Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) is a successful targeted radionuclide therapy in neuroendocrine tumors (NETs). However, complete responses remain elusive. Combined treatments anticipate synergistic effects and thus better responses by combining ionizing radiation with other anti-tumor treatments. Furthermore, multimodal therapies often have a balanced toxicity profile. To date, few studies have evaluated the effect of combination therapies with PRRT, some of them phase I/II trials.
- PRRT
- NET
- combination therapies
- personalized medicine
- somatostatin analogues
- chemotherapy
- molecular targeted treatment
- liver radioembolization
- Lutetium-177
- Yttrium-90
1. Introduction
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are heterogeneous neoplasia that are often diagnosed in the metastasized stage (range 40 to 76%), making them challenging to manage [1][2][3]. Guideline-oriented treatment options normally target only one specific pathway of the cell cycle. Such options are not always suitable for heterogeneous clones and can eventually result in treatment resistance [4][5][6].
Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) is proven to be an effective and safe treatment (EMA 2017 and FDA 2018 approved) that significantly prolongs survival and improves quality of life. However, according to prospective phase III study data, it has a limited response rate of only 18% [7][8][9]. Furthermore, since PPRT is not a curative treatment, patients eventually relapse. If recurrent tumors still have adequate somatostatin receptor (SSTR) expression, there is a good chance that salvage PRRT [10][11] will be beneficial. On the contrary, dedifferentiated NETs with loss of SSTR expression have a poor outcome with short survival following monotherapy [12]. Thus, combined treatment is a promising option for targeting heterogeneous tumors and avoiding accumulated toxicity. However, the data on combined treatment is still limited.
This review summarizes current data from clinically proven combination treatments with PRRT and aims to help physicians choose a tailored treatment approach for patients with NETs. Combination partners with possible synergistic therapeutic effects seem to be dual-PRRT radiolabeling, liver radioembolization, “non-radiolabeled” somatostatin analogues (SSAs), chemotherapy (e.g., capecitabine/temozolomide), molecular targeted treatment (e.g., everolimus), [131I]I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG), and external beam radiotherapy (EBRT).
Combination Treatment Decision Making
As represented in Figure 1, before starting a treatment, physicians should not only prioritize maximizing tumor response and patient survival but also minimize adverse events and patient morbidity. Substantial factors to consider in this decision-making are the age and health condition of the patient; genetic factors, tumor characteristics such as the origin, localization, size, and immunohistochemical proliferation marker Ki67; and tumor uptake in molecular imaging such as SSTR-positron emission tomography (PET) and [18F]F-Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG). Furthermore, an institution’s access to multidisciplinary medical care and medical center experience are important features for treatment planning [13][14][15]. Figure 2 represents the various antitumor effects of combination partners of PRRT. The objective response rates, PFS, OS and adverse events of combination partners of PRRT are listed in Table 1.
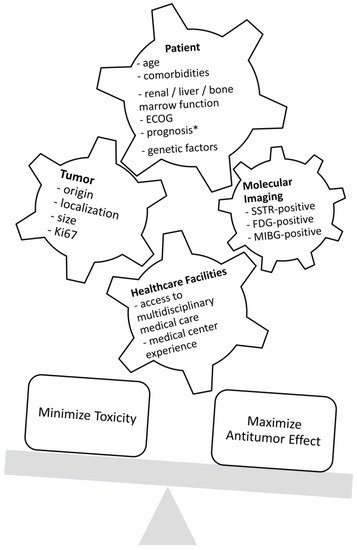
Figure 1. Factors that influence decision-making regarding treatment. ECOG = Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status; SSTR = somatostatin receptor; FDG = fluorodeoxyglucose; MIBG = metaiodobenzylguanidine; * life expectancy of at least 3 months.
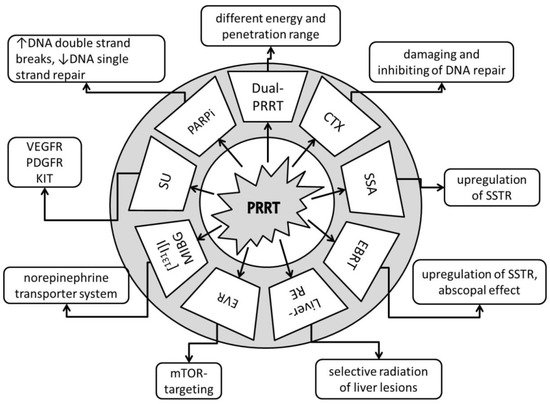
Figure 2. Anti-tumor effects of combination partners of PRRT. Dual-PRRT = dual-radionuclide peptide receptor therapy: a combination of different energy and penetration range levels to better target metastatic lesions with different sizes and nonhomogeneous somatostatin receptor (SSTR) distributions [16][17]. CTX = chemotherapy: damaging and inhibiting DNA repair, cell proliferation arrest, tumor cell reoxygenation, and synchronization of the cell cycle or apoptosis [18]. SSA = somatostatin receptor analogues: upregulation of SSTR, increasing number of targets for PRRT [19]. EBRT = fractionated external beam radiotherapy: upregulation of SSTR, increasing number of targets for PRRT, potential abscopal effect with triggering of immuno-mediated antitumor effects [20][21]. Liver-RE = liver radioembolization: selective radiation of liver tumor lesions; potential abscopal effect with triggering of immuno-mediated antitumor effects [22][23]. EVR = everolimus: targets the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), with growth-inhibitory and anti-angeogenic effects [24][25]. [131I]I-MIBG = [131I]I-metaiodobenzylguanidine: targets the norepinephrine transporter system [26]. SU = sunitinib: tumor growth arrest via targeting of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGFR), and receptor tyrosine kinase KIT [27]. PARPi = poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitors: increases DNA double-strand breaks; blocks DNA single-strand repair [28].
