Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Biology
Circadian rhythms, the changes or processes that follow a 24-h light–dark cycle, while endogenously programmed, are also influenced by environmental factors, especially in sessile organisms such as plants, which can impact ecosystems and crop productivity.
- circadian rhythmicity
- climate change
- crop development
- legumes
- plant molecular biology
1. Introduction
Circadian rhythms are broadly defined as endogenous biological processes that occur within an oscillation of approximately 24 h. Also referred to as biological clocks, circadian rhythms are subject to both environmental entrainment and temperature compensation [1]. This phenomenon enables organisms to anticipate periodic changes in the environment and subsequently adjust or synchronize their developmental and physiological responses to the best time of the day and make efficient use of available resources [2]. Efficient resource management is especially important for sessile organisms, such as plants, which cannot evade unfavorable conditions [2]. In general, the circadian rhythms in plants, which are often regulated by multiple feedback loops, have a higher complexity than those in animals, which are governed mostly by a centralized pacemaker [1,3]. Plants have multiple tissue- and organ-specific clocks that allow fine-tuning of physiological adaptations to changing environmental conditions. Plant circadian rhythms are key to plant survival in diverse environmental conditions [4] and hence, have become a major focus in plant research. Understanding plant circadian rhythm and its manipulation may revolutionize modern food crop production and enhance food security [3,5].
The current state of knowledge of biological clocks in plants stems primarily from the research on the model plant species Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) through a combination of omics approaches [1]. Figure 1 shows a simplified circadian gene regulation network of Arabidopsis, illustrating various physiological processes that are influenced by circadian rhythmicity. The core loop, which is interconnected with the morning and evening loops, consists of the main Myb-related transcription factors; CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED 1 (CCA1) and LATE ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL (LHY), and the transcriptional repressor TIMING OF CAB EXPRESSION 1 (TOC1) that reciprocally regulate the morning and evening loops. For example, the CCA1 and LHY in the morning loop activate the pseudo-response regulators (PRRs), including PRR5, PRR7, and PRR9, which in turn inhibit the expression of CCA1 and LHY genes. On the other hand, the evening complex (EC) in the evening loop, which is a protein complex consisting of EARLY FLOWERING 3 (ELF3), EARLY FLOWERING 4 (ELF4), and LUX ARRHYTHMO (LUX) proteins, inhibits the expression of PRR7 and PRR9 (Figure 1). It is important to note that the EC components are themselves rhythmic, commonly through repression by the products of the CCA1 and LHY [6].
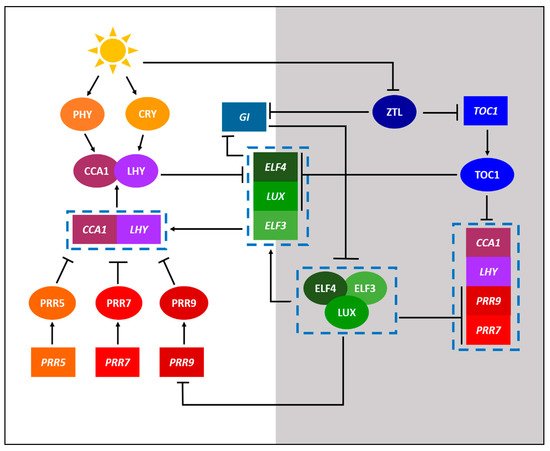
Figure 1. A simplified model displaying the core components of the circadian gene regulation network of model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Components with a white and grey background depict day and night processes, respectively. The circadian regulation of A. thaliana consists of a complex interconnected series of feedback loops. Activation is indicated by lines with arrowheads while repression is indicated by lines with perpendicular heads. Proteins are indicated by ellipses while genes are indicated by rectangles. Genes and proteins acting concurrently or as a complex are indicated within the dashed boxes.
With the declaration of 2016 as the International Year of Pulses, the importance of pulse utilization and development in supporting sustainable food systems has been widely recognized [7]. Pulses, the edible seeds of legumes, are generally considered a good and affordable source of protein and fibers [8,9]. Moreover, legumes are prominent nitrogen fixers that can help improve soil quality and fertility [10]. In recent years, some underutilized legumes, such as winged bean (Psophocarpus tetragonolobus) and lablab (Lablab purpureus), have been promoted as climate-resilient crops, playing a critical role in achieving a suite of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) that focus on tackling global food insecurity and climate change [8]. The targeted goals include, among others, Zero Hunger (Goal 2), Good Health and Well-being (Goal 3), and Climate Action (Goal 13). Although there is an increasing interest in legume biology, numerous knowledge gaps have yet to be filled for these crops, including the molecular basis and physiological importance of their circadian rhythms [7].
