Exosomes are small vesicles of 100 nm in size that are released from every cell constantly. They contain different molecules (DNA, RNA, lipids, metabolites, etc.) that reflect the content of the cell they come from. Exosomes can be found in all biological fluids. In cancer, exosomes are involved in several events such as tumor growth, metastasis, and the immune response, by delivering their cargos to recipient cells. Due to their unique features, exosomes have become promising analytes in the field of liquid biopsy, which searches for biomarkers to manage different steps of the tumor process.
- exosomes
- cancer
- liquid biopsy
- biomarkers
1. Exosome Biogenesis and Composition—Reflecting Their Origin
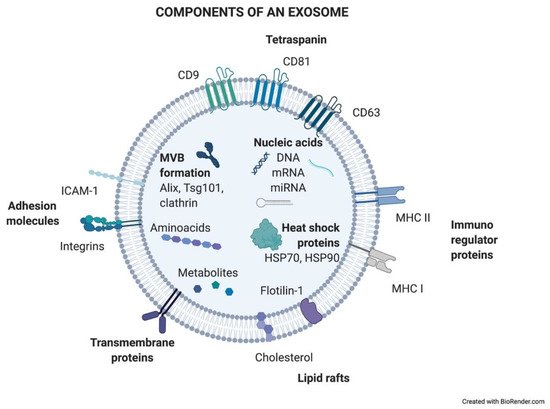
2. Exosomes: A Source of Biomarkers
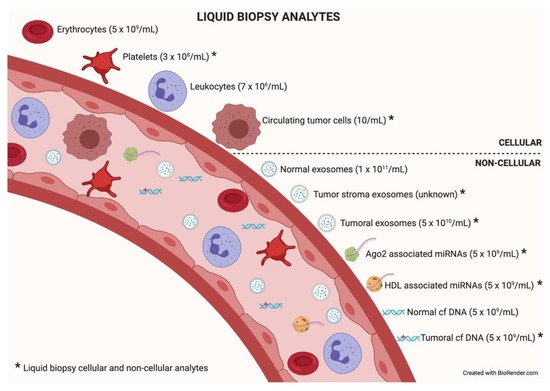
| Traits | Liquid Biopsy Analyte | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTCs 1 | ctDNA 2 | Exosomes | ctRNA 3 | miRNA | |
| Origin | |||||
| Viable cells | ✔ 4 | ✖ 5 | ✔ | ? 6 | ? |
| Apoptotic cells | ✔ | ✔ | ? | ? | ? |
| Components | |||||
| DNA | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | N.A. 7 | N.A. |
| RNA | ✔ | N.A. | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Proteins | ✔ | N.A. | ✔ | N.A. | N.A. |
| Metabolites | ✔ | N.A. | ? | N.A. | N.A. |
| Extractable information | |||||
| Copy number variation | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✖ | ✖ |
| Mutations | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✖ |
| Epigenetic information | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✖ | ✖ |
| Fusion genes | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✖ |
| Splice variants | ✔ | ✖ | ✔ | ✔ | ✖ |
| Single-cell information | ✔ | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ |
| Application in personalized medicine | |||||
| Diagnosis | ✔ | ✔ 8 | ✔ | ? | ✔ |
| Classification of molecular subtypes | ✔ | ✔ | ? | ? | ✖ |
| Clonal evolution tracking | ✔ | ✔ | ? | ✖ | ✖ |
| Prognosis | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ? | ✔ |
| Recurrence | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✖ |
| Predictive | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ? | ✖ |
| Resistance prediction | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ? | ✖ |
| Monitoring treatment | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ? | ? |