Table 1. Efficacy and safety of combination treatment with PRRT.
| Combination Partner | ORR (%) | OS (Month) |
PFS (Month) |
SAE (%) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual PRRT Lu-177 and Y-90 | 42 | 66–127 | - | 2% MDS, 2% nephrotoxicity, 7% hematotoxicity |
[17][29][30][31][32][33][34] |
| Capecitabine | 24–30 | not reached | 31 | <15% anemia/thrombocytopenia/neutropenia 5% fatigue/diarrhea |
[35][36][37] |
| CAPTEM | 53–70 | not reached | 22–48 | 6% neutropenia, 3% nausea | [38][39][40] |
| 5-fluorouracil | 25 | not reached | - | - | [41] |
| SSA | 37 | 91 | 48 | 3% hepatotoxicity | [42][43] |
| EBRT | 0 | not reached | 108 | 0% | [44] |
| Liver embolization | 16 (Y-90) 43 (Ho-166) |
42–68 | - | 10% abdominal pain, 3% fatigue/nausea, >20% lymphocytopenia, 5% radiation-induced gastric ulceration, 2% radiation pneumonitis, 2% liver abscess, 2% cholangitis, 50% liver enzyme elevation, <5% liver failure (2–3% fatal) |
[45][46][47] |
| Everolimus | 44 | not reached | not reached (63% at 24 months) | mainly hematotoxicity (thrombocytopenia, anemia) in the 10 mg/d everolimus dose group 100%, one case (6%) hepatotoxicity | [48] |
| [131I]I-MIBG | 0 | - | - | one case of three (33%) thrombocytopenia | [49] |
ORR = objective response rate; OS = overall survival; PFS = progression-free survival; SAE = serious adverse events according to CTCAE; Cave! In the table are listed collective SAE from different references. These SAE correlate only with the studied cohort in the particular investigation; Ref = references; MDS = myelodysplastic syndrome; CAPTEM = capecitabine and temozolomide; SSA = somatostatin receptor analogues; [131I]I-MIBG = [131I]I-metaiodobenzylguanidine; EBRT = fractionated external beam radiotherapy.
Dual-imaging SSTR-PET and FDG-PET can help clinicians plan individualized treatments [50]. Chan et al. developed a scoring system (NETPET grade) to distinguish between tumors with both SSTR- and FDG-positive lesions, only SSTR- or FDG-positive lesions, and both SSTR- and FDG-negative lesions. The NETPET grade is prognostic for survival and can help to determine which patients are likely to benefit from combination therapy, such as PRRT and chemotherapy [51][52].
2. Dual PRRT
Several agents are used for PRRT in advanced somatostatin receptor positive NETs. The essential components of radiopharmaceuticals are an SSA, which targets the somatostatin receptors, a radioisotope, and a linking molecule (chelator) between them. The pioneer in PRRT was diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid-(DTPA)-D-[Phe1]- Octreotide labelled with Indium-111. Indium-111 emits Auger electrons and conversion electrons with a potentially cytotoxic effect after internalization of the radiolabeled agent. Furthermore, the gamma emission of Indium-111 enables imaging of SSTR-positive tumors. However, standard treatment with [111In]In-DTPA-Octreotide rarely resulted in objective responses (<10%) [53]. High activity treatment seems to be more effective (13% complete remission, 20% partial remission), but the time to disease progression remains relatively short, with a median of 9 months [54]. Nowadays, the most commonly used and studied agents for the therapy are [[90Y]Y-DOTA,D-Phe1,Tyr3]-octreotide ([90Y]Y-DOTATOC) and [[177Lu]Lu-DOTA0,Tyr3]-octreotate ([177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE).
PRRT with Lutetium-177 has less detrimental effects in large, bulky NET metastases with nonhomogeneous SSTR distribution in comparison to Yttrium-90 due to its lower energy and shorter penetration range (maximum 2–4 mm vs. 11 mm). On the one hand, the radiation energy of Yttrium-90 is not completely absorbed in smaller tumors. On the other, Lutetium-177 alone may fail to induce a complete remission in large tumors. Therefore, PRRT combined with Lutetium-177 and Yttrium-90 might be a solution in such cases [16][17].
According to several similar studies, tandem PRRT leads to better results than monotherapy with Yttrium-90-PRRT: overall survival (OS) of 5.51 years vs. 3.96 years with [90Y]Y-Octreotide alone (p = 0.006), a high response rate of 42%, and still comparable toxicity (2% MDS, 2% grade 3 nephrotoxicity, and 7% grade 3/4 hematotoxicity) [17][29][30][31][32][33][34]. However, there are no comparative studies between the dual PRRT and the FDA-approved treatment LUTATHERA®.
