Plants are constantly exposed to environmental stresses during their growth and development. Owing to their immobility, plants possess stress-sensing abilities and adaptive responses to cope with the abiotic and biotic stresses caused by extreme temperatures, drought, flooding, salinity, heavy metals and pathogens. Acyl-CoA-binding proteins (ACBPs), a family of conserved proteins among prokaryotes and eukaryotes, bind to a variety of acyl-CoA esters with different affinities and play a role in the transport and maintenance of subcellular acyl-CoA pools. In plants, studies have revealed ACBP functions in development and stress responses through their interactions with lipids and protein partners.
- abiotic stress
- acyl-CoA-binding proteins
- biotic stress
- lipids
- protein interactors
- stress signalling
1. Plant ACBPs
| Class | Protein Name | Signal Peptide | TM Domain | ACB Domain | Ankyrin Repeats | Kelch Motifs | Subcellular Locations | Size (kDa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | AtACBP6 | − | − | + | − | − | Cytosol | 10.4 |
| OsACBP1 | − | − | + | − | − | Cytosol | 10.2 | |
| OsACBP2 | − | − | + | − | − | Cytosol | 10.3 | |
| OsACBP3 | − | − | + | − | − | Cytosol | 17.7 | |
| ZmACBP1 | − | − | + | − | − | Cytosol | 10.1 | |
| HaACBP6 | − | − | + | − | − | Cytosol, Nucleus | 10.9 | |
| II | AtACBP1 | − | + | + | + | − | ER, PM | 37.5 |
| AtACBP2 | − | + | + | + | − | ER, PM | 38.5 | |
| OsACBP4 | + | + | + | + | − | ER | 36 | |
| ZmACBP3 | − | − | + | + | − | ER | 34.8 | |
| EgACBP2 | − | + | + | + | − | PM | ND | |
| III | AtACBP3 | + | + | + | − | − | Apoplast | 39.3 |
| OsACBP5 | + | + | + | − | − | ER | 61.2 | |
| ZmACBP6 | − | − | + | − | − | Cytosol, PM | 35.2 | |
| IV | AtACBP4 | − | − | + | − | + | Cytosol | 73.2 |
| AtACBP5 | − | − | + | − | + | Cytosol | 71 | |
| OsACBP6 | − | + | + | − | + | Peroxisomes | 71.4 | |
| ZmACBP7 | − | − | + | − | + | Cytosol, PM | 72.1 |
| Proteins | Species | Acyl-CoA Binding | Phospholipid Binding | Protein Interactors | Stress Responses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AtACBP1 | A. thaliana | 16:0, 18:1, 18:2, 18:3, 20:4, 24:0, 25:0, 26:0 [26,108,133] | PC [78] PA [88] |
PLDα1 [78] | Freezing [88] |
| RAP2.12 [77,128,134] | Hypoxia [77,128] | ||||
| AREB1 [80] | Salinity, osmotic damage [80] | ||||
| − | Heavy metal [135] | ||||
| − | Pathogen [26] | ||||
| AtACBP2 | A. thaliana | 16:0, 18:1, 18:2, 18:3, 20:4 [75,108,114] | PC [116] lysoPC [76] |
AtEBP [73], RAP2.12 [77,128] | Hypoxia [73,77] |
| LYSOPL2 [76,82], AtFP6 [75] | Heavy metal [75,76,82] | ||||
| − | Drought [90] | ||||
| − | Salinity [94] | ||||
| − | Oxidation [75] | ||||
| AtACBP3 | A. thaliana | 12:0, 14:0, 16:0, 18:1, 18:2, 18:3, 20:4, 22:0, 24:0 [108,112,126,136] | PC [112] PE [112,117] |
− | Drought [25] |
| − | Hypoxia [136,137] | ||||
| − | Wounding [126] | ||||
| − | Pathogen [25,108,121] | ||||
| AtACBP4 | A. thaliana | 14:0, 16:0, 18:0, 18:1, 18:2, 18:3 [113,115] | PC [115] | AtEBP [74] | Pathogen [25,74] |
| − | Drought [25] | ||||
| − | Heavy metal [124] | ||||
| AtACBP6 | A. thaliana | 14:0, 16:0, 18:0, 18:1, 18:2, 18:3, 20:4 [95,113,115] | PC [87] | − | Freezing [87,123] |
| − | Drought [25] | ||||
| − | Wounding [125] | ||||
| − | Pathogen [25] | ||||
| OsACBP4 | O. sativa | 16:0, 18:0, 18:1, 18:2, 18:3 [89,94] | PC, PA [91] | − | Salinity [89,94] |
| OsACBP5 | O. sativa | 16:0, 18:3 [89,93] | PC, PA [91] | − | Pathogen [89,93,127] |
| − | Wounding [89] | ||||
| OsACBP6 | O. sativa | 18:1, 18:2 [89] | PC, PA [91] | − | Wounding [89] |
| ZmACBP1 | Z. mays | − | − | − | Salinity, drought [103] |
| ZmACBP3 | Z. mays | − | − | − | Salinity, drought [103] |
| ChACBP1 | Chlorella sp. | − | PC [92] | − | Freezing, salinity, oxidation, heavy metal [92] |
| VvACBP | V. vinifera | − | − | − | Freezing, heat, ER, pathogen [100] |
2. Membrane Lipids and ACBPs in Abiotic Stress Signalling
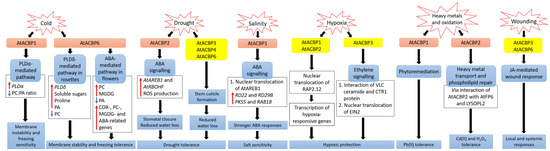
2.1. Cold Stress
2.2. Drought Stress
2.3. Salinity Stress
2.4. Hypoxic Stress
2.5. Heavy Metal and Oxidative Stresses
2.6. Wounding
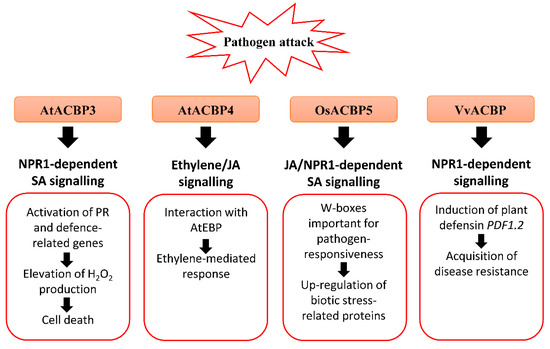
3. Membrane Lipids and ACBPs in Pathogen Defense
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/cells10051064
