino acids |
0.3 |
Phosphorus |
2.0–15.0 |
||
|
Sodium |
1.6–17.0 |
||||
|
Zinc |
0.05–2.00 |
||||
|
Se |
0.001–0.003 |
||||
2.2. Key Compositional Standards
|
Criteria |
Values |
|---|---|
|
Moisture content (%) |
≤20.0 |
|
Fructose and glucose (Sum, g/100 g) |
≥60 |
|
Sucrose (g/100 g) |
≤5.0 |
|
Water-insoluble content (g/100 g) |
<0.1 |
|
Electrical conductivity (mS/cm) |
≤0.8 |
|
Free acid (meq/kg) |
≤50.0 |
|
Diastase activity (Schade scale) |
≥8.0 |
|
Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF, mg/kg) |
≤40.0 |
2.3. Antioxidant Capacity
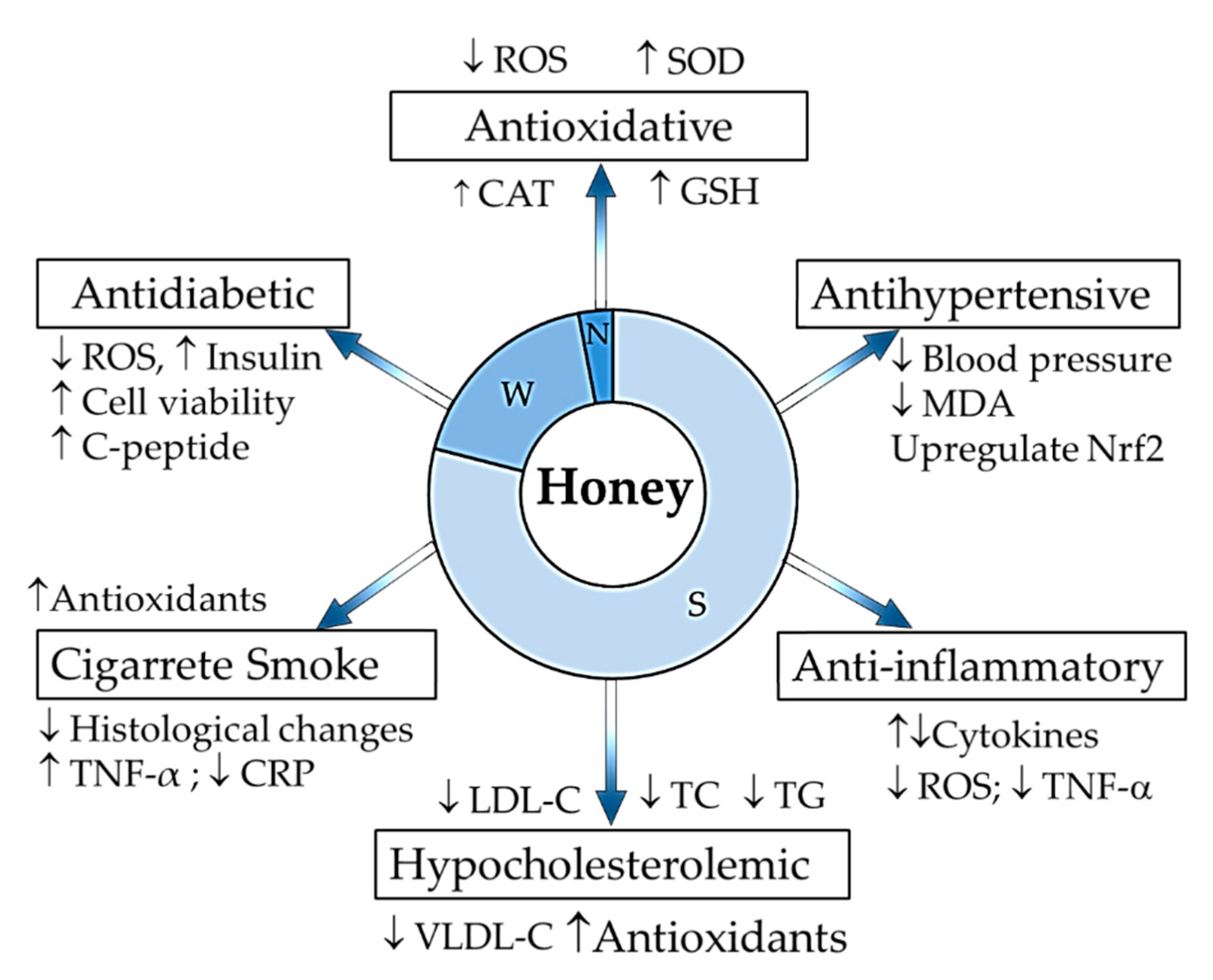
3. Honey in Relieving Multiple Facets of Atherosclerosis
3.1. Oxidative Damage
|
Honey Type |
Research Model |
Main Findings on Honey Effects |
Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Local honey |
Rat kidney, brain, liver and lung homogenates |
↓ Lipid hydroperoxides and malondialdehyde (MDA) value |
[49] |
|
Christmas vine, Morning glory, black mangrove, linen vine singing bean honey |
Rat liver homogenates |
Highest radical scavenging capacity in linen vine honey ↓ Lipid peroxidation |
[50] |
|
Fireweed, tupelo, Hawaiian Christmas berry clover, acacia, buckwheat, soybean honey |
Human blood serum |
AOC is different among honeys, ↓ Lipoprotein oxidation (LPO) Correlation of ORAC value and LPO inhibition. |
[29] |
|
Acacia, coriander, sider and palm honey |
Human LDL |
High antioxidant activity in xanthine-xanthine oxidase system and LDL oxidation |
[51] |
|
Buckwheat honey |
Human blood serum |
↑ Serum antioxidant capacity |
[52] |
|
Multifloral honey |
Human red blood cells (RBC) |
↓ Lipid peroxidation |
[53] |
|
Multifloral honey |
RBC |
↓ Extracellular ferricyanide level |
[54] |
|
Christmas vine, linen vine honey |
RBC |
Protection of human erythrocyte membranes from oxidative damage ↑ Defence responses and ↑ cell functions |
|
|
Native multifloral honey |
Endothelial cell (EA.hy926) |
Protection of EA.hy926 from hydrogen peroxide and peroxyl radical Synergistic effect of phenolic antioxidants in honey |
[57] |
|
Gelam honey |
Rat blood sample |
↑ Antioxidant enzyme activities |
[58] |
|
Multifloral honey |
Rat plasma and heart tissue |
↓ Hypertriglyceridemia and pro-oxidative effects ↑ Plasma α-tocopherol and α-tocopherol/triglycerides, ↓ plasma NOx, ↓ peroxidation |
[59] |
|
Buckwheat honey |
Human blood plasma |
↑ Plasma antioxidant activity, ↑ defences against oxidative stress |
[60] |
AOC: antioxidant capacity, ORAC: oxygen radical absorbance capacity, LPO: lipoprotein oxidation, LDL: low density lipoprotein, RBC: Human red blood cells, TG: triglycerides, NOx: nitrogen oxides.
