Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Chemistry, Medicinal
The genus Maytenus is a member of the Celastraceae family, of which several species have long been used in traditional medicine. Between 1976 and 2021, nearly 270 new compounds have been isolated and elucidated from the genus Maytenus. Among these, maytansine and its homologues are extremely rare in nature. Owing to its unique skeleton and remarkable bioactivities, maytansine has attracted many synthetic endeavors in order to construct its core structure.
- Maytenus
- triterpenoids
- sesquiterpenes
- alkaloids
- synthesis of maytansine
1. Introduction
Plants of the genus Maytenus, a widely distributed member of the Celastraceae family, include approximately 300 plant species that are spread in tropical and subtropical regions of the world [1]. The genus Maytenus is widely used in folk medicines around the world, with the roots, bark and leaves being used for the treatment of cancer, gastric ulcers and arthritis because of their anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antiallergic and antitumor properties [2][3][4][5]. Studies have shown that a diverse group of chemical substances, triterpenoids, sesquiterpenes and alkaloids, are responsible for the various biological activities of the plants in this genus [6]. Among them, the macrolide alkaloid, maytansine, was first isolated from M. serrata [7], and was shown to be an anti-tumor agent with a novel structure, having some clinical potential. In a clinical trial, maytansine was shown to have promising anti-tumor activities against lymphocytic leukemia, lymphoma, ovarian cancer, breast cancer and melanomas [8][9]. Owing to its unique skeleton and remarkable bioactivity, maytansine has attracted a lot of interest for the possible reconstruction of its core structure. Many synthetic studies of the partial structure of maytansine have been reported. Furthermore, several friedelane triterpenoids with their aromatized characteristic structures and sesquiterpene pyridine alkaloids have been isolated from the genus Maytenus, and these have also showed good anti-tumor [10][11] and anti-bacterial [12] characteristics. The new chemical constituents and biological activities of Maytenus are given in this review of work from the past 45 years, as well as several chemical synthesis methods of maytansine or maytansine fragments, with the view of realizing their potential development and utilization in the medical field.
2. Chemical Constituents of Maytenus
Over the past decades, a large variety of biologically active secondary metabolites have been isolated and identified from the members of the genus Maytenus, which include a series of triterpenoids, such as friedelane triterpenoids, lupane triterpenes, oleanane triterpenes, sesquiterpenes and their alkaloids, along with some potent anti-tumor maytansinoids. Many scholars have extensively investigated the species, which belong to the genus Maytenus, and they have isolated several novel compounds with a wide variety of structures, which may prove to be useful against different diseases.
2.1. Triterpenoids
The genus Maytenus is a rich source of triterpenoids. These types of compounds are characteristic components found in this genus. The known triterpenoids from 1995 to 2005 were summarized by Zhang et al. [13] and Pu et al. [14][15]. Since then, several new triterpenoids have been discovered. Therefore, we have attempted to update all the data relating to the new triterpenoids isolated from the genus Maytenus from 1976 to 2021.
2.1.1. Friedelane Friterpenoids
Friedelane triterpenoids are important characteristic components of the Celastraceae family. Moreover, they are endowed with novel chemical diversity and possess a broad spectrum of biological activities. The friedelane triterpenoids are pentacyclic triterpenes composed of 30 carbons, which are converted from oleanolic acid by methyl shifts. In the five six-membered rings, the A/B, B/C and C/D rings are all trans and the D/E rings are mostly cis (i.e., H-18β). There is one β-CH3 substitution at each of the C-4, C-5, C-9, C-14 and C-17 positions. The C-3 position is often substituted with a hydroxyl group, although sometimes the hydroxyl group is oxidized to a carbonyl group.
The compound pristimerin (1) was isolated from M. chuchuhuasca [16]. A new nortriterpene quinone methide, 15α-hydroxy-21-keto-pristimerine (2), has been obtained from the root bark of M. catingarum [17]. Fourteen compounds, including 2,3,22β-trihydroxy-24,29-dinor-1,3,5(10), 7-friedelatetraene-6,21-dione-23-al (3), 2,22β-dihydroxyl-3-methoxy-24,29-dinor-1,3,5(10), 7-friedelatetraene-6,21-dione (4), 2,3,22β-triihydroxy-23,24,29-trinor-1,3,5(10), 7-friedelatetr aene-6,21-dione (5), 2,22β-dihydroxyl-3-methoxy-24,29-dinor-1,3,5(10), 7-friedelatetraene-6,21-dione (6), 2,3,22β-trihydroxy-24,29-dinor-1,3,5(10)-friedelatetraene-6,21-dione (7), 2,15α,22β-trihydroxy-3-methoxy-24,29-dinor-1,3,5(10)-friedelatriene-21-one (8), 3,22β-dihydroxy-24,29-dinor-l(10)-3,5-friedelatriene-2,7,21-trione (9), 3,22β-dihydroxy-24,29-dinor-l(10), 3,5-friedelatriene-21-one (10), 2,3,22β-trihydroxy-24,29-dinor-25(9→8)-1,3,5(10), 7-friedelatetraene-21-one-23-al (11), 23-oxo-iso-tingenone (12), (8S)-7,8-dihydro-7-oxo-tingenoe (13), (7S,8S)-7-hydroxy-7,8-dihydro-tingenone (14), (8S)-7,8-dihydro-6-oxo-tingenol (15) and 23-nor-6-oxo-tingenol (16) were isolated from the roots of M. amazonica [18][19]. Compounds 28-hydroxy-friedelane-1,3-dione (17) and macrocarpins A–D (18–21) were obtained from the roots of M. macrocarpa [20][21], while maytenfolone (22) has been isolated from M. diversifolia [22]. Three compounds 6-oxo-iguesterol (23), 6-oxo-tingenol (24) and 3-O-methoxy-6-oxo-tingenol (25) have been obtained from the root bark of M. canariensis [12]. Four new triterpenes blepharotriol (26), 6-deoxoblepharodol (27), isoblepharodol (28) and 7-oxo-blepharodol (29) were separated from M. blepharodes [23].
Compounds 15α-hydroxy-tingenone (30), 15-dehydro-pristimerin (31), vitideasin (32) and 20β-hydroxy-scutione (33) were separated from the roots of M. vitis-idaea [24]. Six new compounds, including 7-oxo-7, 8-dihydro-scutione (34), 6,23-dioxo-7,8-dihydro-pristimerol-23-oic Acid (35), 23-nor-blepharodol (36), 3-methoxy-6-oxo-tingenol-23-oic Acid (37), retusonine (38) and 21-Oxopristimerine (39) were isolated from the root bark of M. retusa [25]. A new compound 3-O-Methyl-6-oxo-pristimerol (40) has been isolated from the hexane/Et2O 1:1 extract of the root bark of M. chubutensis [26]. Compounds 3β,24-epoxy-2α,3α-dihydroxy-D:A-friedooleanan-29-oic acid methyl ester (41), 2α-acetoxy-3β,24-epoxy-3α-hydroxy-D:A-friedooleanan-29-oic acid methyl ester (42), 3α-hydroxy-D:A-friedooleanan-28-oic acid (43) and 3-oxo-D:A-friedooleanan-28,30-olide (44) were obtained from the root bark of M. jelskii [27]. Compounds 3β,11β-dihydroxyfriedelane (45) and 3,4-seco-friedelan-3,11β-olide (46) have been obtained from the hexane extracts of the leaves of M. robusta [28], while (16β)-16-hydroxy-pristimerin (47) was from M. salicifolia [29]. A new triterpenoid, 12,16-dihydroxyfriedelan-3-one (48), was isolated from an ethyl acetate extract of M. oblongata [30]. Compounds 3β,24β-epoxy-29-methoxy-2α,3α,6α-trihydroxy-D:A-friedelane (49) and 3β,24β-epoxy-29-methoxy-2α,3α,6α-triacetoxy-D:A-friedelane (49a) were obtained from the root bark extracts of M. cuzcoina [31]. Three new pentacyclic triterpenoids, friedel-1-en-3,16-dione (50), 1α,29-dihydroxyfriedelan-3-one (51) and 16β,28,29-trihydroxyfriedelan-3-one (52) have been separated from M. robusta [32]. Dispemroquinone (53) was isolated from M. dispermus [33]. A new norquinonemethide triterpene with a netzahualcoyene type skeleton, scutione (54), was isolated from the root bark of M. scutioides [34]. Compounds zeylasterone (55) and demethylzeylasterone (56) were obtained from M. blepharodes [35], and compound 3,15-dioxo-21α-hydroxy friedelane (57) was isolated from the methanol extracts of M. robusta [36]. Maytenfoliol (58) was separated from M. diversifolium [37]. Four new cytotoxic triterpenoid dimers, including cangorosin A (59), atropcangorosin A (60), dihydroatropcangorosin A (61) and cangorosin B (62) were obtained from the extracts of M. ilicifolia [38]. Two new triterpenes, umbellatin α (63) and umbeilatin β (64), have been separated from M. umbellata [39]. Two novel trimer triscutins, A and B (65–66), have been isolated from extracts of the root bark of M. scutioides [40]. Four new triterpene dimers, xuxuarine Eα (67), scutionin αB (68), 6′,7′-dihydro-scutionin αB (69) and 6′β-methoxy-6′,7′dihydro-scutionin αB (70), have been isolated from the extracts of the roots of M. blepharodes and M. magellanica [41][42] (Table 1 and Figure 1).
