The development of hydrogen technologies and a wider use of hydrogen fuel cell systems require new materials that can store large amounts of hydrogen at relatively low pressures with small volume, low weight, and fast kinetics for recharging. Among the most challenging materials for hydrogen storage are porous coordination polymers, also called metal–organic frameworks (MOFs). MOFs are two- or three-dimensional porous crystalline materials with infinite lattices. As a result of their ultra-high surface area values (more than 2500 m2·g–1 measured by the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) approach), they were found to be promising gas adsorbers for small gaseous molecules, including CH4, CHCl3, CCl4, C6H6, C6H12, CO2, Ar, N2, and H2. The main benefit of MOFs is their reversible and high-rate hydrogen adsorption process. A reasonable number of H2 molecules inside the body of MOFs may only be obtained at very low temperatures. To date, MOFs have shown significant progress in applications of gas separation, catalysis, and coordination chemistry.
- adsorption
- hydrogen
- MOF
- nanoconfinement
- metal hydrides
1. Introduction
The development of hydrogen technologies and a wider use of hydrogen fuel cell systems require new materials that can store large amounts of hydrogen at relatively low pressures with small volume, low weight, and fast kinetics for recharging. Various materials were studied in this respect, e.g., metal hydride systems; however, numerous problems are associated with the use of the high temperature H2 storage materials (interstitial and complex metal hydrides or their reactive hydride composites), namely, their high cost, low specific uptake by weight, unfavorable kinetics requiring heating cycles, and susceptibility to contamination by impurities. In addition, various carbon-based adsorbents (carbon black, intercalated graphite, carbon nanotubes, and nanoporous polymer networks) have been widely studied and categorized as low temperature H2 storage materials.Among the most challenging materials for hydrogen storage are porous coordination polymers, also called metal–organic frameworks (MOFs). MOFs are two- or three-dimensional porous crystalline materials with infinite lattices. As a result of their ultra-high surface area values, they were found to be promising gas adsorbers for small gaseous molecules, including CH4, CHCl3, CCl4, C6H6, C6H12, CO2, Ar, N2, and H2. The main benefit of MOFs is their reversible and high-rate hydrogen adsorption process.
2. Interaction between solid porous MOFs and gaseous hydrogen
Gas adsorption and desorption (where the latter is the reverse to adsorption) of the sorbate (e.g., gaseous hydrogen) by the sorbent (e.g., MOFs) is a dynamic process. Absorption occurs when the adsorbate may be incorporated into the internal structure of the adsorbent; hence, the structure and properties of the absorbate and absorbent may be modified. Heat values of hydrogen adsorption for most nanoporous materials, including MOFs, crosslinked polymers, or porous carbons, are within the range of 4–7 kJ·mol–1 [1].In monolayer adsorption, all adsorbed H2 molecules are in contact with the sorbent surface. The monolayer hydrogen capacity (na,m) is determined as the number of H2 molecules sufficient to completely cover the sorbent surface. The surface coverage (θ) is assigned as the ratio of the adsorbed amount of H2 to the monolayer hydrogen capacity. The surface area (As) of the sorbent is usually calculated from the monolayer hydrogen capacity when the area effectively occupied by the H2 molecules in the complete monolayer (σm) is known:
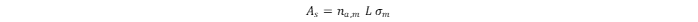
where L is Avogadro’s constant. The specific surface area (as) can be calculated as the ratio of As to the mass (m) of the sorbent:
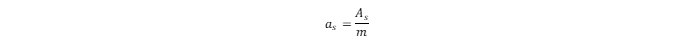
The total adsorbed amount of hydrogen in the MOF is:
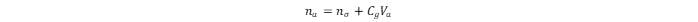
where na and nσ values are in mg·g-1; Cg is the compressed gas concentration at a given temperature and pressure, in g·cm–3; and Va is the volume of the adsorption space in cm3. The na value can be derived from the excess adsorption isotherm, which is the relationship between the nσ value and the equilibrium pressure of the gas (p) at constant temperature. At gas adsorption temperatures below the critical point, the p/po value is usually considered, whereas at those above the critical point, only the p value must be considered, because no saturation vapor pressure (po) exists.
Using adsorption isotherms obtained at different temperatures, the energetics data assessment leads to the isosteric heat of hydrogen adsorption (Qst). The energy of hydrogen physisorption can be obtained directly from the hydrogen adsorption calorimetry (which is more reliable) or indirectly using the Clausius–Clapeyron relation:
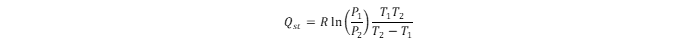
3. MOFs studied for hydrogen adsorption
3.1. MOF-5 and isorecticular compounds
The group of Yaghi described famous MOFs, known as MOF-5 [2], in the mid-1990s. Subsequently, significant research interest has been shown in these materials, which have been tested for applications such as gas storage, separation, and conversion. The overall structure of MOF-5 is composed of larger cavities (15.1 Å in diameter) and smaller cavities (11.0 Å in diameter) in an alternating manner, so that the unit cell consists of four larger and four smaller cavities [2]. The calculated surface area of MOF-5 is about 2500–3000 m2·g–1.
