Over the years, there have been several improvements in ultrasound technologies including high-resolution ultrasonography, linear transducer, radiant flow, three-/ four-dimensional (3D/4D) ultrasound, speckle tracking of the fetal heart, and artificial intelligence. The aims of this entry are to evaluate the use of these advanced technologies in obstetrics in the midst of new guidelines on and new techniques of obstetric ultrasonography. In particular, whether these technologies can improve the diagnostic capability, functional analysis, workflow and ergonomics of obstetric ultrasound examinations will be discussed.
- obstetrics
- ultrasound
- 3D
- 4D
- Doppler
- artificial intelligence
1. Introduction
Ultrasound is widely used in obstetric practice to detect fetal abnormalities with a view to provide prenatal opportunities for further investigations including genetic testing and discussion of management options. In 2010, International Societies of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology (ISUOG) published the practice guidelines on the minimal and optional requirements for a routine mid-trimester ultrasound scan [1]. Recently, The American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine (AIUM) suggests a detailed diagnostic second/third trimester scan for high-risk pregnancies [2], and fetal echocardiography for at-risk pregnancies [3]. ISUOG has published recent guidelines on indications and practice of targeted neurosonography [4][5]. Although the introduction of prenatal cell-free DNA-based screening for Down syndrome has changed the role of the first trimester scan, the latter should still be offered to women [6]. Around 50% of major structural abnormalities can be detected in the first trimester [7]. In addition, a recent study showed that a routine scan at around 36 weeks’ gestation can detect around 0.5% of previously undetected fetal abnormalities, as well as fetal growth restriction (FGR) [8].
The detection rate of fetal abnormalities varies, depending on anatomy survey protocol, ultrasound equipment and setting, among other factors [9]. A high-resolution ultrasound can facilitate a detailed diagnostic scan and a first-trimester scan and allow the detection of a small or subtle abnormality [10][11][12]. Although a detailed diagnostic scan is not required for all pregnant women, the indications include family history of congenital malformation, maternal age 35 or above, gestational diabetes mellitus, artificial reproduction technology, body mass index >= 30, teratogen , fetal nuchal translucency >= 3mm, and many other conditions [2]. In the midst of such increasing standards of obstetric ultrasound examination, there is a demand on improving the diagnostic capability, functional analysis, workflow, and ergonomics. Over the years, there have been several improvements in ultrasound technologies including high-resolution ultrasonography, linear transducer, radiant flow, three/four-dimensional (3D/4D) ultrasound, speckle tracking of the fetal heart, and artificial intelligence.
2. High-Resolution Ultrasonography
High-resolution ultrasonography includes the use of a high-frequency transducer, and the means of enhancing image and signal processing including harmonic imaging (HI), spatial compound imaging (SCI), and speckle reduction imaging (SRI). Compared to a transducer with the low-frequency range (2 to 5 MHz), a transducer with the high-frequency range (5 to 9 MHz) can allow for improved resolution though with limited tissue penetration. HI, utilizing the physics of non-linear propagation of ultrasound through the body tissues, can produce high-resolution images with few artifacts. SCI, combining multiple lines of sight to form a single composite image at real-time frame rates, can reduce angle-dependent artifacts. The use of SRI can reduce speckles or disturbances that result from the echo, which is projected from an ultrasound transducer.
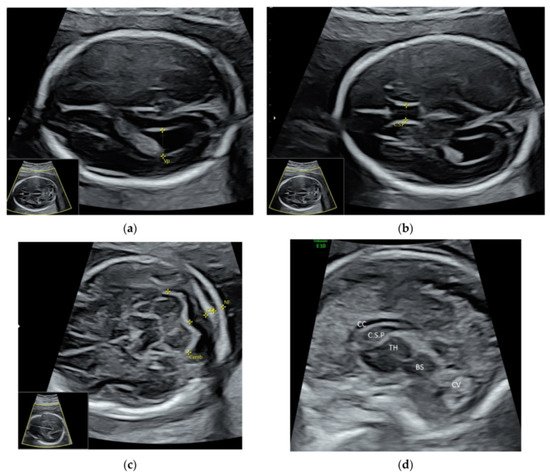
For a targeted neurosonographic examination, ISUOG recommends the use of high- resolution transvaginal transducers whenever possible [5]. An alternative is to use high-resolution transabdominal transducers with high frequency reaching 8–9 MHz [5]. The anatomy of the fetal brain is examined in details on a continuum of transverse, sagittal and coronal planes ( Figure 1 a–d, Video S2a,b ).
