Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Respiratory System
Asthma is a widespread chronic disease of the bronchopulmonary system with a heterogeneous course due to the complex etiopathogenesis. Natural-climatic and anthropogenic factors play an important role in the development and progression of this pathology.
- asthma
- temperature
- thermosensory transient receptor potential ion channels
- genes
1. Introduction
Asthma is a widespread, chronic heterogeneous disease with a complex etiopathogenesis and constantly improving approaches to therapy. Nowadays, over 350 million people of all ages worldwide suffer from asthma, and about 350 thousand people per year die from the disease. The growing prevalence of this pathology among people of different age groups is of particular concern. Uncontrolled asthma that is diagnosed in 45% of patients with a high frequency of exacerbations and hospitalizations remains an important global health problem [1]. In Europe, about 15% of school-age children suffer from asthma; 5% of them have difficult-to-control asthma. According to the Global Burden of Disease Study, asthma occupies the 14th ranking place among the leading causes of disability. The global burden of asthma is associated with direct economic costs and indirect social and economic consequences [2]. Obviously, achieving asthma control and reducing exacerbation frequency in patients with the pathology are among the most pressing problems of our time.
According to current research, bronchospasm and asthma-like symptoms in asthma patients can occur under the influence of trigger factors, such as the combination of cold temperatures and high/low air humidity, as well as hot temperatures and high air humidity [3,4,5]. The contribution of high and low temperatures in airway inflammation in asthma as well as the main molecular mechanism underlying the disease have not yet been fully understood [5,6]. The high sensitivity of the bronchi to environmental factors is caused by impaired regulation of afferent nerves of the respiratory tract and chronic neurogenic inflammation [7]. Vagal sensory nerves, of which 75% are non-myelinated nociceptive C-fibers of the lungs, innervate the respiratory tract. In addition, nociceptor neurons are involved in the activation of the bronchoconstrictor mechanism in airway inflammation. The sensitivity of lung nociceptors is mediated by thermosensory channels, members of a subfamily of the transient receptor potential (TRP) ion channels [8]. The channels are considered as main sensors of physicochemical environmental stimuli involved in the regulation of body temperature [5]. The channels are activated by temperature changes [9]. TRP channels are expressed by neuronal cells and cells of the respiratory tract (bronchial epithelium and endothelium, smooth muscle cells, unmyelinated nociceptive C-fibers of the lungs) [10,11,12,13]. TRP channel activation in the nerve endings of the respiratory tract leads to the stimulation of protective reflexes, but under certain conditions, it can be the pathogenetic basis of asthma [12,13,14,15]. The role of TRP channels in asthma pathogenesis has been demonstrated [13,16,17,18,19,20,21], which makes them promising targets for disease therapy [12,13].
Asthma is initiated not only by the influence of natural and climatic factors but also by the interaction between these factors and the genetic component of the body. However, not all asthma patients react to changes in the temperature and humidity of inhaled air, which may be related to genetic factors [22]. Recently, there has been considerable interest in the genetic contribution to asthma pathogenesis [23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32]. Of particular interest is the identification of SNPs of TRP genes and their interaction with physicochemical environmental factors.
2. The Role of Natural-Climatic Factors in Asthma Pathogenesis
In recent years, a number of studies have shown that high and low air temperatures impact on the development and exacerbation of asthma [6,33,34]. In addition, the temperature effect is modulated by other environmental conditions (humidity, visibility, cloud cover, air pressure, wind speed, air pollution, etc.). For example, simultaneous exposure to low temperature and poor air quality is an important factor for the appearance of asthma symptoms [35]. Cold moist air induces more respiratory symptoms in asthma patients than cold dry air. Therefore, people suffering from this pathology should avoid adverse environmental conditions and should limit their outdoor activities during periods of extreme temperatures, as well as during periods of high humidity combined with low/high temperature and low humidity combined with low temperature [33].
Under normal conditions, nasal breathing partially compensates for the cold air exposure, and low airway symptoms at rest or during light exercise do not occur. Intensive exercise in cold weather generates only a short-term acute bronchospasm and cough symptoms in healthy people [36]. Nevertheless, the cold air is an important trigger factor for severe asthma in patients with cold airway hyperresponsiveness. Asthma patients exhibit an increase in the frequency of cold-air-induced symptoms by 50% compared with healthy subjects. The risk of developing respiratory symptoms provoked by cold air (shortness of breath, wheezing, sputum discharge) is more elevated in patients with asthma coexisting with allergic rhinitis [4]. M. D’Amato et al. have revealed that breathing of +20 °C air at 15 L/min reduces the temperature of the trachea proximal sections to 34 °C, while breathing the same air at 100 L/min decreases this temperature to 31 °C [37]. In addition to bronchoconstriction, cold air hyperventilation also brings about coughing. Cough and bronchospasm are independent reactions since pretreatment with salbutamol blocks bronchoconstriction but does not affect cold-air-induced cough. Additionally, cold air is dry, and consequently, cold air hyperventilation causes airway dehydration, leading to the release of mediators initiating bronchospasm [5].
