Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) is a rare disorder and one of the most severe forms of polycystic kidney disease, leading to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) in childhood. PKHD1 is the gene that is responsible for the vast majority of ARPKD. However, some cases have been related to a new gene that was recently identified (DZIP1L gene), as well as several ciliary genes that can mimic a ARPKD-like phenotypic spectrum. In addition, a number of molecular pathways involved in the ARPKD pathogenesis and progression were elucidated using cellular and animal models. However, the function of the ARPKD proteins and the molecular mechanism of the disease currently remain incompletely understood.
- ARPKD
- cyst
- rare monogenic disease
- nephrology
1. Introduction
2. Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease Clinical Presentation
3. Diagnosis
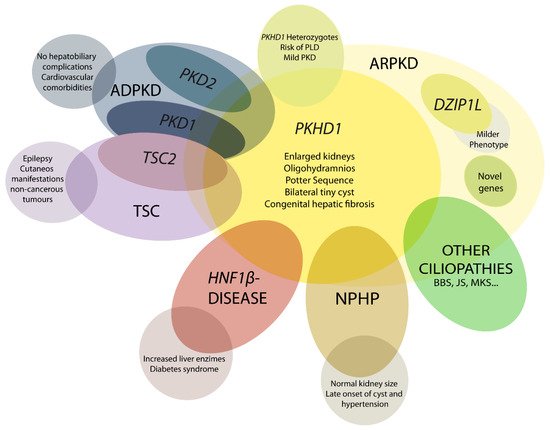
4. Differential Diagnosis
5. Genetics of ARPKD
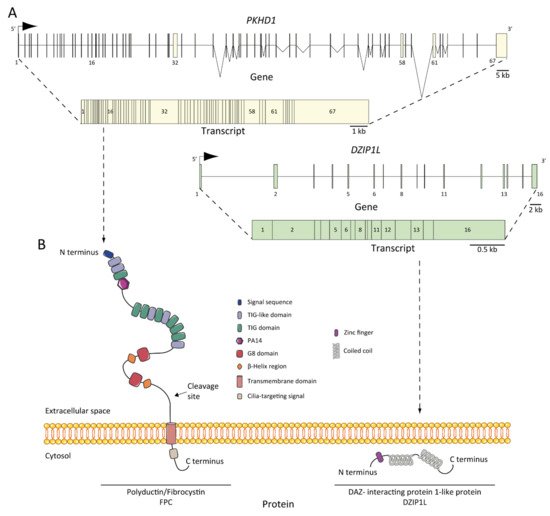
6. ARPKD Proteins: Structure and Function
7. Pathogenesis of ARPKD/Molecular Basis/Disease Mechanism
7.1. ARPKD Rodent Models: Lessons from Animal Models
7.2. Abnormalities of EGFR-Axis Expression and Fluid Secretion
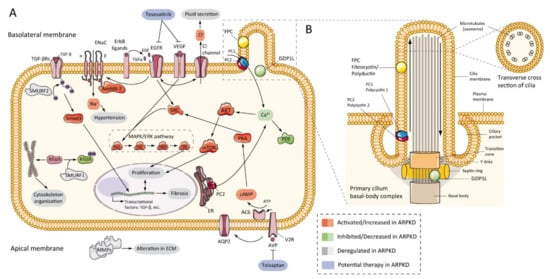
7.3. cAMP and Proliferation
7.4. Other Pathways Involved in ARPKD Physiopathology
7.5. Role of Cilia
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms22126523
