Plasmonic photocatalysts combining metallic nanoparticles and semiconductors have been aimed as versatile alternatives to drive light-assisted catalytic chemical reactions beyond the ultraviolet (UV) regions, and overcome one of the major drawbacks of the most exploited photocatalysts (TiO2 or ZnO). The strong size and morphology dependence of metallic nanostructures to tune their visible to near-infrared (vis-NIR) light harvesting capabilities has been combined with the design of a wide variety of architectures for the semiconductor supports to promote the selective activity of specific crystallographic facets. The search for efficient heterojunctions has been subjected to numerous studies, especially those involving gold nanostructures and titania semiconductors. In the present review, we paid special attention to the most recent advances in the design of gold-semiconductor hetero-nanostructures including emerging metal oxides such as cerium oxide or copper oxide (CeO2 or Cu2O) or metal chalcogenides such as copper sulfide or cadmium sulfides (CuS or CdS). These alternative hybrid materials were thoroughly built in past years to target research fields of strong impact, such as solar energy conversion, water splitting, environmental chemistry, or nanomedicine.
- Non-Titania Based Semiconductors
- Gold Plasmonics
- Heteronanostructures
1. Introduction
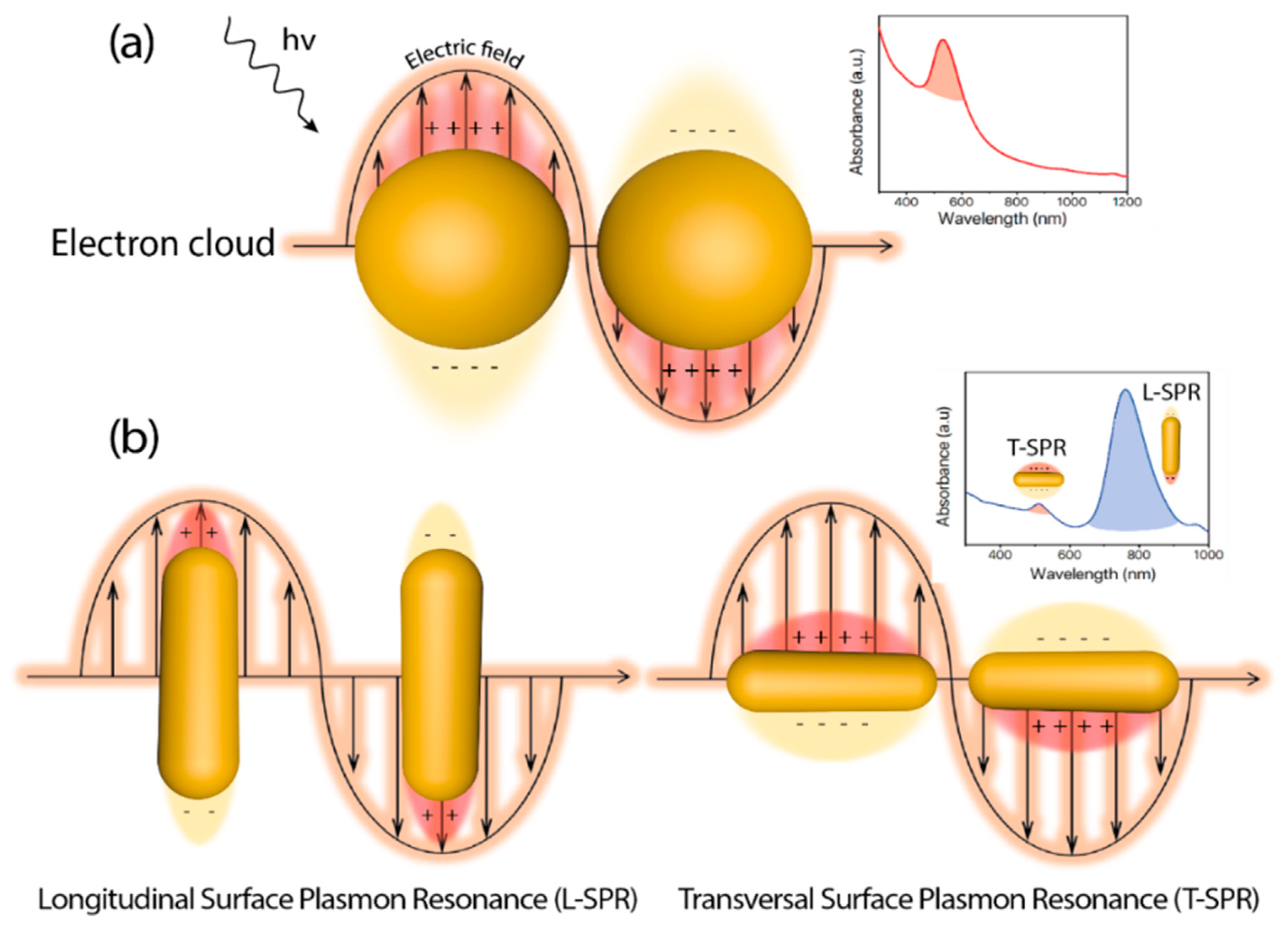
Since the first reported example of heterogeneous photocatalysis in 1911 applied to the degradation of Prussian Blue by ZnO powder and illumination [1], the degree of sophistication and complexity in photocatalyst design has experienced a huge development [2]. In heterogeneous photocatalysis, the process is initiated by the interaction between incident photons and the catalyst. The photon absorption by the catalyst (typically a semiconductor) leads to the promotion of valence band electrons into the conduction band, thereby creating electron-hole pairs. Those carriers can induce the subsequent generation of free radicals (e.g., hydroxyl (OH), superoxide (O2−)) to target specific chemical reactions. As a requirement, the energy of the incident photon (hν) must be equal or higher than the energy band gap (Eg) of the catalyst, meaning that the incident electromagnetic wavelength must be energetic enough to overcome the barrier to excite an electron from the highest occupied energy levels to the lowest unoccupied levels. Well-established semiconductor-based photocatalysts, such as TiO2 or ZnO possess high Eg values (3.05 [3] and 3.3 [4] eV, respectively) and are constrained to the more energetic ranges of the solar spectrum (i.e., UV window representing only up to 5% of the solar radiation) for an effective photoactivation. Abundant efforts have been devoted in the past decades to expand the photocatalytic response of heterogeneous semiconductor photocatalysts towards the visible and infrared ranges in order to maximize the absorption of the solar spectrum [5][6][7][8][9]. One of the most promising and explored strategies has consisted on the combination of semiconductor structures with noble-metal based nanoparticles [10][11][12]. Recent reviews available in the literature have deepened into the synergistic action of small metal nanoparticles decorating semiconductors and on how the controlled architecture of the latter may have a strong influence on the final photocatalytic outcome [13][14][15][16][17][18][19][20]. Another interesting aspect of metallic nanostructures correlates with their unique optical response that can be modulated upon variations of their specific size and morphology [19][20][21][22][23]. At the interface