Harmful cyanobacterial blooms pose an environmental health hazard due to the release of water-soluble cyanotoxins. One of the most prevalent cyanotoxins in nature is microcystins (MCs), a class of cyclic heptapeptide hepatotoxins, and they are produced by several common cyanobacteria in aquatic environments. Once released from cyanobacterial cells, MCs are subjected to physical chemical and biological transformations in natural environments. MCs can also be taken up and accumulated in aquatic organisms and their grazers/predators and induce toxic effects in several organisms, including humans.
- microcystins
- hepatotoxin
- cyanotoxins
1. Introduction
Microcystins (MCs) are a class of liver toxins that are toxic to humans and animals, alike [1]. MCs are produced as secondary metabolites by a number of widely distributed freshwater cyanobacteria, including Microcystis , Planktothrix , Anabaena, and Oscillatoria genera [2]. Once synthesized, MCs are stored intracellularly and only released into the water following cell lysis, either by viral infection or during cell senescence [3]. During growth seasons, MCs are often measured at concentrations that exceed the guideline values published by the World Health Organization for safe use for drinking (>1 µg/L) and recreational purposes (>20 µg/L for moderate probability for adverse health effects) in freshwaters across the world, even in some of the largest lakes, like Lake Erie [4] (United States) and Lake Taihu [5] (China).
Several MC research, including chemical structures, detection [6,7], ecological impacts [8], human health risk [9], mechanism of toxicity [10,11], synthesis [12], degradation/removal pathways [13,14], and more. Among these different aspects, cellular toxicity has been relatively under studied, which has been addressed in this review. However, a review that encompasses the multifaceted features of MC research is lacking, which is necessary to yield a comprehensive understanding of the health effects and ecosystem impact of MCs.
MCs congeners share a common cyclic structure that is formed by seven amino acid residues, cyclo-(D-Ala 1)-X 2-(D-MeAsp 3)-Z 4-Adda 5-(D-Glu 6)-Mdha 7 [15] ( Figure 1 ). The percentage variation for the amino acid residue has been depicted in Figure 1 . The two L-amino acids of MCs at positions 2 and 4, i.e., X 2 and Z 4, are the most variable by substitution and account for the most diversity of MC congeners [15]. The structures of the rest of the amino acid residues are largely constant, although variations at each of these positions have been reported ( Figure 1 ). The number of identified MC congeners has been consistently increasing and reached 279 very recently [16]; more are expected to be discovered [17].
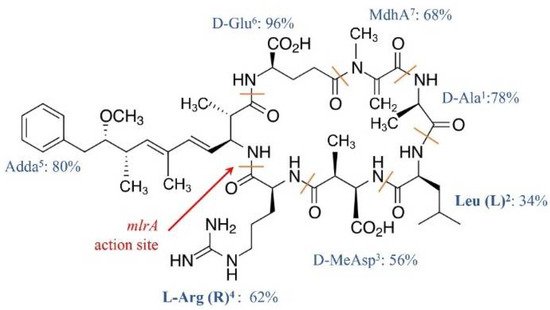
Ala 1, MeAsp 3, and Glu 6 were D-amino acids. Adda 5, or C 20 amino acid (3-amino-9-methoxy-2, 6, 8-trimethyl-10-phenyldeca-4, 6-dienoic acid), and MdhA 7 are non-proteinogenic amino acids; they contribute significantly to the toxicity of MCs and are also found in the structure of another cyanotoxin, i.e., nodularin [18].
2. Exposure and Toxicology
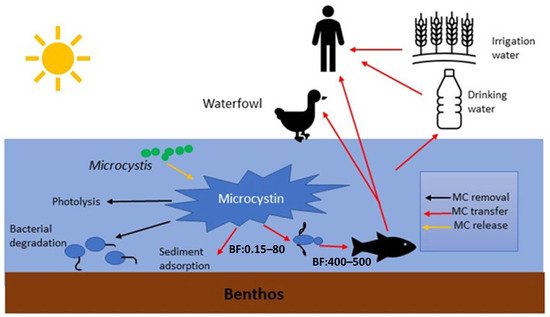
MCs in natural waters can affect humans via various routes, including chronic and accidental ingestion of contaminated drinking or recreational water, inhalation or contact with the nasal mucous membrane, dermal contact with toxins during recreational activities, and consumption of contaminated food irrigated with (vegetables, fruits) or grown in (i.e., fish and shellfish) contaminated water [24] ( Figure 2 ).
Developing a better understanding of the toxicity of MCs will enable us to assess the risk of exposure to these commonly encountered cyanotoxins. The primary cytotoxicity of MCs is the inhibition of Protein Phosphatases 1 and 2a (PP1 and 2a), which leads to several subsequent harmful effects. Acute exposure via ingestion of MCs by humans at concentrations over 10 µg /L can cause various symptoms, including vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and blistering around the mouth, or it can even ultimately lead to liver failure [25]. However, MCs are rarely ingested directly at acute lethal doses by humans. Chronic and frequent exposure to MCs at low concentrations can ultimately lead to liver failure due to chronic liver cell apoptosis or uncontrolled cell proliferation, leading to primary liver cancer [26,27,28].
