Drought stress restricts plant growth and development by altering metabolic activity and biological functions. However, plants have evolved several cellular and molecular mechanisms to overcome drought stress. Drought tolerance is a multiplex trait involving the activation of signaling mechanisms and differentially expressed molecular responses. Broadly, drought tolerance comprises two steps: stress sensing/signaling and activation of various parallel stress responses (including physiological, molecular, and biochemical mechanisms) in plants. At the cellular level, drought induces oxidative stress by overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS), ultimately causing the cell membrane to rupture and stimulating various stress signaling pathways (ROS, mitogen-activated-protein-kinase, Ca2+, and hormone-mediated signaling). Drought-induced transcription factors activation and abscisic acid concentration co-ordinate the stress signaling and responses in cotton. The key responses against drought stress, are root development, stomatal closure, photosynthesis, hormone production, and ROS scavenging. The genetic basis, quantitative trait loci and genes of cotton drought tolerance are presented as examples of genetic resources in plants. Sustainable genetic improvements could be achieved through functional genomic approaches and genome modification techniques such as the CRISPR/Cas9 system aid the characterization of genes, sorted out from stress-related candidate single nucleotide polymorphisms, quantitative trait loci, and genes. Exploration of the genetic basis for superior candidate genes linked to stress physiology can be facilitated by integrated functional genomic approaches. We propose a third-generation sequencing approach coupled with genome-wide studies and functional genomic tools, including a comparative sequenced data (transcriptomics, proteomics, and epigenomic) analysis, which offer a platform to identify and characterize novel genes. This will provide information for better understanding the complex stress cellular biology of plants.
- cellular stress signaling
- drought stress responses
1. Introduction
2. Role of TFs in Drought Stress Signaling Pathways
| Gene | Type | Phenotypic Effect/Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| GhHUB2 | Histone H2B monoubiquitinatin E3 ligase encoding gene | Drought tolerance through increased soluble sugar, proline, and leaf relative water contents | [43] |
| GrMAPKKK and GhMAPKKK | MAPK gene family | Drought and salt responsive | [20] |
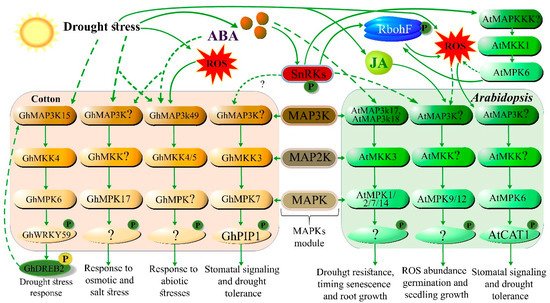
| GhMAP3K1, GhMKK4, and GhMPK6 | MAPK signaling gene | Regulates the drought stress response by interacting with GhWRKY59–GhDREB2 | [26] |
| GhMKK3 | MAPK signaling gene | Enhanced drought tolerance | [25] |
| GhMAP3K40 | MAPK signaling gene | Salt and drought stress tolerance at the germination stage | [44] |
| GhMPK4 | MAPK signaling gene | Increased sensitivity to ABA, salt, and drought | [45] |
| GhMPK17 | MAPK signaling gene | Osmotic and salt stress tolerance | [46] |
| GbMPK3 | MAPK signaling gene | Enhanced oxidative and drought stress tolerance | [47] |
| GhMPK6a | MAPK signaling gene | Drought and salinity | [48] |
| GhMKK1 | MAPK signaling gene | Drought and salinity | [49] |