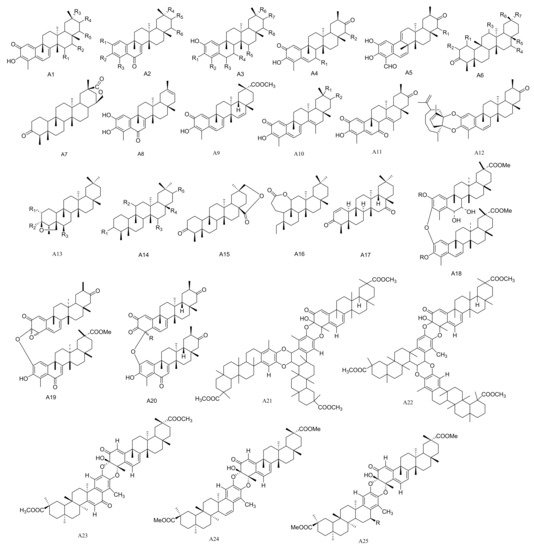
Figure 1. Twenty-five types (A1–A25) of friedelane triterpenoids skeletons.
Table 1. The friedelane triterpenes isolated from Maytenus.
2.1.2. Lupane Triterpenes
Lupane triterpenes are characterized by the combination of C-21 and C-19, clustered into a five-membered carbocyclic E ring. There is an isopropyl group substituted at the 19th position of the E ring with an α configuration, as well as a double bond at the C-20(29) position. The rings of the A/B, B/C, C/D and D/E types are all trans. The new triterpenes 3β,28,30-Lup-20(29)-ene triol (71) and 28,30-Dihyroxylup-20(29)-ene-3-one (72) were obtained from M. canariensis [43], while compound maytefolin A (73) was isolated from the leaves of a Brazilian medicinal plant, M. ilicifolia [44]. 3-oxo-lup-20(29)-en-30-al (74), 30-hydroxylup-20(29)-en-3-one (75), (11α)-11-hydroxylup-20(29)-en-3-one (76) and (3β)-lup-20(30)-ene-3,29-diol (77) have been obtained from the hexane extracts of the stems and branches of M. imbricate [45]. Compounds 11α-hydroxy-epi-betuin (78), 6β-hydroxybetulin (79), 24-hydroxybetulin (80), rigidenol-28-aldehyde (81) and 28-hydroxyglochidone (82) have been isolated from M. cuzcoina and M. chiapensis [46]. Compounds 11α-hydroxy-glochidone (83), 3-epi-nepeticin (84) and 3-epi-calenduladiol (85) were separated from the root barks of M. cuzcoina and the leaves of M. chiapensis [47]. Four new triterpenes, including 3α,16β,28-Trihydroxylup-20(29)-ene (86), 3α,16β-dihydroxylup-12-ene (87), 3β,16β-dihydroxylup-12-ene (88) and 16β-3,4-Secolup-20(29)-en-3-oic acid (89), were obtained from the aerial parts of M. apurimacensis [48], while compound 3-(E)-β-coumaroylnepeticin (90) was isolated from M. retusa [25]. Compound 3,4-seco-lupa-4(23): 20(29)-diene-3,28-dioic acid 28-methyl ester (91) has been separated from the hexane/Et2O 1:1 extracts of the root barks of M. magellanica [26]. 1β-Hydroxy-3β-caffeate lup-20(29)-ene (92) was isolated from the roots of M. apurimacensis [49]. Compounds 3-oxo-21β-H-hop-22(29)-ene (93), 3β-hydroxy-21β-H-hop-22(29)-ene (94) and 3,4-seco-21β-H-hop-22(29)-en-3-oic acid (95) were isolated from the leaves of M. robusta [28] (Table 2 and Figure 2).
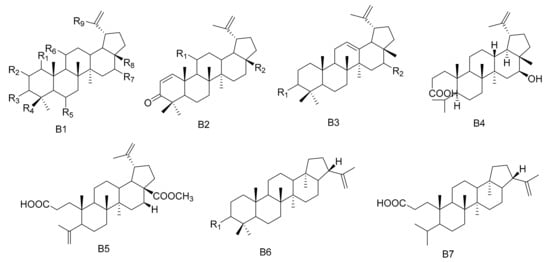
Figure 2. Seven types (B1–B7) of lupane triterpenes skeletons.
Table 2. The lupane triterpenes isolated from Maytenus.
2.1.3. Oleanane Triterpenes
Oleanane triterpenes are widely distributed in the plant kingdom. The configuration of the rings is A/B, B/C and C/D, and they are all of the trans configuration, while the D/E ring is cis. There are eight methyl groups on the core nuclei, and the methyl groups at positions C-10, C-8 and C-17 are all β configuration. The methyl group at the C-14 position is α configuration, while the C-4 and C-20 positions each have two methyl groups. There may also be other substituents present in the molecule. Two new oleanane triterpenes, 3β,19α-dihydroxyolean-12-en-29-oic acid (96) and 3α,19α-dihydroxyolean-12-en-29-oic acid (97), were obtained from M. austyoyunnanensis [14]. Compound 3-oxo-11α-methoxyolean-12-ene (98) was obtained from the extracts of the roots of M. spinosa [24], while 22α-hydroxy-29-methoxy-3β-tetradecanoate-olean-12-ene (99) was separated from the root bark extracts of M. cuzcoina [31]. The new compound maytefolin B (100) was separated from the leaves of a Brazilian medicinal plant, M. ilicifolia [44]. One new triterpene, 3β-peroxy-7β,25-epoxy-D:B-friedoolean-5-ene (101), was separated from the aerial parts of M. apurimacensis [48]. Compounds krukovines A (28-hydroxyolean-12-ene-3,11-dione) (102) and krukovines C (6β,28-dihydroxyolean-12-ene-3,11-dione) (103) have been obtained from a South American medicinal plant known as “chuchuhuasi” (M. krukovii) [50]. The aerial parts of M. undata yielded four new 12-oleanene and 3,4-seco-12-oleanene triterpene acids, namely, 3-oxo-11α-methoxyolean-12-ene-30-oic acid (104), 3-oxo-11α-hydroxyolean-12-ene-30-oic acid (105), 3-oxo-olean-9(11), 12-diene-30-oic acid (106) and 3,4-seco-olean-4(23), 12-diene-3,29-dioic acid (107) [51], while 3α-22β-dihydroxyolean-12-en-29-oicacid (108) was obtained from the methanol extracts of the barks of M. laevis [52]. Compound olean-9(11):12-dien-3β-ol (109) was isolated from the roots of M. acanthophylla [53] and compound 3β-hydroxy-D:B-friedo-olean-5-ene (110) was isolated from M. salicifolia Reissek [54]. Compound 19α-hydroxy-3-olean-12-en-29-oic acid (111) was isolated from M. austyoyunnanensis [55] (Table 3 and Figure 3).