For MOF-5, the measured adsorption isotherm at 77 K showed type I behavior [3] with H2 adsorption capacity of 4.7 wt% of H2 at P(H2) = 50 bar [4]. The experimentally observed fast hydrogen adsorption at low hydrogen pressure indicates favorable sorption interactions between the MOF-5 and H2 molecules [5]. The hydrogen adsorption isotherm at 298 K was approximately linear because the MOF-5 framework was under-saturated with gas within the range of 5–20 bar of H2.
MOF-5 is a prototype for a class of porous materials with similar structure constructed from octahedral [Zn-O-C] clusters made of organo-dicarboxylate linkers (struts), where “organo” represents, for example, biphenyl, tetrahydropyrene, pyrene, or terphenyl. These isostructural compounds are referred to as IRMOFs and have the same framework topology. Pore size in IRMOFs can be incrementally varied from 3.8 to 28.8 Å, and the open space can represent up to 91.1% of the crystal volume [6]. IRMOFs can be prepared with an organic linker substituted by -Br, -NH2, -OC3H7, -OC5H11, -C2H4, or C4H4. From the IRMOF series, IRMOF-20, which is formed by thieno[3,2-b]thiophene-2,5-dicarboxylate fragments, is of particular interest from a hydrogen adsorption perspective because, above 1 bar, IRMOF-20 shows higher gravimetric and volumetric hydrogen density than MOF-5, as shown by an isothermal pressure swing experiment between Pmin = 5 bar and Pmax = 35, 50, or 100 bar [7].
3.2. Other MOFs formed by metal clusters interconnected by carboxylate linkers
Another type of MOF that may be promising for hydrogen adsorption is represented by a framework with a cubic structure based on metal clusters interconnected by polytopic carboxylate linkers. The well-known representatives of this MOF family are UiO (where UiO means the University of Oslo) and HKUST-1 (HKUST meaning the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology), MIL family (MIL meaning Matériaux de l′Institut Lavoisier), DUT (DUT meaning Dresden University of Technology).
Recently, two novel MOFs, with significant hydrogen adsorption capacities were reported, PCN-610/NU-100 and NU-1501. Compound PCN-610/NU-100 contains ligands with C3 symmetry, namely 5,50,500-(((benzene-1,3,5-triyltris(ethyne-2,1-diyl))tris(benzene-4,1-diyl))tris-(ethyne-2,1-diyl))triisophthalic acid (H6ttei), with three coplanar isophthalate moieties. A solvothermal reaction of H6ttei and copper(II) nitrate in DMF/HBF4 yielded Cu3(H2O)3(ttei)×19H2O×22DMF, whose X-ray crystal structure revealed cubic Fm-3m symmetry with a noninterpenetrating (3,24)-connected framework formed from Cu2-paddle-wheel units (see symbol “A” in Figure 1). Interconnection of these paddle wheel Cu2(-COO)4 units with the H6ttei ligand results in formation of three types of voids (see symbols “B”, “C”, and “D” in Figure 1) with sizes 26.0, 18.6, and 12.0 Å, respectively. These voids can be described as cuboctahedra, truncated tetrahedra, and truncated octahedra [8].
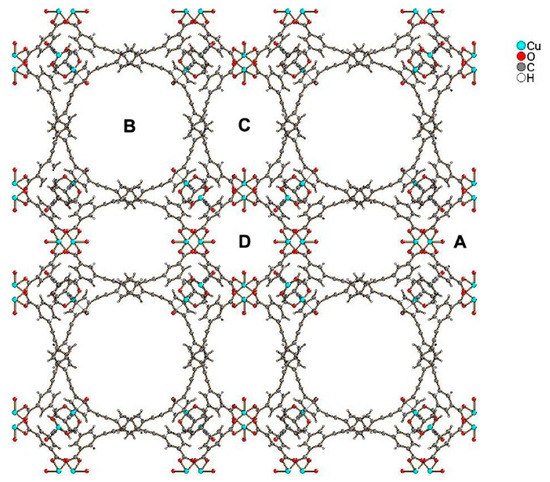
Figure 1. View of the structure of PCN-610/NU-100, where “A” shows paddle wheel Cu2(-COO)4 units, and “B”, “C”, and “D” show three types of voids of different sizes present in the structure.
