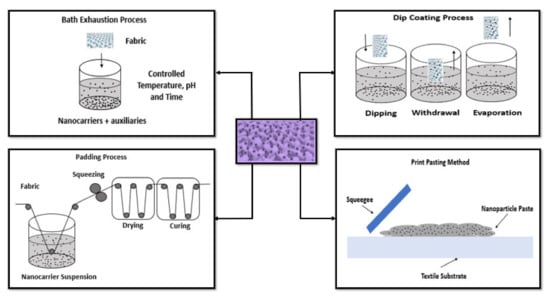
The use of nanoparticles is a multidisciplinary approach to provide UV blocking, antimicrobial, water repellent, colorant, flame retardant, sensing, and self-cleaning properties to textiles. Particularly, the antimicrobial textiles with improved functionalities find several applications, namely, in health and hygiene products, infection control, and barrier material. Depositing nanoparticles in textiles have been a promising strategy to achieve multifunctional materials. Particularly, antimicrobial properties are highly valuable due to the emergence of new pathogens and the spread of existing ones. Various techniques have been used by researchers to functionalize natural and synthetic fibers with AuNPs such as sputtering, electrostatic assembly, chemical reduction in solution, dip-coating, electroless plating, drop and dry, biosynthesis, and print pasting method.
- gold nanoparticles
- in situ
- textiles
- antibacterial properties
1. Gold Nanoparticles
2. Methods to Prepare Textile Materials Functionalized with AuNPs
| Method for Synthesis of AuNPs | Deposition Method | Fabric/Textile | Precursor Salt | Reducing Agent | Stabilizing Agent | Additional Information | Size of NPs | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical reduction | Drop-wise deposition | Cotton, silk, wool, polyester and nylon—F | Chloroauric acid (0.001 M) | Sodium borohydride solution of (0.1 M, 3 mL) | Sodium citrate 3 mL solution of 0.001 M | Sodium citrate also act as capping agent | n.a. | Wearable sensors | [48] |
| Chemical reduction | Padding | Cotton—F | Chloroauric acid (0.01 Wt %, 50 mL) | Trisodium citrate (1 wt%) | No stabilizing agent | Keratin coating (360 mL of keratin solution (10 mg/mL concentration). | 71.8 nm | Antimicrobial textiles | [49] |
| Chemical reduction | Printing and paste method | Polyester—F | Gold (III) chloride hydrate | Sodium citrate | No stabilizing agent | One step green procedure | 13–20 nm | Coloration, UV protection | [42] |
| Chemical reduction, seed-mediated growth | Immersion | Silk and cotton—F | Tetrachloroauric acid (0.01 M, 0.25 mL) Tetrachloroauric acid (0.01 M, 20 mL) |
Sodium borohydride (0.01 M, 0.6 mL) Ascorbic acid (0.1 M, 3.2 mL) |
CTAB (0.1 M) 9.75 mL CTAB (0.1 M) 400 mL |
Au nanorods with spherical shape. | 19 nm | Textile’s collation, UV protection, and antibacterial | [50] |
| In situ chemical reduction | Immersion and heating | Nylon—F | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (0.05, 0.10, 0.15 and 0.20 mM) | Trisodium citrate | Trisodium citrate | pH value is in the range of 5.0–6.5 as per the concentration. | n.a. | UV blocking textiles | [51] |
| Chemical reduction | Exhaustion | Soybean—KF | Tetrachloroauric acid 0.01% W/V | Sodium citrate dihydrate (1% W/V, 2 mL) | Chitosan | Treatment with chitosan; spherical shape. | 34.6 ± 0.5 nm | UV blocking and antimicrobial textiles | [52] |
| In situ chemical reduction | Impregnation | Cotton, silk, and wool—F | Hydrogen tetrachloroaurate (III) trihydrate | Sodium borohydride (1.3 g/L) | n.a. | AuNPs are mixed with other nanoparticles such as Ag and Pt; AuNPs have spherical shape. | 6.64 nm | Antimicrobial textiles | [53] |
| In situ synthesis, groups on silk | Immersion and constant shaking at 85 °C | Silk—F | Gold (III) chloride (0.5–2 mM) | Silk macro molecular chains | Silk fabric | Hydrogen peroxide used for activation of silk macro molecules. | 22–66 and 18–49 nm | Fabric coloration and antimicrobial properties | [54] |
| In situ synthesis, sericin from silk | Soaking and sonication | Silk—F | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (10 mg/mL, 500 mL) | Reduction by sericin from silk | n.a. | Spherical and ellipsoidal; pH = 12. | 11 ± 4 nm | Antimicrobial textiles | [55] |
