Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs) are a reservoir for tissue homeostasis and repair that age during organismal aging. Beside the fundamental in vivo role of MSCs, they have also emerged in the last years as extremely promising therapeutic agents for a wide variety of clinical conditions. MSC use frequently requires in vitro expansion, thus exposing cells to replicative senescence. Aging of MSCs (both in vivo and in vitro) can affect not only their replicative potential, but also their properties, like immunomodulation and secretory profile, thus possibly compromising their therapeutic effect. It is therefore of critical importance to unveil the underlying mechanisms of MSC senescence and to define shared methods to assess MSC aging status.
1. Introduction
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs) or adult stem cells are tissue-specific pools of progenitor cells with long-term self-renewal ability and differentiation potential, with a fundamental role in tissue and organ homeostasis [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6]. These cells possess both differentiation plasticity (stemness) and tissue supportive functions (stromalness) that can coexist and overlap, with differences depending on tissue source, donor characteristics, culture conditions and delivery strategies, leading to alternative best fittings for the term “stem” or “stromal” [
7]. MSCs represent a lifelong reservoir for the generation of somatic cells and for cell replacement. They emerged in the last years as powerful tools in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering, mostly for their easy of isolation and expansion, for their immunomodulatory [
8,
9,
10,
11] and paracrine activities, exerted through the release of soluble factors [
12], exosomes and microvesicles [
13], thus modulating tissue microenvironment, counteracting inflammation and stimulating repair [
2,
8,
14].
During aging of the organism, MSCs also age, and this implies an impairment of stem cell functions contributing to the progressive decrease in tissue maintenance and repair, a characteristic of the aging process. Actually, stem cell exhaustion is considered one of the promoters of aging. One example is the delay in fracture healing with advanced age, attributed to a decreased number and function of MSCs [
15].
Due to the low abundance of MSCs in human adult tissues (about 1/10
6 cells in adult bone marrow and 1/10
3–4 cells in adipose tissue and umbilical cord) [
16], frequently ex-vivo expansion precedes therapeutic administration, to obtain a clinically relevant number of cells. However, in vitro expansion drives senescence and reduces DNA synthesis and repair efficiency, finally leading to DNA damage accumulation [
2,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24]. Persistent DNA damage can block transcription and replication and drives the aging process [
25].
The most relevant effect of in vitro expansion is progression to replicative senescence [
21,
22,
24] accompanied by morphological and functional alterations, and modification of the secretory phenotype. With aging, MSCs show reduced immunomodulation [
26,
27], proliferation, differentiation potential and homing ability [
28,
29,
30,
31]. They develop the so-called senescence-associated secretory phenotype, SASP [
21,
24,
32,
33], and modify their transcriptional profile [
34]. All these modifications can impair MSC functional properties and are critical for the efficacy and safety of MSC treatments, since they can cause not only therapeutic failure, but also unwanted effects, such as the exacerbation of the inflammatory response and the tumor-promoting activity mediated by the SASP, thus raising a safety issue [
2]. It appears therefore of critical importance to evaluate the impact of senescence on MSC biological properties and to monitor senescence of MSC preparations before application [
35].
2. MSC Senescence
MSC senescence represents a relevant driver of organismal aging and contributes to the pathogenesis of age-related diseases. Accordingly, senescent cells accumulate in aged tissues [
56]. Key regulators of MSC aging are still incompletely identified and can represent therapeutic targets to counteract age-associated diseases and organismal aging. MSC senescence can arise from different stimuli, including oxidative stress, irradiation, chemicals (inducing acute senescence) or replicative exhaustion (inducing chronic senescence) [
39].
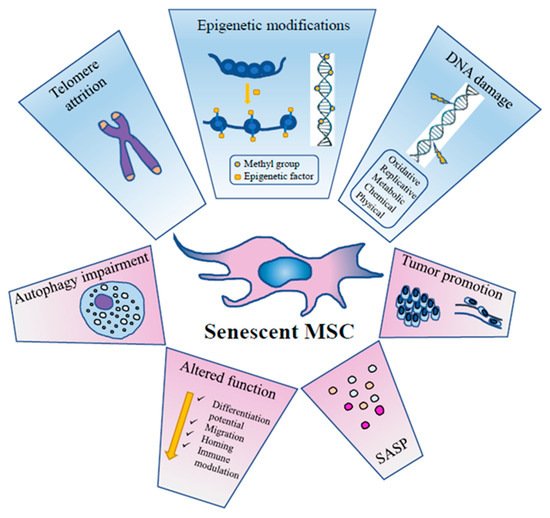
As for other cellular types, aging of MSCs is a dynamic process taking place through a series of steps that follow the initial growth decline [
31,
57]. It is accompanied by functional alterations due to metabolic, genetic, epigenetic, transcriptional and translational changes [
31,
58,
59,
60] ().