Ultramicroporous MOFs, namely NU-1501-M (M = Al or Fe), based on metal trinuclear clusters, have been reported [9]. The high porosity and surface area of these MOFs yielded impressive gravimetric and volumetric storage performances for hydrogen and methane. In contrast to the compounds described above, the structure of these MOFs has hexagonal rather than cubic symmetry, and the space group The compound is founded on the prismatic triptycene-based organic ligand, peripherally extended triptycene (H6PET-2), see Figure 2. The combination of these rigid trigonal prismatic linkers and M3O metal trimers (M = Al3+, Fe3+) forms MOFs with the formula [Al3(m3-O)(H2O)2(OH)(PET-2)] [9]. The compound exhibits 6-c acs topology, and have one type of open hexagonal channel with a pore size of ~2.2 nm (see Figure 2).
The ultramicroporous MOF, NU-1501-Al, exhibits high values for both gravimetric and volumetric BET areas (7310 m2·g–1 and 2060 m2·cm−3, respectively [9]). These were considered the main reasons for the high value of hydrogen storage capacity (14.0 wt% and 46.2 g·dm−3) under a combined T and P(H2) change from 77 K and 100 bar to 160 K and 5 bar.
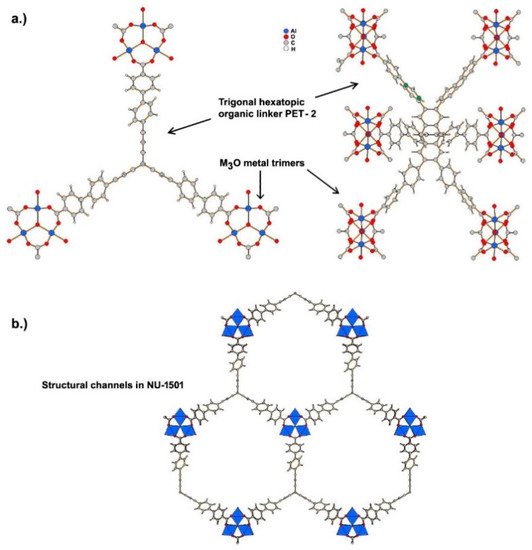
Figure 2. (a) Coordination of peripherally extended triptycene (H6PET-2) to metal cations forming M3O metal trimers. (b) Structural channels in NU-1501 viewed along c axis.
4. Current approaches to increasing hydrogen adsorption in MOFs
Unfortunately, no MOFs currently satisfy the proposed DoE target under ambient conditions. The porous MOFs adsorb molecular hydrogen physically; therefore, H2 adsorption capacity sharply decreases at higher temperatures. The obtained theoretical results suggest the existence of three adsorption modes at 77 K: (1) at low pressure (~1 bar of H2), the na value is proportional to the value of Qst; (2) at ~30 bar of H2, the na value is proportional to As; and (3) at ~120 bar of H2, the na value is proportional to Va.
4.1. Factor of the surface area and pore volume
A linear relationship between the H2 adsorption capacity at 77 K and the As value has been confirmed in numerous publications [10]. As a result that the Va value is proportional to As, higher values of both Va and As are recommended to improve hydrogen adsorption in MOF at 77 K. The adsorption capacity at 77 K and 1 bar of H2 is related to the As values within the range of 100–2000 m2·g–1 and does not correlate in the case of higher As values. This may be because the sorbent surface cannot be fully covered by H2 molecules at these high As and low P(H2) values. In addition, it is most likely that the H2 molecules will preferentially bind on the most thermodynamically favorable sites in MOFs with the largest affinity to hydrogen. In the porous MOFs at a low pressure of 77 K, H2 adsorption may be affected by ligand functionalization, catenation, open metal sites, and pore size, whereas high-pressure H2 adsorption is directly proportional to the As value.
4.1.1. Length of organic linkers
For a given crystal structure of MOFs, the As value can be increased using longer ligands (linkers). For example, BBC (4,4',4"-[benzene-1,3,5-trilytris(benzene-4,1-diyl)]tribenzoate) may be considered to a longer model of BTB (4,4',4"-benzene-1,3,5-triyl-tribenzoate). MOF-200, which comprises the BBC linker, demonstrates an As value of 4520 m2·g–1, and MOF-177 with the BTB linker has an As value of 4750 m2·g–1 (both using the BET method) [11]. A thorough comparison of isostructural UiO-66 and UiO-67 was made in [12]. These MOFs are constructed from Zr6O4(OH)4 nodes, and organic linkers 1,4-benzene-dicarboxylate and 4,4′-biphenyldicarboxylate for UiO-66 and UiO-67, respectively. Resulting from of the longer linker in the case of UiO-67, the value of As (Langmuir) was 2483 m2·g–1, which is higher than that value of 1281 m2·g–1 in the case of UiO-66. A similar effect was observed for the Va value (0.85 vs. 0.43 cm3·g–1). As a consequence, the hydrogen adsorption capacity measured at 77 K and 38 bar of H2 was almost twice as high for UiO-67 (4.6 wt%) as for UiO-66 (2.4 wt%).
