Glycogen storage diseases (GSDs) are metabolic disorders of glycogen metabolism. In aggregate, GSDs are not considered rare diseases, but every individual type are. The overall estimated GSD incidence is 1 case per 20,000-43,000 live births, and a prevalence of 1:100,000 is considered for main types (including I, II, II, V and IX). There are 19 types which are classified by enzyme deficiency and affected tissue. Most of them are inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, except for one X-linked GSDIX and Danon subtypes. Disorders related with creation, deposits and degradation of glycogen, may primarily affect the liver (hepatic GSDs), the muscles (muscle GSDs), or in a multiorganic manner (mainly Pompe). The common characteristic of all types of GSDs is the alteration of some step in glycogenolysis/glycolysis pathway, as can be seen in figures 1a and 1b.
- Glycogen storage disease (GSD)
- Pompe disease
- hepatic GSD
- muscle GSD
- biomarkers
- Glycogen metabolism
[1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13]1. Introduction
Glycogen storage diseases (GSDs) are metabolic disorders of glycogen metabolism. In aggregate, GSDs are not considered rare diseases, but every individual type are. The overall estimated GSD incidence is 1 case per 20,000-43,000 live births [1], and a prevalence of 1:100,000 is considered for main types (including I, II, II, V and IX). There are 19 types which are classified by enzyme deficiency and affected tissue. Most of them are inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, except for one X-linked GSDIX and Danon subtypes. Disorders related with creation, deposits and degradation of glycogen, may primarily affect the liver (hepatic GSDs), the muscles (muscle GSDs), or in a multiorganic manner (mainly Pompe) [2]. The common characteristic of all types of GSDs is the alteration of some step in glycogenolysis/glycolysis pathway, as can be seen in figures 1a and 1b.
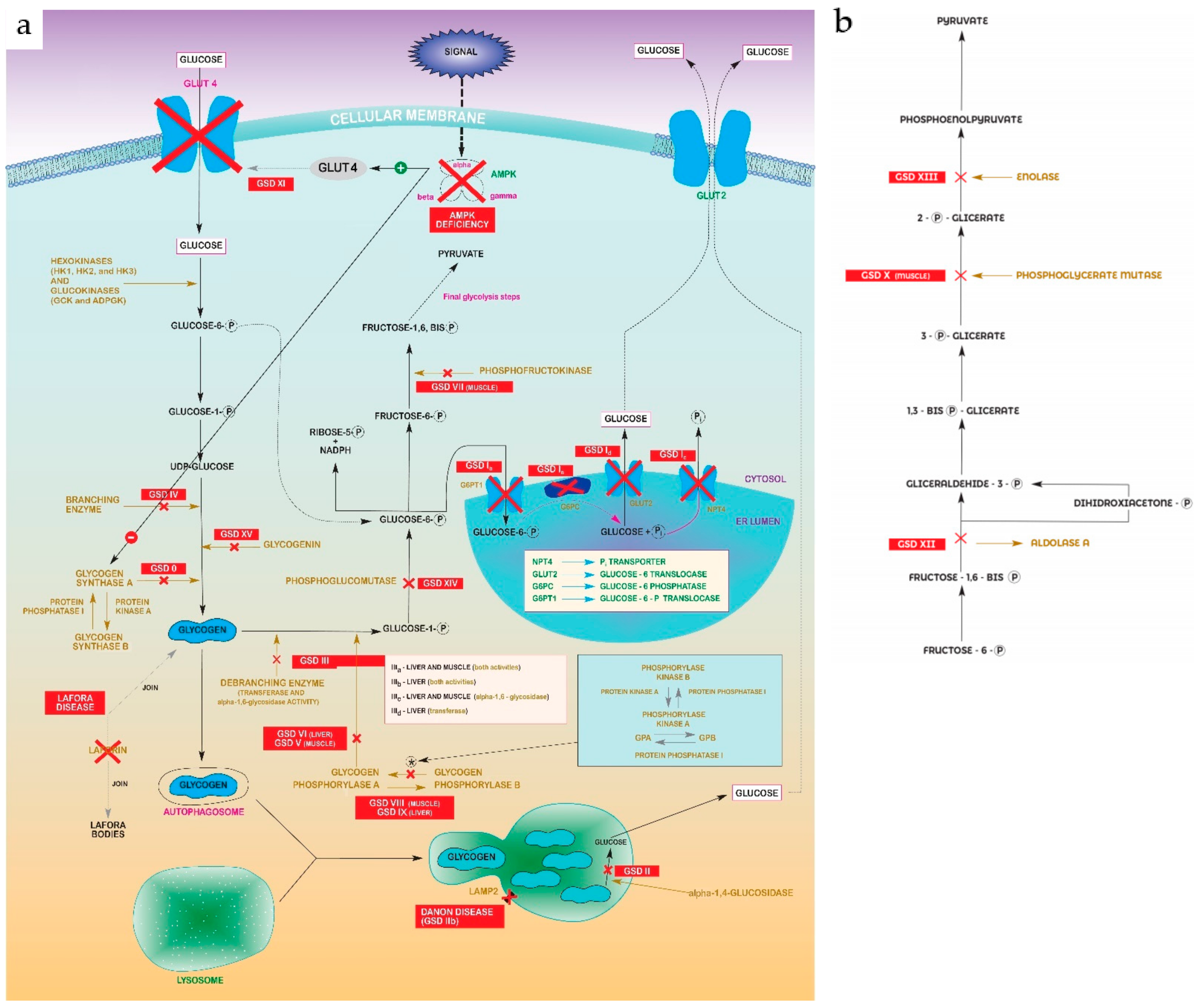