| Chemical reduction | Immersion | Polypropylene—NW | Tetrachloroauric Acid (1 mM) | Gallic acid (0.5 mM) | Without stabilizer | Surface activation by dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) and diffuse coplanar surface barrier discharge (DCSBD). | 20 nm | Antimicrobial textiles | [56] |
| n.a. | Deposition-precipitation | Poly(ethylene terephthalate—NW | Tetrachloroauric acid (5 mmol/L) | n.a. | n.a. | Fabric coated with ZrO2 fine particles before deposition of AuNPs at pH = 7 | n.a. | Air filter | [57] |
| In situ chemical reduction | Immersion | Cotton—F | Tetrachloroauric acid (10 mM) | Polydopamine (2 mg/mL) | n.a. | Treated with polydopamine before depositing nanoparticles; AgNPs were deposited prior to AuNPs at pH = 8.5. | n.a. | Catalysis | [58] |
| In situ chemical reduction | Immersion and stirring | Cotton—F | Hydrogen tetra-chloroaurate (III) trihydrate HAuCl4 (1 mL, 20 mM) | N-vinyl pyrrolidone (0.1 mL) | 1-Hexadecylamine | Surface modification by ATS is crucial for the formation of gold nano particles; spherical shaped. | 2–7 nm | Textile coloration | [59] |
| Chemical reduction | Dip coating | Cotton—F | Sodium tetrachlorocuprate (III) dihydrate (1%, 90 µL) | Trisodium citrate (1%, 2.7 mL) | n.a. | Cotton fabric precoated with Zn nanorods before deposition of AuNPs. | 18.5 ± 2.8 nm | Photocatalysis | [60] |
| In situ chemical reduction | Soaked in solution | Polyethylene-coated polypropylene—NW | Chloroauric acid | Amine groups grafted in textile surface | Amine groups grafted in textile surface | PE-coated PP fabric was used as a ligand and template; fabric is treated by the electron beam; spherical shape. | 5–20 nm | n.a. | [61] |
| Chemical reduction | Soaked in solution of AuNPs solution | Nylon-6—F | Tetrachloroauric acid (0.0863 g) | Oleylamine | n.a. | – | 14.6 ± 1.4 nm | Catalytic systems | [62] |
| In situ synthesis, tyrosine groups on silk fiber | Immersed in solution and heating | Silk—F | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid Various concentrations |
Tyrosine groups on silk fiber | Tyrosine groups on silk fiber | Different shapes were observed according to the Wt % of the precursor solution. | 21.3 ± 3.4 nm | Textile colorations and antimicrobial effect | [63] |
| In situ synthesis | Immersion and heating | Silk—F | Tetrachloroauric acid (0.1–0.6 mM, 50 mL) | n.a. | n.a. | Spherical, triangular nanoplates, truncated nanoprisms, and polygonal; depend on concentration of the precursor solution. | n.a. | Fabric coloration | [64] |
| In situ synthesis, sericin from silk | Immersion and heating | Silk—F | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (0.3 mM) | n.a. | n.a. | The pH value of solutions was adjusted to 3; spherical and platelike shape. | n.a. | Fabric coloration and antimicrobial properties | [65] |
| Biological reduction | Pad-dry-cure | Cotton—F | Chloroauric acid (0.001 M, 2.5 mL) | Acorus calamus rhizome extract (2.5 mL) | Plant extract | Small spherical ball and bigger spherical ball, and it depends on the concentration at pH = 4, 7 and 9.2. | (0.001 M) below 100 nm (0.01 M) 100–500 nm |
Antibacterial and UV blocking | [66] |
| Biological reduction |
Sonication | Cotton and viscose—KF | Tetrachloroauric acid (3 mM, 100 mL) | Bacterial isolates (Streptomyces Sp) | Streptomyces Sp | Plasma treatment along with the combination of TiO2NPs and ZnONPs spherical shape. | 4–13 nm | Antimicrobial and UV- blocking textiles | [67] |