Figure 1. The principal events inducing MSC senescence and their effects on MSC activity, metabolism and function.
Senescent MSCs loose metabolic flexibility, they show an impairment of the autophagic flux with reduced active vacuoles, and an impairment of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, the main proteolytic cellular system to degrade damaged proteins [
39].
MSC senescence involves multiple signaling pathways such as p53/p21, retinoblastoma (p16/RB), protein kinase B (Akt)/mTOR, mitogen activated protein (p38MAP) kinase and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), finally causing a permanent cell cycle arrest and irreversible damage [
57,
61,
62,
63].
Redox control has a central role in MSC senescence development. At a steady state, MSCs prevalently perform glycolysis and have low ROS levels [
64]. However, with progressive replications, a marked production of ROS occurs, inducing damage to cellular macromolecules, with the involvement of several cellular pathways including p53, forkhead box transcription factors of the class O (FOXO1), nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor (2Nrf2), micro RNAs (miRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) (for a comprehensive review, see [
65]). Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) is upregulated in senescent human umbilical cord MSCs (UC-MSCs) and can drive senescence through the Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) pathway, a key regulator factor in senescent cells. Interestingly, the process is driven by a toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3)-dependent SASP autocrine loop where interferon β (IFN-β) upregulates in turn TLR3 [
66]. The conserved small nuclear non-coding RNA Rn7SK is overexpressed in senescent adipose-derived MSCs (ASCs) and, conversely, its transient knockdown leads to delayed senescence [
67].
2.1. DNA Damage
DNA damage is one of the key drivers of aging and there is strong evidence that age-related accumulation of DNA damage in MSCs is partly responsible for age-related cellular dysfunctions [
23]. Signals generated downstream DNA damage are mostly addressed to counteract transformation but can also promote tissue dysfunction. A variety of mechanisms can contribute to DNA damage accumulation in MSC aging: telomere shortening, replicative stress and reduced DNA repair system efficiency [
18,
68]. Accumulation of DNA damage can lead to genomic instability and ultimately affect differentiation ability, self-renewal ability or induce cell transformation [
2]. DNA lesions trigger ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) and ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related protein (ATR) pathways and checkpoint activation, inducing in turn cell cycle arrest (to allow for damage repair) or, conversely, senescence and apoptosis (to avoid replication of damaged cells in case of too high levels of DNA damage). While the ATM pathway is mostly involved in double strand break (DSB) repair [
69], the ATR one is prevalently involved in single strand break (SSB) and replicative stress-derived damage repair [
70]. Murine bone marrow MSCs (BM-MSCs) in long-term expansion progressively lose their ability to recognize DSBs (as detected by phosphorylated histone H2AX-γH2AX- and 53BP1 foci); they show a slower repair kinetics and a consequent increased number of residual DSBs, due to an impaired ATM-mediated DNA damage response [
68].
2.2. Chromatin Remodelling
One of the characteristics of aged MSCs is a general chromatin reorganization. MSCs have a peculiar chromatin architecture correlated with their uncommitment, multipotency and self-renewal. Heterochromatin domains (chromatin regions structurally inaccessible and usually transcriptionally inactive) are critical for gene expression regulation, DNA repair and maintenance of genomic stability. They are progressively lost during aging, whereas heterochromatin reestablishment promotes longevity [
71,
72]. Interestingly, DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8 (DGCR8, a critical component of the canonical microprocessor complex for miRNA biogenesis, downregulated in naturally and pathologically aged MSCs) was found to play a role in heterochromatin organization maintenance and aging attenuation, thus emerging as a possible therapeutic target for age-related disorders. This DGCR8 activity is miRNA processing-independent and it is played through interaction with nuclear Lamin B1 and other heterochromatin-associated proteins [
73]. A role in heterochromatin reorganization in relationship to MSC aging was also described for lysine-K- specific demethylase 3A (KDM3A) and lysine-K- specific demethylase 4C (KDM4C) enzymes, two H3K9 demethylases. They activate condensing components during MSC senescence and inversely correlated with aging. Their suppression induces a strong DNA damage response and aggravates cellular senescence, whereas their upregulation blocks DNA damage response, thus highlighting a protective role of these enzymes as a surveillance mechanism to limit DNA damage accumulation [
43]. As multifunctional modulator of gene expression with the ability to regulate chromatin architecture, methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MECP2) has a key role in stem cell function and aging. In a mouse model of Rett Syndrome, impaired MECP2 expression is associated to increased senescence and accumulation of DNA damage, through RB2/P130-p16 pathway activation and without impairment of the autophagic process [
60].