Figure 1. (a) Glycolysis–gluconeogenesis pathway showing steps disrupted in every GSD. Abbreviations: Glycogen Synthase Deficiency (GSD 0); Von Gierke Disease (GSD Ia, Ib, Ic, Id); Pompe disease (GSD II); Cori-Forbes Disease (GSD III); Andersen Disease (GSD IV); McArdle Disease (GSD V); Hers Disease (GSD VI); Phosphofructokinase Deficiency (GSD VII); Muscle Phosphorylase b Kinase Deficiency (GSD VIII); Liver Phosphorylase Kinase Deficiency (GSD IX); Fanconi-Bickel Syndrome (GSD XI); Phosphoglucomutase 1 Deficiency (GSD XIV); Glycogenin Deficiency (XV). (b) “Zoomed in” detail of pyruvate formation in final glycolysis steps from Figure 1a. Abbreviations: Muscle Phosphoglycerate Mutase Deficiency (GSDX); Aldolase A Deficiency (GSDXII); Enolase 3 Deficiency (GSDXIII).
2. The Most Prevalent Diseases
-
GSDIa, caused by a deficiency of glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase or G6PC1) catalytic activity;
-
GSDIb, GSDIc and GSDId, caused by different defects in the glucose-6-phosphate transporter (SLC37A4).
-
Infantile-onset Pompe disease (IOPD); in children younger than 12 months, the clinical manifestations include cardiomyopathy, which may already be evident in the uterus. However, the most typical onset of the disease occurs at around 4 months. In this case, patients most frequently present with hypotonia, a muscle weakness that occurs in a generalized manner, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. These patients usually have serious difficulties feeding and breathing. If not treated with enzyme replacement therapy (ERT), patients with IOPD usually die after two years from progressive left ventricular outflow obstruction and respiratory insufficiency.
-
Late-onset Pompe disease (LOPD; including (a) individuals with onset before the age of 12 months without cardiomyopathy and (b) all individuals with onset after the age of 12 months) is characterized by proximal muscle weakness and respiratory insufficiency. Clinically significant cardiac involvement is uncommon.
