LncRNA can act as gene regulators, and like other epigenetic mechanisms are involved in numerous biological processes. They achieve their regulatory function with their ability to interact with a wide range of biological molecules, such as other nucleic acids and proteins. These lncRNA-protein interactions (LPI) are involved in many biological pathways including development and disease. A variety of computational LPI predictors exist, each applying different strategies to achieve their goals, and are dependent on a few biological databases containing subsets of experimentally validated LPI. Most modern lncRNA-protein interaction (LPI) prediction algorithms use machine learning approaches, where algorithms are trained on large datasets with attributes of interest.
- LPI
- lncRNA
- ncRNA
- protein
- transcriptomics
- molecular docking
- machine learning
- deep learning
- databases
This is a summarised version of our original article in: 10.3390/ncrna7020033
1. Introduction
Transcriptomics is the study of a complete set of RNA transcripts in a cell, measuring variable expression levels of the genome under different conditions. Modern transcriptomics is performed with high-throughput sequencing to investigate the function of genes and biological pathways, commonly with bioinformatics methods applying differential gene expression analyses, splice site identification, transcript variant identification or determining alternative promoter usage for protein-coding transcripts [1]. A large proportion of the genome generates RNA transcripts which do not directly code for protein products [2]. In this review, we specifically consider the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) category of ncRNA and their interaction with proteins, an important functional mechanism of lncRNA.
LncRNA can act as gene regulators, and like other epigenetic mechanisms are involved in numerous biological processes. They achieve their regulatory function with their ability to interact with a wide range of biological molecules, such as other nucleic acids and proteins [5], as well as with small molecules [4]. Among their more direct modes of action are sequestering and releasing transcripts to modulate gene expression, stabilising transcripts and binding to DNA to sterically hinder transcription initiation [6]. More indirectly, they can recruit proteins and other molecules to form a functional complex, or act as a scaffold for targeted chromatin formation [7] (Figure 1).
Figure 1: The importance and cycle of identifying long non-coding RNA-protein interactions.
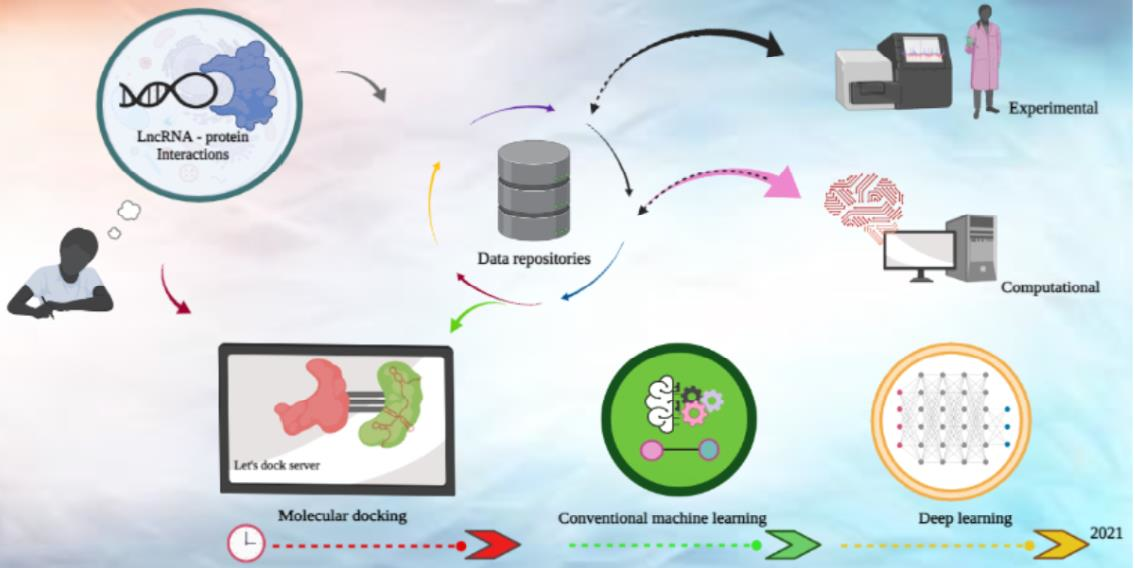
We illustrate the importance of LPI in developmental and abiotic stress pathways with several examples encompassing multiple distinct species. In the plant Arabidopsis thaliana, LPI control alternative splicing within the nucleus by selectively displacing existing transcripts and subsequently altering root development [10,11]. Response to abiotic stress is also governed by LPI, as shown by an lncRNA recruiting histone methylases to suppress Arabidopsis thaliana flowering during cold conditions [12]. Dario renio LPI are also observed to interface with transcription factors and other RNA-binding proteins during embryonic development, although their exact mechanism of action is not well known [13]. LPI also act as mediators of other epigenetic mechanisms, for instance as chromatin scaffolds to organise the three-dimensional structure of the genome in Mus musculus [14].