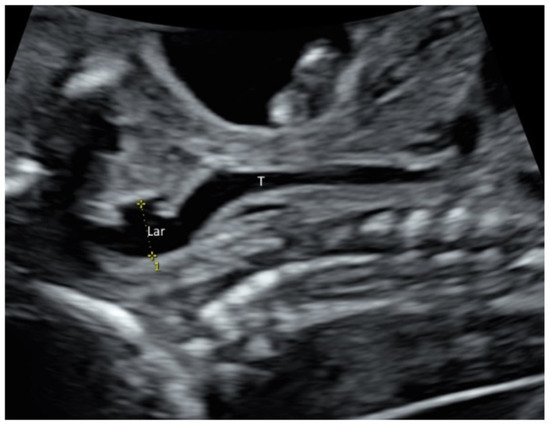
Larynx and its movement can be assessed by prenatal ultrasound ( Figure 2 and Video S4 ). In at-risk fetuses such as those with laryngeal atresia [13] and congenital diaphragmatic hernia, prenatal ultrasound allows systematic examination of the larynx, including vocal cords to detect laryngeal anomalies [13][14].
3. Linear Transducer
With a high-frequency ultrasound, a linear transducer can produce high-resolution images of shallow structures and small parts. Unlike curved transducers, linear transducers produce a rectangular field of view with uniform beam density throughout all tissue levels and without divergence in deeper tissue. The use of a transabdominal linear transducer can enhance the examination of the spinal cord and conus medullaris in the midsagittal view of the spine [5]. Some abnormalities such as cataract [15] and laryngeal atresia [13] can be well demonstrated using a linear transducer.
A linear transducer can be used to examine fetal structures in the first trimester ( Figure 3 a–d). However, a linear transducer is not suitable for using if the structures of interest are deep or the maternal abdominal wall is thick. Although a linear transducer can allow the examination of the fetal cardiac anatomy at 11–13 weeks [16], it is the use of color flow mapping but not of a linear transducer that improves the examination [17].
4. 3D/4D Ultrasound
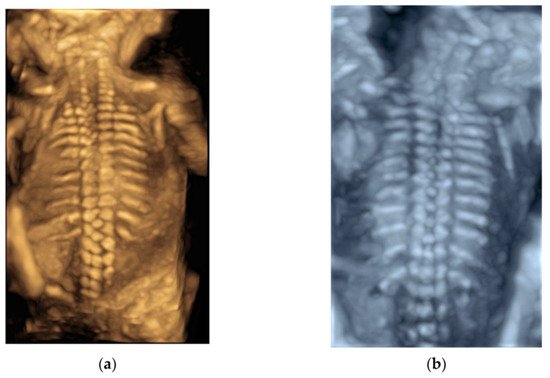
After a 3D volume acquisition of the fetal spine at mid-sagittal plane, a rendered view of the fetal spine can be well displayed with various modes ( Figure 4 a,b). In addition, the coronal planes at the level of the vertebral bodies and/or posterior arches can be reconstructed on multiplanar analysis [5].
It is difficult to visualize esophagus on 2D ultrasound examination. The use of 3D ultrasound with multiplanar analysis and Crystal Vue rendering may make the visualization possible [18]. Three-dimensional (3D) volumes are acquired from a midsagittal section of the thorax and upper abdomen with the fetus lying in supine position.
With advances in STIC, the derived data can be used for 3D printing of the fetal heart, which is a fast-moving structure [19]. In a recent case report, the authors found that the 3D model was useful in showing the complex anatomy of fetal transposition of great arteries and in providing prenatal parental counseling [20].
Previously, after acquisition of a 3D/STIC volume dataset, a number of post-processing steps are required to convert it from Cartesian.vol file through segmentation, refinement, and optimization to a STL (Standard Triangle Language) file, the industry standard file type for 3D Printing [19]. These steps take a long time, and whether the final produced STL file is good enough for 3D printing is not certain before processing. With recent advances in ultrasound technology, a 3D/STIC volume dataset can be directly exported from the ultrasound machine as an STL file that is ready for viewing on a personal computer using common software as well as for 3D printing ( Figure 5).
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/diagnostics11071217
References
- Salomon, L.J.; Alfirevic, Z.; Berghella, V.; Bilardo, C.; Hernandez-Andrade, E.; Johnsen, S.L.; Kalache, K.; Leung, K.Y.; Malinger, G.; Munoz, H.; et al. ISUOG Clinical Standards Committee. Practice guidelines for performance of the routine mid-trimester fetal ultrasound scan. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 37, 116–126.
- Anonymous. AIUM Practice Parameter for the Performance of Detailed Second- and Third-Trimester Diagnostic Obstetric Ultrasound Examinations. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 3093–3100.
- Anonymous. AIUM Practice Parameter for the Performance of Fetal Echocardiography. J. Ultrasound Med. 2020, 39, E5–E16.