between the metal surface and other medium (with different dielectric properties), exist a phenomenon known as Localized Surface Plasmon (LSP) that consist on a coherent delocalized electron oscillation leading to the generation of an electromagnetic field both outside and inside the metal. An excitation with radiation of the right wavelength causes a resonance interaction and subsequent collective oscillation of conduction electrons, in the case of metallic materials, due to the restoring force between electrons and nuclei through Coulombic attraction (Figure 1). This phenomenon is called Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance (LSPR), and for metals like Au, Ag, or Cu, the LSPR may take place over a wide range of 400–1300 nm [24] as a function of their size and shape (Figure 1). Thus, metallic nanoparticles emerge as perfect candidates as visible near infrared (NIR) light harvesters to combine and improve the efficiency of semiconductor photocatalysts.
So far, TiO2 has been set as one of the most explored semiconductors to form hetero-nanostructures in combination with metals to overcome its limited photo-response beyond UV window [25][26] that can overcome its one of the most widely used semiconductors to carry out photocatalytic reactions. Systematic evaluation of Au-TiO2 hybrid systems exploring the role and influence of shape, specific configuration, heterojunction conformations, and so on, have been developed in the past years. Numerous and varied architecture designs have been successfully reported including core-shell (concentric and eccentric) [27][28], yolk-shell [29], Janus type structures [28], or even multi-component heterostructures [30][31] and their performance successfully tested towards energy and environmental applications [17][18][31][32][33]. The generation and assembly of these hetero-nanostructures offers multiple advantages but the number of alternative candidates to TiO2 still remains as an open challenge. The present review intends to overview the most recent advances described in the literature involving the design of hybrid photocatalysts combining plasmonic Au nanoparticles and non-titania based semiconductor coatings organized in a wide variety of nanoarchitectures (vide infra). Herein, we paid special attention to plasmonic hybrids that involved the selection of anisotropic Au nanostructures (mostly nanorods (AuNRs) and nanostars (AuNSs)) and a controlled growth of semiconductors beyond the most typically studied (i.e., TiO2 [27][34][35] or ZnO [5][36][37]). This approach allows a fine control of sizes for both metal and semiconductor, reduces the probability of recombination of carriers, and maximizes an intimate contact to form efficient heterojunctions [38]. In contrast, other methodologies lack sufficient control on the size and dispersion of metal nanoparticles or the corresponding supports. Furthermore, many times these semiconductor nanoparticle supports require additional tuning or post-treatments to ensure the exposure of preferential facets that do not necessarily prevent numerous bulk recombination events due to their inherent polydispersity [13]. Hence, recent research innovative trends, such as cancer therapy, require more accurate control of the photocatalysts dimension for proper internalization in cells and accurate reproducibility [39]. Therefore, we consider that the efforts made to improve the generation of novel plasmonic photocatalysts with a controlled size and distribution in a core-shell (or analogous nanoarchitecture) and/or semiconductor supports represents a very promising alternative to other metal-semiconductor configurations [13].