The number of aromatic benzene rings may also influence the hydrogen sorption, as determined from the study of IRMOFs. The hydrogen sorption changed within the range of 0.89–1.73 wt% H2 [13].
4.1.2. Catenation process
From a thermodynamic perspective, the value of surface energy must be as low as possible to form a compact structure of the material. Therefore, when large pores in an MOF from a long organic linker are anticipated using only the geometrical calculation, an interweaving or interpenetration of the MOF framework may occur in practice. Interweaving and interpenetration are considered to be two types of the catenation process (bonding of atoms of the same element into a chain) where, respectively, a minimal and maximal displacement occurs between the catenated frameworks [14]. It was proposed that catenation of MOFs may be controlled by adding a template during the solvothermal MOF synthesis (e.g., the oxalic acid used as a template promotes a non-catenated MOF framework). Using a brominated and non-brominated ligand, in which a non-catenated and catenated MOF framework was produced, the authors of [15] concluded that catenation may be controlled by the organic linker design. As a result of the synthesis of organic linkers and their organization in the MOF structure depending on the reaction parameters (e.g., the precursor concentration, temperature, and time of stirring), the catenation process in a different form is strongly guided by the MOF synthesis conditions.
It is obvious that catenation directly affects the H2 adsorption in MOFs. The copper paddle wheel node and the TATB linker (4,4',4"-s-triazine2,4,6-triyltribenzoate) are the building units for both porous coordination networks (PCNs), catenated PCN-6 and non-catenated PCN-60, and their general formula is Cu3(TATB)2 [16]. After sample activation at 323 K, the hydrogen adsorption capacity at 77 K and 1 bar of H2 was 1.74 and 1.35 wt% for PCN-6 and PCN-60, whereas after activation at 423 K, these values increased to 1.9 and 1.62 wt%, respectively. The larger improvement in H2 adsorption for the non-catenated PCN-60 was explained by the open metal sites, which were blocked in the catenated PCN-6.
4.1.3. Different organic linkers
A combination of two types of organic linker within the same MOF structure could be another approach to increase the pore characteristics of MOFs. For example, the SNU-6 framework was constructed from the BPnDC (4,4'-benzophenone dicarboxylate) ligand and the bpy (4,4'-bipyridine) ligand, together with Cu2+ nodes [17]. This MOF was characterized by large pores (the pore diameter of 18.2 Å), and the As values obtained by the BET and Langmuir methods were 2590 and 2910 m2·g–1, respectively. The hydrogen adsorption capacity at 77 K and 1 bar of H2 was relatively low (1.68 wt%); however, at high pressure (77 K and 70 bar of H2), the na and nσ values were 10.0 and 4.87 wt%, respectively.
Approaches using different organic linkers have been recently developed with a mixed–matrix hybrid strategy to provide a tool for facile characterization of molecular transport in MOFs. For example, in [18], incorporation of the MOF crystals into polymers resulted in hybrid membranes with excellent molecular sieving properties. The improved membrane performance resulted from precise control of the organic linkers in the MOF, which delimited the entrance to the pores.
4.1.4. Flexible organic linkers
Dynamic MOFs can respond to external conditions (e.g., T, P, electric or magnetic fields, and chemical insertion) and reversibly change their channels by a large magnitude while maintaining the same or similar topologies. Therefore, this type of MOF is often associated with reversible transformations between the expansion and the contraction states, which are called the “breathing” or “sponge” effect. For 3D dynamic MOFs, three situations have been distinguished [19]. As a result of the interlayer extension and shortening, reversible transformations may occur using suitable flexible pillars (class a), sponge-like dynamic behavior (class b) or interpenetration (class c).
A systemic synthesis and characterization of a series of MOFs with the pillared layer structure was carried out in [20]. The [Zn4(bpta)2(H2O)2] (H4bpta = 1,1’-biphenyl-2,2’,6,6’-tetracarboxylic acid) layers were connected by length-controllable bipyridine pillars. The authors developed a synthetic strategy that allowed systematic variation of the pillar to construct open frameworks with a similar structure. It was concluded that pore design could be adjusted by the selection of pillar ligands, and hence lead to different hydrogen adsorption properties. The results obtained indicated that the activation process of these MOFs could affect the Qst value.