| In situ synthesis, hydroxyl groups on cellulose | In situ synthesis | Cotton—KF | Tetrachloroauric acid (0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.10, and 0.125 mM) | Hydroxyl groups from cellulose | n.a. | Cotton also acted as a reducing agent; spherical and triangular nanoplates. | 8.7 ± 1.2, 8.6 ± 1.3, 14.1 ± 3.0, 17.4 ± 3.0, and 20.5 ± 3.8 nm | Catalytic, UV blocking, and antibacterial textiles | [68] |
| In situ synthesis, hydroxyl groups on cellulose | Dip and dry | Cotton and polyester—F | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (5.88 × 10−4 M, 198 mL,) | Hydroxyl groups on cellulose | Natural rubber latex | – | 31 nm | Catalytic textiles | [69] |
| Biological reduction | Pad dry cure | Cotton—F | Tetrachloroauric acid (0.001 M and 0.1 M, 2.5 mL) | Coleus aromaticus leaf extract (2.5 mL) | Coleus aromaticus leaf extract | Spherical, rod, and triangular shapes, pH = 7. | Different sizes (<20 nm) | Antimicrobial textiles | [70] |
| Biological reduction |
Pad-dry-cure | Cotton—F | Chloroauric acid (0.001 M) | Croton sparsiflorus leaves Extract | Croton Sparsiflorus leaves extract | Low concentration: bulbous shape high concentration: spherical shape; the fabric was pre-treated through scouring and bleaching. |
12.2–12.7 High concertation 16.6 nm. |
UV protection, antibacterial, and anticancer | [71] |
| Biological reduction | Dry-jet wet spinning process | Cellulose—NW | Tetrachloroauric acid (0.03 mL/g, 50 mM) | Bleached birch pre-hydrolyzed kraft pulp | n.a. | – | n.a. | UV blocking | [72] |
| In situ biological reduction | Immersion | Silk and cotton—F | Tetrachloroauric acid (2.00 × 10−4 M, 80 mL) | Ginkgo biloba Linn leaf powder extract | n.a. | Rectangular, spherical, hexagonal with smooth edges, or roughly circular in shape. | 10–75 nm | Textile colorations and antimicrobial effect | [73] |
| In situ chemical reduction | Immersion | Silk and cotton—F | Tetrachloroauric acid (2.00 × 10−4 M, 80 mL) | Potassium borohydride | n.a. | – | n.a. | ||
| In situ biological and chemical reduction | Immersion | Silk and cotton—F | Tetrachloroauric acid (2.00 × 10−4 M, 80 mL) | Ginkgo biloba Linn leaf powder extract and potassium borohydride | n.a. | – | n.a. | ||
| In situ photoreduction | Immersion | Silk—F | Tetrachloroauric acid (0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, and 0.7 mM) | n.a. | n.a. | In situ synthesized AuNPs on through the induction of sunlight; spherical shape. | 16.9 ± 1.2, 24.1 ± 1.7, 23.0 ± 2.1, 20.6 ± 1.2, 19.9 ± 1.3, and 28.4 ± 1.6 nm | Fabric coloration | [74] |
| Heating and photochemical | Exhaustion | Wool—F | Tetrachloroauric acid (0.2 mM) | Trisodium citrate, D-Malic acid disodium salt or disodium tartrate (1 mM) |
Trisodium citrate | Spherical and egg shapes were observed for heating method and photochemical synthesis at pH 4, respectively. | Various sizes | Textile coloration | [75] |
| n.a. | Electrodeposition | Polyester—F | Gold (III) chloride trihydrate (20 mM) | n.a. | n.a. | Coating single-walled carbon nanotubes on the polyester textile substrate before AuNPs deposition. | 50 nm | Fuel cells—conductive fabrics | [76] |
2.1. Functionalization of Fabrics with AuNPs
2.1.1. Chemical Reduction Method without Pre-Treatments on Fabrics
2.1.2. Chemical Reduction Method with Pre-Treatments on Fabrics
2.1.3. Chemical Reduction Method Using Thermal Treatment
2.1.4. Green-Bio Synthesis
2.1.5. Electrochemical Synthesis
2.2. Functionalization of Fibers/Yarns/Threads with AuNPs
| Method for Synthesis of AuNPs | Deposition Method | Fabric/Textile | Precursor Salt | Reducing Agent | Stabilizing Agent | Additional Information | Size of NPs | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photochemical reduction | Exhaustion | Silk and nylon—Fb | Tetrachloroauric acid (0.2 mM) | Trisodium citrate, D-malic acid disodium slat, and disodium tartrate (1 mM) | Trisodium citrate | Spherical and egg shapes were observed for heating method and photo chemical synthesis at pH = 4, respectively | Various sizes | Textile coloration | [75] |