In a recent report from a Warsaw study group, patients reached an OS of 7.46 years, calculated from the first tandem PRRT, and 10.61 years from the first NET diagnosis. In the subgroup analysis, patients with G1 and large bowel NET had the longest PFS/OS. The risk of progression in the first 2 years was 42% [55].
A phase II comparative study is now recruiting NET patients who are receiving PRRT with Yttrium-90 (4 × 3.7 GBq), PRRT with Lutetium-177 (4 × 5.55 GBq) or mixed therapy (4 × 3.7 GBq). The treatment will consist of 4 cycles 8 ± 2 weeks apart. Approximately 150 participants with GEP-NETs and non-GEP-NETs, including bronchopulmonary NETs, pheochromocytoma/paragangliomas and NETs of an unknown primary, are expected to be included in the study. The analysis will strive to have a long follow-up (up to 8 years) to determine progression-free survival (PFS), OS, and safety (CI: NCT04029428).
Novel combined dual PRRT is the combination of alpha-emitter PRRT and beta-emitter PRRT. Tumor hypoxia is a significant factor for resistance of cancer cells to β-emitters. Thus, α-emitters can be advantageous in some cases due to a higher energy transfer and smaller penetration range. In the clinical setting alpha-emitter PRRT is applied in case of tumor resistance to conventional PRRT. Most studied isotopes for alpha radionuclide therapy are Bismuth-213 and Actinium-225. [56][57][58][59][60]. Newer promising developments are SSTR-agonists labelled with Lead-212, such as AlphaMedix® [61][62][63]. The first results of the prospective phase I trial show good tolerability in PRRT-naïve patients (CI: NCT03466216).
3. Chemotherapy
Low-dose chemotherapy may have a radiosensitizing effect via increased DNA damage, inhibition of DNA repair, cell proliferation arrest, tumor cell re-oxygenation, synchronization of the cell cycle, or apoptosis [18]. The most commonly used radiosensitizing substances are capecitabine, temozolomide, and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU).
G3-neuroendocrine neoplasia (NEN) with Ki67 < 55% seems to be less responsive to chemotherapy than G3-NEN with Ki67 > 55% [64]. The OS of patients with Ki67 < 55% treated with chemotherapy in the NORDIC trial was 14 months (Sorbye et al., 2013). In contrast, patients with SSTR-positive tumors with Ki67 < 55% treated with combined PRRT and chemotherapy (PRCRT) reached, according to retrospective analyses, an OS of 46 months [64][65]. Other retrospective studies have reported a disease control rate of 55–70% in multiple relapsed and extensively pre-treated NETs [66][67].
The Melbourne study group analyzed 68 patients after combined PRRT with 5-FU. The first cycle PPRT was given alone. The 5-FU (200 mg/m2/d) started 4 days before the second PRRT and continued for 3 weeks. Objective responses in computed tomography (CT) were seen in 25% of cases, and an additional 7% of cases showed minor responses. The majority of patients had stable disease [41].
A study conducted in Rotterdam evaluated the safety of four cycles of PPRT (7.4 GBq [177Lu]Lu-Octreotate) combined with capecitabine (1650 mg/m2 per day for two weeks). Of the seven patients included in the study, there was one case of grade 3 anemia and one case of grade 3 thrombocytopenia. No other severe adverse events were observed [35].
An Australian study (phase II) investigated the efficacy of patients after PRRT combined with capecitabine under a similar protocol. About one-fourth of patients had an objective response, only 6% progressed, and the majority had stable disease [36]. In a similar study by Nicolini et al., the combined PRRT plus capecitabine in 37 selected patients reached both somatostatin receptor- and FDG-positive GEP-NETs (Ki67% < 55%), PFS of 31 months; OS after a median follow-up of 38 months was not reached. The most common G3/G4 toxicities were neutropenia (11%), fatigue (5%), and diarrhea (5%). According to RECIST 1.1, 30% of patients responded, and 55% were stable [37].
Better responses with similar toxicities have been observed with a combination of PRRT and CAPTEM: capecitabine (14 days of 1500 mg/m2) and temozolomide (5 days of 200 mg/m2. About 3% of patients had grade 3 nausea, and 6% had grade 3 neutropenia. About 53–70% had an objective response. The proportion of complete responses was relatively high, at 13–15% [38][39]. Patients achieved a median PFS of 48 months, and OS after a median follow-up of 33 months was not reached [39]. Rarely there can be life-threatening neutropenia. An interesting report from Berlin described a case of neutropenic sepsis accompanied by fungal pulmonary infection and necrotizing mastitis about four weeks after the first cycle of combined PRRT plus CAPTEM. Still, the treatment has been continued after stabilization of the patient and resulted in a nearly complete response [68]. Surprisingly, recent retrospectively generated data from Mumbai showed no significant difference in PFS after combined treatment of PRRT plus CAPTEM compared to CAPTEM alone in patients with both SSTR- and FDG-positive G2/G3-NETs. In the multivariate analysis, CAPTEM alone or with PRRT significantly improved (p = 0.04) the outcomes of dual positive NET patients with a Ki-67 index > 5% [40].