The hydrogen adsorption analysis of three flexible sulfur-containing MOF materials named M-URJC-n (M = Co, Cu, Zn) based on the 5,5’-thiodiisophthalic acid linker (H4TBTC) showed that these compounds display a gate-opening type adsorption mechanism at low pressures, attributed to the flexible nature of the ligand [21]. The hydrogen adsorption capacities of the compounds were not high, with levels of 2.81, 2.21, and 1.99 wt%, for Co-, Cu-, and Zn modification, respectively, at 77 K and up to 18 bar, and 0.12, 0.14, and 0.13 wt%, at 298 K and 170 bar, due to the presence of flexible ligands. These compounds showed an interesting gate-opening type adsorption mechanism. Considering the flexibility and the dynamic nature of the new structures, these compounds are candidates for applications such as hydrogen selective adsorption and gas separation processes, including hydrogen purification in precombustion mixtures of H2/CO2 [21].
4.2. Factor of isosteric enthalpy of hydrogen adsorption
Among MOFs with high As values, some of the MOF examples have high values of hydrogen adsorption capacity but only at cryogenic temperature. In practice, the hydrogen adsorption capacity at moderate temperatures designed by DoE falls to less than 1/10 of the value obtained at 77 K, and the Qst values in most porous MOFs is within the range of 5–10 kJ·mol–1 [22]. As a result of physical sorption of H2 molecules, van der Waals interaction between H2 molecules and the pore surface of MOFs is very weak. To increase the interaction at the ambient temperature, two recommendations have been made: (1) strong adsorption sites incorporated into the pores; and (2) optimization of the internal surface of MOF. In practice, creation of open metal sites, introduction of cations generating a strong electrostatic field within the cavities, doping with metal ions, infiltration of metal nanoparticles, and organic linker functionalization have been used to increase molecular hydrogen affinity to MOFs. It was concluded that MOFs can reach approximately 6 wt% H2 when they are characterized by a Qst value of 10–15 kJ·mol–1 and a free volume within the range of 1.6–2.4 cm3·g–1, or Qst > 20 kJ·mol–1 and a free volume smaller than 1.5 cm3·g–1. The authors of [23] studied H2 adsorption in an MOF at 298 K and 1.5 or 120 bar of H2, and measured deliverable capacity as the difference between the na value at the high and the low hydrogen pressure. Their GCMC calculations suggested that for the maximum H2 delivery at 298 K, the optimal Qst value must be around ~20 kJ·mol–1.
4.2.1. Open metal sites at secondary building units and organic linkers
It is known that metal centers unsaturated in coordination, often called “open” or “accessible” metal sites, may increase the Qst value. In practice, the H2 adsorption values measured at 298 K for MOFs with open metal sites are higher than those for MOFs without open metal sites. In addition, this tendency is pronounced for MOFs with a high As value (>3000 m2·g–1). Based on experiments involving the introduction of open metal sites in MOFs, a number of possible approaches have been highlighted: (1) metal nodes with open metal sites; (2) metal clusters coordinating solvent molecules, in which the solvent is removable; (3) organometallic complexes connected with the aromatic organic linkers; (4) metal complexes intercalated through electrostatic forces; and (5) metal cations in the anionic frameworks.
Open metal sites in MOFs may be constructed of metal cluster SBUs coordinating solvent molecules, followed by removal of the solvent using thermal treatment. In this case, the SBUs are very often the bimetallic paddle wheel units of M2(O2CR)4 (M=Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+), in which solvent molecules are coordinated at the axial sites. The fluorite-like structure of the [CoII4(μ-OH2)4(MTB)2(H2O)4]n·13nDMF·11nH2O framework (SNU-15) promotes 3D channels in which every Co2+ ion coordinates the aqua ligand, and the Co-Co distances are 3.550 and 3.428 Å. When the coordinated H2O molecules are removed, the vacant coordination sites are created on the Co2+ ions. Due to the values of the Co–Co distance, H2 molecules can be bonded in a side-on manner that results in the Qst value of 15 kJ·mol-1 at zero coverage [23].
The open metal sites at organic linkers are also a highly popular approach used to increase the Qst value. For example, the structures of MOFs constructed from various types of porphyrin complexes are very well known [24]. They contain open metal sites with respect to the square-planar coordination plane, therefore the porphyrin-based MOFs may be recommended for effective H2 adsorption.