Deregulation of the chromatin remodeling complex switch/sucrose non-fermentable (SWI/SNF) through Brahma-related gene 1 (BRG1, an ATPase subunit of the complex) can trigger MSC senescence by suppressing homeobox transcription factor (NANOG) transcription and by modulating the expression of proteins involved in nuclear architecture, suggesting a role of BRG1 as a global regulator of gene expression [
74].
2.3. Epigenetics
Epigenetics (heritable changes in gene expression without DNA sequence alterations) include DNA methylation, histone modifications, chromatin remodelling, all influencing chromatin architecture and in turn gene expression. Epigenetics has a fundamental role in stem cell biology (reviewed by [
75]), including stem cell senescence. Recent evidences highlighted that epigenetic regulation is involved in MSC senescence [
2,
75,
76,
77]. A comprehensive evaluation of the dynamic of epigenetic changes and its effects on stemness and senescence is still missing [
75]. Lu et al. [
78] showed that octamer-binding transcription factor 4 (OCT4) maintains the self-renewal ability of human hair follicle MSCs and reverses senescence by suppressing the expression of p21 through the upregulation of DNMTs (DNA methyltransferases) leading to an overmethylation of p21 promoter and thus inhibiting its transcription and activity. Epigenetic dysregulation of histone H3 acetylation in K9 and K14 in the promoter regions of stemness genes OCT4 and sex determining region Y-box 2 (SOX2) plays a key role in MSC aging [
77]. Moreover, inhibition of histone deacetylase (HDAC) function promotes apoptosis and senescence in human MSCs [
75]. General DNA methylation levels appear to decrease with MSC aging and this is associated to DNMT downregulation [
75]. DNMT1 and 3b inhibition with specific siRNA (short interfering RNA) or 5-azacytidine, induced senescence in UC-MSCs and p16 and p21 upregulation. Interestingly, DNMT inhibition changed histone marks in active form and induced CpG island demethylation in p16 and p21 promoter regions. It also downregulated polycomb proteins and upregulated miRNAs targeting polycomb proteins expression levels [
79,
80]. All these data point to a critical role of DNMTs and HDACs in regulating MSC senescence. Through molecular profiling, the role of epigenetic factors (including miRNAs) in cellular senescence has been studied [
45,
47,
81,
82]. One of the most interesting recent findings is the association of aging to very reproducible DNA methylation patterns. A specific CpG methylation pattern can therefore represent a biomarker to estimate chronological age, thus functioning as an “epigenetic clock” [
83]. In a similar way, regulated and reproducible DNA methylation changes occur during in vitro replicative senescence and can be used to monitor senescence of cell preparations [
81,
82,
84]. Another epigenetic modification of DNA bases is represented by 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), recently proposed as additional epigenetic age-related biomarker, associated to 5 methylcytosine (5mC) loss [
85].
2.4. Autophagy
Recent studies indicated that autophagy is required to maintain stemness and differentiation capacity of stem cells and that autophagy is impaired in stem cell aging (reviewed by [
55]). This deficiency can be restored by rapamycin and spermidine treatment [
86,
87]. Correct functioning of autophagy has also the potential to preserve the anti-inflammatory properties of MSCs, that are mainly exerted through their secretome [
88], particularly through the released exosomes and microvesicles [
89]. Conversely, evidence is accumulating that vesicles released from MSCs have the ability to rescue autophagy in the target cells [
90].