A multicenter randomized clinical trial from Australia is currently recruiting patients with G1/G2 NETs to compare the benefits of PRRT vs. CAPTEM vs. combined PRRT and CAPTEM. The combination treatment will start with capecitabine 750 mg/m2 on days 1–14, followed by 7.8 GBq PPRT with [177Lu]Lu-Octreotate on day 10 and, at the end of the cycle, temozolomide 75mg/m2 b.i.d. on days 10–14. The treatment will include 4 cycles, 8 weeks apart (CI: NCT02358356). Another ongoing prospective trial evaluating combined treatment should be completed soon (CI: NCT02736448).
4. Somatostatin Analogues
Treatment with SSAs can result in the upregulation of SSTR [19]. The overexpression of the tumor targets SSTR2 in NETs could increase the effectiveness of PRRT without increasing the toxicity profile.
SSAs, like PRRT, have a high affinity to SSTR2 and therefore might act competitively in binding the tumor cells of NETs or lead to saturation. In current protocols, long-acting SSA should be discontinued about 4 weeks before PRRT to avoid interactions with radiolabeled SSAs [69]. Several studies suggest that discontinuation of somatostatin agonists prior to PRRT/SSTR-PET/CT is not necessary. In fact, the uptake in the tumor was unaffected or slightly increased, and the uptake in normal tissues, such as spleen and liver, decreased [70][71][72]. The explanation for this effect might be the saturation of SSTRs in healthy tissues and the upregulation of SSTR in tumor cells [6]. However, more investigations to determine the interaction between PRRT and SSA are needed to change standard protocols.
The NETTER-1 phase III trial showed, in advanced midgut NETs, that PRRT combined with SSA significantly prolonged PFS compared to SSA alone [8]. Recent analysis showed clinically improved median OS of 48 vs. 36 months compared to the control arm. However, the difference was not statistically significant between both groups, probably because of the high rate of cross-over-treatment in the study (36%) [73]. A debatable point of the NETTER-1 study is whether the effect of PRRT has been potentiated by SSA. A recent retrospective study aimed to examine whether a superior survival benefit of PRRT combined with SSAs exists over monotherapy with PRRT. The analysis showed that SSA combined with PRRT and/or as a maintenance treatment after PRRT significantly prolongs survival compared to PRRT alone (PFS 48 months vs. 27 months; OS 91 months vs. 47 months). Furthermore, the death event rates in patients with combined treatment were lower: 26% vs. 63% [43]. A multicenter retrospective trial PRELUDE examined the effects of the SSA lanreotide autogel/depot (LAN) combined with PRRT in progressive NETs. No increased adverse drug reactions were reported. More than one-third of patients had an objective response, and 95% were, at the last follow-up visit (12 months post-treatment), still progression-free. Naturally, these are retrospective data and might be prone to bias. However, if a patient tolerates treatment with SSA, there is no reason to withdraw SSA before or after PRRT. Furthermore, SSA may improve the outcomes of patients who receive PRRT [43]. To validate these data, prospective studies in a larger population using standardized treatment protocols are warranted.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ph14101005
References
- Das, S.; Dasari, A. Epidemiology, Incidence, and Prevalence of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Are There Global Differences? Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 43.
- Riihimäki, M.; Hemminki, A.; Sundquist, K.; Sundquist, J.; Hemminki, K. The epidemiology of metastases in neuroendocrine tumors. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 2679–2686.
- Pedraza-Arévalo, S.; Gahete, M.D.; Alors-Pérez, E.; Luque, R.M.; Castaño, J.P. Multilayered heterogeneity as an intrinsic hallmark of neuroendocrine tumors. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2018, 19, 179–192.
- Grozinsky-Glasberg, S.; Shimon, I.; Korbonits, M.; Grossman, A.B. Somatostatin analogues in the control of neuroendocrine tumours: Efficacy and mechanisms. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2008, 15, 701–720.
- Oberg, K.; Casanovas, O.; Castaño, J.P.; Chung, D.; Delle Fave, G.; Denèfle, P.; Harris, P.; Khan, M.S.; Kulke, M.H.; Scarpa, A.; et al. Molecular pathogenesis of neuroendocrine tumors: Implications for current and future therapeutic approaches. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2842–2849.
- Adant, S.; Shah, G.M.; Beauregard, J.-M. Combination treatments to enhance peptide receptor radionuclide therapy of neuroendocrine tumours. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 907–921.
- Hennrich, U.; Kopka, K. Lutathera®: The First FDA- and EMA-Approved Radiopharmaceutical for Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 114.
- Strosberg, J.; El-Haddad, G.; Wolin, E.; Hendifar, A.; Yao, J.; Chasen, B.; Mittra, E.; Kunz, P.L.; Kulke, M.H.; Jacene, H.; et al. Phase 3 Trial of (177)Lu-Dotatate for Midgut Neuroendocrine Tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 125–135.
- Strosberg, J.; Wolin, E.; Chasen, B.; Kulke, M.; Bushnell, D.; Caplin, M.; Baum, R.P.; Kunz, P.; Hobday, T.; Hendifar, A.; et al. Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With Progressive Midgut Neuroendocrine Tumors Treated With (177)Lu-Dotatate in the Phase III NETTER-1 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2578–2584.
- Sabet, A.; Haslerud, T.; Pape, U.-F.; Sabet, A.; Ahmadzadehfar, H.; Grünwald, F.; Guhlke, S.; Biersack, H.-J.; Ezziddin, S. Outcome and toxicity of salvage therapy with 177Lu-octreotate in patients with metastatic gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 205–210.