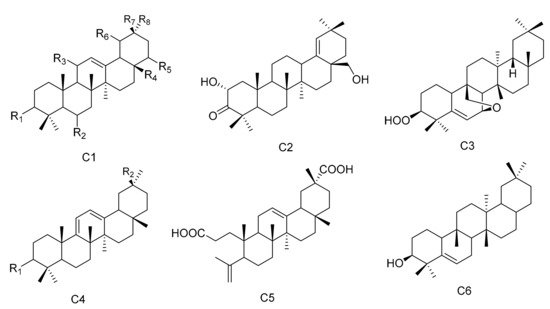
Figure 3. Six types (C1–C6) of oleanane triterpenes skeletons.
Table 3. The oleanane triterpenes isolated from Maytenus.
2.1.4. Other Triterpenes
In addition to the above, other types of triterpene compounds have also been isolated from Maytenus. These include triterpene dimers, ursane triterpenes and dammarane triterpenes. The compound 3-Oxo-methoxyurs-12-ene (112) was isolated from M. spinosa [24]. Three ursane triterpenes, krukovines B, D and E (113–115), were obtained from M. krukovii [50]. Compound maytefolin C (116) has been isolated from the leaves of M. ilicifolia [44], while 28-hydroxy-12-ursene-3β-yl-caffeate (uvaol-3-caffeate) (117) has been isolated from the methanol extracts of the barks of M. laevis [52]. An ursane triterpene 3β-stearyloxy-urs-12-ene (118) was obtained from M. salicifolia [56]. The stem bark exudates of M. macrocarpa yielded ten dammarane triterpenes, namely, 24-(E)-3-oxo-dammara-20,24-dien-26-al (119), 24-(Z)-3-oxo-dammara-20,24-dien-26-al (120), 24-(E)-3-oxo-dammara-20,24-dien-26-ol (121), 24-(E)-3-oxo-dammara-23-α-hydroxy-20,24-dien-26-al (122), 24-(E)-3-oxo-dammara-23-β-hydroxy-20,24-dien-26-al (123), 24-(E)-3-oxo-dammara-6-β-hydroxy-20, 24-dien-26-al (124), 24-(E)-3-oxo-dammara-6-β-hydroxy-20,24-dien-26-ol (125), 23-(Z)-3, 25-dioxo-25-nor-dammara-20,24-diene (126), 24-(E)-3-oxo-23-methylene-dammara-20,24-dien-26-oico (127), 24(Z)-3-oxodammara20(21),24-dien-27-oic acid (128) and octa-nor-13-hydroxydammara-1-en-3,17-dione (129). This was in 1997, and it was the first time that dammrane triterpenes were isolated from Celastraceae [57][58] (Table 4 and Figure 4).
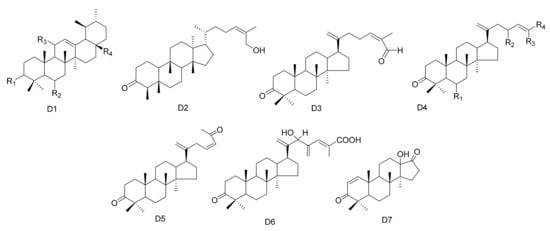
Figure 4. Seven types (D1–D7) of other triterpenes skeletons.
Table 4. The other triterpenes isolated from Maytenus.
2.2. Sesqiterpenoids
The most widespread and characteristic metabolites isolated from the Celastraceae family are a large group of unusual and highly oxygenated sesquiterpenoids, based on the [5,11-epoxy-5β,10α-eduesman-4(14)-ene] skeleton known as dihydro-β-agarofum. Sesquiterpenes have multiple substitution sites in their structure, and common substituents include -OH, -OAc, -Ofu, -Obz and -Onic, which is due to the diversification of their positions and types. There is a high probability that there are several new compounds from this group that still need to be discovered [59].
Two sesquiterpene polyesters with new polyhydroxy skeletons, 1α,9α-dibenzoyloxy-6β,8α,15-triacetoxy-4β-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofurane (130) and 1α,9α-dibenzoyloxy-2α,6β,8α,15-tetracetoxy-4β-hydroxydihydro-β-agrofurane (131), were isolated from the aerial portions of M. canariensis [60]. Compounds 6β,8β-15-triacetoxy-1α,9α-dibenzoyloxy-4β-hydroxy-β-dihydroagarofuran (132), 1α,6β,8β,15-tetraacetoxy-9α-benzoyloxy-4β-hydroxy-β-dihydroagarofuran (133) and (1S,4S,6R,7R,8R,9R)-1,6,15-triacetoxy-8,9-dibenzoyloxy-4β-hydroxy-β-dihydroagarofuran (134) were isolated from the aerial parts of M. macrocarpa [61]. Compounds (1R,2S,4S,5S,6R,7R,9S,10S)-6,15-diacetoxy-1,2,9-tribenzoyloxy-4-hrdroxy-8-oxo-dihydro-β-agarofuran (135) and 9β-cinnamoyloxy-2β,3β-diacetoxy-6β-hydroxy-lα-nicotinoyloxydihidro-β-agarofuran (136) were separated from M. blepharodes [41]. Eight sesquiterpenoids, including 1α-acetoxy-2α,6β,9β-trtifuroyloxy-4β-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (137), 1α,2α-diacetoxy-6β,9β-difuroyloxy-4β-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (138), 1α-acetoxy-6β,9β-difuroyloxy-2α,4β-dihydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (139), 1α-acetoxy-2α-benzoyloxy-6β,9β-difuroyloxy-4β-dihydro-β-agarofuran (140), 1α-acetoxy-6β,9β-difuroyloxy-2α-propyonyloxy-4β-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (141), 1α-acetoxy-6α,9β-difuroyloxy-2α-(2)-methylbutyroyloxy-4β-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (142), 1α,2α,15-triacetoxy-6β,9β-difuroyloxy-4β-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (143) and 1α,2α,15-triacetoxy-6β,9β-dibenzoyloxy-4β-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (144) were obtained from the n-hexane: Et2O (1:1) extracts of the fruits of M. cuzcoina [59].