Due to the widespread involvement of LPI in epigenetics, dysregulation of certain LPI contributes to disease states, particularly cancers. Severity of a human pancreatic cancer phenotype is driven by an lncRNA-protein complex, which triggers a positive feedback loop of protein overexpression leading to poor patient outcomes [15]. Similarly, formation of an lncRNA-protein complex is associated with poorer prognosis in breast cancer [16], colon cancer [16] and lymphoma [17] by blocking phosphorylation sites, stabilising other epigenetic factors and through an unknown mechanism, respectively. Therefore, insight into LPI will be valuable in complex disease research, potentially resulting in improved diagnosis and treatment procedures.
Multiple high-throughput laboratory assays were developed to investigate LPI, some of which will be briefly discussed in this review article. Hence, computational methods are necessary to screen these high-throughput assays for potential LPI which can then be subsequently experimentally validated, similar to transcriptomics workflows for conventional protein-coding RNA A variety of these computational LPI predictors exist, each applying different strategies to achieve their goals, and are dependent on a few biological databases containing subsets of experimentally validated LPI. In this review, we will discuss recent bioinformatics resources for studying LPI, with an emphasis on software and databases, together with their advantages as well as limitations.
2. LncRNA-Protein Resource Databases
Starbase [39], POSTAR [40], RAIN [41], RNAInter [42], NPInter [43], ATtRACT [44] and oRNAment [45] are examples of databases that contain information associated with lncRNA-protein interactions obtained by the previously discussed laboratory assays, computational analysis and literature mining. Two broad classes exist: databases containing curated lncRNA-protein interactions and databases containing RNA-binding motifs (Table 1).
Table 1. A comparison of databases containing information on lncRNA-protein interactions. Important attributes of these databases are listed (all weblinks are accessed on 27 May 2021).
Starbase, RNAInter, POSTAR, NPInter and RAIN all contain details of curated lncRNA-protein interactions, and many additional attributes (including functional annotation) associated with the interactions, derived from a combination of the laboratory assays discussed in the previous section (Table 1). These are not limited exclusively to lncRNA, and contain various other pieces of interaction information, including interactions with other ncRNA, other nucleic acids and proteins [36,37,38]. Starbase, POSTAR and RAIN contain LPI information from a small number (two to four) of species, while RNAInter and NPInter host a wide range of species. To improve usability, Starbase, RNAInter and RAIN feature third party tool integration to streamline bioinformatics workflows.
ATtRACT and oRNAment databases contain details of RBP (RNA-binding protein) motifs. While not directly containing LPI, these can be applied to predict putative LPI and are a useful starting point or supplementary tool in screening for LPI.