- 3). Glycogen storage disease type III (GSDIII, Cori-Forbes disease), with an incidence of 1:100,000 too, is characterized by variable liver, cardiac muscle, and skeletal muscle involvement. GSDIIIa is the most common subtype, present in about 85% of affected individuals [16]. It manifests with liver and muscle involvement. GSDIIIb, with liver involvement only, comprises about 15% of all GSDIII. The clinical significance of GSDIII ranges from almost no symptoms to severe cardiac dysfunction, congestive heart failure, and, rarely, sudden death. Skeletal myopathy manifests as muscle weakness but is rarely evident in childhood because it progresses slowly. This acquires greater relevance in the third to fourth decades of life. The diagnosis is made by identifying biallelic pathogenic variants in glycogen debranching enzyme, amylo-alpha-1,6-glucosidase, or 4-alpha-glucanotransferase (AGL).
- 4). Type V glycogen storage disease (GSDV, McArdle’s disease) is a metabolic myopathy whose main characteristic is exercise intolerance. Incidence roughly reaches 1:100,000 [17]. Symptomatologically, patients present with rapid onset fatigue, myalgia, and muscle cramps [18]. The symptomatology is more acute with exercise, and symptoms are usually isometric or sustained aerobic exercise. It is common for patients to experience greater exercise by exploiting the “second wind” phenomenon, which relieves myalgia and fatigue after resting for a few minutes. Normally GSDV symptoms appears in the first decade of life. Twenty-five percent of patients will present with weakness that mainly affects the proximal muscles. The diagnosis is made using PYGM molecular genetic tests (which encode glycogen phosphorylase, muscle form). This is the only known gene associated with GSDV.
- 5). Glycogen storage disease types VIII and IX (GSDVIII and GSDIX), results from a liver phosphorylase b kinase enzyme deficiency, which plays an important role in the decomposition of glycogen [19]. One type is hepatic PhK deficiency (GSDIX), characterized by the presence of early-onset hepatomegaly. There is also growth retardation and, often, fasting ketosis and hypoglycaemia. Another variant is muscle PhK deficiency (GSDVIII), much less common and related to physical exercise intolerance, myalgia, muscular cramps, myoglobinuria, and progressive muscular weakness. The PhK enzyme comprises four subunits (α, β, γ, and δ). Pathogenic variants of PHKA1, which encodes the α subunit, cause the rare muscular deficiency of the X-linked disorder. The pathogenic variants of PHKA2, which also codes for the α subunit, are responsible for the most frequent variant, hepatic PhK deficiency (X-linked hepatic glycogenosis). Incidence for GSD IXα is about 1:100,000 individuals [20]. Pathogenic variants of PHKB, which encodes the β subunit, cause PhK deficiency in both the liver and muscle. Those of PHKG2, which encodes the γ subunit, cause PhK deficiency in the liver. The diagnosis is enhanced by clinical findings from assessing the activity of PhK in erythrocytes or the liver or muscle tissues (depending on the variant to be treated), and definitive confirmation from molecular genetic testing.
An overall clinical summary of GSDs are in table 1.
