To date, natural products are widely used as pharmaceutical agents for many human diseases and cancers. One of the most popular natural products that have been studied for anticancer properties is thymoquinone (TQ). As a bioactive compound of Nigella sativa, TQ has shown anticancer activities through the inhibition of cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. The anticancer efficacy of TQ is being investigated in several human cancers such as pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, colon cancer, hepatic cancer, cervical cancer, and leukemia.
- thymoquinone
- cancers
- proliferation
- apoptosis
- angiogenesis
- nanoparticle
Note: The following contents are extract from your paper. The entry will be online only after author check and submit it.
1. Introduction
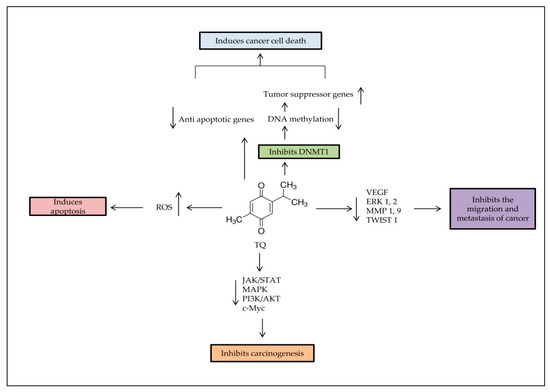
Thymoquinone (TQ) is one of the bioactive constituents in Nigella sativa (N. sativa), black seed, or Alhabba Al-Sauda [1]. TQ and other N. sativa components such as α-pinene, p-cymene, and monoterpenes have been used as an antineoplastic, antioxidant, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory agent [2]. It has shown effectiveness against several diseases, such as liver diseases [3] and brain disorders, like Parkinson’s [4] and Alzheimer’s diseases [5]. TQ enhances the immune system and prevents oxidative damage of healthy cells [6]. TQ has shown different anticancer activities through cell proliferation inhibition, apoptosis induction, or interference with other tumorigenic processes, such as cell migration, invasion, and altering epigenetic events alteration in cancer cells [7,8]. TQ selectively inhibits the cancer cells’ proliferation in leukemia [9], breast [10], lungs [11], larynx [12], colon [13,14], and osteosarcoma [15]. However, there is no effect against healthy cells [16]. TQ also demonstrates antitumor properties by regulating different targets, such as nuclear factor kappa B (NF-Kb), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ), and c-Myc [1], which resulted in caspases protein activation [17]. It also re-expressed tumor suppressor genes (TSG), such as p53 and Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) in lung cancer [18]. In the present study, data from more than 60 relevant published experimental articles on TQ effects individually or combined with other compounds, on cancers between January 2015 to June 2020 were included by using Google Scholar and PubMed search engines. Books, chapters or review articles published were excluded.
2. Properties and Pharmacological Features of TQ
3. TQ and Nanotechnology
3.1. Polymeric TQ Nanoparticles

3.2. Lipid-Based TQ Nanoparticles
3.3. Chitosan-Based TQ Nanoparticles
4. Anti-Cancer Effects of TQ
4.1. Breast Cancer
4.2. Lung Cancer
| Name of Drug | Action of Drug | References |
|---|---|---|
| Cisplatin | Induction of DNA damage through Pt-mediated DNA crosslinking (Alkylating-like mechanism) | [71] |
| Temozolomide (TMZ) | DNA damage through alkylation and cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase | [72] |
| Tamoxifen (TAM) | Anti-estrogens (compete with estrogen to bind with estrogen receptor) | [73] |
| Topotecan (TP) | Topoisomerase-I inhibitor | [74] |
| Paclitaxel (Pac) | Interfere in mitotic spindle formation through stabilization of microtubule assembly | [64] |
| Docetaxel | Microtubule disrupting agent | [75] |
| miR-34a | MicroRNA | [76] |
4.3. Gastric Cancer
4.4. Colon Cancer
4.5. Prostate Cancer
4.6. Skin Cancer
4.7. Ovarian Cancer
4.8. Liver Cancer
4.9. Cervical Cancer
4.10. Leukemia
4.11. Head and Neck Cancer
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ph14040369
