In solid tumors, vasculogenic mimicry (VM) is the formation of vascular structures by cancer cells, allowing to generate a channel-network able to transport blood and tumor cells. While angiogenesis is undertaken by endothelial cells, VM is assumed by cancer cells. Besides the participation of VM in tumor neovascularization, the clinical relevance of this process resides in its ability to favor metastasis and to drive resistance to antiangiogenic therapy. VM occurs in many tumor types, including breast cancer, where it has been associated with a more malignant phenotype, such as triple-negative and HER2-positive tumors. The latter may be explained by known drivers of VM, like hypoxia, TGFB, TWIST1, EPHA2, VEGF, matrix metalloproteinases, and other tumor microenvironment-derived factors, which altogether induce the transformation of tumor cells to a mesenchymal phenotype with a high expression rate of stemness markers.
- vasculogenic mimicry
- breast cancer
- tumor neovascularization
1. What Is Vascular Mimicry?
| Vasculogenic Mimicry | Angiogenesis | References |
|---|---|---|
| Formation of vascular channels from cancer stem cells (tumor cells). | Development of new blood vessels and capillaries from pre-existing ones. | [1,12] |
| Patterned networks of interconnected loops and cords formation | Formation by sprouting or intussusception | [1,7] |
| Formed by tumor cells and cancer stem cells | Formed by endothelial cells | [7] |
| Aberrant expression of VE-Cadherin | VE-Cadherin localization in cell membranes | [13] |
| PAS+, CD31−/low staining | PAS−/low, CD31+ staining | [7] |
| Factor VIII-related antigen negative or low | Factor VIII-related antigen highly positive | [7] |
| Unaffected by endostatin and other antiangiogenic factors | Inhibited by antiangiogenic factors | [14,15] |
| EPHA2, TIE1, LAMC2, overexpression | EPHA2, TIE1, LAMC2 generally negative. | [16] |
| Express stemness markers, e.g., CD133, ALDH1 | CD133 positivity mostly in endothelial precursor cells | [17,18,19,20] |
| More abundant in poorly differentiated tumors, such as HER2+ and TNBC | Present in embryogenesis, wound healing and tumor growth | [16,21] |
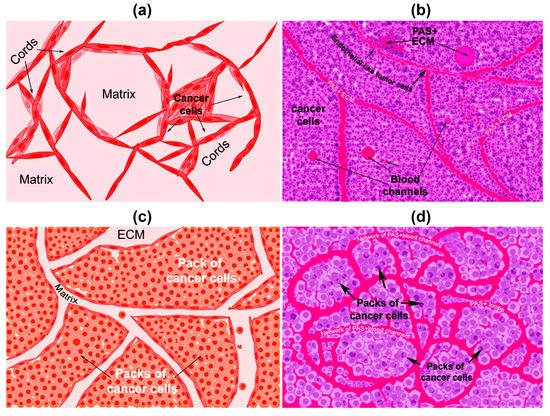
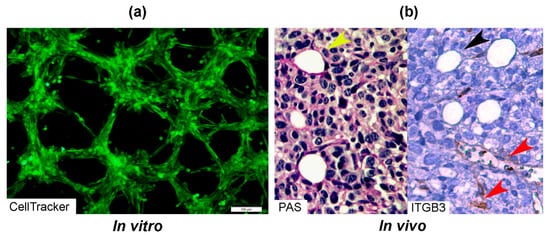
2. First Highlights of VM in Breast Cancer
3. Clinical Relevance of VM in Breast Cancer and Association with Clinicopathological Parameters
4. Relationship between VM and Tumor Phenotype
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/cells10071758