| Chemical reduction | Soaked in solution | Cotton—T | Hydrogen tetrachloroaurate (0.65 mM) | Sodium citrate tribasic dihydrate | n.a. | SERS technique was used to detect and analyze adsorbed gold nanoparticles. | 20 and 60 nm | Diagnostics for surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) spectroscopy | [77] |
| Chemical reduction | Immersion and capillary action | Cotton—T | Tetrachloroauric acid solution 2% (V/V) | Sodium citrate (2% (M/V)) | n.a. | Spherical shape; used HCl and NaOH for pH. | 20–40 nm | Surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection | [78] |
| Chemical reduction | Sonication | Cellulose—Fb | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (0.5 mM, 20 mL) | Sodium squarate in water | Sodium squarate in water | AuNPs synthesized in water; Spherical in shape. | 21.01 nm | Catalysis | [79] |
| Chemical reduction | Immersion and stirring | Cotton—Y | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (1 mM) | Trisodium citrate dihydrate (4 mM) | Citrate | pH 3–4. | 13 nm | Human motion sensor/wearable sensor | [80] |
| In situ chemical reduction | Soaking in solution | Silk fibroin—Fb | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (10 mmol L−1) | Sulfonated polyaniline (20 mL of 5 wt %) | n.a. | Sulfonated polyaniline modified fibers catalytic reduction reaction of p-nitrophenol by NaBH4 |
50–100 nm | Catalysis | [81] |
| In situ chemical reduction | Immersion | Ramie—Fb | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid with different concentrations | Sodium borohydride | n.a. | AuNPs were synthesized in acidic condition, pH = 2–6. | n.a. | Textile coloration and antimicrobial textiles | [82] |
| In situ chemical reduction | Immersion and stirring | Cellulose—Fb | Tetracholoroaurate (0.5 mM) | Sodium rhodizonate | Sodium rhodizonate | Size depends on temperature; spherical shape. | 11 nm at 23 °C and 7 nm at 80 °C | Catalysis | [83] |
| Chemical reduction | Immersion and stirring | Cellulose—Fb | Gold chloride (AuCl3) | p-nitro-aniline (2 mM) Sodium borohydride (150 mM) |
Cellulosic macromolecules | n.a. | 26.1 nm | Catalysis | [84] |
| Chemical reduction | Electroless deposition | Gold/graphene—Y | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (1.6 mM) | Hydroxylamine | n.a. | Spherical to plate; dependent on reaction time. | 40 nm | Wearable electronics | [85] |
| Chemical reduction | Immersion | Regenerated cellulose—Fb | Gold (III) chloride triydrate (1 mM) | Trisodium citrate (1%, 2.2 mL) | Trisodium citrate | Fibers were grafted with positive charge; spherical shape | 40–50 nm | colorimetry and surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) assays | [86] |
| Chemical reduction | Sonication | Cotton—T | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (0.01%, W/V) | Trisodium citrate | n.a. | AuNPs coated on CNTs CNTs were functionalized with PDDA; homogenous surface. |
15 nm | Immunological chromatographic sensor | [87] |
| Chemical reduction | Centrifugation | Cotton—T | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (0.01%, W/V) | Trisodium citrate | n.a. | AuNPs coated on CNTs CNTs were functionalized with PDDA; homogenous surface. |
15 ± 3 nm | Immunological chromatographic sensor | [88] |
| In situ green synthesis | Immersion | Cotton—Fb | Hydrogen tetrachloroaurate (III) hydrate (0.05 mM) | Osmanthus fragrans 10% (m/v) | Osmanthus fragrans | Spherical and hexagonal shape. | 40 and 60 nm | Heterogeneous catalyst | [89] |