2. Defining the Important Components of Clock Research
The circadian system is a highly intricate network, with extensive crosstalk among output pathways that can be influenced by external conditions. External (or environmental) signals, such as light and temperature, are integrated by the central oscillator that coordinates various physiological processes [3,11]. A proper regular clock function is essential for the coordination of multiple physiological pathways, which include flowering time, growth and metabolism, hormone signaling, and responses to biotic and abiotic stresses (Figure 2). The orchestration of these complex interconnections yields a robust network that is paramount to the coordination of plant physiology in natural environments [5,12]. In Arabidopsis, the circadian clock system consists of a central oscillator that generates the endogenous circadian rhythms with input and output pathways that integrate environmental cues to the oscillator function and control various physiological processes, respectively. While light is considered the main signal that alters the plant circadian clock [13], many studies have revealed that the feedback regulation of the Arabidopsis clock is also affected by a wide spectrum of stress signals [1,14,15].
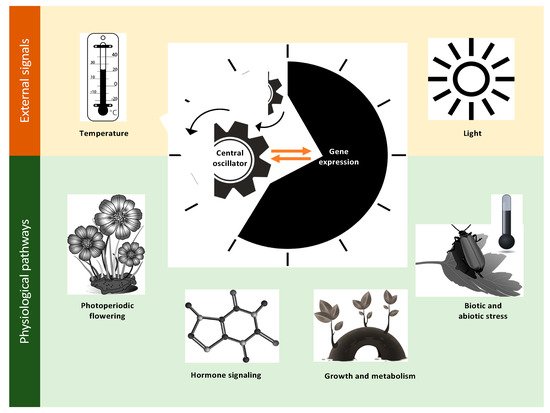
Figure 2. Light and temperature as examples of environmental signals integrated by the central oscillator of a plant to coordinate major physiological processes, including photoperiodic flowering, growth and metabolism, hormone signaling, and responses to biotic and abiotic stress in the natural environment.
2.1. Photoperiodic Flowering
Flowering time, the period at which a plant produces the first floral bud, is a key factor associated with adaptation and yield responses of a particular species to various environments, locations, and agricultural practices [16]. Although morphological and flowering time variations have been documented in many crop legumes, most molecular studies of flowering time control have focused on the short-day (SD) legume soybean and the long-day (LD) legume common pea [17]. These studies, along with genetic analyses, such as reverse genetics in the model legumes barrel medic (Medicago truncatula) and birds-foot trefoil (Lotus japonicus), have laid a foundation for the exploration and characterization of flowering genes in a range of other legumes [18,19,20]. Within the papilionoid legumes, the galegoid and phaseoloid are two main sister clades that host major cool-season (such as common pea and chickpea) and warm-season (soybean and common bean) crop legumes, respectively [21]. In most cases, species within the galegoid clade are LD plants from temperate regions while those in the phaseoloid clade are SD plants from lower latitudes. The galegoid legumes were reported to have only a single ortholog for CCA1 and LHY [22,23], while other clock genes, including the TOC1, GI, and ELF3 are present as duplicate copies in some species within the two legume groups. Interestingly, the CONSTANS protein, which promotes flowering in LD plants such as Arabidopsis, is represented by only one co-ortholog in the LD legumes and two in the SD legumes [24].
Both genes and environmental factors affect the vegetative-to-reproductive transition in some leguminous species. In a broad sense, flowering time plays a fundamental role in deciding when and how a plant can allocate resources, participating in a complex network of interactions with other developmental processes [14]. The FLOWERING LOCUS T/TERMINAL FLOWER 1 (FT/TFL1) gene family, which integrates environmental signaling for floral induction in Arabidopsis, has expanded in legumes and was reported to control the fate of meristems during flowering. Both galegoid and phaseoloid legumes have multiple TFL1 genes and generally have three distinct subclades of FT gene (FTa, FTb, and FTc) [25]. Additionally, the MADS-box gene family, which regulates flower organ identity, has been characterized in certain legumes, such as barrel medic and soybean, where additional SHORT VEGETATIVE PHASE (SVP) and SUPPRESSOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CONSTANS 1 (SOC1) genes were found [17,23].