- Yordanova, A.; Mayer, K.; Brossart, P.; Gonzalez-Carmona, M.A.; Strassburg, C.P.; Essler, M.; Ahmadzadehfar, H. Safety of multiple repeated cycles of 177Lu-octreotate in patients with recurrent neuroendocrine tumour. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 1207–1214.
- Werner, R.A.; Weich, A.; Higuchi, T.; Schmid, J.S.; Schirbel, A.; Lassmann, M.; Wild, V.; Rudelius, M.; Kudlich, T.; Herrmann, K.; et al. Imaging of Chemokine Receptor 4 Expression in Neuroendocrine Tumors—A Triple Tracer Comparative Approach. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1489–1498.
- Soukup, T.; Lamb, B.W.; Weigl, M.; Green, J.S.A.; Sevdalis, N. An Integrated Literature Review of Time-on-Task Effects with a Pragmatic Framework for Understanding and Improving Decision-Making in Multidisciplinary Oncology Team Meetings. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1245.
- Yordanova, A. Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy. In Clinical Nuclear Medicine; Ahmadzadehfar, H., Biersack, H.-J., Freeman, L.M., Zuckier, L.S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 867–898. ISBN 978-3-030-39455-4.
- Yordanova, A.; Ahmadzadehfar, H.; Gonzalez-Carmona, M.; Strassburg, C.; Mayer, K.; Feldmann, G.; Schmidt-Wolf, I.; Lingohr, P.; Fischer, S.; Kristiansen, G.; et al. A Step-by-Step Clinical Approach for the Management of Neuroendocrine Tumours. Horm. Metab. Res. 2017, 49, 77–85.
- Parghane, R.V.; Mitra, A.; Bannore, T.U.; Rakshit, S.; Banerjee, S.; Basu, S. Initial clinical evaluation of indigenous (90)Y-DOTATATE in sequential duo-PRRT approach ((177)Lu-DOTATATE and (90)Y-DOTATATE) in neuroendocrine tumors with large bulky disease: Observation on tolerability, (90)Y-DOTATATE post-PRRT imaging characteristics (bremsstrahlung and PETCT) and early adverse effects. World J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 20, 73–81.
- de Jong, M.; Breeman, W.A.P.; Valkema, R.; Bernard, B.F.; Krenning, E.P. Combination radionuclide therapy using 177Lu- and 90Y-labeled somatostatin analogs. J. Nucl. Med. 2005, 46 (Suppl. S1), 13S–17S.
- Bison, S.M.; Konijnenberg, M.W.; Melis, M.; Pool, S.E.; Bernsen, M.R.; Teunissen, J.J.M.; Kwekkeboom, D.J.; de Jong, M. Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy using radiolabeled somatostatin analogs: Focus on future developments. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2014, 2, 55–66.
- Presky, D.H.; Schonbrunn, A. Somatostatin pretreatment increases the number of somatostatin receptors in GH4C1 pituitary cells and does not reduce cellular responsiveness to somatostatin. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 714–721.
- Oddstig, J.; Bernhardt, P.; Nilsson, O.; Ahlman, H.; Forssell-Aronsson, E. Radiation induces up-regulation of somatostatin receptors 1, 2, and 5 in small cell lung cancer in vitro also at low absorbed doses. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2011, 26, 759–765.
- Reynders, K.; Illidge, T.; Siva, S.; Chang, J.Y.; De Ruysscher, D. The abscopal effect of local radiotherapy: Using immunotherapy to make a rare event clinically relevant. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2015, 41, 503–510.
- Ahmadzadehfar, H.; Biersack, H.-J.; Ezziddin, S. Radioembolization of Liver Tumors with Yttrium-90 Microspheres. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2010, 40, 105–121.
- Edeline, J.; Rolland, Y.; Garin, E. Abscopal Effect After SIRT: It Exists, but How Could We Use It? CardioVasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 43, 1650–1651.
- Multhoff, G.; Radons, J.; Vaupel, P. Critical role of aberrant angiogenesis in the development of tumor hypoxia and associated radioresistance. Cancers 2014, 6, 813–828.
- D’Onofrio, M.; Cingarlini, S.; Ortolani, S.; Crosara, S.; de Robertis, R.; Vallerio, P.; Grego, E.; Ciaravino, V.; Ruzzenente, A.; Landoni, L.; et al. Perfusion CT Changes in Liver Metastases from Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors During Everolimus Treatment. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 1305–1311.
- Pandit-Taskar, N.; Modak, S. Norepinephrine Transporter as a Target for Imaging and Therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 39S.
- Faivre, S.; Niccoli, P.; Castellano, D.; Valle, J.W.; Hammel, P.; Raoul, J.-L.; Vinik, A.; van Cutsem, E.; Bang, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; et al. Sunitinib in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: Updated progression-free survival and final overall survival from a phase III randomized study. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 339–343.
- Caron, M.-C.; Sharma, A.K.; O’Sullivan, J.; Myler, L.R.; Ferreira, M.T.; Rodrigue, A.; Coulombe, Y.; Ethier, C.; Gagné, J.-P.; Langelier, M.-F.; et al. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 antagonizes DNA resection at double-strand breaks. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2954.