- Malinger, G.; Paladini, D.; Haratz, K.K.; Monteagudo, A.; Pilu, G.L.; Timor-Tritsch, I.E. ISUOG Practice Guidelines (updated): Sonographic examination of the fetal central nervous system. Part 1: Performance of screening examination and indications for targeted neurosonography. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 56, 476–484.
- Paladini, D.; Malinger, G.; Birnbaum, R.; Monteagudo, A.; Pilu, G.; Salomon, L.J.; Timor-Tritsch, I.E. ISUOG Practice Guidelines (updated): Sonographic examination of the fetal central nervous system. Part 2: Performance of targeted neurosonography. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 57, 661–671.
- Salomon, L.J.; Alfirevic, Z.; Audibert, F.; Kagan, K.O.; Paladini, D.; Yeo, G.; Raine-Fenning, N.; ISUOG Clinical Standards Committee. ISUOG consensus statement on the impact of non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) on prenatal ultrasound practice. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 44, 122–123.
- Kenkhuis, M.J.A.; Bakker, M.; Bardi, F.; Fontanella, F.; Bakker, M.K.; Fleurke-Rozema, J.H.; Bilardo, C.M. Effectiveness of a 12-13-week scan for the early diagnosis of fetal congenital anomalies in the cell-free DNA era. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 51, 463–469.
- Ficara, A.; Syngelaki, A.; Hammami, A.; Akolekar, R.; Nicolaides, K.H. Value of routine ultrasound examination at 35–37 weeks’ gestation in diagnosis of fetal abnormalities. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 55, 75–80.
- Edwards, L.; Hui, L. First and second trimester screening for fetal structural anomalies. Semin. Fetal. Neonatal. Med. 2018, 23, 102–111.
- International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology; Carvalho, J.S.; Allan, L.D.; Chaoui, R.; Copel, J.A.; DeVore, G.R.; Hecher, K.; Lee, W.; Munoz, H.; Paladini, D.; et al. ISUOG Practice Guidelines (updated): Sonographic screening examination of the fetal heart. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 41, 348–359.
- Platt, L.D. Should the first trimester ultrasound include anatomy survey? Semin. Perinatol. 2013, 37, 310–322.
- Pooh, R.K.; Kurjak, A. 3D/4D sonography moved prenatal diagnosis of fetal anomalies from the second to the first trimester of pregnancy. J. Matern. Fetal. Neonatal. Med. 2012, 25, 433–455.
- Yu, F.; Leung, K.Y. Prenatal sonographic appearance of laryngeal atresia: A case report. J. Clin. Ultrasound. 2020, 48, 244–246.
- Rogelio, C.M.; Alma, G.V.; Miguel, M.R.; Jonahtan, L.G.; Hugo, L.B.; Eréndira, C.G.; Israel, J.M.; Areli, R.N.; Rosa, V.G.; César, F.H. Prenatal diagnosis of laryngo-tracheo-esophageal anomalies in fetuses with congenital diaphragmatic hernia by ultrasound evaluation of the vocal cords and fetal laryngoesophagoscopy. Prenat. Diagn. 2020, 40, 1540–1546.
- Mak, A.S.L.; Leung, K.Y. Prenatal ultrasonography of craniofacial abnormalities. Ultrasonography 2019, 38, 13–24.
- Persico, N.; Moratalla, J.; Lombardi, C.M.; Zidere, V.; Allan, L.; Nicolaides, K.H. Fetal echocardiography at 11-13 weeks by transabdominal high-frequency ultrasound. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 37, 296–301.
- Votino, C.; Kacem, Y.; Dobrescu, O.; Dessy, H.; Cos, T.; Foulon, W.; Jani, J. Use of a high-frequency linear transducer and MTI filtered color flow mapping in the assessment of fetal heart anatomy at the routine 11 to 13 + 6-week scan: A randomized trial. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 39, 145–151.
- Dall’Asta, A.; Grisolia, G.; Nanni, M.; Volpe, N.; Schera, G.B.L.; Frusca, T.; Ghi, T. Sonographic demonstration of fetal esophagus using three-dimensional ultrasound imaging. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 54, 746–751.
- Chen, S.A.; Ong, C.S.; Hibino, N.; Baschat, A.A.; Garcia, J.R.; Miller, J.L. 3D printing of fetal heart using 3D ultrasound imaging data. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 52, 808–809.
- Veronese, P.; Bertelli, F.; Cattapan, C.; Andolfatto, M.; Gervasi, M.T.; Vida, V.L. Three-Dimensional Printing of Fetal Heart With d-Transposition of the Great Arteries From Ultrasound Imaging Data. World J. Pediatr. Congenit. Heart Surg. 2021, 12, 291–292.