2.2. Growth and Metabolism
Plants with circadian rhythms that synchronize with their environment are reported to gain growth or metabolic advantages over those that are not synchronized [12,26]. The present understanding of how the environment affects plant circadian rhythms came mainly from studies with Arabidopsis where regulation is mainly composed of three transcription feedback loops—the central, morning, and evening loops [12,27]. This functional configuration allows the clock to work in a rhythmic manner within a cycle of approximately 24 h. Dysfunctional clocks can decrease visible leaf area and net photosynthesis, leading to distorted development and reduced biomass and grain yield [28,29]. Studies on a handful of crop species, including the major legume soybean, suggested that shifting the circadian phase of key biological processes, such as photosynthesis, could impact the growth and development of the crops. For example, Pan et al. [29] reported the significant relationship between circadian rhythms and Lhcb (CAB2 and CAB1) transcripts associated with chlorophyll synthesis and photosynthesis. These genes encode light-harvesting chlorophyll-binding proteins that form up to 50% of the thylakoid membrane protein and have cis-elements associated both with light-induced transcription and circadian control [29].
2.3. Hormone Signaling
Circadian and dial regulation of the levels of phytohormones is widespread in plants, likely involving a complex network of hormone signaling pathways. Circadian oscillations in the major growth-related phytohormones, including ethylene (ET), auxin/indole-3-acetic acid proteins (Aux/IAAs), cytokinins (CKs), gibberellins (GAs), and brassinosteroids (BRs), have been studied in multiple species that demonstrated species- and/or tissue-specific variations [30,31,32,33,34,35]. It is worth noting that defense-related hormones such as jasmonic acid (JA) and salicylic acid (SA) also undergo circadian oscillations. For instance, JA and SA levels have been found to be clock regulated in Arabidopsis, with peak accumulation in the middle of the day and night, respectively [36].
There are several ways in which the plant circadian system can interact with hormone metabolic pathways. The expression of specific genes that encode hormone biosynthesis enzymes in plants has been reported to be clock regulated. For example, many GA biosynthesis genes demonstrated regular daily rhythms in Arabidopsis and common pea [37,38], whereby the plant responsiveness to GA is controlled by the clock [39]. It was reported that the plant circadian clock regulates more than 50% of the genes that encode major enzymes of the methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) and mevalonate (MVA) pathways, which involve the synthesis of isoprenoid, the precursor of certain phytohormones (such as GAs, BRs, and CKs). In Arabidopsis, key genes in the MEP pathway were found to be controlled by the central clock proteins CCA1 and LHY [40]. IAA, the most studied auxin, is a key regulator of growth and development in plants that is derived mainly from tryptophan via the tryptophan aminotransferase/flavin monooxygenase (YUCCA) pathway. Rawat et al. [41] reported that the clock regulates auxin levels through a mechanism involving the circadian-regulated MYB-like transcription factor RVE1, which directly promotes the expression of the auxin biosynthesis gene YUCCA8, leading to increased auxin production during the day. In Arabidopsis, the daily rhythms in ABA, BR, IAA, and GA signaling are complex and modulated at many steps [42]. Although emissions of major phytohormones have long been recognized as clock-controlled, the complex mechanisms underlying these regulations in legumes remain elusive.
2.4. Biotic and Abiotic Stress
Apart from light and temperature, biotic and abiotic stresses activate plant response pathways that can alter the plant circadian clock. Little is known about the impacts of these stresses on the circadian clock of crop plant species, although major clock genes that are associated with some agronomic traits have been reported. The limited understanding of how different stresses can influence crop circadian clocks is considered one of the key knowledge gaps that impedes the identification of specific circadian traits for further germplasm improvement in breeding programs. Among legumes, abiotic stresses such as heat, drought, and iron deficiency have been reported to change the timing of the expression of core clock genes in soybean, with different stresses causing different physiological effects [43]. However, the interconnection between the changes in clock gene expressions and physiological changes remains elusive [44]. The study conducted by Li et al. [43] revealed that different soybean varieties with different iron uptake efficiencies may involve phase modulation as a mechanism to alleviate iron deficiency symptoms, demonstrating that it is important to dissect crop circadian clocks. Deciphering the complex interaction network between crop circadian clock and stress signals can help enhance abiotic stress tolerance of the crop. For example, ectopic expression of the Arabidopsis light-signaling B-box domain gene AtBBX32 in soybean was found to increase the grain yield of multiple transgenic events in field trials [45].