3. Exosome Heterogeneity: An Unknown Wealth?
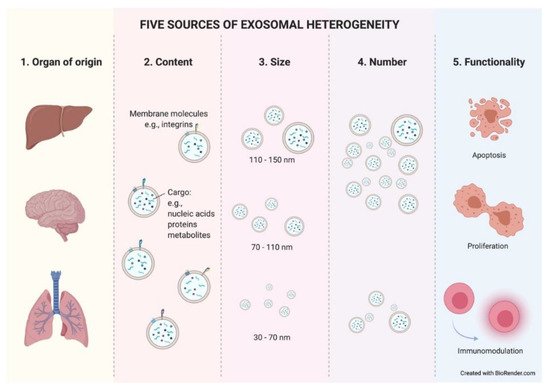
4. Sending a Message: The Role of Exosomes in Intercellular Communication
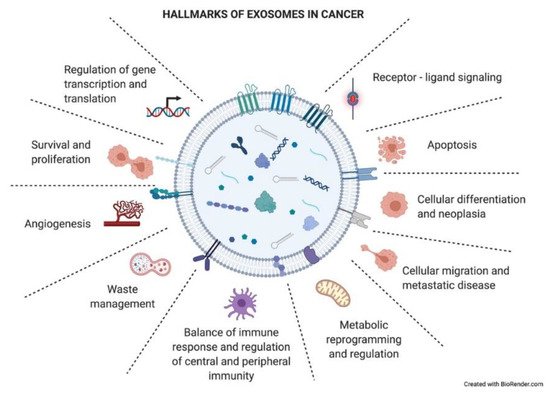
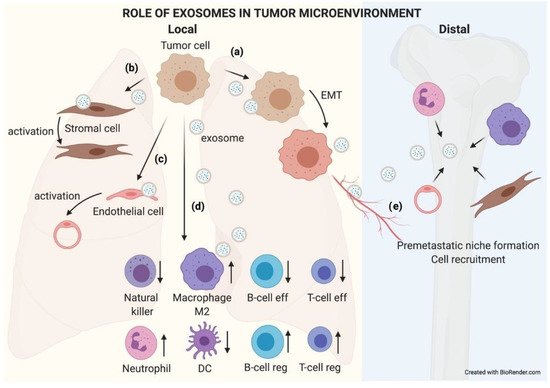
4.1. A Short-Range Shipment: The Role of Exosomes in the Tumor Microenvironment
4.2. A Long-Range Shipment: The Role of Exosomes in Metastatic Organs
5. TEX Biomarkers in Clinics: A List of Possibilities
| Exosomal miRNAs as Cancer Biomarkers | ||||
| miRNA | Cancer type | Clinical value | Biofluid | Reference |
| Let-7b-5p, -122-5p, -146b-5p, -210-3p, -215-5p | Breast cancer | Diagnosis | Plasma | [84] |
| miR-224 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Diagnosis/Prognosis | Serum | [85] |
| miR-106b, miR-1269a | Lung cancer | Diagnosis/Prognosis | Serum | [86,87] |
| miR-375, -1307 | Ovarian cancer | Diagnosis | Serum | [88] |
| Exosomal lncRNAs as Cancer Biomarkers | ||||
| lncRNA | Cancer type | Clinical value | Biofluid | Reference |
| PCAT-1, UBC1 and SNHG16 | Bladder cancer | Diagnosis/Prognosis | Urine | [89] |
| MALAT-1 | Lung cancer | Diagnosis | Serum | [90] |
| Exosomal mRNA as Cancer Biomarkers | ||||
| mRNA | Cancer type | Clinical value | Biofluid | Reference |
| BRAF, KRAS (mutant) | Colorectal cancer | Diagnosis | Serum | [91] |
| Exosomal mutated DNA as Cancer Biomarkers | ||||
| DNA | Cancer type | Clinical value | Biofluid | Reference |
| IDH1 | Glioblastoma | Diagnosis/Prognosis | Plasma | [92] |
| EGFR | Lung cancer | Diagnosis/Prognosis | Plasma/Bronchioalveolar lavage | [93,94,95,96] |
| BRAF | Melanoma | Therapeutic monitoring | Plasma | [97] |
| KRAS, P53 | Pancreatic cancer | Diagnosis/Prognosis | Serum/Plasma | [98,99] |
| MYC, P53, MLH1, PTEN, AR | Prostate cancer | Diagnosis/Prognosis | Plasma | [100,101] |
| Exosomal proteins as Cancer Biomarkers | ||||
| Protein | Cancer type | Clinical value | Biofluid | Reference |
| PDL-1 | Melanoma | Prognosis | Plasma | [102] |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/cancers13092147