It was demonstrated that autophagy plays a role in the maintenance of BM-MSCs during aging: autophagy declines in BM-MSCs and bone cells with age; its activation could alleviate aging of BM-MSCs and restore aged BM-MSC osteogenic differentiation and proliferation. Autophagy activation also partially restores bone loss in mice, via regulating ROS levels and p53 expression. Conversely, autophagy inhibition could cause senescence of young BM-MSCs [
91]. Young quiescent MSCs display a constitutive autophagy activity decreasing with aging. The impairment occurring in old cells is related to their lack in autophagosome formation capacity. Moreover, genetic impairment of autophagy in young MSCs promotes the entry into premature senescence [
86].
Available data on the relationship between autophagy and senescence are partly contradictory: actually, autophagy may promote or counteract senescence depending on the cellular context and on the kind of stress [
39]. Autophagy can protect BM-MSCs from oxidative stress [
92] and, conversely, it has been proven to be a requirement for maintenance of replicative senescence of MSCs [
93]. A possible interpretation of these contradictory results is that MSCs try to lead with stress by inducing autophagy to remove damaged components thus counteracting aging; however, in case of impaired autophagic flux and therefore of persistent cell damage, autophagy could worsen senescence.
2.5. SASP
Cell senescence is a dynamic process that can be influenced by cell to cell communication and signals from the microenvironment, including paracrine/autocrine soluble factors, gap junctions, extracellular vesicles (EVs). EVs include exosomes and microvesicles (MVs) transporting lipids, proteins, miRNAs, delivering signals to other cells via endocytosis and membrane fusion. They are fundamental mediators of MSC activity. Recently, MSC-derived EVs gained much attention for MSC-based therapies as responsible for MSC activity and as possible cell-free alternative to MSC cellular treatments [
94]. EV content is not static, but highly influenced by the niche/microenvironment the MSCs are imbedded in [
13]. In fact, EVs from BM-MSCs of differently aged donors show significant age-dependent differences in their content and consequently immune profile [
95]. MVs from young or old MSCs contain youth or senescence signals, respectively. In a murine model, old hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) showed restored functionality and rejuvenation after intercellular transfer of MVs from young MSCs, containing higher levels of autophagy-related mRNAs and sirtuins [
96].
In an attempt to define common and specific SASP components, Ozcan et al. [
32] exposed human ASCs and BM-MSCs to different genotoxic stresses (oxidative, chemical, physical and replicative) and analyzed the resulting cell secretome. By mass spectrometry followed by gene ontology analysis they were able to distinguish four SASP classes (extracellular matrix; cytoskeleton; cell junctions, metabolic processes, ox-redox factors; regulators of gene expression) common among the different stressor conditions. They also found 11 proteins exclusively expressed in all conditions possibly representing a senescence signature [
32].
3. Detection of Senescent MSCs
Different molecules and biological processes have been proposed for senescence state determination and monitoring: proliferation arrest, telomere attrition, DNA damage, epigenetic, transcriptional and metabolic changes. Features to identify senescent cells: flattened and enlarged morphology; cell cycle arrest; increased SA-β-gal activity; senescence-associated heterochromatin foci (SAHF, specialized heterochromatin domains contributing to silencing of proliferation-promoting genes); altered gene expression (p53, p21, p16 increased expression); shortened or dysfunctional telomeres; SASP and DNA-scars (DNA segments with chromatin alterations reinforcing senescence) [
39].
However, specific and univocal markers are still missing and, to be reliable, the evaluation of cell senescence should rely on the in vitro assessment of several markers. Since senescence can affect cell functions, it appears essential to evaluate the percentage of senescent cells in each MSC preparation to be delivered to patients. The identification of reliable senescence markers is therefore a critical, pivotal issue for quality assessment and for in vitro monitoring of MSC preparations before clinical application. Several papers focused on this topic, as reviewed in [
184]. Here we only present a summary () including the most frequently used analyses to assess senescence. For each technique the relevant use, i.e., which senescence feature it addresses, as well as specific advantages and disadvantages, are indicated.
Table 1. Markers of MSC senescence and techniques most frequently used for their detection.
| Senescence Marker |
|
Techniques for Detection |
Senescent Features, Pros and Cons |
| Cell morphology |
 |
 |
Microscopy [185]
Flow cytometry [186]
(FSC for size, SSC for granularity) |
Senescent MSCs show enlarged and granular cell morphology.