The n-hexane/Et2O (1:1) extracts of the root barks of M. magellanica yielded eight new dihydro-β-agarofuran sesquiterpenes (145–152), and the n-hexane/Et2O (1:1) extracts of the root barks of M. chubutensis yielded two more new compounds of this family (153–154). Their structures were elucidated as (1R,2R,4S,5R,7S,9S,10R)-2-acetoxy-1-benzoyloxy-9-cinnamoyloxy-4-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (145), (1R,2S,3S,5R,7R,9S,10R)-2-acetoxy-9-benzoyloxy-1-cinnamoyloxy-3-nicotinoyloxy-4-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (146), (1R,2S,3S,4S,5S,6R,7R,9S,10R)-2,6-diacetoxy-1-benzoyloxy-9-cinnamoyloxy-3-nicotinoyloxy-4-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (147), (1R,2S,3S,4S,5S,6R,7R,9S,10R)-2,6-diacetoxy-1,9-dibenzoyloxy-3-nicotinoyloxy-4-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (148), (1R,2S,3S,4S,5R,7S,8S,9R,10R)-2,3-diacetoxy-8,9-dibenzoyloxy-1-nicotinoyloxy-4-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (149), (1R,2S,4S,5S,6R,7R,8S,9R,10S)-6,8-diacetoxy-1,2,9-tribenzoyloxy-4-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (150), (1R,2S,3S,4S,5R,7S,8S,9R,10R)-2,8-diacetoxy-3,9-dibenzoyloxy-1-nicotinoyloxy-4-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (151), (1R, 2S,4R,5S,6R,7R,8S,9R,10S)-6,8-diacetoxy-1,9-dibenzoyloxy-2-nicotinoyloxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (152), 1α,15-diacetoxy-6β,9β-dibenzoyloxy-2α-nicotinoyloxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (153) and 1α,15-diacetoxy-6β,9β-dibenzoyloxy-2α-nicotinoyloxy-4β-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (154) [62]. Compounds (1R,2S,4S,5S,6R,7R,9S,10S)-1,2,6,9,15-pentaacetoxy-4-hydroxy-8-oxo-dihydro-β-agarofuran (155), (1R,2S,4S,5S,6R,7R,9S,10S)-1,2,9,15-taacetoxy-4,6-dihydroxy-8-oxo-dihydro-β-agarofuran (156), (1R,2S,4S,5S,6R,7R,9S,10S)-1,9,15-triacetoxy-2,4,6-trihydroxy-8-oxo-dihydro-β-agarofuran (157), (1R,2S,3S,4S,5S,6R,7R,9S,10S)-1,2,3,6,9,12,15-heptaacetoxy-4-hydroxy-8-oxo-dihydro-β-agarofuran (158) and 1α,2α,3β,6β,8α,9α,12,15-octaacetoxy-4β-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (159) were isolated from the leaves of M. chiapensis [63]. In addition, (1S,4S,5S,6R,7R,8S,9R,10R)-8-acetoxy-1,9-dibenzoyloxy-6-nicotynoyloxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (160) and (1S,4R,5R,6R,7R,8S,9R,10R)-8-acetoxy-1,9-dibenzoyloxy-4-hydroxy-nicotynoyloxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (161) have been isolated from the roots of M. apurimacensis [49].
Thirteen sesquiterpenes, including (1R,2S,4S,5S,6R,7R,9S,10R)-115-diacetoxy-2,6-dibenzoyloxy-9-(3-furoyloxy)-4-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (162), (1R,2S,4S,5S,6R,7R,9S,10R)-1,2,15-triacetoxy-6-benzoyloxy-9-(3-furoyloxy)-4-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (163), (1R,2S,4S,5S,6R,7R,9S,10R)-1,15-diacetoxy-6-benzoyloxy-9-(3-furoyloxy)-2,4-dihydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (164), (1R,2S,4S,5S,6R,7R,9S,10R)-1,15-diacetoxy-6,9-dibenzoyloxy-2,4-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (165), (1R,2S,4S,5S,6R,7R,9S,10R)-1,2,6,15-tetracetoxy-9-(3-furoyloxy)-4-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (166), (1R,2S,4S,5S,6R,7R,9S,10R)-1-Acetoxy-2,6-dibenzoyloxy-9-(3-furoyloxy)-4-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (167), (1S,2S,3S,4S,5R,7R,9S,10R)-2,3-diacetoxy-9-benzoyloxy-1-(3-furoyloxy)-4-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (168), (1S,2R,4S,5R,7R,9S,10R)-2-acetoxy-9-benzoyloxy-1-(3-furoyloxy)-4-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (169), (1S,2R,4S,5R,7R,9S,10R)-2-Acetoxy-1,9-di-(3-furoyloxy)-4-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (170), (1S,2R,4S,5R,7R,9S,10R)-2-Acetoxy-9-trans-cynamoiloxy-1-(3-furoyloxy)-4-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (171), (1S,4S,5R,7R,9S,10S)-9-Benzoyloxy-1-(3-furoyloxy)-4-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (172), (1S,2R,3R,4R,5S,7R,9S,10R)-2,3-diacetoxy-9-benzoyloxy-1-(3-furoyloxy)-dihydro-β-agarofuran (173) and (1S,2R,4R,5S,7R,9S,10R)-2-Acetoxy-9-benzoyloxy-1-(3-furoyloxy)-dihydro-β-agarofuran (174) have been isolated from the hexanee-Et2O extracts of the fruits of M. jelskii [64]. Nine new β-dihydroagarofurans, 1α2α,9β,15-tetracetoxy-8β-benzoyloxy-β-dihydroagarofuran (175), 1α-benzoyloxy-2α,6β,8α-triacetoxy-9α-methyllbutyroyloxy-β-dihydroagarofuran (176), 1α,6β-diacetoxy-2α,8α,9α-tribenzoyloxy-β-dihydroagarofuran (177), 1α-benzoyloxy-2α,6β,8α,9α-tetraacetoxy-β-dihydroagarofuran (178), 1α,6β,8α-triacetoxy-9α-benzoyloxy-2α-hydroxy-β-dihydroagarofuran (179), (1R,2S,4R,5S,6R,7R,8R,9S,10S)-1,6-diacetoxy-8,9-dibenzoyloxy-2-h ydroxy-β-dihydroagarofuran (180), 1α,6β,15-triacetoxy-8α-methylbutyroyloxy-9α-benzoyloxy-2α-hydroxy-β-dihydroagaro-furan (181), 1α,6β,15-triacetoxy-8α,9α-dibenzoyloxy-2α-hydroxy-β-dihydroagarofuran (182) and 1α,6β,8β,15-tetracetoxy-2α-hydroxy-9α-benzoyloxy-β-dihydroagarofuran (183), were isolated from the leaves of M. spinosa [65]. Five new compounds, chiapens A–E (184–188), were isolated from M. chiapensis [66].
Compounds 1α,6β-diacetoxy-8α-hydroxy-9β-furoyloxy-β-agarofuran (189), 1α-acetoxy-6β,8α-dihydroxy-9β-furoyloxy-β-agarofuran (190), 1α-benzoyloxy-2α,3β,6β,9β,14-pentaacetoxy-8-oxo-β-agarofuan (191) and 1α-furoyloxy-2α,3β,6β,9β,14-pentaacetoxy-8-oxo-β-agarofuan (192) were obtained from an extract of the seeds of M. boaria [67]. Bilocularins A−I (193–201) were isolated from M. bilocularis. In addition, bilocularins D–F are the first examples of dihydro-b-agarofurans, which bear a hydroxyacetate group [68][69]. Compounds (1S,4S,5S,6R,7R,8R,9R,10S)-6-acetoxy-4,9,10-trihydroxy-2,2,5a,9-tetramethyloctahydro-2H-3,9a-methanobenzo[b]oxepin-5-yl furan-3-carboxylate (202), (1S,4S,5S,6R,7R,8R,9R,10S)-6-acetoxy-4,9-dihydroxy-2,2,5a,9-tetramethyloctahydro-2H-3,9a-methanobenzo[b]oxepine-5,10-diyl bis(furan-3-carboxylate) (203), (1S,4S,5S,6R,7R,9S,10S)-6-acetoxy-9-hydroxy-2,2,5a,9-tetramethyloctahydro-2H-3,9a-methanobenzo[b]oxepine-5, 10-diyl bis(furan-3-carboxylate) (204) and (1S,4S,5S,6R,7R,9S, 10S)-6-acetoxy-10-(benzoyloxy)-9-hydroxy-2,2,5a,9-tetramethyloctahydro-2H-3,9a-methanobenzo[b]-oxepin-5-yl furan-3-carboxylate (205) were isolated from the seeds of M. boaria [70][71]. Compounds 2β,6β-diacetoxy-1α,9β-dibenzoyl-3β-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (206), 1α,2α,6β,8α-tetraacetoxy-9β-benzoyl-15-hydroxy-dihydro-β-agarofuran (207) and 1α,2α,6β,8α,15-pentaacetoxy-9β-benzoyl-dihydro-β-agarofuran (208) have been separated from M. boaria [72]. 1β-acetoxy-9α-benzoyloxy-2β,6α-dinicotinoyloxy-β-dihydroagarofuran (209) was obtained from the anti-microbially active ethanol extracts of M. heterophylla [73]. In addition, an eudesmane glucoside, boarioside (210), has been isolated from M. boaria [74]. Compounds 4-deacetyl-10-oxo-dihydrobotrydial (211) and 4β-acetoxy-9β,10β,15α-trihydroxyp robotrydial (212) were obtained from solid cultures of an endocytic fungal strain, Phomopsis species Lz42, cultivated on M. hookeri [75] (Table 5 and Figure 5).