| GhMKK5 | MAPK signaling gene | Drought and salinity | [50] |
| GhMPK2 | MAPK signaling gene | Drought and salinity | [51] |
| GbRLK | Receptor-like kinase | Drought and salinity | [52] |
| GaHDG11 (HD-ZIP) |
Transcription factor | Drought and heat stress | [53] |
| GhNAC79 | Transcription factor | Improves resistance to drought stress | [42] |
| GhERF38 | Transcription factor | Drought, abscisic acid, and salinity | [54] |
| GhERF2, GhERF3, GhERF6 | Transcription factor | Drought, salt, ethylene, and abscisic acid | [55] |
| GhWRKY59 | Transcription factor | Activates MAPK signaling gene under drought | [26] |
| GhWRKY25 | Transcription factor | Drought and salinity | [56] |
| GhABF2 (bZIP) | Transcription factor | Enhances the activities of CAT and SOD, regulates gene expression related to ABA | [39] |
| GhNAC2 | Transcription factor | Longer roots, and enhanced salt and drought tolerance | [57] |
| GhCBF3, GhAREB1, and GhAREB2 | ABA-induced gene | Small stomatal aperture, enhanced drought- and high salinity-tolerance via the ABA signaling pathway | [58] |
| GhNAC7-GhNAC13 | Transcription factor | Cold, abscisic acid, drought, and salinity | [59] |
| GbMYB5 | Transcription factor | Reduced water loss trough stomatal conductance, and increased proline content and antioxidant enzymes | [27] |
| GhWRKY41 | Transcription factor | Lower malondialdehyde content, higher antioxidant activity, and induced stomatal conductance | [41] |
| GhWRKY17 | Transcription factor | Increases sensitivity to ABA and drought stress | [60] |
| GhNAC8-GhNAC17 | Transcription factor | Drought, salinity, cold, and ABA | [61] |
| GhNAC1-GhNAC6 | Transcription factor | Drought, cold, salinity, and ABA | [62] |
| GhDREB | Transcription factor | Drought, cold, and salinity | [63] |
| GhDREB1 | Transcription factor | Drought, cold, and salinity | [64] |
| GhDBP2 | Transcription factor | Drought, cold, and ABA | [65] |
| GhERF1 | Transcription factor | ABA production and drought stress signaling regulation | [66] |
| GhERF4 | Transcription factor | ABA production and drought stress signaling regulation | [67] |
| GhDREB1L | Transcription factor | Drought, cold, and salinity | [68] |
| GhPYL9–11A | ABA receptor gene | ABA receptor that mediates the response to drought stress | [69] |
| GhSnRK2 | Involved in ABA signaling | Drought, salinity, cold, and ABA | [70] |
| GhCDPK35, GhCDPK28, GhCDPK16, GhCDPK14, GhCDPK11 and GhCDPK3 | Ca2+-activated gene | Drought and salinity stress responsive | [7] |
| GhCIPK6 | Ca2+-activated gene | Increased drought, salinity, and ABA stress tolerance | [30] |
| GhD12G207 | CDK gene family | Increased concentration of antioxidant enzymes (POD, SOD, and CAT), cell membrane stability, and chlorophyll content under drought and salt stress | [71] |
| GaMYB62L | Transcription factor | Increased chlorophyll and proline contents, higher germination rate under drought salt stress | [72] |
| GhTPS11 | Functional gene | Drought, heat, salinity, ABA, and gibberellin acid | [73] |
| GhAVP1 | Functional gene | Drought and salinity tolerance | [74] |
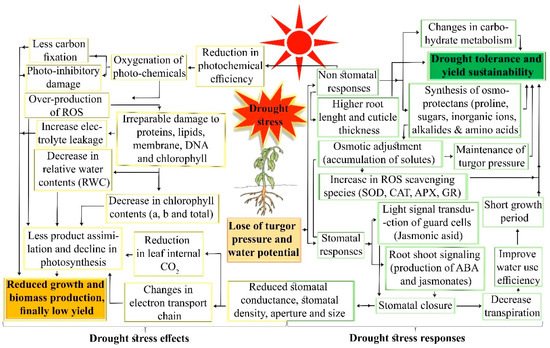
3. Cellular and Molecular Responses to Drought Stress in Plants
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/cells9010105