3.2. Inflammatory Responses
3.3. Hypercholesterolemia
|
Honey Type |
Research Model |
Main Findings of Honey Effect |
Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Honeydew honey |
Rat blood serum |
Similar weight gain and body fat in honey and control group; ↓ HbA1c, ↑ HDL-C |
[82] |
|
Clover honey |
Rat blood serum |
↓ Weight gain and adiposity, ↓ TGs but ↑ non-HDL-C levels |
[83] |
|
Native honey |
Rat blood samples |
↓ glucose and lipids no deteriorated effects on hyperglycaemia and dyslipidaemia |
[84] |
|
Local honey |
Rat blood serum |
↑ Plasma TG, HDL-C and VLDL-C but ↓ plasma LDL-C and TC |
[85] |
|
Tualang honey |
Rat heart tissue |
↑ Antioxidant enzyme levels in heart tissue and ↓ lipoprotein oxidation (LPO) |
[86] |
|
Tualang honey |
Rat blood serum, kidneys |
↓ TC and TG compared to the control at 7 days; ↓ Serum creatinine level than no honey group after 48 h; No structural effect histologically in the HCD-fed rats |
[87] |
|
Gelam, Acacia honey |
Rat blood serum, internal organs |
↓ Excess weight gain and adiposity index; ↓ plasma glucose, TGs, TG and obesity at similar levels to orlistat drug group |
[88] |
|
Malícia honey |
Rat blood serum, liver |
↓ Food consumption, ↑ glucose tolerance and SOD activity; ↓ TC, LDL and AST levels; ↑ beneficial bacteria and organic acids; Colon and liver was protected |
[89] |
|
Natural local honey |
Healthy, diabetic and hyperlipidaemic human subjects, blood samples |
↓ Blood lipids, homocysteine and C-reactive protein (CRP) in normal and hyperlipidaemic subjects; ↓ plasma glucose elevation in diabetics |
[76] |
|
Natural honey |
Human plasma |
↓ TC (3.3%), LDL-C (4.3%), TGs (19%) and CRP (3.3%) in elevated variable subjects; No increased body weight in overweight or obese participants |
[90] |
|
Natural unprocessed honey |
Type 2 diabetes human subjects, weight and blood samples |
↓ Body weight, TC, LDL-C, TGs ↑ HDL-C and HbA1C levels |
[10] |
|
Kanuka honey, formulated with cinnamon, chromium and magnesium |
Type 2 diabetes human subject, weight and blood samples |
↓ Weight Improve blood lipid profile |
[91] |
HbA1c: Haemoglobin A1c, HDL-C: high density lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL-C: low density lipoprotein cholesterol, VLDL-C: very low density lipoprotein cholesterol, TC: total cholesterol, TGs: triglycerides, LPO: lipoprotein oxidation, HCD: high cholesterol diet, AST: aspartate aminotransferase, CRP: C-reactive protein.