4.2.2. Metal ions for an electrostatic field within the cavities
Another approach to increasing the Qst value is to exchange the cations integrated in the anionic framework with metal ions that have higher affinity to H2 molecules. For example, in the Mn3[(Mn4Cl)3(BTT)8]2, (BTT = 1,3,5-benzenetristetrazolate) framework, Mn2+ ions can be exchanged with Li+, Cu+, Fe2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, or Zn2+ ions [25]. Chemical compositions based on the relative ratio of Mn+/Mn2+ showed that the total number of extra framework cations is not higher than five. The Qst values, calculated using a virial fit to the H2 adsorption isotherms at 77 and 87 K, demonstrate a relatively large variation, but they deviate in almost the same region as those for the Mn3[(Mn4Cl)3(BTT)8]2 framework. The values of hydrogen adsorption capacity measured at 77 K and 1.2 bar of H2 for the ion-exchange frameworks and the original Mn3[(Mn4Cl)3(BTT)8]2 are within 2.00–2.29 wt%.
4.3. Catalytic effect and pore design
Due to their high affinity to hydrogen, the platinum group metals were the first catalysts used in various hydrogenation reactions and processes related to H2 molecules. Subsequently, a hydrogen spill-over effect was defined as dissociative chemical sorption (i.e., H2→2H) on the catalyst surface and the later migration of H atoms onto the surface of support. The catalytic effect was also used for MOFs in an attempt to accelerate the hydrogen adsorption process. In addition, the morphology of pores and their extra functionalization were taken into consideration. In the case of microporous MOFs, the morphology of the pores represents their main characteristics, including the geometrical shape (pore width and pore volume) and roughness of the pore walls. A small pore diameter was found to be an important factor for the achievement of a high value of hydrogen adsorption capacity at room temperature.
4.3.1. Incorporated metal nanoparticles
Recently, the idea of the hydrogen spillover effect was transferred to MOFs, and the introduction of several types of metal nanoparticles (NPs) to MOFs was considered. The simplest method involves preparing a coating made of the NP metal on the MOF surface, but without completely wrapping the MOF in a metal thin film. Using a solid grinding approach, Au NPs were attached to the surface of the well-known MOF examples, including MOF-5 [26]. The solution impregnation method was reported to be a convenient tool for preparing metal NPs infiltrated inside MOFs. Typically, the metal precursor solution fills the MOF pores by capillary force, and the chemical reduction (e.g., with H2, NaBH4) then produces the NPs settled in the body of the MOF. This method was successfully used to prepare mono- and bimetallic NPs inside MOFs (e.g., Pt NPs [27][28][29][30] and Pt/Ni NPs [31]). In addition, the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) technique was found to be advantageous in the deposition of metal nanoparticles in MOFs because, during the CVD vapor phase, the precursor is loaded in MOFs, and the precursor is then decomposed or reduced to obtain nanoparticles inside the MOF pores.
Palladium was among the first examples of metal NPs inside MOFs. For example, Pd NPs (with an average size of 2.5 nm) were successfully infiltrated in MIL-100(Al) with a high metal content (10 wt%) without degradation of MOF [27]. As a result of Pd impregnation, the reduction in the nσ value at 77 K and 40 bar of H2 was directly related to the decrease in the As and Va values (from 380 to 1200 m2·g–1, and from 0.33 to 0.65 cm3·g–1, respectively), whereas at 298 K, the nσ value increased, most probably because of the Pd hydride formation. Formation of PdH0.6 was experimentally confirmed for the Pd NPs incorporated in MIL-100(Al), although the spill-over effect was also considered.
Platinum, scandium and titanium are other attractive examples of the incorporation of metal NPs in MOFs.
4.3.2. Morphology of pores and their functionalization
The effect of the pore size may be explained by the fact that the small diameter of pores enables energy potentials to overlap between the opposing walls, resulting in higher interaction energy with H2 molecules. For example, MOFs of M(HBTC) (4,4'-bpy)·3DMF (M = Ni, Co; HBTC = 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid; 4,4'-bipy = 4,4'-bipyridine; DMF = N,N'-dimethylformamide) showed H2 adsorption of 3.42 and 2.05 wt% at 77 K and 1 bar of H2, and 1.20 and 0.96 wt% at 298 K and 70 bar of H2, respectively [28]. The As values measured by the BET method were 1590 and 887 m2·g–1 respectively, but it was noted that these two frameworks had nonlinear rectangular channels with an average size of 7 × 6 Å. Another [Co3(NDC)3(dabco)] (dabco = 1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane) framework with a primitive cubic structure demonstrated 0.89 wt% of H2 at 298 K and P(H2) = 17.2 bar, which was explained by both the As value (1502 m2·g-1) and the average pore diameter (4.5 Å) [32]]. The four-fold interpenetrating networks based on the [OZn4]6+ nodes with 3D channels (<5 Å) might also be considered. These examples indicate that, even with a small As value, hydrogen adsorption can be significant and, most importantly, controlled by pore size (5–7 Å).