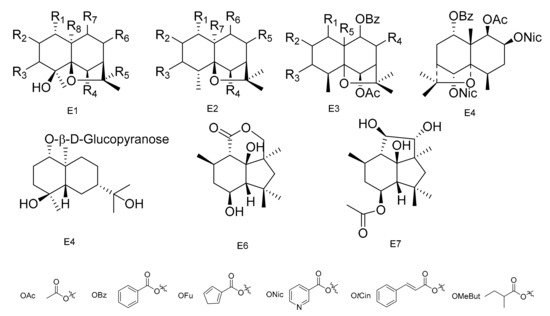
Figure 5. Seven types (E1–E7) of sesqiterpenoids skeletons.
Table 5. The sesqiterpenoids isolated from Maytenus.
2.3. Alkaloids
2.3.1. Sesquiterpene Pyridine Alkaloids
Among the naturally occurring nitrogen containing compounds, the pyridine alkaloids constitute an important group, and these are relatively rare natural products. The Celastraceae family is a rich source of sesquiterpene pyridine alkaloids. These compounds are endowed with a novel type of chemical diversity, and have complicated stereo-chemistries. They also possess a broad spectrum of biological activities, such as having immunosuppressive and anti-tumor properties. The vast majority of macrolide sesquiterpene pyridine alkaloids, from the genus Maytenus, are based on the [5,11-epoxy-5β,10a-eduesman-4(14)-ene] skeleton known as dihydro-β-agarofum. These compounds are characterized by a pyridine dicarboxylic acid macrocyclic bridge (such as evoninic, wilfordic and hydroxywilfordic acids), linked via two ester moieties at the C-3 and C-15 positions [65][76]. Many of these alkaloids have been isolated by organic chemists over recent years. Below we summarize their information, including the names of compounds, their original plant source as well as their structures.
The potent anti-feedant wilforine (213) was isolated from M. rigida [77]. Compounds emarginatines A–H (214–221) and emarginatinine (222) were obtained from M. emarginata and the leaves of M. diversifolia. [11][22][78][79]. Ebenifoline W-I (223), ebenifoline E-I (224) and ebenifoline E-II (225) were separated from the stem bark methanol extracts of M. ebenifolia Reiss [80]. Compounds aquifoliunines E-I-IV (226–229) have been obtained from the root barks of M. aquiJolium. [81][82], while ilicifoliunines A–B (230–231) and mayteine (232) were isolated from the root barks of M. ilicifolia [83]. Laevisines A (233) and B (234) have been separated from the CHCl3:MeOH (9:1) extracts of the barks of M. laevis [84]. Compounds mekongensine (235), 7-epi-mekongensine (236), 1-O-benzoyl-1-deacetylmekongensine (237), 9′-deacetoxymekongensine (238), 1-O-benzoyl-1-deacetyl-9′-deacetoxymekongensine (239), 7-epi-euojaponine A (240), 2-O-benzoyl-2-deacetylmayteine (241) and 7-epi-5-O-benzoyl-5-deacetylperitassine A (242) have been isolated from the roots of M. mekongensis [85]. The compound 5-benzoyl-5-deacetylwilforidine (243) was isolated from M. buchananii (Loes.) R. Wilczek. This appears to be the first sesquiterpene nicotinoyl alkaloid found which was based on hydroxywilfordic acid, with a benzoyl group at C-5 position [86]. Compounds putterines A (244) and B (245) have been separated from the roots of M. putterlickoides [76]. The compound 7-(acetyloxy)-O11-benzoyl-O2,11-deacetyl-7-deoxoevonine (246) was isolated from the methanol extracts of the barks of the Colombian medicinal plant, M. laevis [52]. Chiapenines ES-I (247), ES-II (248), ES-III (249) and ES-IV (250) were isolated from the leaves of M. chiapensis [87]. Compound jelskiine (251) was obtained from M. jelskii and M. cuzcoina [88]. Compounds O9-benzoyl-O9-deacetylevonine (252) and 8β-acetoxy-O1-benzoyl- O1-deacetyl-8-deoxoevonine (253) have been separated from the organic extracts of the roots of M. spinosa [24]. Compounds 1α,2α,6β,8β,9α,15-hexacetoxy-4β-hydroxy-3β,13-[2′-(3-carboxybutyl)] nicotinicacid-dicarbo-lactone-β-dihydroagarofuran (254), 1α,2α,9α,15-tetracetoxy-4β,6β-dihydroxy-8-oxo,3β,13-[4′-(3-carboxybutyl)]nicotinicacid-dicarbolactone-β-dihydroagarofuran (255), 1α,2α,9α,15-tetracetoxy-4β,6β,8β-trihydroxy-3β,13-[4′-(3-carboxybutyl)] nicotinicacid-dicarbolactone-β-dihydroagarofuran (256) and 1α,2α,8β,9α,15-pent acetoxy-4β,6β-dihydroxy-3β,13-[4′-(3-carboxybutyl)] nicotinicaciddicarbolactne-β-dihydroagarofuran (257) were isolated from the leaves of M. spinosa [65]. Compounds 4-deoxyalatamine (258), 1-O-benzoyl-1-deacetyl-4-deoxy-alatamine (259), 1,2-O-dibenzoyl-1,2-deacetyl-4-deoxyalatamine (260) and 4-deoxyisowilfordine (261) were obtained from an ethyl acetate extract of M. oblongata stems [31] (Table 6 and Figure 6).
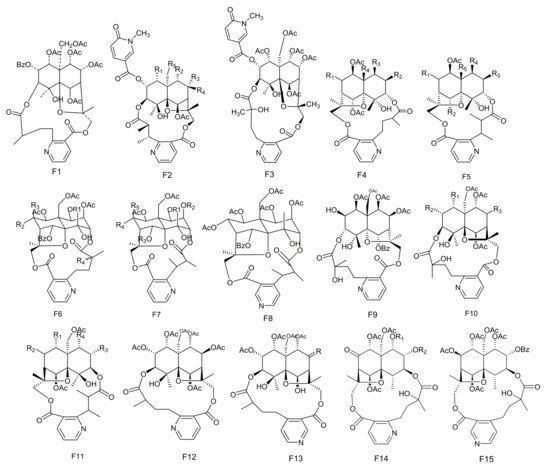
Figure 6. Fifteen types (F1–F15) of sesquiterpene pyridine alkaloids skeletons.
Table 6. The sesquiterpene pyridine alkaloids isolated from Maytenus.
2.3.2. Maytansinoids
In 1972, Kupchan et al. [7] found a macrolide alkaloid, maytansine (262), which was a natural product that had anti-tumor activities, and this was first isolated from M. serrata. Compound 262 is an anti-tumor agent with a novel structure, and, therefore, is of great clinical interest. Subsequently, maytansine (262), maytanprine (263) and maytanbutine (264) were isolated from M. buchananii [89]. Larson et al. [90] also isolated two new maytansinoid compounds, 2′-N-demethylmaytanbutine (265) and maytanbicyclinol (266) from M. buchananii (Figure 7).
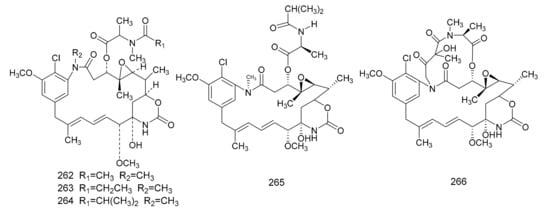
Figure 7. The chemical structures of maytansinoids, isolated from Maytenus.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/molecules26154563
References
- Editorial Committee of Flora of China. Flora of China (Forty-Fifth Volume); Science Press: Beijing, China, 1999.