| Biological reduction | Soaking | Silk—Fb | Tetrachloroauric acid (10−3 M) | Citrus paradisi extract | n.a. | Quasi-spherical | 30 nm | Textile coloration | [90] |
2.2.1. Chemical Reduction Method without Pre-Treatments on Fabrics
2.2.2. Chemical Reduction Method with Pre-Treatments
2.2.3. Reduction with Photochemical Treatments
2.2.4. Green Synthesis
2.3. Functionalization of Nanofibers/Scaffolds/Membranes with AuNPs
| Deposition Method | Fabric/Textile | Precursor Salt | Reducing Agent | Stabilizing Agent | Additional Information | Size of NPs | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method for Synthesis: Biological reduction | ||||||||
| Electrospinning solution | Polyacrylonitrile—NF | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (0.001 M) | Banana peel extract, phenolic compounds and flavonoids | n.a. | Spherical shape. | 9 nm | Electrochemical sensors | [2] |
| Method for Synthesis: Chemical reduction | ||||||||
| Electrospinning solution | Polyimide—NF | Gold (III) chloride hydrate | Thermal treatment at 200 °C in polyimide nanofibers | n.a. | Thermally reduced Au3+ to Au0. | n.a. | n.a. | [18] |
| Immersion | Crystalline cellulose—NF | Tetrachloroauric acid | Sodium borohydride | n.a. | - | <5 nm | Catalysis | [91] |
| Immersion | Bacterial cellulose—NF | Tetrachloroauric acid | Poly (ethyleneimine) | Poly(ethyleneimine) | Spherical shape. | ≈9 nm | Biosensors | [92] |
| Immersion | Bacterial cellulose—NF | Tetrachloroauric acid (20 mM) | Poly (ethyleneimine) | n.a. | BC nanofibers are produced by ultrasonic cell disruption system at room temperature. | ≈9 nm | Biosensors | [93] |
| Immersion | Cellulose acetate (mats)—NF | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (1 Wt %, 3 mL) | Trisodium citrate | Trisodium citrate | LBS self-assembly technique. | – | Antimicrobial textiles | [94] |
| Immersion | Thermoplastic polyurethane—NF | Hydrogen tetrachloroaurate | Trisodium citrate | Chitosan | Precoated with chitosan reduction in 4-nitrophenol by sodium borohydride, pH value 3–11. |
16 nm | Catalysis | [95] |
| Electrospinning solution | PCL/Gelatin—NF/S | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid | Sodium borohydride | n.a. | Process is done in the presence of antibiotic intermediates. | 3 nm | Antimicrobial textiles, wound treatment | [96] |
| Soaking | Bacterial cellulose—M | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (40 mg mL−1) | Sodium borohydride | n.a. | Gold nanoparticles modified with 4,6-Diamino-2-Pyrimidinethiol (DAPT). | ≈3 nm | Antimicrobial textiles, wound treatment | [97] |
| Electrospinning solution | PEI/PVA—NF | Chloroauric acid (0.5 mM) | Sodium borohydride | n.a. | The fibrous were cross-linked via glutaraldehyde (GA) vapor to produce water-stable fibrous mats; round shaped. | 11.8 nm | Catalysis | [98] |
| Electrospinning solution | Polycaprolactone—NF | Chloroauric acid (0.5 mM) | Sodium borohydride (1.25 mM) | n.a. | Round shape. | 5–6 nm | Heterogeneous catalysis and SERS | [99] |
| Immersion and shaking | PET track-etched micro-porous—M | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (1 mg mL−1) | Dopamine on membranes | n.a. | Coated with dopamine. | n.a. | Catalysis | [100] |
| Dropping | Polyamide—NF/M | Hydrogen tetrachloroaurate (III) (1.00 mM) | Trisodium citrate dihydrate (0.30 M) | Trisodium citrate dihydrate | Spherical | 20.1 ± 1.76 nm | Colorimetric sensor | [101] |
| Immersion | Bacterial cellulose—NF | Chloroauric acid (0.4 mM) | Sodium borohydride (6 mM) | n.a. | 2,2,3,3-tetramethylpiperidine-l-oxyl (TEMPO)-oxidized (TOBCNS); spherical shape. | 4.30 ± 0.97 nm | Catalysis | [102] |