- Yao, J.C.; Fazio, N.; Singh, S.; Buzzoni, R.; Carnaghi, C.; Wolin, E.; Tomasek, J.; Raderer, M.; Lahner, H.; Voi, M.; et al. Everolimus for the treatment of advanced, non-functional neuroendocrine tumours of the lung or gastrointestinal tract (RADIANT-4): A randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet 2016, 387, 968–977.
- Villard, L.; Romer, A.; Marincek, N.; Brunner, P.; Koller, M.T.; Schindler, C.; Ng, Q.K.T.; Mäcke, H.R.; Müller-Brand, J.; Rochlitz, C.; et al. Cohort study of somatostatin-based radiopeptide therapy with (90)Y-DOTA-TOC versus (90)Y-DOTA-TOC plus (177)Lu-DOTA-TOC in neuroendocrine cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1100–1106.
- Seregni, E.; Maccauro, M.; Chiesa, C.; Mariani, L.; Pascali, C.; Mazzaferro, V.; de Braud, F.; Buzzoni, R.; Milione, M.; Lorenzoni, A.; et al. Treatment with tandem 90YDOTA-TATE and 177LuDOTA-TATE of neuroendocrine tumours refractory to conventional therapy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 223–230.
- Kunikowska, J.; Królicki, L.; Hubalewska-Dydejczyk, A.; Mikołajczak, R.; Sowa-Staszczak, A.; Pawlak, D. Clinical results of radionuclide therapy of neuroendocrine tumours with 90Y-DOTATATE and tandem 90Y/177Lu-DOTATATE: Which is a better therapy option? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 38, 1788–1797.
- Kunikowska, J.; Pawlak, D.; Bąk, M.I.; Kos-Kudła, B.; Mikołajczak, R.; Królicki, L. Long-term results and tolerability of tandem peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with (90)Y/(177)Lu-DOTATATE in neuroendocrine tumors with respect to the primary location: A 10-year study. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2017, 31, 347–356.
- Pfeifer, A.K.; Gregersen, T.; Grønbæk, H.; Hansen, C.P.; Müller-Brand, J.; Herskind Bruun, K.; Krogh, K.; Kjær, A.; Knigge, U. Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with Y-DOTATOC and (177)Lu-DOTATOC in advanced neuroendocrine tumors: Results from a Danish cohort treated in Switzerland. Neuroendocrinology 2011, 93, 189–196.
- van Essen, M.; Krenning, E.P.; Kam, B.L.; de Herder, W.W.; van Aken, M.O.; Kwekkeboom, D.J. Report on short-term side effects of treatments with 177Lu-octreotate in combination with capecitabine in seven patients with gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 743–748.
- Claringbold, P.G.; Brayshaw, P.A.; Price, R.A.; Turner, J.H. Phase II study of radiopeptide 177Lu-octreotate and capecitabine therapy of progressive disseminated neuroendocrine tumours. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 38, 302–311.
- Nicolini, S.; Bodei, L.; Bongiovanni, A.; Sansovini, M.; Grassi, I.; Ibrahim, T.; Monti, M.; Caroli, P.; Sarnelli, A.; Diano, D.; et al. Combined use of 177Lu-DOTATATE and metronomic capecitabine (Lu-X) in FDG-positive gastro-entero-pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 3260–3267.
- Claringbold, P.G.; Price, R.A.; Turner, J.H. Phase I-II study of radiopeptide 177Lu-octreotate in combination with capecitabine and temozolomide in advanced low-grade neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2012, 27, 561–569.
- Claringbold, P.G.; Turner, J.H. Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor Control: Durable Objective Response to Combination 177Lu-Octreotate-Capecitabine-Temozolomide Radiopeptide Chemotherapy. Neuroendocrinology 2016, 103, 432–439.
- Ostwal, V.; Basu, S.; Bhargava, P.; Shah, M.; Parghane, R.V.; Srinivas, S.; Chaudhari, V.; Bhandare, M.S.; Shrikhande, S.V.; Ramaswamy, A. Capecitabine-Temozolomide (CAPTEM) in advanced Grade 2 and grade 3 Neuroendocrine neoplasms (NENs)—Benefits of chemotherapy in NENs with significant 18FDG uptake. Neuroendocrinology 2020, 111, 998–1004.
- Kong, G.; Thompson, M.; Collins, M.; Herschtal, A.; Hofman, M.S.; Johnston, V.; Eu, P.; Michael, M.; Hicks, R.J. Assessment of predictors of response and long-term survival of patients with neuroendocrine tumour treated with peptide receptor chemoradionuclide therapy (PRCRT). Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 1831–1844.
- Prasad, V.; Srirajaskanthan, R.; Toumpanakis, C.; Grana, C.M.; Baldari, S.; Shah, T.; Lamarca, A.; Courbon, F.; Scheidhauer, K.; Baudin, E.; et al. Lessons from a multicentre retrospective study of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy combined with lanreotide for neuroendocrine tumours: A need for standardised practice. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 2358–2371.
- Yordanova, A.; Wicharz, M.M.; Mayer, K.; Brossart, P.; Gonzalez-Carmona, M.A.; Strassburg, C.P.; Fimmers, R.; Essler, M.; Ahmadzadehfar, H. The Role of Adding Somatostatin Analogues to Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy as a Combination and Maintenance Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4672–4679.