2. Metal-Semiconductor Hetero-Nanostructures: Different Configurations and Light-Driven Activation Mechanisms
A key feature of plasmonic photocatalysts is related with the photo-induced generation of highly energetic electrons (hot electrons) generated via LSPR [40]. The distribution of these hot electrons can be described by the Fermi equation using an elevated effective temperature [41]. After light absorption, LSPR decay may occur either radiatively, through re-emitted photons, or non-radiatively, for instance through transfer of hot electrons [42], generally through intraband excitations within the conduction band [40][43] thereby causing electrons from occupied energy levels to be excited above the Fermi energy. Hence, after coupling with metals, typical semiconductors used in photocatalysis can capture these hot electrons and generate reactive species by using visible-NIR light. The formation of metal-semiconductor heterojunctions allows hot electrons to be accepted into semiconductor conduction band and carry on the photocatalytic process (Figure 2a). The energetic barrier formed at the metal-semiconductor interface is called Schottky barrier [44]. Hot electrons are injected into semiconductor conduction band when their energy is superior to Schottky barrier energy (ESB) which is lower than the bandgap of semiconductor (Eg) [45]. After the hot electron generation, holes are also generated in the plasmonic structure as illustrated in Figure 2b. For this mechanism to occur there must be a good interaction between the metal and the support, which make critical the synthesis step of these hybrid materials.
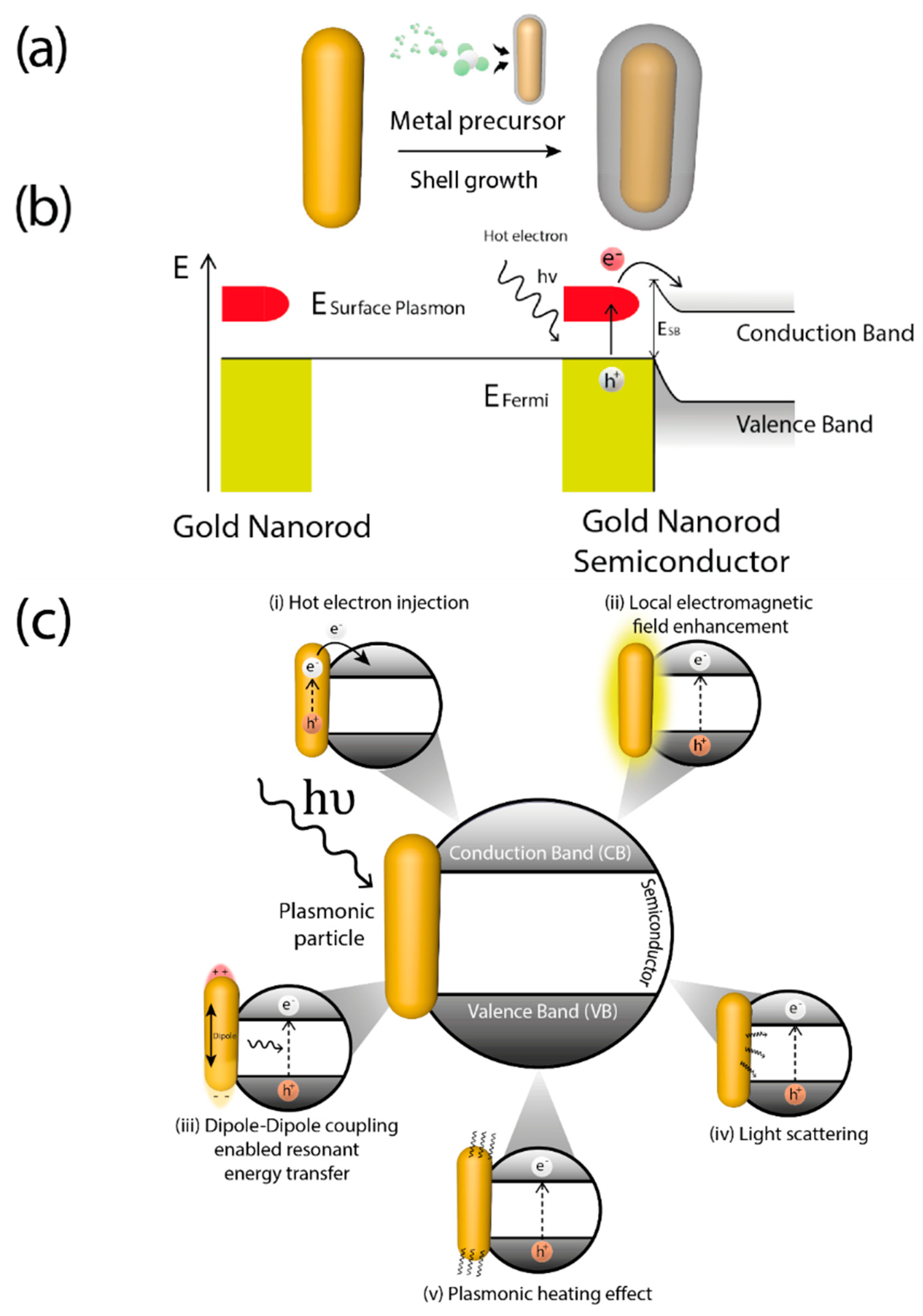