| Immersion | Cellulose—NF | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid solution (0.2 mM) | Hydrazine hydrate | n.a. | Unsupported AuNPs. | 18.3 ± 3.5 nm | Catalysis | [103] |
| Method for Synthesis: In situ chemical reduction | ||||||||
| Electrospinning solution | Polyacrylonitrile—NF | Hydrogen tetrachloroaurate (III) trihydrate | 4-(Dimethylamino) benzaldehyde | n.a. | – | 6 nm | Biosensors | [104] |
| Soaking | Cellulose Acetate—M | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid | Dithiothreitol (DTT) | Porous fiber network | DTT capped AuNPs. | 2.5 ± 0.5 nm | Sensors | [105] |
| Electrospinning solution | Zein—NF | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (20 mM, 0.25 mL) | Poly(ethyleneimine) | n.a. | Spherical shape; value of pH 3.0–7.0. | 90.9 nm | Biosensors | [106] |
| Electrospinning solution | Polyacrylonitrile—NF | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (0.30 mmol) | n.a. | n.a. | Au-PANF was prepared and electrospun to form mats; spherical shape. | 2.3 ± 0.5 nm | Sensors | [107] |
| Electrospinning solution | Polyimide—NF | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (0.5, 1, and 3 Wt %) | Polyimide and high temperature (200 °C) | Polyimide | Reduction takes place due to thermal reactions. | 9–22 nm | High temperature end-of-service indicators | [108] |
| Immersion | Cellulose—M | Potassium gold (III) chloride | Sodium borohydride | Poly(diallyl-dimethylammonium chloride) poly(sodium-p-styrenesulfonate) |
Membranes previously coated with titania gel. | 3.5 ± 0.7 nm | n.a. | [109] |
| Immersion and continuous shaking | PET track-etched microporous—M | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (1 mg mL−1) | Sodium borohydride | n.a. | Coated with dopamine. | n.a. | Catalysis | [100] |
| Method for Synthesis: Photoreduction | ||||||||
| Electrospinning solution | Polystyrene (mats)—NF | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid (3% (W/W) | Ultraviolet irradiation | n.a. | Undergone electrospinning and then mats exposed to UV light. | n.a. | n.a. | [110] |
| Method for Synthesis: In situ photoreduction | ||||||||
| Electrospinning solution | Polyacrylonitrile—NF | Gold (III) chloride hydrate(0.044 M, 0.022 M) | Sodium alginate | n.a. | UV light has been used during electrospinning; spherical shape. | 21.4 nm (0.044 M) 5.8 nm (0.022 M) |
n.a. | [111] |
| Electrospinning solution | Polyacrylonitrile—NF | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid | N,N-dimethylformamide | n.a. | Undergone electrospinning and then mats exposed to UV light. | 4.7–5.4 nm (5 days of UV radiation) | n.a. | [112] |
| Immersion | Cellulose—NF | Tetrachloroauric (III) acid solution (0.2 mM, 20 mL) | Cellulose nanocrystals | Cellulose nanocrystals | CNs were produced from microcrystalline cellulose. | 30.5 ± 13.4 nm | Catalysis | [103] |
| Immersion | Bacterial cellulose—M | Tetrachloroauric acid (0.2, 0.4, 0.6 mM) | n.a. | n.a. | Xenon lamp was used in the process of synthesis of AuNPs; spherical shape. |
n.a. | Sensors | [113] |
| Method for Synthesis: Laser ablation | ||||||||
| Electrospinning solution | Polyacrylonitrile—NF | Gold plate | n.a. | n.a. | Spherical shape; face centered cubic crystal structure with crystallite size of 8 nm. | 17 nm | Glucose sensors | [114] |
2.3.1. Chemical Reduction Method without Pre-Treatments
2.3.2. Chemical Reduction Method with Pre-Treatments
2.3.3. Chemical Reduction by Photo Reduction/UV Radiation/Photo Reduction
2.3.4. Green Synthesis
2.3.5. Reduction with Thermal Treatments
2.3.6. Reduction with Other Treatments
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/nano11051067