Once they have gained exposure to animal cells, MCs first get absorbed into the intestinal tract and then earn entry to the blood stream, where they can be distributed to a range of organs [29]. MCs enter human cells via transmembrane organic anion transporter peptides (OATPs) (Fischer et al., 2005). Receptors of OATPs are abundant on the hepatic cells, making liver a primary target for MCs; about 50–70% of MCs in blood streams can be taken up by the liver [30]. With less abundance, OATPs also exist on cells of other organs, such as kidney and brain cells, making them also susceptible to MC toxicity [30]. In comparison with hepatic cells, non-hepatic cells require a greater MC dose and longer exposure time for cell death to occur [10,31]. When being exposed to the same concentrations of MC-LR (0.8 µM), hepatocytes were found to shrink and lose their viability (dying) within 30 min, while endothelial, fibroblasts, and epithelial cells remained viable for up to 5 days [31].
The final stage of MC intoxication may include cell death due to apoptosis or necrosis 27; the former mechanism has been found to be more common [10]. Many studies found that MCs can induce apoptosis via the intrinsic pathway, starting with the production of reactive oxidative species (ROS), which then increase mitochondrial permeability potential (MPP) followed by the induction of caspase 9 and then 3 in that sequence [32,33,34]. A few recent studies have also suggested the importance of extrinsic apoptosis, which starts with the Fas/Fas-L receptor, followed by the induction of caspase 8, followed by the induction of caspase 3 [35,36,37]. MC can also induce apoptosis via activation of the NF-kB pathway (part of the extrinsic pathway) followed by caspase 9 induction [38] in INS-1 cells, which involves both extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. A recent work has shown the induction of caspase 8 before the induction of caspase 9 when we have a combination of extrinsic and intrinsic pathways in MC-treated hepatic cells [37].
3. Production of MCs and Their Regulating Factors
MC synthesis in cyanobacteria is carried out by a gene cluster that possesses eight genes of a total of over 55 kbp DNA ( mcyA-J ), which encode 48 catalytic reactions [39]. A number of precursors are incorporated during the MC synthesis, including phenylacetate, malonyl-CoA, SAM (S-adenosyl methionine), glutamate, serine, alanine, leucine, D -methyl-iso-aspartate, and arginine [39,40]. The arrangements and sequences of mcy genes in the genome and their products (enzymes/proteins) differ among cyanobacterial species [41] (12); therefore, the prevalence of MC congeners during cyanobacterial blooms is determined by dominant cyanobacterial species [17].
Besides inherent genetic properties, a number of environmental factors can impact MC synthesis. Higher dissolved oxygen in water has been found to increase MC production [42,43,44]. High nitrogen concentrations have been found to limit the amount of MCs produced by Microcystis aeruginosa , while high sulfur and phosphorous supplies behave the opposite [45,46]. Solar irradiance, and UV-B intensities, in particular, has been found to encourage the growth of MC-producing cyanobacteria over non-toxin producing strains [47]. Solar irradiance and nutrient supplies together have also been found to impact not only the amount but also the types of MC congeners produced by Microcystis aeruginosa and Planktothrix agardhii [48,49]. Specifically, these cyanobacteria produced higher amounts of MCs with more toxic variants, like MC-LR, than MC-RR under high solar irradiance and nutrient supply. However, the above observations can be species-specific, as MC productions were not altered by light for M. wesenbergii and Aphanizomenon aphanizomenoides under varied light and nutrients [50].
4. Fate of Extracellular MCs in Environments
The stable ring structure of MCs protects them from proteases that are commonly found in environments and a group of enzymes that is responsible for degradation of many organic compounds [55,61,62].
Most MC-degrading bacteria are isolated from aerobic environments, but studies have also obtained MC degraders from oxygen-limited environments, such as alphaproteobacteria and gammproteobacteria from drinking water sludge [78], deltaproteobacteria from the mucilage of Microcystis cells [79], and commercially available probiotic bacteria [76], which belong to Proteobacteria (alpha, beta, and gamma), Actinobacteria, and Firmicutes.
The rate of microbial degradation of MCs is affected by a number of abiotic factors, including temperature, pH, DOC (dissolved organic carbon), and nutrient availability [81]. Temperature at the 30–40 °C range has been found to favor MC biodegradation [71,82,83]. Temperatures that are lower or higher (±10–20 °C) than this range can slow down the degradation of MCs [82].
Organic nutrients (C.N and P) are commonly found in excess in eutrophic lakes, especially during CyanoHABs [85]. Many studies have revealed that a supply of dissolved organic nutrients may slow down MC degradation [65,81]. However, a few recent studies have found improved or unchanged microcystin degradation by certain bacteria species after additions of an organic C source [71,86].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/w13162147