We discovered that Starbase contains MALAT1–protein interactions supported by CLIP-seq evidence, whereas POSTAR2 provides RNA- and RBP-centric information. RNAInter provides information associated with interacting molecules, RNA editing, RNA structure, RNA localisation, RNA modification, evidence support (experimental evidence) and references, interaction networks (the top 100 interactions) and dynamic expression for the major lncRNAs. oRNAment consists of detailed information on transcripts and RBP along with numerous downloadable graphical representations of the noted lncRNAs with multiple visualisation options. However, none of these databases include any information on emerging lncRNAs such as Lassie and MaTAR25, further highlighting the reliance of the community on these databases.
All databases feature at least mouse and human datasets, likely due to their status as model organisms relevant to human disease, although some incorporate other model organisms as well. In summary, we discovered that there is a surprising lack of specialised LPI databases, with most databases featuring combinations of other nucleic acid and protein combinations. In a separate (unpublished) study we demonstrated that different isoforms of a lncRNA genes can have different interactomes, and hence functions.
3. LPI Prediction Algorithms
Computational strategies for LPI prediction can be divided into two high-level categories, molecular docking and machine learning. Lower-level subdivisions among the methods we surveyed include deep learning, tree-based methods, graph-based methods, similarity networks, image segmentation, matrix factorisation and variants of the Fourier transform. Within the past decade, a large number of prediction algorithms based on machine learning have emerged. Instead, they exploit known interactions between lncRNA and protein and/or biomolecular sequence information directly, although many also leverage known secondary structures to improve their performance (Table 1, Table 2).
Before the current ecosystem of machine learning algorithms was established, molecular docking was the dominant strategy used to predict and investigate LPI or RNA–protein interactions in general. Key factors considered include docking pose, distance and area of interracial sites, energy-based criteria and selection of the most structurally conserved docked complex [46]. Several methods also account for sequence homology or electrical charge between biological molecules [47]. However, at a high level these strategies are applied in different ways, and on different steric features.
Most of the molecular docking methods we reviewed use methods which incorporate at least two of the previously discussed low-level methodologies (Table 2). To provide some context for the building blocks of these more complex methods, we first present examples of methods that use an individual strategy together with a brief discussion of their advantages and disadvantages, which include 3dRPC [48], HexServer [49], FireDOCK [50], HADDOCK [51] While FireDOCK focuses on exploiting side chain information, HADDOCK leverages ambiguous interaction restraints, and is one of the few methods which has the advantage of being applicable to multi-body problems as well as other biomolecular interactions. Among molecular docking tools, PatchDOCK takes a more unconventional strategy by summarising low-level geometric features into higher-level features, and has some conceptual similarities to image segmentation.
| Sl:No | Resource | Resource Type | Advantages and Disadvantages | Weblink | Reference Paper |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | P3DOCK | LncRNA–protein docking server (adapted from conventional docking servers) | Free docking and template-based docking strategies in a hybrid approach, results in an accurate classification | http://www.rnabinding.com/P3DOCK/P3DOCK.html | [55] |
| 2 | HDOCK | LncRNA–protein docking server (adapted from conventional docking servers) | Integrates template-based modelling as well as ab initio free docking, with a scope that extends to both proteins and nucleic acids | http://hdock.phys.hust.edu.cn | [53] |
| 3 | PATCHDOCK | LncRNA–protein docking server (adapted from conventional docking servers) | Low-level geometric features into higher-level features, FireDOCK and PatchDOCK both complement each other, where PatchDOCK can feed output directly into FireDOCK. | https://bioinfo3d.cs.tau.ac.il/PatchDock/ / | [52] |
| 4 | FIREDOCK | LncRNA–protein docking server (adapted from conventional docking servers) | Focuses on exploiting side chain information, optimises the minimum free energy of the lncRNA-protein complex | http://bioinfo3d.cs.tau.ac.il/FireDock/ / | [50] |
| 5 | NPDOCK | Exclusively lncRNA-protein docking server, developed for nucleic acid docking only | Chains multiple methods into a pipeline of tools, which implement mostly FFT-based methods. | http://genesilico.pl/NPDock / | [56] |