3.4. Hypertension
3.5. Diabetes
3.6. Cigarette Smoking
4. Adverse Effects of Honey
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/nu11010167
References
- Toh, B.-H.; Kyaw, T.; Tipping, P.; Bobik, A. Chapter 71—Atherosclerosis. In The Autoimmune Diseases, 5th ed.; Rose, N.R., Mackay, I.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 1049–1066.
- Torres, N.; Guevara-Cruz, M.; Velázquez-Villegas, L.A.; Tovar, A.R. Nutrition and atherosclerosis. Arch. Med. Res. 2015, 46, 408–426.
- Falk, E. Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, C7–C12.
- Zhang, H.; Tsao, R. Dietary polyphenols, oxidative stress and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 8, 33–42.
- Bogdanov, S.; Jurendic, T.; Sieber, R.; Gallmann, P. Honey for Nutrition and Health: A Review. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2013, 27, 677–689.
- Da Silva, P.M.; Gauche, C.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Costa, A.C.O.; Fett, R. Honey: Chemical composition, stability and authenticity. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 309–323.
- Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Giampieri, F.; Battino, M. Honey as a source of dietary antioxidants: Structures, bioavailability and evidence of protective effects against human chronic diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 621–638.
- Nguyen, H.T.L.; Panyoyai, N.; Paramita, V.D.; Mantri, N.; Kasapis, S. Physicochemical and viscoelastic properties of honey from medicinal plants. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 143–149.
- Atkinson, F.S.; Foster-Powell, K.; Brand-Miller, J.C. International tables of glycemic index and glycemic load values: 2008. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 2281–2283.
- Bahrami, M.; Ataie-Jafari, A.; Hosseini, S.; Foruzanfar, M.H.; Rahmani, M.; Pajouhi, M. Effects of natural honey consumption in diabetic patients: An 8-week randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 60, 618–626.
- Bantle, J.P. Dietary fructose and metabolic syndrome and diabetes. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1263S–1268S.
- Deibert, P.; König, D.; Kloock, B.; Groenefeld, M.; Berg, A. Glycaemic and insulinaemic properties of some German honey varieties. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 762.
- Ajibola, A.; Chamunorwa, J.P.; Erlwanger, K.H. Nutraceutical values of natural honey and its contribution to human health and wealth. Nutr. Metab. (Lond.) 2012, 9, 61.
- Nicolson, S.W.; Nepi, M.; Pacini, E. Nectaries and Nectar; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; Volume 4.
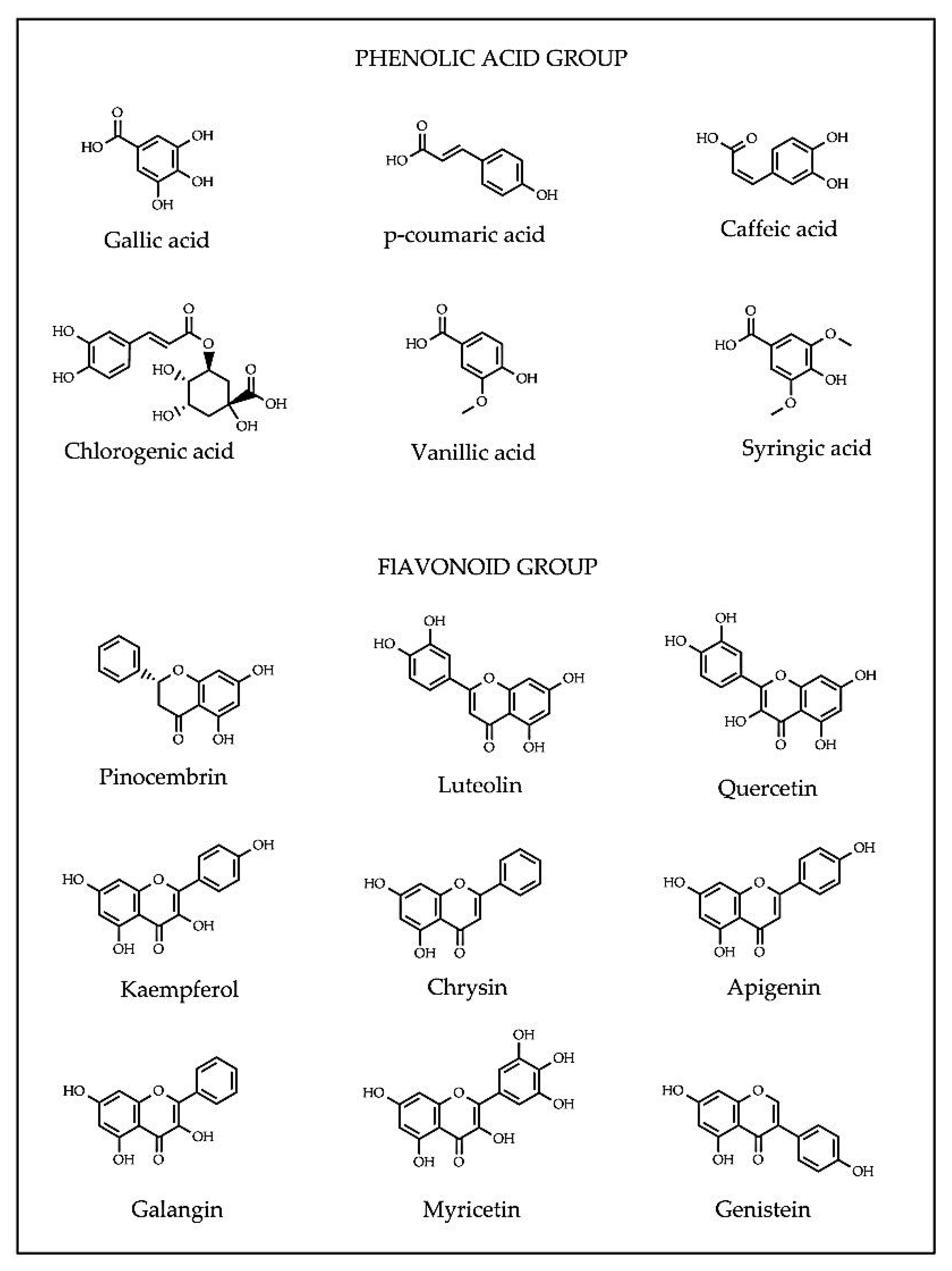
- Balasundram, N.; Sundram, K.; Samman, S. Phenolic compounds in plants and agri-industrial by-products: Antioxidant activity, occurrence, and potential uses. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 191–203.