The effect of conditioned cold air is also injurious to asthma patients. In particular, quick cooling of the indoor air without gradual adaptation to a temperature 2–3 °C lower than the outdoor temperature—and especially with humidity ranging between 40% and 60%—may give rise to asthma exacerbation over several hours or days [37].
There are few data on the negative impact of high ambient temperature on the respiratory tract [5,38,39,40]. Additionally, increased metabolic rate (physical activity) and difficult heat dissipation (for example, in a warm environment) are common causes of hyperthermia [40]. Junior M.A.V.C. et al. have found that exercise-induced bronchospasm is diagnosed in most asthmatic patients living in a hot dry climate, while only 10% of patients with rhinitis and 5% of healthy people living under the same conditions developed exercise-induced bronchospasm [38]. Non-myelinated nociceptive C-fibers of the lungs have been demonstrated to be activated when the intrathoracic temperature was elevated to 39.2 °C. Hot air hyperventilation induces the development of bronchoconstriction in asthma patients, and pretreatment with ipratropium bromide aerosol completely prevented bronchospasm in these patients [40]. Furthermore, hot air breathing provokes cough in these patients, which indicates damage to the respiratory nerves. Thus, hyperventilation with hot humid air raises the temperature of the airways and triggers bronchoconstriction in asthma patients by activating pulmonary C-fibers [40].
The association between asthma hospitalizations and air temperature is of interest. It has been established that in the cold season, temperature is inversely correlated with asthma hospital admissions [33]. Patients with poorly controlled asthma are more likely to exhibit cold-weather-related respiratory symptoms [35]. It is worth noting that the number of hospital admissions among adults depends not only on low temperature but also on high temperature, while this relationship is not observed among children under five years of age. In the hot season, a minimum number of asthma hospitalizations is observed at an ambient temperature of 27 °C; this parameter reaches the maximum at 30 °C and achieves a plateau in the temperature range 30–32 °C. High temperature can have a protective effect for adults but is dangerous for non-adults [41]. The amount of evidence suggesting a nonlinear association between air temperature and the number of asthma hospitalizations among children has been growing [6]. A stronger relationship between ambient temperature and repeat admissions of asthmatic children under five years of age compared with first admission cases has been shown. Repeat admissions demonstrated high sensitivity to both hot temperature in summer and low temperature in winter [34].
Thus, the combination of cold temperatures and high/low air humidity as well as the combination of hot temperatures and high air humidity lead to bronchospastic reactions and asthma-like symptoms (coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath) in asthma patients, thereby increasing the exacerbation frequency and reducing the control of the disease. It is known that thermosensory TRP channels are responsible for the reception of physicochemical environmental stimuli and the regulation of body temperature [5,8,9,42,43,44]. The impairment of their functioning plays an important role in asthma pathogenesis [16,17,18,19,20,21,45], which makes these channels promising targets for disease treatment [12,46].
3. Transient Receptor Potential Ion Channels
TRP channels belong to the voltage-gated ion channel superfamily (voltage-gated K+/Na+/Ca2+ channels, cyclic nucleotide-gated channels) localized mainly on the plasma membrane of cells [47]. The main difference between the TRP channel superfamily and other ion channel families is their activation in response to exogenous stimuli, such as temperature, chemicals, light, and sound [48,49]. The TRP superfamily consists of 28 channels grouped into 7 subfamilies, in each of which several subunits are distinguished [50,51]. The eighth subfamily was recently identified in yeast and named TRPY (Table 1).
Table 1. TRP channel superfamily.
| TRP Channel Subfamily | Subfamily Subunits |
|---|---|
| canonical receptors | TRPC 1–7 |
| vanilloid receptors | TRPV1–6 |
| polycysteine receptors | TRPP1–3 |
| mucolipin receptors | TRPML1–3 |
| ankyrin-like receptors | TRPA1 |
| melastatin receptors | TRPM1–8 |
| Drosophila NOMPC in mammals | TRPN |
The molecular understanding of TRP channels has been improved by structural biology methods [51]. Monomers of TRP channels consist of a six-pass transmembrane protein (S1–S6) and a re-entrant loop between S5 and S6, forming the pore or ion conduction pathway (Figure 1). The C- and N-termini of the TRP channels are in the cytoplasm. Some of the TRP channels contain ankyrin repeat domains in the N-terminus and a TRP-domain in the C-terminus. The number of ankyrin repeats in the ankyrin domains of the TRP subfamilies differs. For example, TRPC channels contain 3–4 repeats, TRPV channels have 6, TRPA has 14–18 repeats, and TRPN has 29. It is believed that the role of the ankyrin domain is in protein–protein interactions: channel tetramerization and binding to ligands and partner proteins. The ankyrin domains TRPV1, TRPV3, and TRPV4 bind ATP, which competes for binding with calmodulin, a protein that inhibits sensitization of TRPV receptors. The coiled-coil domain is another common motif in the proteins of the TRP family. It can be located both at the C-terminus and at the N-terminus and is involved in cytosolic interactions and binding of polyphosphates.