| 6 | HADDOCK | LncRNA–protein docking server (adapted from conventional docking servers) | It averages ambiguous interaction restraints, and it can generalise to multi-body problems as well as other biomolecular interactions, optimises the minimum free energy of the lncRNA-protein complex | https://wenmr.science.uu.nl/haddock2.4/ | [51] |
| 7 | MPRDOCK | LncRNA–protein docking server (adapted from conventional docking servers) | Exploits protein flexibility by applying FFT and considering sequence homology of the target of interest to generate a repertoire of structures for “ensemble docking” | http://huanglab.phys.hust.edu.cn/mprdock/ | [54] |
| 8 | Hexserver | LncRNA–protein docking server (adapted from conventional docking servers) | FFT-based algorithm to exploit shape complementarity as a feature for optimisation | http://hexserver.loria.fr/ | [49] |
MPRDOCK exploits protein flexibility by applying FFT and considering sequence homology of the target of interest to generate a repertoire of structures for “ensemble docking”. P3DOCK’s authors claim that by complementing free docking and template-based docking strategies in a hybrid approach, a more accurate classification is possible. Finally, NPDOCK does not use a hybrid or ensemble strategy, but chains multiple methods into a pipeline of tools, which implement mostly FFT-based methods. The main advantage of using such ensemble methods is a generally improved performance over single-strategy methods as the limitations of each individual method are complemented.
With the exception of one or two methods such as HexServer, many of these algorithms are computationally expensive and time-consuming (hours to days of real time) to run. Some methods, such as HexServer, require advanced hardware such as GPUs and specialised software engineering tools. Biological molecules are complex and dynamic, with their wide range of possible conformations as well as orientations greatly increasing the search space for algorithms. The molecular docking community is mindful of this, and provides their software on publicly accessible and user-friendly web servers for users to run these programs remotely, although time remains a bottleneck for these workflows.
Their strategies can be divided into several broad categories, including graph methods, ensemble learning, matrix factorisation and deep learning. LPI are commonly formulated as similarity matrices, which can then be easily formulated as a matrix factorisation problem. Broader strategies incorporating matrix factorisation, such as ensemble learning and methods which leverage multimodal data, appear to have consistently robust performance [57]. Few deep learning models exist, but they both perform and generalise well in comparison to other methods, and are likely to become more popular as they have become in other areas of biology.
Matrix factorisation is the most common way to formulate LPI for prediction algorithms, including LPI-FKLKRR (lncRNA-protein interaction kernel ridge regression, based on fast kernel learning) [58], LPI-KTASLP (prediction of lncRNA-protein interaction by semi-supervised link learning with multivariate information) [59], LPI-NRLMF (lncRNA-protein interaction prediction by neighbourhood regularised logistic matrix factorisation) [60], LPI-INBRA (long non-coding RNA–protein interaction prediction based on improved bipartite network recommender algorithm) [61] and LPI-BNPRA (long non-coding RNA–protein interaction bipartite network projection recommended algorithm) [62]. These methods share a common theme of formulating lncRNA-protein interactions as a matrix factorisation problem and using them in broader strategies, such as multiple kernel learning or recommender algorithms. In the special case of LPI-FKLKRR, matrices are reformulated into kernels for direct optimisation with kernel ridge regression, increasing performance in the common scenario of class imbalance. LPI-INBRA is robust against false positives, and LPI-BNPRA is effective on closely related species other than humans.
Some graph-based methods for LPI prediction are PBLPI (path-based lncRNA-protein interaction) [PBLPI] and PLPIHS (predicting lncRNA-protein interactions using HeteSim scores) [64]. PBLPI takes into account both functional and semantic similarity between proteins, while PLPIHS uses a custom distance metric to unify co-expression, lncRNA-protein interactions and protein–protein interaction scores to construct a network which is then provided to a SVM classifier. In the case of PBLPI, a disadvantage is that prediction accuracy may be reduced due to technical limitations, while in PLPIHS performance is improved by preserving information regarding the biological network, taking into account lncRNA-protein interactions similar to the target.