5. Prospective views and outlooks
MOFs are unique chemical compounds that can be used in numerous scientific applications, including hydrogen adsorption; however, adapting a pure MOF to the DoE target to be used as an effective hydrogen storage material remains a significant challenge. The factors of surface area and pore volume remain the most critical issue, because at 298 K, the na value correlates mainly with the Va value at low P(H2) and the As value at high P(H2). Organic linkers have a direct influence on the pore morphology, and therefore, on the surface area of MOFs, their length, chemical composition, and flexibility may explain the catenation and sponge-like dynamic mechanism in MOFs. These effects may change the hydrogen adsorption in pure MOFs, but their absolute quantity of adsorbed hydrogen does not meet the DoE requirements at 298 K, or at 100 bar of H2. The value of Qst may be considered to be a reasonable indicator of the applicability of pure MOFs as a hydrogen storage material. At 298 K, a tendency exists to form a proportional relationship between the Qst and the nσ values, and using the approach of open metal sites or an electrostatic field, isosteric enthalpy of hydrogen adsorption increases slightly in pure MOFs. Numerous calculations suggest that the value of Qst within the range of 15–25 kJ·mol–1, with a Va value of ~2.5 cm3·g–1 and porosity of ~85%, would be desirable for an MOF as a successful candidate for hydrogen storage with 9 wt% of H2.
Nanoscaffolding materials based on MOFs, sometimes generalized to “hybrid” or “functional” composites, may combine properties of their components. In practice, isosteric enthalpy of hydrogen adsorption and hydrogen adsorption capacity has not been fully examined for this kind of material, and is not reproducible for the same examples. The main reasons for these discrepancies may lie in the morphology of pores and their functionalization, which is highly sensitive to the synthesis procedure and post-synthetic modification of MOFs. Another approach of nanoscaffolding materials based on MOFs may be nanoconfinement of metal hydrides inside the frameworks, in which MOFs are considered to be nanoscaffolds rather than H2 sorbents. The main advantages of nanoconfined hydrides relate to their faster kinetics, higher reversibility, and the change in the mechanism of hydrogen interaction. The additional weight of nanoscaffolds leads to lower gravimetric hydrogen sorption capacity in the composite material.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/nano11071638
References
- Germain, J.; Frechet, J. M. J.; Svec, F. Nanoporous Polymers for Hydrogen Storage. Small 2009, 5, 1098–1111.
- Li, H.; Eddaoudi, M.; O'Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O. M. Design and synthesis of an exceptionally stable and highly porous metal-organic framework. Nature 1999, 402, 276–279.
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A. V.; Olivier, J. P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K. S. W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069.
- Panella, B.; Hirscher, M.; Pütter, H.; Müller, U. Hydrogen adsorption in metal-organic frameworks: Cu-MOFs and Zn-MOFs compared. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 520–524.
- Rosi, N. L.; Eckert, J.; Eddaoudi, M.; Vodak, D. T.; Kim, J.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O. M. Hydrogen storage in microporous metal-organic frameworks. Science 2003, 300, 1127–1129.
- Eddaoudi, M.; Kim, J.; Rosi, N.; Vodak, D.; Wachter, J.; O'Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O. M. Systematic design of pore size and functionality in isoreticular MOFs and their application in methane storage. Science 2002, 295, 469–472.
- Ahmed, A.; Liu, Y.; Purewal, J.; Tran, L. D.; Wong-Foy, A. G.; Veenstra, M.; Matzger, A. J.; Siegel, D. J. Balancing gravimetric and volumetric hydrogen density in MOFs. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 2459–2471.
- Ahmed, A.; Seth, S.; Purewal, J.; Wong-Foy, A. G.; Veenstra, M.; Matzger, A. J.; Siegel, D. J. Exceptional hydrogen storage achieved by screening nearly half a million metal-organic frameworks. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1568.
- Chen, Z.; Li, P.; Anderson, R.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Robison, L.; Redfern, L. R.; Moribe, S.; Islamoglu, T.; Gómez-Gualdrón, D. A.; Yildirim, T.; Stoddart, J. F.; Farha, O.K. Balancing volumetric and gravimetric uptake in highly porous materials for clean energy. Science 2020, 368, 297–303.
- Suh, M. P.; Park, H. J.; Prasad, T. K.; Lim, D.-W. Hydrogen Storage in Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 782–835.
- Furukawa, H.; Miller, M. A.; Yaghi, O. M. Independent verification of the saturation hydrogen uptake in MOF-177 and establishment of a benchmark for hydrogen adsorption in metal–organic frameworks. J.Mater.Chem. 2007, 17, 3197–3204.
- Chavan, S.; Vitillo, J. G.; Gianolio, D.; Zavorotynska, O.; Civalleri, B.; Jakobsen, S.; Nilsen, M. H.; Valenzano, L.; Lamberti, C.; Lillerud, K. P.; Bordiga, S. H2 storage in isostructural UiO-67 and UiO-66 MOFs. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 1614–1626.