- Teixeira, J.; Gaspar, A.; Garrido, E.M.; Garrido, J.; Borges, F. Hydroxycinnamic acid antioxidants: An electrochemical overview. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 251754.
- Hollman, P.C.H.; Katan, M.B. Dietary flavonoids: Intake, health effects and bioavailability. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 937–942.
- Procházková, D.; Boušová, I.; Wilhelmová, N. Antioxidant and prooxidant properties of flavonoids. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 513–523.
- Tomas-Barberan, F.A.; Martos, I.; Ferreres, F.; Radovic, B.S.; Anklam, E. HPLC flavonoid profiles as markers for the botanical origin of European unifloral honeys. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 485–496.
- Yao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Singanusong, R.; D’Arcy, B.; Datta, N.; Caffin, N.; Raymont, K. Flavonoids in Australian Melaleuca, Guioa, Lophostemon, Banksia and Helianthus honeys and their potential for floral authentication. Food Res. Int. 2004, 37, 166–174.
- Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Gasparrini, M.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Mazzoni, L.; Giampieri, F. The composition and biological activity of honey: A focus on Manuka honey. Foods 2014, 3, 420–432.
- Anklam, E. A review of the analytical methods to determine the geographical and botanical origin of honey. Food Chem. 1998, 63, 549–562.
- Yao, L.; Data, N.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Ferreres, F.; Martos, I.; Singanusong, R. Flavonoids, phenolic acids and abscisic acid in Australian and New Zealand Leptospermum honeys. Food Chem. 2003, 81, 159–168.
- Pisani, A.; Protano, G.; Riccobono, F. Minor and trace elements in different honey types produced in Siena County (Italy). Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1553–1560.
- Chua, L.S.; Abdul-Rahaman, N.L.; Sarmidi, M.R.; Aziz, R. Multi-elemental composition and physical properties of honey samples from Malaysia. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 880–887.
- EU. Council Directive 2001/110 relating to honey. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2001, L 10, 47–52.
- Commission, C.A. Codex Standard for Honey, CODEX STAN 12-1981; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy; The World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001.
- Musa Özcan, M.; Al Juhaimi, F. Honey as source of natural antioxidants. J. Apic. Res. 2015, 54, 145–154.
- Gheldof, N.; Engeseth, N. Antioxidant capacity of honeys from various floral sources based on the determination of oxygen radical absorbance capacity and inhibition of in vitro lipoprotein oxidation in human serum samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3050–3055.