- Hartrampf, P.E.; Hänscheid, H.; Kertels, O.; Schirbel, A.; Kreissl, M.C.; Flentje, M.; Sweeney, R.A.; Buck, A.K.; Polat, B.; Lapa, C. Long-term results of multimodal peptide receptor radionuclide therapy and fractionated external beam radiotherapy for treatment of advanced symptomatic meningioma. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 22, 29–32.
- Braat, A.J.A.T.; Ahmadzadehfar, H.; Kappadath, S.C.; Stothers, C.L.; Frilling, A.; Deroose, C.M.; Flamen, P.; Brown, D.B.; Sze, D.Y.; Mahvash, A.; et al. Radioembolization with (90)Y Resin Microspheres of Neuroendocrine Liver Metastases After Initial Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy. CardioVasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 43, 246–253.
- Braat, A.J.; Bruijnen, R.C.; van Rooij, R.; Braat, M.N.; Wessels, F.J.; van Leeuwaarde, R.S.; van Treijen, M.J.; de Herder, W.W.; Hofland, J.; Tesselaar, M.E.; et al. Additional holmium-166 radioembolisation after lutetium-177-dotatate in patients with neuroendocrine tumour liver metastases (HEPAR PLuS): A single-centre, single-arm, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 561–570.
- Yilmaz, E.; Engin, M.N.; Özkan, Z.G.; Kovan, B.; Büyükkaya, F.; Poyanli, A.; Sağlam, S.; Başaran, M.; Türkmen, C. Y90 selective internal radiation therapy and peptide receptor radionuclide therapy for the treatment of metastatic neuroendocrine tumors: Combination or not? Nucl. Med. Commun. 2020, 41, 1242–1249.
- Claringbold, P.G.; Turner, J.H. NeuroEndocrine Tumor Therapy with Lutetium-177-octreotate and Everolimus (NETTLE): A Phase I Study. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2015, 30, 261–269.
- Bushnell, D.L.; Bodeker, K.L.; O’Dorisio, T.M.; Madsen, M.T.; Menda, Y.; Graves, S.A.; O’Dorisio, M.S.; Zamba, G.K.D. Addition Of (131)I MIBG To PRRT ((90)Y DOTATOC) For Personalized Treatment of Selected Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62.
- Hindié, E. The NETPET Score: Combining FDG and Somatostatin Receptor Imaging for Optimal Management of Patients with Metastatic Well-Differentiated Neuroendocrine Tumors. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1159–1163.
- Chan, D.L.; Pavlakis, N.; Schembri, G.P.; Bernard, E.J.; Hsiao, E.; Hayes, A.; Barnes, T.; Diakos, C.; Khasraw, M.; Samra, J.; et al. Dual Somatostatin Receptor/FDG PET/CT Imaging in Metastatic Neuroendocrine Tumours: Proposal for a Novel Grading Scheme with Prognostic Significance. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1149–1158.
- Has Simsek, D.; Kuyumcu, S.; Turkmen, C.; Sanlı, Y.; Aykan, F.; Unal, S.; Adalet, I. Can complementary 68Ga-DOTATATE and 18F-FDG PET/CT establish the missing link between histopathology and therapeutic approach in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors? J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1811–1817.
- Anthony, L.B.; Woltering, E.A.; Espenan, G.D.; Cronin, M.D.; Maloney, T.J.; McCarthy, K.E. Indium-111-pentetreotide prolongs survival in gastroenteropancreatic malignancies. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2002, 32, 123–132.
- Buscombe, J.R.; Caplin, M.E.; Hilson, A.J.W. Long-term efficacy of high-activity 111in-pentetreotide therapy in patients with disseminated neuroendocrine tumors. J. Nucl. Med. 2003, 44, 1–6.
- Kunikowska, J.; Zemczak, A.; Kołodziej, M.; Gut, P.; Łoń, I.; Pawlak, D.; Mikołajczak, R.; Kamiński, G.; Ruchała, M.; Kos-Kudła, B.; et al. Tandem peptide receptor radionuclide therapy using (90)Y/(177)Lu-DOTATATE for neuroendocrine tumors efficacy and side-effects—Polish multicenter experience. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 922–933.
- Kratochwil, C.; Giesel, F.L.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Mier, W.; Apostolidis, C.; Boll, R.; Murphy, K.; Haberkorn, U.; Morgenstern, A. 213Bi-DOTATOC receptor-targeted alpha-radionuclide therapy induces remission in neuroendocrine tumours refractory to beta radiation: A first-in-human experience. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 2106–2119.
- Chan, H.S.; Konijnenberg, M.W.; Daniels, T.; Nysus, M.; Makvandi, M.; de Blois, E.; Breeman, W.A.; Atcher, R.W.; de Jong, M.; Norenberg, J.P. Improved safety and efficacy of (213)Bi-DOTATATE-targeted alpha therapy of somatostatin receptor-expressing neuroendocrine tumors in mice pre-treated with L-lysine. EJNMMI Res. 2016, 6, 83.
- Miederer, M.; Henriksen, G.; Alke, A.; Mossbrugger, I.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Senekowitsch-Schmidtke, R.; Essler, M. Preclinical evaluation of the alpha-particle generator nuclide 225Ac for somatostatin receptor radiotherapy of neuroendocrine tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 3555–3561.