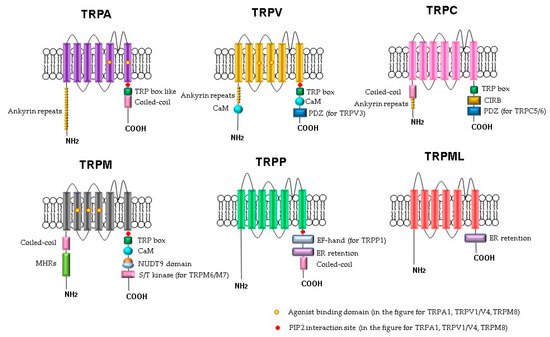
Figure 1. Schematic structure of TRP channels. Monomers of TRP channels consist of six transmembrane segments and a pore-forming return loop between S5 and S6. The intracellular N- and C-termini are distinguished in the length and domains. The TRP box is similar for TRPC, TRPV, TRPM, and a TRP box-like region for the TRPA1 channel. Coiled-coil domains (CC) are located in the C-terminus of TRPA and in the N-terminus of TRPC and TRPM. TRPM share melastatine high homology regions in their N-terminus, (MHRs). The TRPC subfamily of TRP channels has binding domains for calmodulin (CaM), inositol triphosphate receptor binding site (CIRB), and the PDZ-binding specific motif (PDZ). Substrates of NUDT9 are the adenosine 5′-diphosphoribose (ADPR) or the ADPR-2′-phosphate (ADPRP). NUDT9 domain is specific for TRPM2. TRPM6 and TRPM7 contain a serine/threonine kinase domain (S/T kinase). TRPP1 presents a calcium-binding motif (EF-hand), while TRPP and TRPML exhibit an endoplasmic reticulum retention (ER retention) domain. TRP channels are modulated by phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2).
The operating principle of these receptors is the activation of cation influx in response to stimuli [47]. These channels are involved in the processes of apoptosis and proliferation, and they affect vascular tone. TRP channels are expressed primarily by neuronal cells. At the same time, the channels were also found on other cells, particularly in the respiratory tract (bronchial epithelium and endothelium, smooth muscle cells, non-myelinated nociceptive C-fibers of the lungs) [11,16,18,19,20,43,50,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59] (Table 2).
Table 2. Tissue or cells expressing thermosensory TRP channels.
| TRP Channels | Tissue or Cells | References |
|---|---|---|
| TRPA1 | T cells B cells peptidergic and non-peptidergic neurons myelinated Aβ-fibers epithelial cells melanocytes mast cells fibroblasts enterochromaffin cells lung cells |
[11,43,48,49] |
| TRPV1 | epithelial cells melanocytes mast cells fibroblasts enterochromaffin cells lung cells airway-specific neurons C fibres Aδ-fibres central nervous system (neurons, glial cells, astrocytes) pulmonary arteries aorta gastrointestinal tract |
[52,53,54] |
| TRPV2 | neuronal and non-neuronal tissues pulmonary arteries aorta gastrointestinal tract |
[52] |
| TRPV3 | epithelial cells of skin oral cavity gastrointestinal tract tongue dorsal root ganglion trigeminal ganglion spinal cordbrain lung cells neuronspulmonary arteries aorta |
[52,55] |
| TRPV4 | gastrointestinal tract prostate smooth muscle cells vascular endothelium pulmonary arteries aorta epidermal keratinocyte cells fallopian tubes epithelial cells of the human cornea insulin secreting β cells of the pancreas urothelial cells in the renal pelvis ureters urethra urinary bladder enterocytes and enteroendocrine cells fibroblasts macrophages submucosal glands lung cells central nervous system (neurons, glial cells, astrocytes) peripheral nervous systems |
[16,47,52,56] |
| TRPM3 | lung cells pulmonary arteries aorta cancerous tissues dorsal root ganglia cardiomyocytes insulin secreting β cells of the pancreas |
[50,57] |
| TRPM8 | lung cells pulmonary arteries aorta afferent neurons in cold-sensitive afferents expressed in the upper and lower airways nasal trigeminal neurons retrogradely labelled jugular neurons cancerous tissues |
[19,20,44,50,58] |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/biomedicines9070816
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