Table 1. Main gene and clinical characteristics of GSDs types. Abbreviations: G6PC1 (glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit), SLC37A4 (Solute Carrier Family 37 Member 4), GAA (acid alpha-glucosidase), AGL (amylo-alpha-1,6-glucosidase), PYGM (glycogen phosphorylase, muscle form), PYGL (glycogen phosphorylase, liver form), PHKA1 (phosphorylase kinase regulatory subunit alpha 1), PHKA2 (phosphorylase kinase regulatory subunit alpha 2), PHKB (phosphorylase kinase regulatory subunit beta), PHKG2 (phosphorylase kinase regulatory subunit gamma 2), GYS1 (glycogen synthase 1), GYS2 (glycogen synthase 2), LAMP2 (lysosomal-associated membrane protein 2), GBE1 (1,4-alpha-glucan-branching enzyme), PFKM (phosphofructokinase, muscle), PGAM2 (phosphoglycerate mutase 2), SLC2A2 (solute carrier family 2 member 2), ALDOA (aldolase A), ENO3 (beta-enolase), PGM1 (phosphoglucomutase 1), GYG1 (glycogenin 1), EPM2A (Glucan Phosphatase, Laforin), NHLRC1 (NHL Repeat Containing E3 Ubiquitin Protein Ligase 1)
|
GSD TYPE |
ORGAN INVOLVEMENT |
VARIANT |
MUTATED GENE |
MAIN FINDINGS |
|
0 (glycogen synthase deficiency) [10] |
Liver |
a |
GYS2 |
Fasting ketotic hypoglycemia, short stature, osteopenia |
|
Skeletal muscle |
b [11] |
GYS1 |
Exercise intolerance, epilepsy, long QT syndrome, recurrent attacks of exertional syncope, muscle weakness, cardiac arrest |
|
|
I (Von Gierke Disease) [3] |
Liver |
a |
G6PC1 |
Severe hypoglycaemia, hepatomegaly, lactic acidosis, hyperuricemia, hyperlipidaemia, hypertriglyceridemia, hypoglycaemic seizures, bleeding, epistaxis |
|
b |
SLC37A4 |
Same as “a” variant plus impaired neutrophil and monocyte function, chronic neutropenia, recurrent bacterial infections, oral and intestinal mucosal ulcers |
||
|
II (Pompe Disease) [4] |
Multiorganic |
Infantile-onset Pompe disease (IOPD) |
GAA |
Hypotonia, generalized muscle weakness, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy |
|
Late-onset Pompe disease (LOPD) |
Proximal muscle weakness, respiratory insufficiency |
|||
|
II (Danon Disease, X-linked) [12] |
b |
LAMP2 |
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, cardiac conduction abnormalities, weakness, retinopathy |
|
|
III (Cori-Forbes disease) [5] |
Liver and muscle |
a |
AGL |
Ketotic hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, hyperlipidemia, elevated hepatic transaminases, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, skeletal myopathy, weakness |
|
Liver |
b |
Ketotic hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, hyperlipidemia, elevated hepatic transaminases |
||
|
IV (Andersen disease) [13] |
Skeletal muscle |
fatal perinatal neuromuscular |
GBE1 |
Fetal akinesia deformation sequence, polyhydramnios, fetal hydrops, arthrogryposis, severe hypotonia, muscle atrophy at birth |
|
congenital neuromuscular |
Hypotonia at birth, respiratory distress, dilated cardiomyopathy |
|||
|
Liver |
classic (progressive) |
Hepatomegaly, liver dysfunction, progressive liver cirrhosis, hypotonia, cardiomyopathy |
||
|
non-progressive |
Hepatomegaly, liver dysfunction, myopathy, hypotonia |
|||
|
Skeletal muscle |
childhood neuromuscular |
Chronic and progressive myopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy |
||
|
Adult Polyglucosan Body Disease [14] |
- |
- |
Progressive neurogenic bladder, spasticity, weakness, sensory loss in extremities, autonomic dysfunction, mild cognitive difficulties |
|
|
V (McArdle disease) [6,7] |
- |
- |
PYGM |
Fatigue, myalgia, muscle cramps, “second wind” phenomenon |
|
VI (Hers disease) [15] |
Liver |
- |
PYGL |
Hepatomegaly, poor growth, ketotic hypoglycemia, elevated hepatic transaminases, hyperlipidemia, low prealbumin level short stature, delayed puberty, osteopenia, osteoporosis (symptoms improve with age) |