Nevertheless, several mechanisms could be involved independently or, most often, concurrently in photocatalysis using hybrid plasmonic materials [46]. Depending on the interaction of the plasmonic nanoparticle with the support and the electronic characteristic of the latter, plasmonic excitation can improve the photocatalytic properties of materials in several ways: (i) increasing absorption and scattering of light [47]; (ii) enhancing of the localized electric field [48]; (iii) hot charge carriers generation and transfer [49], already mentioned; (iv) dipole induction on non-polar molecules [50]; (v) local heat generation [46][51], depicted in Figure 2c.
Since nature, size, shape, and crystalline structure of the nanoparticle determine the energy of the LSPR [52] and in consequence the wavelength of the light used in photocatalysis, the control of those cited parameters is fundamental for the synthesis of suitable hybrid materials [53][54][55]. Concretely, the introduction of anisotropy in plasmonic-semiconductor systems adds a superior level of performance. Plasmonic Au cores exhibit a wide range of anisotropic nanostructures (nanoshells, nanorods, hollow spheres, nanoprisms, triangles, cubes, nanostars, urchins, etc.) with different LSPR [8][18][24][31][52][56] (Figure 3a). Typically, plasmon energy is concentrated on the sharpest edges of the anisotropic plasmonic nanostructures of high curvature [57][58][59] where light harvesting will take place more efficiently [60].
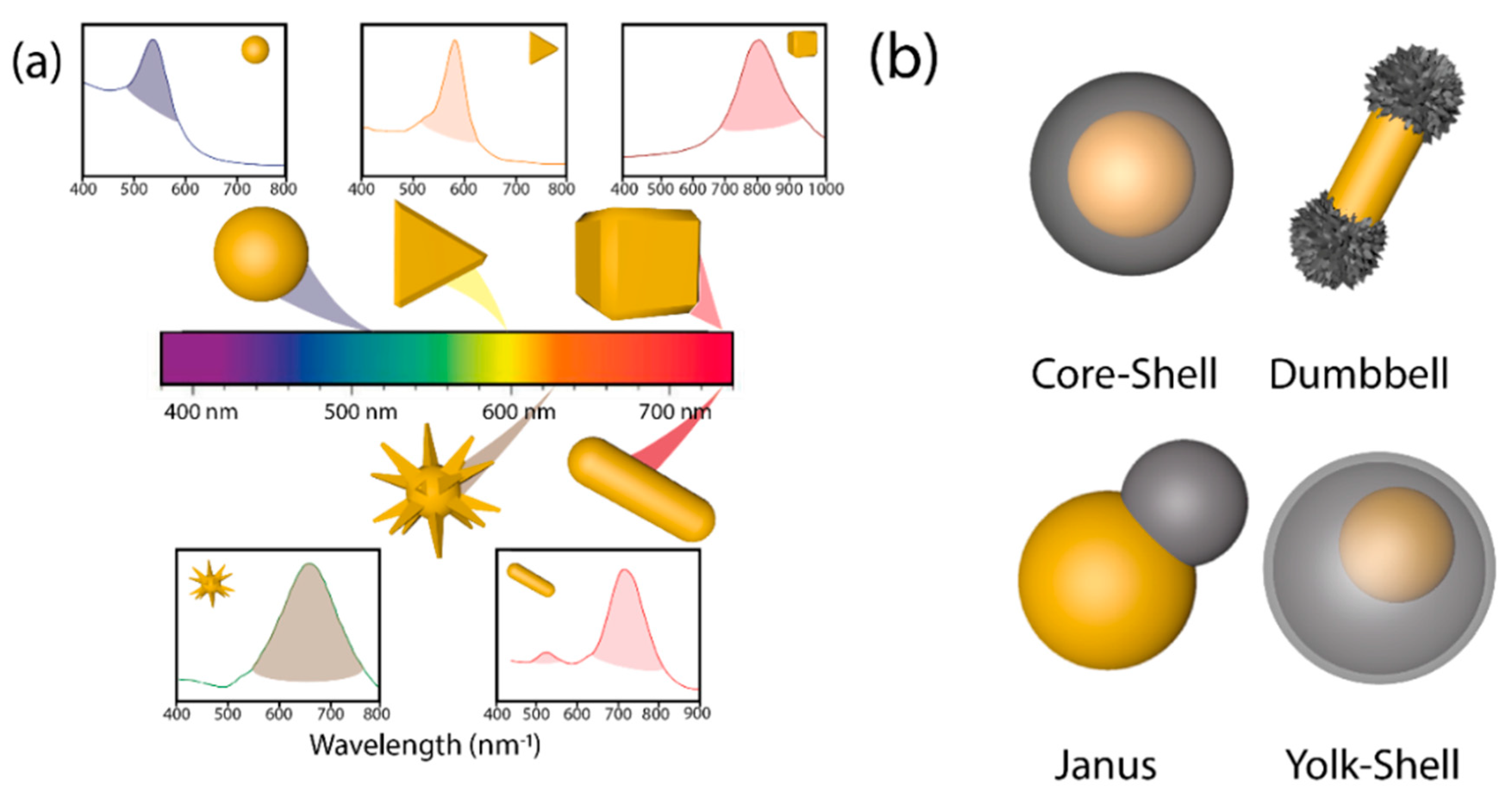
As shown in Figure 3b, it is possible to differentiate between core-shell, dumbbell, Janus, and yolk-shell configurations attending to the semiconductor distribution around the metallic cores [38] with several implications in their photocatalytic activity. Structures with exposed surfaces of both the metal and the semiconductors (i.e., dumbbell and Janus) exhibit a superior photocatalytic performance due to the continuous exposure of the reactants with the generated charge carriers (e−/h+) [27][40][60][61][62][63][64]. Different anisotropic heterostructures have been prepared with SiO2 [65], Pt [66][67], Fe2O3 [68], Cu2O [60], CeO2 [63], and TiO2 [27]. Yolk-shell structures (Figure 3b) are characterized by a hollow shell and an inner plasmonic core with several benefits for the photocatalytic process: (i) the presence of a hollow shell ensures higher specific surface area as it possesses an inner and external part. (ii) The small thickness of shells shortens charge diffusion distance, reducing possible bulk recombination processes, and (iii) void space present allows reflection of light inside the hollow shell, causing light scattering, and boosting the number of available photons [69].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/catal10121459
References
- Eibner, A.J.C.-Z. Action of light on pigments I. Chem-Ztg 1911, 35, 753–755.
- Coronado, J.M. A historical introduction to photocatalysis. In Design of Advanced Photocatalytic Materials for Energy and Environmental Applications; Coronado, J.M., Fresno, F., Hernández-Alonso, M.D., Portela, R., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 2013; pp. 1–4.
- Reyes-Coronado, D.; Rodríguez-Gattorno, G.; Espinosa-Pesqueira, M.E.; Cab, C.; de Coss, R.; Oskam, G. Phase-pure TiO2nanoparticles: Anatase, brookite and rutile. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 145605.
- Bakin, A.; El-Shaer, A.; Mofor, A.C.; Al-Suleiman, M.; Schlenker, E.; Waag, A. ZnMgO-ZnO quantum wells embedded in ZnO nanopillars: Towards realisation of nano-LEDs. Phys. Status Solidi C 2007, 4, 158–161.
- Bueno-Alejo, C.J.; Graus, J.; Arenal, R.; Lafuente, M.; Bottega-Pergher, B.; Hueso, J.L. Anisotropic Au-ZnO photocatalyst for the visible-light expanded oxidation of n-hexane. Catal. Today 2020.
- Ortega-Liebana, M.C.; Hueso, J.L.; Ferdousi, S.; Arenal, R.; Irusta, S.; Yeung, K.L.; Santamaria, J. Extraordinary sensitizing effect of co-doped carbon nanodots derived from mate herb: Application to enhanced photocatalytic degradation of chlorinated wastewater compounds under visible light. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 218, 68–79.