Microscopic assessment is easy but only qualitative.
Flow cytometric assessment is quantitative |
| CFU |
 |
Colony formation
in agar culture [187] |
The CFU number is a measure of cell clonogeneity and decreases with MSC age. CFU assessment requires careful plating at low density. |
| Sa-β-gal |
 |
Microscopy (colorimetric activity assay with X-gal) [188]
Flow cytometry (fluorimetric activity assay with C12FDG) [189]
IHC, IF or WB with specific Abs (protein expression) [190] |
Senescent cells at low density express a lysosomal β-galactosidase active at pH 6.0, detectable either with activity assays or with a specific antibody.
The activity assays can give altered results on high density cultures [191] |
| 8-oxo-dG |
 |
IHC, IF, ELISA [192],
HPLC [192]-MS/MS |
8-oxodG is a DNA base derivative, robust marker of oxidative DNA and RNA damage |
| γH2AX |
 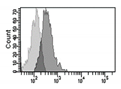 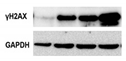 |
IF
Flow cytometry [193]
WB |
Histone H2AX phosphorylation is an indirect measure of DNA double strand breaks due to physical, chemical, oxidative stress.
It indicates that cells organize a DNA damage response, but its persistence sustains senescence of the cells. |
| Telomeres |
 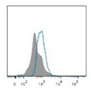 |
Southern blotting [170]
Flow FISH [194]
Real-time PCR [194]
STELA [195] |
Telomere attrition is directly correlated to replicative senescence, but it also occurs after exposure to oxidative damage. The subpopulation heterogeneity must be taken into account and may be addressed with emerging techniques such as STELA, detecting individual telomere length. |
| MSI |
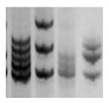 |
PCR followed by gel
or capillary
electrophoresis [196] |
Repeated sequences variations are an indirect indication of genomic instability and deficient DNA repair due to replicative or oxidative stress. They increase with cell aging. |
Gene expression
of senescent
markers at
mRNA level |
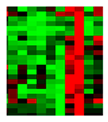 |
Real-time RT-PCR [33]
Microarray
RNAseq |
Expression of genes related to senescence. Several pathways can be analyzed, but gene expression analysis prevalently focuses on p53 and cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors (p16 and p21) |
Expression
of senescent
markers at
protein level |
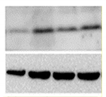  |
WB [197]
IHC
IF
Flow cytometry |
Evaluation of the expression levels of proteins related to senescence (p16, p21, p53, etc.) |
| Global methylation |
 |
NGS after bisulfite treatment [198] |
Genome wide analysis of methylated cytosines. |
Beside the known markers indicated in , a series of new senescence markers has been proposed. The TRAIL (TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand) receptor CD264 was proposed as a marker of BM-MSC cellular age (but not of donor chronological age) since it negatively correlates with proliferation and differentiation potential and parallels p21 expression profile [
199].
The angiotensin converting enzyme CD143 was found to be expressed only in adult MSCs [
200]. Biran et al. [
185] proposed a method to detect senescent cells in tissues by combining flow cytometry and image analysis in order to simultaneously acquire information about beta-galactosidase activity and cellular identity.
Endogenous autofluorescence measured by label-free flow cytometric analysis positively correlates with traditional senescence markers and was proposed as fast and non-invasive tool for real-time quantification of in vitro MSC senescence [
201].
F-actin turnover, studied by real-time labelling with a fluorogenic probe, was demonstrated to be age-dependent and to decrease in in vitro aged-MSCs [
202].
Exploiting high-throughput screening, Ang et al. [
203] identified a senescence-specific fluorescent probe (CyBC9) that accumulates in cell mitochondria, thus allowing for rapid, non-toxic and early detection of senescent MSCs as useful tool to screen clinically intended cell preparations.
For clinical use, potency assays are useful to monitor cell properties predictive of therapeutic efficacy, including evaluation of the effects of aging. An in vitro model of low-density MSC growth was for example recently used to evaluate the effect of age on a series of MSC biophysical properties used as predictors of bioactivity. The findings of the study indicated that MSC age is a predictor of adipogenesis, while cell and nuclear shape are strongly associated to hematopoietic-supportive potency [
204].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/biom10020340