|
VII (phosphofructokinase deficiency) [16] |
Skeletal muscle |
- |
PFKM |
Exercise intolerance, myalgias, cramps, episodic myoglobinuria, hemolytic anaemia, hyperuricemia |
|
VIII (phosphorylase b kinase deficiency, X-linked) [8] |
- |
- |
PHKA1 |
Exercise intolerance, myalgia, muscular cramps, myoglobinuria, weakness |
|
IX (phosphorylase b kinase deficiency, X-linked) [8,9] |
Liver |
- |
PHKA2 |
hepatomegaly, growth retardation, fasting ketosis, hypoglycaemia (symptoms improve with age) |
|
IX (phosphorylase b kinase deficiency) |
Liver and skeletal muscle |
- |
PHKB |
Sum of symptoms for type VIII and IX |
|
Liver |
- |
PHKG2 |
Hepatomegaly, growth retardation, fasting ketosis, hypoglycaemia (symptoms improve with age) |
|
|
X (phosphoglycerate mutase deficiency) [17] |
Skeletal muscle |
- |
PGAM2 |
Myalgia, cramps, muscle necrosis, myoglobinuria |
|
XI (Fanconi-Bickel syndrome) [18] |
Liver |
- |
SLC2A2 |
Hepatomegaly, fasting hypoglycemia, tubular nephropathy, severely stunted growth |
|
XII (aldolase A deficiency) [19] |
Skeletal muscle |
- |
ALDOA |
Non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia, mental retardation, rhabdomyolysis |
|
XIII (beta-enolase deficiency) [20] |
Skeletal muscle |
- |
ENO3 |
Exercise intolerance, myalgia, recurrent rhabdomyolysis |
|
XIV (phosphoglucomutase 1 deficiency) [21] |
Multiorganic |
- |
PGM1 |
Hepatopathy, bifid uvula, malignant hyperthermia, hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, growth retardation, hypoglycemia, myopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, cardiac arrest |
|
XV (glycogenin 1 deficiency) [22] |
Skeletal muscle |
- |
GYG1 |
Progressive, widespread muscle weakness, wasting, cardiac involvement in some cases |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms22094381
References
- Weinstein, D.A.; Correia, C.E.; Saunders, A.C.; Wolfsdorf, J.I. Hepatic glycogen synthase deficiency: An infrequently recognized cause of ketotic hypoglycemia. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism 2006, 87, 284–288.
- Sukigara, S.; Liang, W.C.; Komaki, H.; Fukuda, T.; Miyamoto, T.; Saito, T.; Saito, Y.; Nakagawa, E.; Sugai, K.; Hayashi, Y.K. et al. Muscle glycogen storage disease 0 presenting recurrent syncope with weakness and myalgia. Neuromuscular Disorders 2012, 22, 162–165, doi:10.1016/j.nmd.2011.08.008.
- Taylor, M.R.G.; Adler, E.D. Danon Disease - GeneReviews™ - NCBI Bookshelf. In GeneReviews [internet]; Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Ed.; University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2021: Seattle (WA), 2020; pp. 1–20.
- Magoulas, P.L.; El-Hattab, A.W. Glycogen Storage Disease Type IV - GeneReviews™ - NCBI Bookshelf. In GeneReviews [internet]; Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Ed.; University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2021: Seattle (WA), 2019; pp. 1–16.
- Akman, H.O.; Lossos, A.; Kakhlon, O. GBE1 Adult Polyglucosan Body Disease - GeneReviews™ - NCBI Bookshelf. In GeneReviews [internet]; Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Ed.; University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2021: Seattle (WA), 2020; pp. 1–14.
- Labrador, E.; Weinstein, D.A. Glycogen Storage Disease Type VI - GeneReviews™ - NCBI Bookshelf. In GeneReviews [internet]; Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Ed.; University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2021: Seattle (WA), 2019; pp. 1–14.
- Musumeci, O.; Bruno, C.; Mongini, T.; Rodolico, C.; Aguennouz, M.; Barca, E.; Amati, A.; Cassandrini, D.; Serlenga, L.; Vita, G. et al. Clinical features and new molecular findings in muscle phosphofructokinase deficiency (GSD type VII). Neuromuscular Disorders 2012, 22, 325–330, doi:10.1016/j.nmd.2011.10.022.