- Afroz, R.; Tanvir, E.; Paul, S.; Bhoumik, N.C.; Gan, S.H.; Khalil, M. DNA damage inhibition properties of sundarban honey and its phenolic composition. J. Food Biochem. 2016, 40, 436–445.
- Escuredo, O.; Miguez, M.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, M.; Carmen Seijo, M. Nutritional value and antioxidant activity of honeys produced in a European Atlantic area. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 851–856.
- Estevinho, L.M.; Feás, X.; Seijas, J.A.; Vázquez-Tato, M.P. Organic honey from Trás-Os-Montes region (Portugal): Chemical, palynological, microbiological and bioactive compounds characterization. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 258–264.
- Pontis, J.A.; Costa, L.A.M.A.D.; Silva, S.J.R.D.; Flach, A. Color, phenolic and flavonoid content, and antioxidant activity of honey from Roraima, Brazil. Food Sci. Technol. (Campinas) 2014, 34, 69–73.
- Meda, A.; Lamien, C.E.; Romito, M.; Millogo, J.; Nacoulma, O.G. Determination of the total phenolic, flavonoid and proline contents in Burkina Fasan honey, as well as their radical scavenging activiity. Food Chem. 2005, 91, 571–577.
- Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Giampieri, F.; Brenciani, A.; Mazzoni, L.; Gasparrini, M.; González-Paramás, A.M.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Morroni, G.; Simoni, S.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y. Apis mellifera vs. Melipona beecheii Cuban polifloral honeys: A comparison based on their physicochemical parameters, chemical composition and biological properties. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 87, 272–279.
- Rosa, A.; Tuberoso, C.I.G.; Atzeri, A.; Melis, M.P.; Bifulco, E.; Dessì, M.A. Antioxidant profile of strawberry tree honey and its marker homogentisic acid in several models of oxidative stress. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1045–1053.
- Baltrušaitytė, V.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Čeksterytė, V. Radical scavenging activity of different floral origin honey and beebread phenolic extracts. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 502–514.
- Bertoncelj, J.; Dobersek, U.; Jamnik, M.; Golob, T. Evaluation of the phenolic content, antioxidant activity and colour of Slovenian honey. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 822–828.
- Can, Z.; Yildiz, O.; Sahin, H.; Akyuz Turumtay, E.; Silici, S.; Kolayli, S. An investigation of Turkish honeys: Their physico-chemical properties, antioxidant capacities and phenolic profiles. Food Chem. 2015, 180, 133–141.
- Socha, R.; Juszczak, L.; Pietrzyk, S.; Fortuna, T. Antioxidant activity and phenolic composition of herbhoneys. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 568–574.
- Ulloa, P.A.; Maia, M.; Brigas, A.F. Physicochemical Parameters and Bioactive Compounds of Strawberry Tree (Arbutus unedo L.) Honey. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 602792.
- Anand, S.; Pang, E.; Livanos, G.; Mantri, N. Characterization of Physico-Chemical Properties and Antioxidant Capacities of Bioactive Honey Produced from Australian Grown Agastache rugosa and its Correlation with Colour and Poly-Phenol Content. Molecules 2018, 23, 108.
- Saxena, S.; Gautam, S.; Sharma, A. Physical, biochemical and antioxidant properties of some Indian honeys. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 391–397.
- Apak, R.; Özyürek, M.; Güçlü, K.; Çapanoğlu, E. Antioxidant Activity/Capacity Measurement. 1. Classification, Physicochemical Principles, Mechanisms, and Electron Transfer (ET)-Based Assays. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 997–1027.
- Apak, R.A.; Özyürek, M.; Güçlü, K.; Çapanoğlu, E. Antioxidant activity/capacity measurement. 2. Hydrogen atom transfer (HAT)-based, mixed-mode (electron transfer (ET)/HAT), and lipid peroxidation assays. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 1028–1045.
- Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, C.; Li, T.; McClements, D.J.; Dai, T.; Liu, J. Antioxidant activity of proanthocyanidins-rich fractions from Choerospondias axillaris peels using a combination of chemical-based methods and cellular-based assay. Food Chem. 2016, 208, 309–317.
- Finkel, T.; Holbrook, N. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 2000, 408, 239–247.
- Pisoschi, A.M.; Pop, A. The role of antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 55–74.
- Pérez, E.; Rodríguez-Malaver, A.J.; Vit, P. Antioxidant capacity of Venezuelan honey in wistar rat homogenates. J. Med. Food 2006, 9, 510–516.
- Alvarez Suarez, J.M.; Giampieri, F.; Damiani, E.; Astolfi, P.; Fattorini, D.; Regoli, F.; Quiles, J.L.; Battino, M. Radical-scavenging activity, protective effect against lipid peroxidation and mineral contents of monofloral Cuban honeys. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2012, 67, 31–38.