- Rowsell, J. L. C.; Millward, A. R.; Park, K. S.; Yaghi, O. M. Hydrogen sorption in functionalized metal-organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 5666–5667.
- Kaskel, S. Metal-Organic Frameworks: Design and Application; Ed. MacGillivray, L. R.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, 2010, 349pp.
- Farha, O. K.; Malliakas, C. D.; Kanatzidis, M. G.; Hupp, J. T. Control over catenation in metal−organic frameworks via rational design of the organic building block. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 950–952.
- Zhou, H.-C.; Ma, S. Q.; Sun, D. F.; Ambrogio, M.; Fillinger, J. A.; Parkin, S. Framework-catenation isomerism in metal−organic frameworks and its impact on hydrogen uptake. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1858–1859.
- Park, H. J.; Suh, M. P. Mixed-ligand metal–organic frameworks with large pores: gas sorption properties and single-crystal-to-single-crystal transformation on guest exchange. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 8812–8821.
- Liu, G.; Chernikova, V.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Shekhah , O.; Zhang, C.; Yi, S.; Eddaoudi, M.; Koros, W. J. Mixed matrix formulations with MOF molecular sieving for key energy-intensive separations. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 283–289.
- Lin, Z.-J.; Lü, J.; Hong, M.; Cao, R. Metal–organic frameworks based on flexible ligands (FL-MOFs): structures and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5867–5895.
- Chang, Z.; Zhang, D.-S.; Chen, Q.; Li, R.-F.; Hu, T.-L.; Bu, X.-H. Rational construction of 3D pillared metal–organic frameworks: synthesis, structures, and hydrogen adsorption properties. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 7555–7562.
- Montes-Andrés, H.; Leo, P.; Orcajo, G.; Rodríguez-Diéguez, A.; Choquesillo-Lazarte, D.; Martos, C.; Botas, J. Á.; Calleja, G. Synthesis, structural features, and hydrogen adsorption properties of three new flexible sulfur-containing metal–organic frameworks. Cryst. Growth Des. 2020, 20, 6707–6714.
- Bhatia, S. K.; Myers, A. L. Optimum Conditions for Adsorptive Storage. Langmuir 2006, 22, 1688–1700.
- Bae, Y.-S.; Snurr, R. Q. Optimal isosteric heat of adsorption for hydrogen storage and delivery using metal–organic frameworks. Microp. Mesopor. Mater. 2010, 132, 300–303.
- Deiters, E.; Bulach, V.; Hosseini, M. W. Reversible single-crystal-to-single-crystal guest exchange in a 3-D coordination network based on a zinc porphyrin. Chem. Commun. 2005, 31, 3906–3908.
- Dinca, M.; Long, J. R. High-enthalpy hydrogen adsorption in cation-exchanged variants of the microporous metal-organic framework Mn3[(Mn4Cl)3(BTT)8(CH3OH)10]2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 11172–11176.
- Ishida, T.; Nagaoka, M.; Akita, T.; Haruta, M. Deposition of gold clusters on porous coordination polymers by solid grinding and their catalytic activity in aerobic oxidation of alcohols. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 8456–8460.
- Pan, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Guan, Y.; Wu, P. Pt nanoparticles entrapped in mesoporous metal-organic frameworks MIL-101 as an efficient and recyclable catalyst for the asymmetric hydrogenation of α-ketoesters. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2013, 377, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajavi, H.; Stil, H.A.; Kuipers, H.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F. Shape and transition state selective hydrogenations using egg-shell Pt-MIL-101(Cr) catalyst. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 2617–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Chen, G.; Nie, R.; Li, Y.; Hou, Z. Highly dispersed Pt in MIL-101: An efficient catalyst for the hydrogenation of nitroarenes. Catal. Commun. 2013, 41, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Xu, Q. Catalytic chromium reduction using formic acid and metal nanoparticles immobilized in a metal-organic framework. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3327–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Xu, Q. Metal-organic framework supported bimetallic Ni–Pt nanoparticles as high-performance catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrazine in aqueous solution. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 3000–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.; Jung, H.; Koo, G.; Jeong, H.; Kim, D.-K. Efficient hydrogen sorption in 8-connected MOFs based on trinuclear pinwheel motifs. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 5355–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Xu, Q. Metal-organic framework supported bimetallic Ni–Pt nanoparticles as high-performance catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrazine in aqueous solution. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 3000–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.; Jung, H.; Koo, G.; Jeong, H.; Kim, D.-K. Efficient hydrogen sorption in 8-connected MOFs based on trinuclear pinwheel motifs. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 5355–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