- Naini, A.; Toscano, A.; Musumeci, O.; Vissing, J.; Akman, H.O.; DiMauro, S. Muscle phosphoglycerate mutase deficiency revisited. Archives of Neurology 2009, 66, 394–398, doi:10.1001/archneurol.2008.584.
- Santer, R.; Steinmann, B.; Schaub, J. Fanconi-Bickel Syndrome - A Congenital Defect of Facilitative Glucose Transport. Current Molecular Medicine 2002, 2, 213–227.
- Mamoune, A.; Bahuau, M.; Hamel, Y.; Serre, V.; Pelosi, M.; Habarou, F.; Nguyen Morel, M.A.; Boisson, B.; Vergnaud, S.; Viou, M.T. et al. A Thermolabile Aldolase A Mutant Causes Fever-Induced Recurrent Rhabdomyolysis without Hemolytic Anemia. PLoS Genetics 2014, 10, doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004711.
- Wigley, R.; Scalco, R.S.; Gardiner, A.R.; Godfrey, R.; Booth, S.; Kirk, R.; Hilton-Jones, D.; Houlden, H.; Heales, S.; Quinlivan, R. The need for biochemical testing in beta-enolase deficiency in the genomic era. JIMD Reports 2019, 50, 40–43, doi:10.1002/jmd2.12070.
- Tegtmeyer, L.C.; Rust, S.; Van Scherpenzeel, M.; Ng, B.G.; Losfeld, M.E.; Timal, S.; Raymond, K.; He, P.; Ichikawa, M.; Veltman, J. et al. Multiple phenotypes in phosphoglucomutase 1 deficiency. New England Journal of Medicine 2014, 370, 533–542, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1206605.
- Krag, T.O.; Ruiz-Ruiz, C.; Vissing, J. Glycogen synthesis in glycogenin 1-deficient patients: A role for glycogenin 2 in muscle. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2017, 102, 2690–2700, doi:10.1210/jc.2017-00399.
- Bali, D.S.; Chen, Y.-T.; Austin, S.; Goldstein, J.L. Glycogen Storage Disease Type I. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J., Stephens, K., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington, Seattle: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993.
- Leslie, N.; Bailey, L. Pompe Disease. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J., Stephens, K., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington, Seattle: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993.
- Dagli, A.; Sentner, C.P.; Weinstein, D.A. Glycogen Storage Disease Type III. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J., Stephens, K., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington, Seattle: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993.
- McMillan, B.M.; Hirshberg, J.S.; Cosgrove, S.C. McArdle disease causing rhabdomyolysis following vaginal delivery. Anaesth. Rep. 2019, 7, 73–75.
- Martín, M.A.; Lucía, A.; Arenas, J.; Andreu, A.L. Glycogen Storage Disease Type V. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J., Stephens, K., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington, Seattle: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993.
- Goldstein, J.; Austin, S.; Kishnani, P.; Bali, D. Phosphorylase Kinase Deficiency. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J., Stephens, K., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington, Seattle: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993.
- Zhu, Q.; Wen, X.Y.; Zhang, M.Y.; Jin, Q.L.; Niu, J.Q. Mutation in PHKA2 leading to childhood glycogen storage disease type IXa: A case report and literature review. Medicine 2019, 98, e17775.
- Tegtmeyer, L.C.; Rust, S.; Van Scherpenzeel, M.; Ng, B.G.; Losfeld, M.E.; Timal, S.; Raymond, K.; He, P.; Ichikawa, M.; Veltman, J. et al. Multiple phenotypes in phosphoglucomutase 1 deficiency. New England Journal of Medicine 2014, 370, 533–542, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1206605.
- Krag, T.O.; Ruiz-Ruiz, C.; Vissing, J. Glycogen synthesis in glycogenin 1-deficient patients: A role for glycogenin 2 in muscle. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2017, 102, 2690–2700, doi:10.1210/jc.2017-00399.