- Hegazi, A.G.; Abd El-Hady, F.K. Influence of Honey on the Suppression of Human Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Peroxidation (In Vitro). Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2009, 6, 113–121.
- Gheldof, N.; Wang, X.H.; Engeseth, N.J. Buckwheat honey increases serum antioxidant capacity in humans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 1500–1505.
- Blasa, M.; Candiracci, M.; Accorsi, A.; Piacentini, M.P.; Piatti, E. Honey flavonoids as protection agents against oxidative damage to human red blood cells. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1635–1640.
- Fiorani, M.; Accorsi, A.; Blasa, M.; Diamantini, G.; Piatti, E. Flavonoids from Italian multifloral honeys reduce the extracellular ferricyanide in human red blood cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8328–8334.
- Cesquini, M.; Torsoni, M.; Stoppa, G.; Ogo, S.T. t-BOOH-induced oxidative damage in sickle red blood cells and the role of flavonoids. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2003, 57, 124–129.
- Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Giampieri, F.; González-Paramás, A.M.; Damiani, E.; Astolfi, P.; Martinez-Sanchez, G.; Bompadre, S.; Quiles, J.L.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Battino, M. Phenolics from monofloral honeys protect human erythrocyte membranes against oxidative damage. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 1508–1516.
- Beretta, G.; Orioli, M.; Facino, R.M. Antioxidant and radical scavenging activity of honey in endothelial cell cultures (EA. hy926). Planta Med. 2007, 73, 1182–1189.
- Sahhugi, Z.; Hasenan, S.M.; Jubri, Z. Protective effects of gelam honey against oxidative damage in young and aged rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 673628.
- Busserolles, J.; Gueux, E.; Rock, E.; Mazur, A.; Rayssiguier, Y. Substituting honey for refined carbohydrates protects rats from hypertriglyceridemic and prooxidative effects of fructose. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 3379–3382.
- Schramm, D.D.; Karim, M.; Schrader, H.R.; Holt, R.R.; Cardetti, M.; Keen, C.L. Honey with high levels of antioxidants can provide protection to healthy human subjects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 1732–1735.
- Peake, J.M.; Suzuki, K.; Coombes, J.S. The influence of antioxidant supplementation on markers of inflammation and the relationship to oxidative stress after exercise. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2007, 18, 357–371.
- Erejuwa, O.O.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Wahab, M.S. Effects of honey and its mechanisms of action on the development and progression of cancer. Molecules 2014, 19, 2497–2522.
- Woo, K.J.; Jeong, Y.-J.; Inoue, H.; Park, J.-W.; Kwon, T.K. Chrysin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression through the inhibition of nuclear factor for IL-6 (NF-IL6) DNA-binding activity. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 705–711.
- Kleemann, R.; Verschuren, L.; Morrison, M.; Zadelaar, S.; van Erk, M.J.; Wielinga, P.Y.; Kooistra, T. Anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative and anti-atherosclerotic effects of quercetin in human in vitro and in vivo models. Atherosclerosis 2011, 218, 44–52.
- Kotanidou, A.; Xagorari, A.; Bagli, E.; Kitsanta, P.; Fotsis, T.; Papapetropoulos, A.; Roussos, C. Luteolin reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced lethal toxicity and expression of proinflammatory molecules in mice. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 818–823.
- Kassim, M.; Yusoff, K.M.; Ong, G.; Sekaran, S.; Yusof, M.Y.B.M.; Mansor, M. Gelam honey inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxemia in rats through the induction of heme oxygenase-1 and the inhibition of cytokines, nitric oxide, and high-mobility group protein B1. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 1054–1059.
- Ahmad, A.; Khan, R.A.; Mesaik, M.A. Anti inflammatory effect of natural honey on bovine thrombin-induced oxidative burst in phagocytes. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 801–808.
- Bean, A. Investigating the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Honey. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Waikato, Waikato, New Zealand, 2012.
- Kassim, M.; Achoui, M.; Mustafa, M.R.; Mohd, M.A.; Yusoff, K.M. Ellagic acid, phenolic acids, and flavonoids in Malaysian honey extracts demonstrate in vitro anti-inflammatory activity. Nutr. Res. 2010, 30, 650–659.
- Van den Berg, A.; Van den Worm, E.; van Ufford, H.Q.; Halkes, S.; Hoekstra, M.; Beukelman, C. An in vitro examination of the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of buckwheat honey. J. Wound Care 2008, 17, 172–179.
- Gill, S.; Chow, R.; Brown, A. Sterol regulators of cholesterol homeostasis and beyond: The oxysterol hypothesis revisited and revised. Prog. Lipid Res. 2008, 47, 391–404.