- Suarez, H.; Ramirez, A.; Bueno-Alejo, C.J.; Hueso, J.L. Silver-copper oxide heteronanostructures for the plasmonic-enhanced photocatalytic oxidation of N-hexane in the visible-NIR range. Materials 2019, 12, 3858.
- Graus, J.; Bueno-Alejo, C.J.; Hueso, J.L. In-situ deposition of plasmonic gold nanotriangles and nanoprisms onto layered hydroxides for full-range photocatalytic response towards the selective reduction of p-nitrophenol. Catalysts 2018, 8, 354.
- Mas, N.; Hueso, J.L.; Martinez, G.; Madrid, A.; Mallada, R.; Ortega-Liebana, M.C.; Bueno-Alejo, C.; Santamaria, J. Laser-driven direct synthesis of carbon nanodots and application as sensitizers for visible-light photocatalysis. Carbon 2020, 156, 453–462.
- Kawamura, G.; Matsuda, A. Synthesis of plasmonic photocatalysts for water splitting. Catalysts 2019, 9, 982.
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Mu, X. Plasmonic photocatalysts monitored by tip-enhanced raman spectroscopy. Catalysts 2019, 9, 109.
- Gong, Z.; Ji, J.; Wang, J. Photocatalytic reversible reactions driven by localized surface plasmon resonance. Catalysts 2019, 9, 193.
- Wei, Z.; Janczarek, M.; Wang, K.; Zheng, S.; Kowalska, E. Morphology-governed performance of plasmonic photocatalysts. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1070.
- Fang, J.; Cao, S.-W.; Wang, Z.; Shahjamali, M.M.; Loo, S.C.J.; Barber, J.; Xue, C. Mesoporous plasmonic Au–TiO2 nanocomposites for efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic water reduction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 17853–17861.
- Fragua, D.M.; Abargues, R.; Rodriguez-Canto, P.J.; Sanchez-Royo, J.F.; Agouram, S.; Martinez-Pastor, J.P. Au–ZnO nanocomposite films for plasmonic photocatalysis. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 2, 1500156.
- Kim, M.; Lin, M.; Son, J.; Xu, H.; Nam, J.-M. Hot-electron-mediated photochemical reactions: Principles, recent advances, and challenges. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2017, 5, 1700004.
- Liu, J.; Ma, N.; Wu, W.; He, Q. Recent progress on photocatalytic heterostructures with full solar spectral responses. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124719.
- Volokh, M.; Mokari, T. Metal/semiconductor interfaces in nanoscale objects: Synthesis, emerging properties and applications of hybrid nanostructures. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 930–961.
- Ghosh Chaudhuri, R.; Paria, S. Core/Shell nanoparticles: Classes, properties, synthesis mechanisms, characterization, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2373–2433.
- Dutta, S.K.; Mehetor, S.K.; Pradhan, N. Metal semiconductor heterostructures for photocatalytic conversion of light energy. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 936–944.
- Li, B.; Gu, T.; Ming, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.C. (Gold Core)@(Ceria Shell) nanostructures for plasmon-enhanced catalytic reactions under visible light. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 8152–8162.
- Jia, H.; Du, A.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Jiang, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.-Y. Site-selective growth of crystalline ceria with oxygen vacancies on gold nanocrystals for near-infrared nitrogen photofixation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 5083–5086.
- Chen, T.-M.; Xu, G.-Y.; Ren, H.; Zhang, H.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Li, J.-F. Synthesis of Au@TiO2 core–shell nanoparticles with tunable structures for plasmon-enhanced photocatalysis. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 4522–4528.
- Liu, T.-M.; Conde, J.; Lipiński, T.; Bednarkiewicz, A.; Huang, C.-C. Revisiting the classification of NIR-absorbing/emitting nanomaterials for in vivo bioapplications. NPG Asia Mater. 2016, 8, e295.
- Ola, O.; Maroto-Valer, M.M. Review of material design and reactor engineering on TiO2 photocatalysis for CO2 reduction. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2015, 24, 16–42.
- Habisreutinger, S.N.; Schmidt-Mende, L.; Stolarczyk, J.K. Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 on TiO2 and other semiconductors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7372–7408.
- Wu, B.; Liu, D.; Mubeen, S.; Chuong, T.T.; Moskovits, M.; Stucky, G.D. Anisotropic growth of TiO2 onto gold nanorods for plasmon-enhanced hydrogen production from water reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 1114–1117.
- Seh, Z.W.; Liu, S.; Low, M.; Zhang, S.Y.; Liu, Z.; Mlayah, A.; Han, M.Y. Janus Au-TiO2 photocatalysts with strong localization of plasmonic near-fields for efficient visible-light hydrogen generation. Adv. Mater. (Deerfield Beach Fla.) 2012, 24, 2310–2314.