Examples of hybrid and ensemble learning approaches are IRWNRLPI (integrating random walk and neighbourhood regularised logistic matrix factorisation for lncRNA-protein interaction prediction) IRWNRPLI uses lncRNA-protein interactions and lncRNA/protein sequence similarity as the input into a hybrid approach of random walk and neighbourhood regularised logistic matrix factorisation. An important distinction between these two methods is that GPLPI is trained on known plant lncRNA, and plant non-coding RNA have different properties (some ncRNA lose function even with 1–2 nucleotide changes) to those of animal non-coding RNA [70]. For this model to be effective on non-plant organisms, retraining is likely necessary but viable due to the relatively higher volume of data associated with animals, in particular humans [63].
DeepBind was one of the first applications of deep learning to predict nucleic acid–protein binding, and is applicable to LPI. By reformulating the classical position weight matrix [73] as a convolutional kernel, it operates on raw sequence data to provide a simple prediction score for a nucleic acid–protein interaction [74]. Meanwhile, DeepLPI feeds co-expression, sequence and structural data to a neural network optimised by a conditional random field. Using isoform data makes DeepLPI the only method to date with the ability to predict lncRNA interaction with different protein isoforms.
LPI-SKF uses an integrative approach where verified lncRNA-protein interactions are used to build a network, and similarity kernel fusion is used to integrate protein and lncRNA similarity scores before applying manifold learning. PMKDN uses multiple features from lncRNA (nucleotide composition, expression levels) and protein (amino acid subcategories) to build a similarity matrix for similarity network fusion with a nearest neighbour’s approach. Both these methods have the advantages of being robust against noise and capable of interaction discovery, but like most methods that express LPI as similarity matrices, they make a strong assumption that sequence homology correlates with interactivity, which may not hold in all cases. While this gives LPI-MiRNA the ability to operate on datasets without prior knowledge of lncRNA interactions, a different limitation is introduced of relying on known miRNA–lncRNA and miRNA–protein interactions.
Although lncPro [76] and catRAPID [77] are older methods, these are featured in this manuscript because of their historical significance. Although the authors noted limitations associated with data availability and computational complexity at the time, this method became a template for many other machine learning methods, including those discussed in this manuscript. catRAPID does not apply machine learning, but instead constructs an interaction matrix from known secondary structure and other molecular features. A major limitation of this approach is its reliance on obsolete genomic data, which is expected to reduce prediction accuracy.
Not all methods can predict interactions for novel lncRNA or proteins, and few methods generalise across species [62,69,71]. LPI prediction for different protein isoforms is also not an active area of prediction algorithm development, with only one method having this functionality. Another limitation observed is that some methods exploit sequence similarity as an intermediate metric for LPI prediction, particularly methods which formulate LPI as similarity matrices. At the same time, we consider that small nucleotide changes in biological molecules can cause major functional changes, which can potentially cause improperly trained prediction algorithms to produce misleading results [80].
4. Future Directions
Computational surveying is not a substitute for experimental validation. However, as the intention of computational modelling is to generate a subset of the most likely testable hypotheses for laboratory biologists, we believe that developments in both the laboratory and computational fields will complement each other. With computational modelling reducing the quantity of experiments required, and with the experimentally validated data generated as a result, more efficient algorithms can be developed which further reinforces the developmental cycle. As a result, biologists interested in LPI will gain access to more refined tools, allowing them to streamline their experiments.
Additional reference:
[PBLPI]
- Zhang H, Ming Z, Fan C, Zhao Q, Liu H. A path-based computational model for long non-coding RNA-protein interaction prediction. Genomics. 2020 Mar;112(2):1754-1760. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2019.09.018. Epub 2019 Oct 19. PMID: 31639442.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ncrna7020033