3. Legume Clock Research at a Glance
While the first scientific knowledge of the plant circadian clock was reported nearly 300 years ago, the role of the molecular clock in growth and development is not fully understood and many clock-related components remain to be discovered [1,46]. Recent advances in genetics and genomics have paved the way for a better understanding of clock genes and circadian rhythmicity in crop legumes, particularly for popular species such as soybean and common pea. Over the past two decades, there has been a noticeable increase in the number of leguminous species used to elucidate the role of the clock-related components, including both major and minor (or underutilized) species (Table 1) [17,22,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70]. Figure 3 presents the timeline of important clock research in legumes since the 1930s [17,22,43,50,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81]. This section discusses the key findings in the clock research of these legumes and the critical gaps in the existing literature.
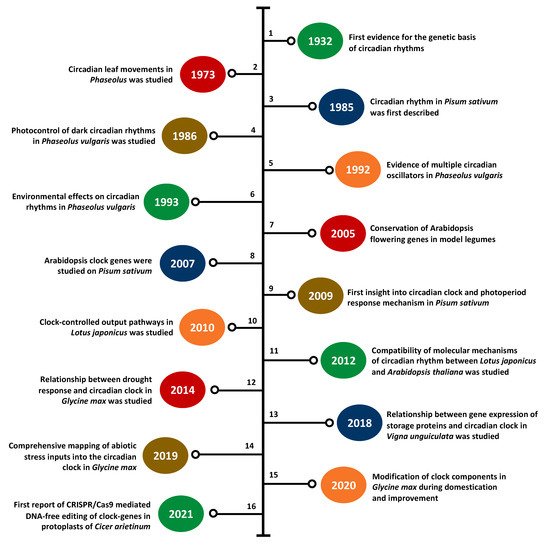
Figure 3. Timeline of major findings in clock research in legumes since the 1930s. 1—Bünning (1932) [71], 2—Bünning (1973) [72], 3—Kloppstsech (1985) [73], 4—Holmes and Klein (1986) [74], 5—Hennessey and Field (1992) [75], 6—Hennessey et al., (1993) [76], 7—Hecht et al., (2005) [17], 8—Hecht et al., (2007) [22], 9—Weller et al., (2009) [77], 10—Ono et al., (2010) [78], 11—Ueoka-Nakanishi et al., (2012) [50], 12—Marcolino-Gomes et al., (2014) [79], 13—Weiss et al., (2018) [70], 14—Li et el. (2019) [43], 15—Li et al. (2020) [80], 16—Badhan et al. (2021) [81].
Table 1. Specific circadian rhythm genes studied in model and/or major legumes.
| Species | Gene | Arabidopsis Homologue | Function(s) | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barrel medic (Medicago truncatula) | MtGI | GI | Circadian clock component, photoperiod response | [47] |
| MtLHY | LHY | Regulation of circadian rhythm in nodules and nyctinastic leaf movement | [48] | |
| Birds-foot trefoil (Lotus japonicus) | LjaPRR5 | PRR5 | Component of the circadian rhythm | [49] |
| LjaPRR7 | PRR7 | |||
| LjaPRR9 | PRR9 | |||
| LjaLUX | LUX | |||
| LjaTOC1 | TOC1 | Central component of the circadian rhythm | ||
| LjaLHY | LHY | |||
| LjCCA1 | CCA1 | Central component of the circadian rhythm | [50] | |
| LjGI | GI | Possible regulation of flowering time | [51] | |
| Soybean (Glycine max) | GmTOC1 | TOC1 | Central component of the soybean circadian clock (expressed as an evening gene) | [52] |
| GmELF4 | ELF4 | Circadian clock function. | [53] | |
| GmGIa | GI | Photoperiod response, flowering time regulation | [54] | |
| GmLCL1 | LHY/CCA1 | Central component of the soybean circadian clock (expressed as a morning gene) | [52] | |
| GmLCL2 | ||||
| GmLHY | LHY | Regulate plant height | [55] | |
| GmLUXa | LUX | Control flowering time | [56] | |
| GmLUXb | ||||
| GmLUXc | ||||
| GmZTL3 | ZTL | Control of flowering time (inhibitor of flowering induction) and photoreceptor. | [57] | |
| GmPRR37 | PRR3 & 7 | Control of soybean photoperiodic flowering | [58] | |
| Common pea (Pisum sativum) | PsTOC1 | TOC1 | Circadian clock component | [17,59] |
| DNE | ELF4 | Circadian clock component, flowering time regulation | [60,61] | |
| HR | ELF3 | Circadian clock component, flowering time regulation, light response | [61] | |
| LATE1 | GI | Photoperiod response | [22,60] | |
| MYB1/LHY | CCA1/LHY | Circadian clock component | [60] | |
| SN | LUX | Circadian clock component | [62] | |
| PsPRR37 | PRR | Component of phospho-relay signal transduction system | [59] | |
| PsPRR59 | ||||
| Chickpea (Cicer arietinum) | Efl1 | ELF3 | Flowering regulation (light input to the circadian clock) | [63] |
| GI | GI | Flowering time regulation | [64] | |
| Common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) | PvLHY | LHY | Circadian mechanism regulation | [65,66] |
| PvTOC1 | TOC1 | Mediating light responsiveness to circadian clock mechanism | [67,68] | |
| PvELF4 | ELF4 | Evening-expressed gene | [67] | |
| PvGI | GI | Circadian clock component | [69] | |
| PvZTL | ZTL | |||
| Pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan) | CcGI | GI | Determinacy and flower patterning | [69] |
| Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) | VunTOC1 | TOC1 | Circadian clock function in seed filling and leaves | [70] |
| VunLHY | LHY | |||
| VunELF3 | ELF3 | |||
| VunGI | GI | |||
| Lentil (Lens culinaris) | HR | ELF3 | Flowering time regulation | [61] |
| White lupin (Lupinis albus) | GI | GI | Flowering regulation; anthracnose resistance | [64] |
3.1. Clock Research in Model Legumes
3.1.1. Barrel Medic
Barrel medic (Medicago truncatula) is a tiny annual legume that is used widely in legume genomics research. Native to the Mediterranean region, this forage legume has been used to study many aspects of plant biology, especially since the first release of a genome sequence in 2011 [82]. Many effective transformation methods, such as Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated and A. rhizogenes-mediated hairy root transformation, have been developed for functional genomic studies in this model legume [83]. Moreover, the ability of barrel medic to be efficiently nodulated by rhizobium has contributed to a better understanding of plant–microbe interactions, particularly the symbiotic relationship between various species of legumes and nitrogen-fixing bacteria [84,85].
Recently, Ma et al. [86] reported a comprehensive analysis of 36 circadian-related genes, namely those containing the CCT domain. The CCT (CONSTANTS-CONSTANS LIKE-TIMING OF CAB 1) genes have been previously implicated in flowering time regulation and biomass accumulation [87]. Gene clustering analysis for barrel medic associated the CCT genes with flowering time regulation, abiotic stress response, and regulation of growth and development [86]. A recent study revealed that the LHY (LATE ELONGATED HYPOCOTYLS) gene also plays an essential role in the regulation of the endogenous biological clock in barrel medic [48]. Functional loss of MtLHY can severely impact the transcription of several key circadian genes, and its over-expression may result in delayed flowering and hypocotyl elongation. The study also reported reduced nitrogen fixation with altered biological clocks in Mtlhy mutants, causing abnormal nyctinastic leaf movement and biomass reduction. The amenability of barrel medic to be genetically transformed by various methods has made it well-accepted as a model legume species that likely will continue to attract interest from crop researchers across different biological disciplines.
3.1.2. Birds-Foot Trefoil
Similar to barrel medic, birds-foot trefoil (Lotus japonicus) is physically small and has a short generation time [54], allowing easy cultivation with transformation systems and multiple ecotypes and mutant resources available. Duangkhet et al. [88] studied the induction of Ljmybr, an MYB-related gene, with a possible role in nitrogen fixation regulation. The study identified Ljmybr as a possible CCA1-related gene sharing a conserved SHAQKY domain. MYB transcription factors are known to be associated with plant development, response to environmental signals, and hormone regulation [89]. MYB proteins of the CCA1-like subgroup, in particular, have been linked to biological clock regulation in soybean, maize (Zea mays), and Arabidopsis [90]. A comprehensive study on clock-associated F-box proteins, which are one of the main components of the S-phase-kinase-associated protein 1 (SKP1), Cullin-1, and F-box protein (SCF)-complex, conducted on three model species—birds-foot trefoil, barrel medic, and Arabidopsis—indicated that F-box proteins could be conserved among these model plants and play a crucial role in their growth and development [91]. In particular, the F-box proteins were associated with embryogenesis and nodulation. Further knockdown experiments highlighted the possible role of F-box proteins in cell cycle control, and that these proteins could be conserved among all three model plants [91]. A recent genome-wide association study on birds-foot trefoil found that clock-regulated adaptive flowering time traits and phenotype association signals for overwintering were direct targets of selection during colonization of Japan, indicating that these traits are critical for legume adaptation to cold climates [92].