- Sun, H.; He, Q.; Zeng, S.; She, P.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Z. Controllable growth of Au@TiO2 yolk–shell nanoparticles and their geometry parameter effects on photocatalytic activity. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 7244–7252.
- Li, J.-M.; Tsao, C.-W.; Fang, M.-J.; Chen, C.-C.; Liu, C.-W.; Hsu, Y.-J. TiO2-Au-Cu2O photocathodes: Au-mediated z-scheme charge transfer for efficient solar-driven photoelectrochemical reduction. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 6843–6853.
- Han, C.; Qi, M.-Y.; Tang, Z.-R.; Gong, J.; Xu, Y.-J. Gold nanorods-based hybrids with tailored structures for photoredox catalysis: Fundamental science, materials design and applications. Nano Today 2019, 27, 48–72.
- Yu, X.; Liu, F.; Bi, J.; Wang, B.; Yang, S. Improving the plasmonic efficiency of the Au nanorod-semiconductor photocatalysis toward water reduction by constructing a unique hot-dog nanostructure. Nano Energy 2017, 33, 469–475.
- Zhu, M.; Wang, Y.; Deng, Y.-H.; Peng, X.; Wang, X.; Yuan, H.; Yang, Z.-J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Strategic modulation of energy transfer in Au-TiO2-Pt nanodumbbells: Plasmon-enhanced hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 7035–7044.
- Wang, L.; Chong, J.; Fu, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, J.; Huang, M. A novel strategy for the design of Au@CdS yolk-shell nanostructures and their photocatalytic properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 834, 155051.
- Atta, S.; Pennington, A.M.; Celik, F.E.; Fabris, L. TiO2 on Gold Nanostars Enhances Photocatalytic Water Reduction in the Near-Infrared Regime. Chem 2018, 4, 2140–2153.
- Sun, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, T.; Chen, G.; Zhang, F.; Liu, D.; Cai, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, C. Complete Au@ZnO core–shell nanoparticles with enhanced plasmonic absorption enabling significantly improved photocatalysis. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 10774–10782.
- Shao, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, B.; Shao, L.; Wu, Y. Au@ZnO core–shell nanostructures with plasmon-induced visible-light photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical properties. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 934–943.
- Jiang, R.; Li, B.; Fang, C.; Wang, J. Metal/Semiconductor hybrid nanostructures for plasmon-enhanced applications. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5274–5309.
- Zhou, N.; López-Puente, V.; Wang, Q.; Polavarapu, L.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Xu, Q.-H. Plasmon-enhanced light harvesting: Applications in enhanced photocatalysis, photodynamic therapy and photovoltaics. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 29076–29097.
- Clavero, C. Plasmon-induced hot-electron generation at nanoparticle/metal-oxide interfaces for photovoltaic and photocatalytic devices. Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 95–103.
- Semenov, A.D.; Gol tsman, G.N.; Sobolewski, R. Hot-electron effect in superconductors and its applications for radiation sensors. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 2002, 15, R1–R16.
- Knight, M.W.; Wang, Y.; Urban, A.S.; Sobhani, A.; Zheng, B.Y.; Nordlander, P.; Halas, N.J. Embedding plasmonic nanostructure diodes enhances hot electron emission. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 1687–1692.
- White, T.P.; Catchpole, K.R. Plasmon-enhanced internal photoemission for photovoltaics: Theoretical efficiency limits. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 073905.
- Tung, R.T. The physics and chemistry of the Schottky barrier height. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2014, 1, 011304.
- Knight, M.W.; Sobhani, H.; Nordlander, P.; Halas, N.J. Photodetection with active optical antennas. Science 2011, 332, 702.
- Zhang, N.; Han, C.; Fu, X.; Xu, Y.-J. Function-oriented engineering of metal-based nanohybrids for photoredox catalysis: Exerting plasmonic effect and beyond. Chem 2018, 4, 1832–1861.
- Kochuveedu, S.T.; Jang, Y.H.; Kim, D.H. A study on the mechanism for the interaction of light with noble metal-metal oxide semiconductor nanostructures for various photophysical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8467–8493.
- Liu, Z.; Hou, W.; Pavaskar, P.; Aykol, M.; Cronin, S.B. Plasmon resonant enhancement of photocatalytic water splitting under visible illumination. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 1111–1116.
- Tian, Y.; Tatsuma, T. Plasmon-induced photoelectrochemistry at metal nanoparticles supported on nanoporous TiO2. Chem. Commun. 2004, 1810–1811.