- Zhang, J.; Kulkarni, H.R.; Baum, R.P. Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy Using 225Ac-DOTATOC Achieves Partial Remission in a Patient with Progressive Neuroendocrine Liver Metastases After Repeated β-Emitter Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2020, 45, 241–243.
- Ballal, S.; Yadav, M.P.; Bal, C.; Sahoo, R.K.; Tripathi, M. Broadening horizons with (225)Ac-DOTATATE targeted alpha therapy for gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumour patients stable or refractory to (177)Lu-DOTATATE PRRT: First clinical experience on the efficacy and safety. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 934–946.
- Lee, D.; Graves, S.; Liu, D.; Wen, H.; Zepeda-Orozco, D.; Madsen, M.; Walsh, S.; Watkins, G.; Menda, Y.; Schultz, M.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of 212Pb-based alpha-particle therapy for neuroendocrine tumors: Dosimetry and potential toxicities. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 663.
- Delpassand, E.; Tworowska, I.; Esfandiari, R.; Torgue, J.; Hurt, J.D.; Nunez, R. Phase I dose-escalation study of AlphaMedix for targeted-alpha-emitter therapy of PRRT-naive neuroendocrine patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 4117.
- Stallons, T.A.R.; Saidi, A.; Tworowska, I.; Delpassand, E.S.; Torgue, J.J. Preclinical Investigation of (212)Pb-DOTAMTATE for Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy in a Neuroendocrine Tumor Model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1012–1021.
- Sorbye, H.; Welin, S.; Langer, S.W.; Vestermark, L.W.; Holt, N.; Osterlund, P.; Dueland, S.; Hofsli, E.; Guren, M.G.; Ohrling, K.; et al. Predictive and prognostic factors for treatment and survival in 305 patients with advanced gastrointestinal neuroendocrine carcinoma (WHO G3): The NORDIC NEC study. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 152–160.
- Thang, S.P.; Lung, M.S.; Kong, G.; Hofman, M.S.; Callahan, J.; Michael, M.; Hicks, R.J. Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) in European Neuroendocrine Tumour Society (ENETS) grade 3 (G3) neuroendocrine neoplasia (NEN)—A single-institution retrospective analysis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 262–277.
- Nicolini, S.; Severi, S.; Ianniello, A.; Sansovini, M.; Ambrosetti, A.; Bongiovanni, A.; Scarpi, E.; Di Mauro, F.; Rossi, A.; Matteucci, F.; et al. Investigation of receptor radionuclide therapy with (177)Lu-DOTATATE in patients with GEP-NEN and a high Ki-67 proliferation index. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 923–930.
- Yordanova, A.; Ahrens, H.; Feldmann, G.; Brossart, P.; Gaertner, F.C.; Fottner, C.; Weber, M.M.; Ahmadzadehfar, H.; Schreckenberger, M.; Miederer, M.; et al. Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy Combined with Chemotherapy in Patients With Neuroendocrine Tumors. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2019, 44, e329–e335.
- Özdirik, B.; Amthauer, H.; Schatka, I.; Goretzki, P.E.; Mogl, M.T.; Fehrenbach, U.; Tacke, F.; Jann, H.; Roderburg, C. A rare case of a patient with a high grade neuroendocrine tumor developing neutropenic sepsis after receiving PRRT combined with Capecitabine or Temozolomide: A case report. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 14, 20.
- Hicks, R.J.; Kwekkeboom, D.J.; Krenning, E.; Bodei, L.; Grozinsky-Glasberg, S.; Arnold, R.; Borbath, I.; Cwikla, J.; Toumpanakis, C.; Kaltsas, G.; et al. ENETS Consensus Guidelines for the Standards of Care in Neuroendocrine Neoplasia: Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy with Radiolabeled Somatostatin Analogues. Neuroendocrinology 2017, 105, 295–309.
- Haug, A.R.; Rominger, A.; Mustafa, M.; Auernhammer, C.; Göke, B.; Schmidt, G.P.; Wängler, B.; Cumming, P.; Bartenstein, P.; Hacker, M. Treatment with Octreotide Does Not Reduce Tumor Uptake of 68Ga-DOTATATE as Measured by PET/CT in Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 1679–1683.
- Cherk, M.H.; Kong, G.; Hicks, R.J.; Hofman, M.S. Changes in biodistribution on (68)Ga-DOTA-Octreotate PET/CT after long acting somatostatin analogue therapy in neuroendocrine tumour patients may result in pseudoprogression. Cancer Imaging 2018, 18, 3.
- Aalbersberg, E.A.; de Wit-van der Veen, B.J.; Versleijen, M.W.J.; Saveur, L.J.; Valk, G.D.; Tesselaar, M.E.T.; Stokkel, M.P.M. Influence of lanreotide on uptake of (68)Ga-DOTATATE in patients with neuroendocrine tumours: A prospective intra-patient evaluation. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 696–703.
- Strosberg, J.R.; Caplin, M.E.; Kunz, P.L.; Ruszniewski, P.B.; Bodei, L.; Hendifar, A.E.; Mittra, E.; Wolin, E.M.; Yao, J.C.; Pavel, M.E.; et al. Final overall survival in the phase 3 NETTER-1 study of lutetium-177-DOTATATE in patients with midgut neuroendocrine tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 4112.
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