3.1.3. Soybean
Soybean (Glycine max), a globally traded legume, serves as a prime source of protein and vegetable oils for human consumption. Deemed the “king of beans”, this major legume is also widely used for animal feed and biofuel production. Recent years have seen rapid improvement in the quantity and quality of soybean seeds due mainly to the advances in genetic and metabolic engineering [93]. Although the first soybean transformation was reported in the late 1980s, the stable transformation of soybeans remains one of the major challenges because of its low transformation and regeneration efficiency [87,93,94]. Nonetheless, genetic engineering has been widely used in soybean, especially for the improvement of its nutritional value where significant efforts have been devoted to securing the global need for biofortified food [80].
Among the major evening complex genes such as ELF3, ELF4, and LUX found in plants, the GmELF4 gene of soybean has been functionally characterized [72]. Similar to the function of AtELF4 in Arabidopsis, GmELF4 acts as a negative controller of flowering, delaying flowering via a range of unidentified molecular pathways. Other clock components that have been studied in soybean include GmLCL1, GmTOC1, GmPRR9, and GmGI, which revealed an arsenic stress response that can affect physiological responses, such as stomatal aperture, that naturally exhibit diurnal oscillations [44]. Arsenic, which is commonly found in soil as arsenate and arsenite, is an extremely toxic metalloid that affects soybean growth and productivity. However, further studies are required to fully understand the link between arsenic exposure and the circadian rhythm of soybean [44]. The circadian clock components in soybean are known to be modified as a result of domestication and improvement, and further studies are needed to exploit these modifications to improve soybean productivity [80].
3.1.4. Common Pea
Another common crop legume is the common pea (Pisum sativum), which is also the model plant used by the father of genetics, Gregor Mendel, to study the laws of inheritance. Since the first description of circadian rhythm in common pea [73], a considerable body of research has been conducted concerning its various molecular pathways, ranging from temperature stress response [95,96] to the diurnal regulation of axillary budding [97]. Understanding the response to abiotic stressors, particularly heat and cold stresses, forms a fundamental portion of pea molecular research. Being a cool season legume, it is generally more sensitive to heat stress as compared to its warm season counterparts such as pigeon pea and mungbean. The study conducted by García-García et al. [97] unraveled the oxidative response of both common pea and bean to sustained irrigation deficit and concluded that the value of these legumes as dietary sources of bioactive compounds depends on species, variety, and also growing conditions.
The first research into the circadian clock and photoperiod response mechanism in common pea was reported by Weller et al. [77], highlighting progress in gene and mutant isolation, candidate gene assessment, expression analyses, and physiological studies. The study identified several loci as orthologues of AtGIGANTEA (or AtGI) and AtELF4, including LATE BLOOMER1 (LATE1) and DIE NEUTRALIS (DNE). According to Liew et al. [62], the STERILE NODES (SN) locus in common pea was among the first photoperiod response genes to be studied, demonstrating the genetic control of flowering-time regulation through long-distance signaling. The study reported that SN formed a complex network with two other circadian clock genes, DNE and HIGH RESPONSE TO PHOTOPERIOD (HR), where HR regulates the expression of SN while SN influences the role of HR and DNE in controlling flowering. The common pea axillary bud transcriptome analysis demonstrated rapid changes in the temporal expression of diurnally regulated genes within the short 170-min time frame, suggesting that future gene expression studies in this crop should take into account the possibility of fast diurnal changes in gene expression [98].
3.2. Clock Research in Underutilized Legumes
During the past decade, it has been observed that unlocking the potential of underutilized legumes, such as winged bean and lentil, is equally important as the improvement of major legumes such as soybean and common pea [7,8]. These leguminous species have recently been promoted as the protein alternatives to soybean and meat, being part of the solution to future food and nutrition insecurity amidst climate change [8]. However, the current state of knowledge of circadian clocks in leguminous species stems primarily from the research on the model and/or economically important legume species as discussed in Section 3.1 and Section 3.2. Clock research in underutilized legumes is scarce in literature. One notable study is the identification of an ELF3 homolog in lentil, along with common pea (HR locus), as the genetic factor underlying flowering time variation [23]. More research to understand the molecular mechanisms of circadian rhythmicity in potential underutilized crops is crucial to help ensure the sustainability for future food or protein. All things considered, optimizing circadian function can offer opportunities to enhance the productivity of potential legumes and crops in general, including those grown over broad latitudinal ranges [3].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms22094588
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