- Cushing, S.K.; Li, J.; Meng, F.; Senty, T.R.; Suri, S.; Zhi, M.; Li, M.; Bristow, A.D.; Wu, N. Photocatalytic activity enhanced by plasmonic resonant energy transfer from metal to semiconductor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 15033–15041.
- Christopher, P.; Ingram, D.B.; Linic, S. Enhancing photochemical activity of semiconductor nanoparticles with optically active Ag nanostructures: Photochemistry mediated by ag surface plasmons. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 9173–9177.
- Kelly, K.L.; Coronado, E.; Zhao, L.L.; Schatz, G.C. The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: The influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 668–677.
- Tian, N.; Zhou, Z.-Y.; Sun, S.-G.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Synthesis of tetrahexahedral platinum nanocrystals with high-index facets and high electro-oxidation activity. Science 2007, 316, 732.
- Ming, T.; Feng, W.; Tang, Q.; Wang, F.; Sun, L.; Wang, J.; Yan, C. Growth of tetrahexahedral gold nanocrystals with high-index facets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16350–16351.
- Wang, F.; Li, C.; Sun, L.-D.; Wu, H.; Ming, T.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.C.; Yan, C.-H. Heteroepitaxial growth of high-index-faceted palladium nanoshells and their catalytic performance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 1106–1111.
- Lu, B.; Liu, A.; Wu, H.; Shen, Q.; Zhao, T.; Wang, J. Hollow Au–Cu2O core–shell nanoparticles with geometry-dependent optical properties as efficient plasmonic photocatalysts under visible light. Langmuir 2016, 32, 3085–3094.
- Xia, X.; Zeng, J.; McDearmon, B.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Xia, Y. Silver nanocrystals with concave surfaces and their optical and surface-enhanced raman scattering properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 12542–12546.
- Yin, P.-G.; You, T.-T.; Tan, E.-Z.; Li, J.; Lang, X.-F.; Jiang, L.; Guo, L. Characterization of tetrahexahedral gold nanocrystals: A combined study by surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy and computational simulations. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 18061–18069.
- Rodríguez-Lorenzo, L.; Álvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Mazzucco, S.; Stéphan, O.; Kociak, M.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; García de Abajo, F.J. Zeptomol detection through controlled ultrasensitive surface-enhanced raman scattering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4616–4618.
- Hong, J.W.; Wi, D.H.; Lee, S.-U.; Han, S.W. Metal–semiconductor heteronanocrystals with desired configurations for plasmonic photocatalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 15766–15773.
- Simon, T.; Bouchonville, N.; Berr, M.J.; Vaneski, A.; Adrović, A.; Volbers, D.; Wyrwich, R.; Döblinger, M.; Susha, A.S.; Rogach, A.L.; et al. Redox shuttle mechanism enhances photocatalytic H2 generation on Ni-decorated CdS nanorods. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 1013–1018.
- Zhao, Q.; Ji, M.; Qian, H.; Dai, B.; Weng, L.; Gui, J.; Zhang, J.; Ouyang, M.; Zhu, H. Controlling structural symmetry of a hybrid nanostructure and its effect on efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1387–1392.
- Pan, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Shi, Z.; Wang, X.; Song, S.; Zhang, H. Half-encapsulated Au nanorods@CeO2 Core@Shell nanostructures for near-infrared plasmon-enhanced catalysis. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1516–1524.
- Mubeen, S.; Lee, J.; Singh, N.; Krämer, S.; Stucky, G.D.; Moskovits, M. An autonomous photosynthetic device in which all charge carriers derive from surface plasmons. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 247–251.
- Wang, F.; Cheng, S.; Bao, Z.; Wang, J. Anisotropic overgrowth of metal heterostructures induced by a site-selective silica coating. Angew. Chem. (Int. Ed. Engl.) 2013, 52, 10344–10348.
- Zheng, Z.; Tachikawa, T.; Majima, T. Single-particle study of Pt-modified Au nanorods for plasmon-enhanced hydrogen generation in visible to near-infrared region. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6870–6873.
- Yang, H.; Wang, Z.-H.; Zheng, Y.-Y.; He, L.-Q.; Zhan, C.; Lu, X.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Fang, P.-P.; Tong, Y. Tunable wavelength enhanced photoelectrochemical cells from surface plasmon resonance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 16204–16207.
- Bao, Z.; Sun, Z.; Li, Z.; Tian, L.; Ngai, T.; Wang, J. Plasmonic gold−superparamagnetic hematite heterostructures. Langmuir 2011, 27, 5071–5075.
- Li, A.; Zhu, W.; Li, C.; Wang, T.; Gong, J. Rational design of yolk–shell nanostructures for photocatalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1874–1907.