- Yung, L.; Leung, F.; Wong, W.; Tian, X.; Yung, L.; Chen, Z.; Yao, X.; Huang, Y. Tea polyphenols benefit vascular function. Inflammopharmacology 2008, 16, 230–234.
- Hoffmann, D. Healthy Heart: Strengthen Your Cardiovascular System Naturally; Storey Publishing: North Adams, MA, USA, 2017.
- Duarte, M.; Loro, V.; Rocha, J.; Leal, D.; Bem, A.; Dorneles, A.; Morsch, V.; Schetinger, M. Enzymes that hydrolyze adenine nucleotides of patients with hypercholesterolemia and inflammatory processes. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 2707–2714.
- Dobrosielski, D.A.; Papandreou, C.; Patil, S.P.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Diet and exercise in the management of obstructive sleep apnoea and cardiovascular disease risk. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 26, 160110.
- Al Waili, N.S. Natural honey lowers plasma glucose, C-reactive protein, homocysteine, and blood lipids in healthy, diabetic, and hyperlipidemic subjects: Comparison with dextrose and sucrose. J. Med. Food 2004, 7, 100–107.
- Khalil, M.; Sulaiman, S. The potential role of honey and its polyphenols in preventing heart disease: A review. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2010, 7, 315–321.
- Ademosun, A.O.; Oboh, G.; Passamonti, S.; Tramer, F.; Ziberna, L.; Boligon, A.A.; Athayde, M.L. Phenolics from grapefruit peels inhibit HMG-CoA reductase and angiotensin-I converting enzyme and show antioxidative properties in endothelial EA. Hy 926 cells. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2015, 4, 80–85.
- Al-Naqeb, G.; Ismail, M.; Bagalkotkar, G.; Adamu, H.A. Vanillin rich fraction regulates LDLR and HMGCR gene expression in HepG2 cells. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 2437–2443.
- Wong, T.Y.; Lin, S.-M.; Leung, L.K. The flavone luteolin suppresses SREBP-2 expression and post-translational activation in hepatic cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135637.
- Mbikay, M.; Sirois, F.; Simoes, S.; Mayne, J.; Chrétien, M. Quercetin-3-glucoside increases low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) expression, attenuates proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9 (PCSK9) secretion, and stimulates LDL uptake by Huh7 human hepatocytes in culture. FEBS Open Bio 2014, 4, 755–762.
- Chepulis, L.; Starkey, N. The Long-Term Effects of Feeding Honey Compared with Sucrose and a Sugar-Free Diet on Weight Gain, Lipid Profiles, and DEXA Measurements in Rats. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, H1–H7.
- Nemoseck, T.M.; Carmody, E.G.; Furchner-Evanson, A.; Gleason, M.; Li, A.; Potter, H.; Rezende, L.M.; Lane, K.J.; Kern, M. Honey promotes lower weight gain, adiposity, and triglycerides than sucrose in rats. Nutr. Res. 2011, 31, 55–60.
- Erejuwa, O.O.; Nwobodo, N.N.; Akpan, J.L.; Okorie, U.A.; Ezeonu, C.T.; Ezeokpo, B.C.; Nwadike, K.I.; Erhiano, E.; Abdul Wahab, M.S.; Sulaiman, S.A. Nigerian Honey Ameliorates Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats. Nutrients 2016, 8, 95.
- Alagwu, E.; Okwara, J.; Nneli, R.; Osim, E. Effect of honey intake on serum cholesterol, triglycerides and lipoprotein levels in albino rats and potential benefits on risks of coronary heart disease. Niger. J. Physiol. Sci. 2011, 26, 161–165.
- Khalil, M.; Tanvir, E.; Afroz, R.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Gan, S.H. Cardioprotective effects of tualang honey: Amelioration of cholesterol and cardiac enzymes levels. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 286051.
- Mohamed, Z.B.H.; Alfarisi, H.A.H.; Abdullah, N.Z.; Harun, N.; Muhammad, N.; Rahim, R.A. Renoprotective Role of Tualang Honey against High Cholesterol Diet Induced Acute Kidney Diseases in an Animal Model. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 7, 97–101.
- Samat, S.; Kanyan Enchang, F.; Nor Hussein, F.; Ismail, W.; Iryani, W. Four-Week Consumption of Malaysian Honey Reduces Excess Weight Gain and Improves Obesity-Related Parameters in High Fat Diet Induced Obese Rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 1342150.
- Bezerra, M.L.R.R.; de Souza, E.L.; Sousa, J.B.; Lima, M.; Alves, A.F.; das Graças Almeida, M.; Alves, R.C.C.; de Araújo, E.V.V.; Soares, N.L.; da Silva, G.D.A. Effects of honey from Mimosa quadrivalvis L.(malicia) produced by the Melipona subnitida D.(jandaira) stingless bee on lipid metabolism, antioxidant status and intestinal health of dyslipidaemic rats. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4480–4492.