- Ghazanfar, S.A. Handbook of Arabian Medicinal Plants; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994.
- Gonzalez, J.G.; Delle, M.G.; Delle Monache, F.; Marini-Bettolò, G.B. Chuchuhuasha-a drug used in folk medicine in the Amazonian and Andean areas, a chemical study of Maytenus laevis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1982, 5, 73–75.
- Veloso, C.C.; Oliveira, M.C.; Rodrigues, V.G.; Oliveira, C.C.; Duarte, L.P.; Teixeira, M.M.; Ferreira, A.V.M.; Perez, A.C. Evaluation of the effects of extracts of Maytenus imbricata (Celastraceae) on the treatment of inflammatory and metabolic dysfunction induced by high-refined carbohydrate diet. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 27, 539–548.
- Elmer, L.C.; Henry, M.S.; Alexander, M.V.; Karola, M.C.; María, M.R.; Zaida, L.C.; Carlos, P.M.; Alberto, S.G. Anti-Inflammatory and Neurobehavioral Effects of the Leaves from Maytenus macrocarpa (Ruiz and Pavón) Briquet in Mice. Pharmacogn. J. 2019, 11, 75–80.
- Tang, H.; Li, F.; Wei, X.; Li, H.; Huang, X.Y. Advance of researches on medicnal plants of maytenus. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2009, 48, 2275–2277.
- Kupchan, S.M.; Komoda, Y.; Branfman, A.R.; Sneden, A.T.; Court, W.A.; Thomas, G.J.; Hintz, H.P.; Smith, R.M.; Karim, A.; Howie, G.A.; et al. The maytansinoids, isolation, structural elucidation and chemical interrelation of novel anse macrolides. J. Org. Chem. 1972, 42, 2349–2357.
- Pei, S.J.; Shen, P.Q.; Li, C.Y. Some thoughts on the Anti-cancer Research of Maytenus. Chin. Acad. Med. Org. 2003, 70, 70–72.
- American Cancer Research Institute. American Institute of Cancer Research on the study of maytansin. Drugs Clinic 1981, 2, 9–14.
- Hiroshi, M.; Yusuke, H.; Akihiro, M.; Tadashi, Y.; Setsuko, S.; Osamu, S. Antimitotic quinoid triterpenes from Maytenus chuchuhuasca. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 1050–1052.
- Kuo, Y.H.; King, M.L.; Chen, C.F.; Chen, H.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, K.; Lee, K.H. Two new macrolide sesquiterpene pyridine alkaloids from Maytenus emarginata: Emarginatine G and the cytotoxic emarginatine F. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 263–269.
- Gonzalez, A.G.; Alvarenga, N.L.; Ravelo, A.G.; Jimenez, I.A.; Bazzocchi, I.L.; Canela, N.J.; Moujir, L.M. Antibiotic phenol nortriterpenes from Maytenus canariensis. Phtochemistry 1996, 43, 129–132.
- Zhang, X.Y.; Feng, J.T.; Zhang, X. Advances in studies on triterpenes constituents and their biological activities in species of Maytenus. Acta Bot. Boreali Occident. Sin. 2007, 27, 1484–1490.
- Pu, D.B. Study on the Chemical Consituents and Anti-Tumor Activity of M. austroyunnanensis. Master’s Thesis, Kun Ming University of Science and Technology, Yunnan, China, 2014.
- Pu, D.B.; Gao, Y.; Li, R.T.; Li, H.Z. Structures and 13C NMR Features Triterpenoid Compounds in Maytenus: A Review. Chin. J. Magn. Reson. 2014, 31, 437–445.
- Martinod, P. Separation eupirone and Prisminin from M. chuchuhuasca. Phytochemistry 1976, 15, 562.
- Alvarenga, N.L.; Velázquez, C.A.; Gomez, R.; Canela, N.J.; Bazzocchi, I.L.; Ferro, E.A. A new antibiotic nortriterpene quinone methide from Maytenus catingarum. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 750–751.
- Chávez, H.; Valdivi, E.; Estévez-Braun, A.; Ravelo, Á.G. Structure of new bioactive triterpenes related to 22-β-hydroxy-tingenone. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 13579–13590.
- Chávez, H.; Estévez-Braun, A.; Ravelo, A.G.; Gonzalez, A.G. New phenolic and quinone methide triterpenes from Maytenus amazonica. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 434–436.
- Chávez, H.; Estevez-Braun, A.; Ravelo, A.G.; Gonzalez, A.G. Friedelane triterpenoids from Maytenus macrocarpa. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 82–85.
- Chávez, H.; Rodriguez, G.; Estevez-Braun, A.; Ravelo, A.G.; Estévez-Reyes, R.; González, A.D.; Fdez-Puente, J.L.; García-Grávalos, D. Macrocarpins A-D, new cytotoxic nor-triterpenes from Maytenus macrocarpa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2000, 10, 759–762.
- Kuo, Y.H.; Ou, J.C.; Lee, K.H.; Chen, C.F. A new triterpene lactone, maytenfolone, and a new sesquiterpene pyridine alkaloid, emarginatine H, from the leaves of Maytenus diversifolia. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 1103–1108.
- Rodrguez, F.M.; Lopez, M.R.; Jimenez, I.A.; Moujir, L.; Ravelo, A.G.; Bazzocchi, I.L. New phenolic triterpenes from Maytenus blepharodes, semisynthesis of deoxobleoharodol from pristimerin. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 2513–2519.
- de Almeida, M.T.R.; Rios-Luci, C.; Padron, J.M.; Palermo, J.A. Antiproliferative terpenoids and alkaloids from the roots of Maytenus vitis-idaea and Maytenus spinosa. Phtochemistry 2010, 71, 1741–1748.
- Oramas-Royo, S.M.; Chavez, H.; Martin-Rodriguez, P.; Fernandez-Perez, L.; Ravelo, A.G.; Estevez-Braun, A. Cytotoxic triterpenoids from Maytenus retusa. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 2029–2034.
- Kennedy, M.L.; Llanos, G.G.; Castanys, S.; Gamarro, F.; Bazzocchi, I.L.; Jiménez, I.A. Terpenoids from Maytenus species and assessment of their reversal activity against a multidrug-resistant leishmania tropica line. Chem. Biodivers. 2011, 8, 2191–2298.
- Ardiles, A.E.; González-Rodríguez, Á.; Núñez, M.J.; Perestelo, N.R.; Pardo, V.; Jiménez, I.A.; Valverde, Á.M.; Bazzocchi, I.L. Studies of naturally occurring friedelane triterpenoids as insulin sensitizers in the treatment type 2 diabetes mellitus. Phtochemistry 2012, 84, 116–124.
- Sousa, G.F.; Duarte, L.P.; Alcântara, A.F.; Silva, G.D.; Vieira-Filho, S.A.; Silva, R.R.; Oliveira, D.M.; Takahashi, J.A. New triterpenes from Maytenus robusta: Structural elucidation based on NMR experimental data and theoretical calculations. Molecules 2012, 17, 13439–13456.
- Magalhães, C.G.; de Fátima Silva, G.D.; Duartel, L.P.; Bazzocchi, I.L.; Diaz, A.J.; Moujir, L.; López, M.R.; Figueiredo, R.C.; Vieira Filho, S.A. Salicassin, an unprecedented chalconediterpene adduct and a quinone methide triterpenoid from Maytenus salicifolia. Helv. Chim. Acta 2013, 96, 1046–1054.
- Touré, S.; Nirma, C.; Falkowski, M.; Dusfour, I.; Boulogne, I.; Jahn-Oyac, A.; Coke, M.; Azam, D.; Girod, R.; Moriou, C.; et al. Aedes aegypti larvicidal sesquiterpene alkaloids from Maytenus oblongata. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 384–390.
- Reyes, C.P.; Jiménez, I.A.; Bazzocchi, I.L. Pentacyclic Triterpenoids from Maytenus cuzcoina. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 12, 675–678.
- de Sousa, G.F.; de Aguilar, M.G.; Dias, D.F.; Takahashi, J.A.; Moreira, M.E.C.; Vieira Filho, S.A.; Silva, G.D.F.; Rodrigues, S.B.V.; Braga, M.M.C.T.; Duarte, L.P. Anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activities of friedelanes from Maytenus robusta branches and isolation of further triterpenoids. Phytochem. Lett. 2017, 21, 61–65.
- Martin, J.D. The structure of dispermoquinone: A triterpenoid quinone methide from Maytenus dispermus. Tetrahedron 1973, 29, 2997–3000.
- González, A.G.; Alvarenga, N.L.; Ravelo, A.G.; Bazzocchi, I.L.; Ferro, E.A.; Navarro, A.G.; Moujir, L.M. Scutione, a new bioactive norquinonemethide triterpene from Maytenus scutioides (Celastraceae). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1996, 4, 815–820.
- De León, L.; Moujir, L. Activity and mechanism of the action of zeylasterone against Bacillus subtilis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 1266–1274.
- Niero, R.; Mafra, A.P.; Lenzi, A.C.; Cechinel-Filho, V.; Tischer, C.; Malheiros, A.; De Souza, M.M.; Yunes, R.A.; Delle Monache, F. A new triterpene with antinociceptive activity from Maytenus robusta. Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 20, 1315–1320.
- Nozaki, H.; Suzuki, H.; Lee, K.H.; McPhail, A.T. Structure and stereochemistry of maytenfolic acid and maytenfoliol, two new antileukemic triterpenes from Maytenus diversifolia: X-ray crystal structures. J. Chem. Soc. 1982, 18, 1048–1051.
- Itokawa, H.; Shirota, O.; Morita, H.; Takeya, K.; Tomioka, N.; Itai, A. New triterpene dimers from Maytenus ilicifolia. Tetrahedron Lett. 1990, 31, 6881–6882.
- Gonzlez, A.G.; Jimenez, J.S.; Moujir, L.M.; Ravelo, A.G.; Luis, J.G.; Bazzocchi, I.L.; Gutierrez, A.M. Two new triterpene dimers from Celastraceae, their partial synthesis and antimicrobial activity. Tetrahedron 1992, 48, 769–774.
- Gonzalez, A.G.; Alvarenga, N.L.; Bazzocchi, I.L.; Ravelo, A.G.; Laila, M. Triterpenet trimers from Maytenus scutioides: Cycioaddition compounds. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1185–1187.
- Gonzalez, A.G.; Rodriguez, F.M.; Bazzocchi, I.L.; Ravelo, A.G. New terpenoids from Maytenus blepharodes. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 48–51.
- Gonzalez, A.G.; Kennedy, M.L.; Rodriguez, F.M.; Bazzocchi, I.L.; Jimenez, I.A.; Ravelo, A.G.; Moujir, L. Absolute configuration of triterpen dimers from Maytenus species(Celastraceae). Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 1283–1287.
- González, A.G.; Jiménez, I.A.; Ravelo, A.G. Triterpenes from Maytenus canariensis and synthesis of a derivative from Betulin. Phtochemistry 1992, 31, 2069–2072.
- Ohsaki, A.; Imai, Y.; Naruse, M.; Ayabe, S.; Komiyama, K.; Takashima, J. Four new triterpenoids from Maytenus ilicifolia. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 469–471.
- Ribeiro de Souza e Silva, S.; de Fátima Silva, G.D.; de Almeida Barbosa, L.C.; Duarte, L.P.; Filho, S.A.V. Lupane pentacyclic triterpenes isolated from stems and branches of Maytenus imbricata (Celastraceae). Helv. Chim. Acta 2005, 88, 1102–1109.
- Nunez, M.J.; Reyes, C.P.; Jiménez, I.A.; Moujir, L.; Bazzocchi, I.L. Lupane triterpenoids from Maytenus species. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1018–1021.
- Reyes, C.P.; Nunez, M.J.; Jiménez, I.A.; Busserolles, J.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Bazzocchi, I.L. Activity of lupane truterpenoids from Maytenus species as inhibitors of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 1573–1579.
- Vazdeki, N.E.; Chávez, H.; Estevez-Braun, A.; Ravelo, A.G. Triterpenoids and a lignan from the aerial parts of Maytenus apurimacensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1045–1048.
- Delgado-Méndez, P.; Herrera, N.; Chávez, H.; Estévez-Braun, A.; Ravelo, Á.G.; Cortes, F.; Castanys, S.; Gamarro, F. New terpenoids from Maytenus apurimacensis as MDR reversal agents in the parasite Leishmania. Bioorg. Met. Chem. 2008, 16, 1425–1430.
- Shirota, O.; Tamemura, T.; Morita, H.; Takeya, K.; Itokawa, H. Triterpenes from brazilian medicinal plant “chuchuhuasi” (Maytenus krukovii). J. Mat. Prod. 1996, 59, 1072–1075.
- Muhammad, I.; El Sayed, K.A.; Mossa, J.S.; Al-Said, M.S.; El-Feraly, F.S.; Clark, A.M.; Hufford, C.D.; Oh, S.; Mayer, A.M.S. Bioactive 12-oleanene triterpene and secotriterpene acids from Maytenus undata. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 605–610.
- Nakagawa, H.; Takaishi, Y.; Fujimoto, Y.; Duque, C.; Garzon, C.; Sato, M.; Okamoto, M.; Oshikawa, T.; Ahmed, S.U. Chemical constituents from the colombian medicinal plant Maytenus laevis. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1919–1924.
- de Oliveira, D.M.; de Fátima Silva, G.D.; Duarte, L.P.; Vieira Filho, S.A. Chemical constituents isolated from roots of Maytenus acanthophylla reissk (Celastraceae). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2006, 34, 661–665.
- Valladao, F.N.; De Miranda, R.R.; de Oliveira, G.S.; Silva, G.D.; Duarte, L.P.; Sidney Filho, A.V. Constituents of furuit pulp of Maytenus salicifolia and complete 1D/2D NMR date of 3β-hydroxy-D:B-friedo-olean-5-enen. Chem. Matural Compd. 2010, 46, 686–691.
- Tan, W.; Pu, D.; Feng, Y.; Li, H. A new triterpenoid from Maytenus austroyunnanensis. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2016, 28, 173–178.
- Miranda, R.R.S.; Silva, G.D.F.; Duarte, L.P.; Fortes1, I.C.P.; Filho, S.V. Structural determination of 3β-stearyloxy-urs-12-ene from Maytenus salicifolia by 1D and 2D NMR and quantitative 13C NMR spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2006, 44, 127–131.
- Chavez, H.; Estevez-Braum, A.; Ravelo, A.G.; Gonzalea, A.G. First examples of dammarane triterpenes isolated form Celastraceae. Tetrahedro 1997, 53, 6465–6472.
- Torpocco, V.; Chavez, H.; Estevez-Braum, A.; Ravelo, A.G.; Gonzalea, A.G. New damarane triterpenes from Maytenus macrocarpa. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 812–814.
- González, A.G.; Tincusi, B.M.; Bazzocchi, I.L.; Tokuda, H.; Nishino, H.; Konoshima, T.; Jiménez, I.A.; Ravelo, A.G. Anti-tumor promoting effects of sesquiterpenes from Maytenus cuzcoina (Celastraceae). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2000, 8, 1773–1778.
- González, A.C.; Jiménez, I.A.; Ravelo, A.G.; Luis, J.G.; Bazzocchi, I.L. β-Agarofurane sesquiterpene esters from Maytenus canariensis. Phtochemistry 1989, 28, 173–175.