- Yaghoobi, N.; Al Waili, N.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Parizadeh, S.M.; Abasalti, Z.; Yaghoobi, Z.; Yaghoobi, F.; Esmaeili, H.; Kazemi-Bajestani, S.M.; Aghasizadeh, R.; et al. Natural honey and cardiovascular risk factors; effects on blood glucose, cholesterol, triacylglycerole, CRP, and body weight compared with sucrose. Sci. World J. 2008, 8, 463–469.
- Whitfield, P.; Parry-Strong, A.; Walsh, E.; Weatherall, M.; Krebs, J.D. The effect of a cinnamon-, chromium- and magnesium-formulated honey on glycaemic control, weight loss and lipid parameters in type 2 diabetes: An open-label cross-over randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 1123–1131.
- Erejuwa, O.O.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Ab Wahab, M.S.; Sirajudeen, K.N.S.; Salleh, S.; Gurtu, S. Honey Supplementation in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Elicits Antihypertensive Effect via Amelioration of Renal Oxidative Stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 374037.
- Erejuwa, O.; Sulaiman, S.; Suhaimi, M.; Sirajudeen, K.; Salleh, S.; Gurtu, S. Impaired Nrf2-ARE pathway contributes to increased oxidative damage in kidney of spontaneously hypertensive rats: Effect of antioxidant (honey). Int. J. Cardiol. 2011, 152, S45.
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Gan, R.-Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, A.-N.; Xu, D.-P.; Li, H.-B. Antioxidant phytochemicals for the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases. Molecules 2015, 20, 21138–21156.
- Batumalaie, K.; Qvist, R.; Yusof, K.M.; Ismail, I.S.; Sekaran, S.D. The antioxidant effect of the Malaysian Gelam honey on pancreatic hamster cells cultured under hyperglycemic conditions. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 14, 185–195.
- Gholami, M.; Hemmati, M.; Taheri-Ghahfarokhi, A.; Hoshyar, R.; Moossavi, M. Expression of glucokinase, glucose 6-phosphatase, and stress protein in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats treated with natural honey. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries. 2016, 36, 125–131.
- Abdulrhman, M.; El-Hefnawy, M.; Hussein, R.; El-Goud, A.A. The glycemic and peak incremental indices of honey, sucrose and glucose in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: Effects on C-peptide level—A pilot study. Acta Diabetol. 2011, 48, 89–94.
- Ambrose, J.A.; Barua, R.S. The pathophysiology of cigarette smoking and cardiovascular disease: An update. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 1731–1737.
- Mohamed, M.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Jaafar, H.; Sirajudeen, K.N.S. Antioxidant protective effect of honey in cigarette smoke-induced testicular damage in rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5508–5521.
- Ghazali, W.S.W.; Romli, A.C.; Mohamed, M. Effects of honey supplementation on inflammatory markers among chronic smokers: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 175.
- Wahdan, H.A.L. Causes of the antimicrobial activity of honey. Infection 1998, 26, 26–31.
- Kwakman, P.H.; te Velde, A.A.; de Boer, L.; Speijer, D.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.; Zaat, S.A. How honey kills bacteria. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 2576–2582.
- Nevas, M.; Hielm, S.; Lindström, M.; Horn, H.; Koivulehto, K.; Korkeala, H. High prevalence of Clostridium botulinum types A and B in honey samples detected by polymerase chain reaction. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 72, 45–52.
- Al-Waili, N.; Salom, K.; Al-Ghamdi, A.; Ansari, M.J. Antibiotic, pesticide, and microbial contaminants of honey: Human health hazards. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 930849.
- Schocken-Iturrino, R.P.; Carneiro, M.C.; Kato, E.; Sorbara, J.O.; Rossi, O.D.; Gerbasi, L.E. Study of the presence of the spores of Clostridium botulinum in honey in Brazil. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 1999, 24, 379–382.
- Satorres, S.; Alcaraz, L.; Centorbi, H.; Fernández, R. Detection of Clostridium botulinum spores in honey. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 1997, 29, 147–151.
- Nakano, H.; Sakagucki, G. An unusually heavy contamination of honey products by Clostridium botulinum type F and Bacillus alvei. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1991, 79, 171–178.
- Ahmed, A.K.J.; Hoekstra, M.J.; Hage, J.J.; Karim, R.B. Honey-medicated dressing: Transformation of an ancient remedy into modern therapy. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2003, 50, 143–148.
- Okuyan, E.; Uslu, A.; Ozan Levent, M. Cardiac effects of “mad honey”: A case series. Clin. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 528–532.