- Chavez, H.; Callo, N.; Estevez-Braun, A.; Ravelo, A.G.; Gonzalez, A.G. Sesquiterpene polyol esters from the leaves of Maytenus macrocarpa. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1576–1577.
- Kennedy, M.L.; Corts-Selva, F.; Prez-Victoria, J.M.; Jimnez, I.A.; Gonzlez, A.G.; Muoz, O.M.; Gamarro, F.; Castanys, S.; Ravelo, A.G. Chemosensitization of a multidrug-resistant leishmania tropica line by new sesquiterpenes from Maytenus magellanica and Maytenus chubutensis. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 4668–4676.
- Nunez, M.J.; Cortes-Selva, F.; Bazzocchi, I.L.; Jimenez, I.A.; Gonzalez, A.G.; Ravelo, A.G.; Gavin, J.A. Absolute configuration and complete assignment of 13C NMR data for new sesquiterpenes from Maytenus chiapensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 572–574.
- Perestelo, N.R.; Sánchez-Cañete, M.P.; Gamarro, F.; Jiménez, I.A.; Castanys, S.; Bazzocchi, I.L. Overcoming human P-glycoprotein-dependent multidrug resistance with novel dihydro-β-agarofuran sesquiterpenes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 4915–4923.
- Gutiérrez-Nicolás, F.; Oberti, J.C.; Ravelo, Á.G.; Estévez-Braun, A. β-Agarofurans and Sesquiterpene Pyridine Alkaloids from Maytenus spinosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1853–1863.
- Núñez, M.J.; Jiménez, I.A.; Mendoza, C.R.; Chavez-Sifontes, M.; Martinez, M.L.; Ichiishi, E.; Tokuda, R.; Tokuda, H.; Bazzocchi, I.L. Dihydro-β-agarofuran sesquiterpenes from celastraceae species as anti-tumour-promoting agents: Structure-activity relationship(Article). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 111, 95–102.
- Alarcon, J.; Becerra, J.; Silva, M.; Morgenstern, T.; Jakupovic, J. β–Agarofuran from seeds of Maytenus boaria. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 1457–1460.
- Wibowo, M.; Levrier, C.; Sadowski, M.C.; Nelson, C.C.; Wang, Q.; Holst, J.; Healy, P.C.; Hofmann, A.; Davis, R.A. Bioactive dihydro-β-agarofuran sesquiterpenoids from the Australian rainforest plant Maytenus bilocularis. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1445–1453.
- Wibowo, M.; Wang, Q.; Holst, J.; White, J.M.; Hofmann, A.; Davis, R.A. Dihydro-β-agarofurans from the roots of the Australian endemic rainforest tree Maytenus bilocularis act as leucine transport inhibitors. Phytochemistry 2018, 148, 71–77.
- Paz, C.; Von Dossow, D.; Tiznado, V.; Suarez, S.; Cukiernik, F.D.; Baggio, R. A dihydro-β-agarofuran sesquiterpene from Maytenus boaria. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C 2017, 73, 451–457.
- Paz, C.; Heydenreich, M.; Schmidt, B.; Vadra, N.; Baggio, R. Three new dihydro-β-agarofuran sesquiterpenes from the seeds of Maytenus boaria. Ricardo Baggioe 2018, 74, 564–570.
- Alarcon, J.; Cespedes, C.L. Triterpenes and β-agarofurane sesquiterpenes from tissue culture of Maytenus boaria. Boletín Latinoam. Y Del Caribe De Plantas Med. Y Aromáticas 2016, 15, 206–214.
- Orabi, K.Y.; Al-Qasoumi, S.I.; El-Olemy, M.M.; Mossa, J.S.; Muhammad, I. Dihydroagarofuran alkaloid and triterpenes from Maytenus heterophylla and Maytenus arbutifolia. Phytochemistry 2001, 58, 475–480.
- Munoz, O.; Galeffi, C.; Federici, E.; Garbarino, J.A.; Piovano, M.; Nicoletti, M. Boarioside, a eudesmane glucoside from Maytenus boaria. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 853–855.
- Yuan, L.; Ma, J.; Wang, T.; Li, G.H.; Shen, Y.M.; Zhao, P.J. Chemical constituents from endophytic Phomopsis sp. Lz42 of Maytenus hookeri. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2009, 30, 78–81.
- Schaneberg, B.T.; Green, D.K.; Sneden, A.T. Dihydroagarofuran sesquiterpene alkaloids from Maytenus putterlickoides. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 624–626.
- Monache, F.D.; Bettolo, G.M.; Bernays, E.A. Isolation of insect antifeedant alkaloids from Maytenus rigida (Celastraceae). Z. Fur Angew. Entomol. 1984, 97, 406–414.
- Kuo, Y.H.; Chen, C.H.; Kuo, L.M.Y.; King, M.L.; Wu, T.S.; Haruna, M.; Lee, K.H. Antitumor agents, 112. Emarginatine B, a novel potent cytotoxic sesquiterpene pyridine alkaloid from Maytenus emarginata. J. Nat. Prod. 1990, 53, 422–428.
- Kuo, Y.H.; Chen, C.H.; King, M.L.; Wu, T.S.; Lee, K.H. Sesquiterpene pyridine alkaloids from Maytenus emarginata: Emarginatine-C and -D and cytotoxic emarginatine-E and emarginatinine. Phytochemistry 1994, 35, 803–807.
- Itokawa, H.; Shirota, O.; Morita, H.; Takeya, K. Sesquiterpene alkaloids obtained from Maytenus ebenifolia. Heterocycles 1992, 34, 885–889.
- Corsino, J.; da Silva Bolzani, V.; Pereira, A.M.S.; Franca, S.C.; Furlan, M. Bioactive sesquiterpene pyridine alkaloids from Maytenus aquifolium. Phytochemistry 1998, 48, 137–140.
- Corsino, J.; Da Silva Bolzan, V.; Pereira, A.M.S.; Franca, S.C.; Furlan, M. Further sesquiterpene pyridine alkaloids from Maytenus aquifolium. Phytochemistry 1998, 49, 2181–2183.
- Santos, V.A.; Regasini, L.O.; Nogueira, C.R.; Passerini, G.D.; Martinez, I.; da Silva, B.V.; Graminha, M.A.S.; Cicarelli, R.M.B.; Furlan, M. Antiprotozoal sesquiterpene pyridine alkaloids from Maytenus ilicifolia. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 991–995.
- Piacente, S.; Tommasi, N.D.; Pizza, C. Laevisines A and B: Two new sesquiterpene-pyridine alkaloids from Maytenus laevis. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 161–163.
- Lhinhatrakool, T.; Prabpai, S.; Kongsaeree, P.; Sutthivaiyakit, S. Antiplasmodial Sesquiterpene Alkaloids from the Roots of Maytenus mekongensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1386–1391.
- Sekar, K.V.; Campagne, J.M.; Sneden, A.T. 5-benzoyl-5-deacetylwilforidine: A new sesquiterpene nicotinoyl alkaloid from Maytenus buchananii. Planta Med. 1996, 62, 368–370.
- Nunez, M.J.; Guadano, A.; Jimenez, I.A.; Ravelo, A.G.; Gonzalez-Coloma, A.; Bazzocchi, I.L. Insecticidal sesquiterpene pyridine alkaloids from Maytenus chiapensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 14–18.
- Callies, O.; Núnez, M.J.; Perestelo, N.R.; Reyes, C.P.; Torres-Romero, D.; Jiménez, I.A.; Bazzocchi, I.L. Distinct sesquiterpene pyridine alkaloids from in Salvadoran and Peruvian Celastraceae species. Phytochemistry 2017, 142, 21–29.
- Sneden, A.T.; Beemsterboer, G.L. Maytansine, a new antileukemic ansa macrolide from Maytenus buchananii. J. Nat. Prod. 1980, 43, 637–640.
- Larson, G.M.; Schaneberg, B.T.; Sneden, A.T. Two new maytansinoids from Maytenus buchananii. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 361–363.
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
