Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Engineering, Civil
The Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry is one of the most dangerous industries due to its unique nature. Safety is a critical issue in developed and developing countries. Barriers that hinder the implementation of safety in projects and ways to improve safety performance was illustrated in this entry.
- safety practice
- barriers
1. Introduction
Accidents and injuries can lead to significant losses for individuals themselves, organizations, and communities [1], but occupational safety is still neglected in developing countries because of competing social, economic, and political barriers [2]. Reference [3] pointed out that poor performance safety increases overall health and safety (H&S) costs. Barriers in developing countries are diverse, lacking the development and implementation of occupational health and safety (OHS) standards, in general [4]. In addition, work strategies do not include OHS regulations, and the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry continues to rely on labor more than equipment, which includes 2.5 to 10 times the number of workers per activity [4]. One of the possible reasons for safety research to be a major concern among construction companies may be the cost of accidents, either directly or indirectly [5]. In general, safety performance is still affected by several barriers [6]. So, it is necessary to investigate the root causes of construction accidents for the purpose of improvement construction safety [7]. Based on that, this study will concentrate on safety barrier identification, classification, and ways to improve safety performance in the interest of enhancement in the safety practice.
1.1. Management Barriers
Safety management is the procedure used to identify Health & Safety (H&S) risks and to implement procedures to reduce the probability of risk and minimize or eliminate the potential results of H&S risks to the project [8]. The sound management of individuals, equipment, and the environment are of particular importance [9]. However, the OHS management system has turned out to be a neglected area and a function which has not been systematically applied to the AEC industry [10], wherein contractors often respond to time and cost constraints by limiting investment in safety management, which can increase the frequency and intensity of construction site accidents.
The working environment is more dangerous for small institutions than for large corporations [11]. For example, in Europe, 82% of all occupational accidents occur in small institutions with higher work-related accident rates than in large companies in all industrial sectors. In addition, risk management interventions in small institutions are inefficient [12].
The main problem in developing countries is the legislation on OHS at workplace. The concept of occupational hazards and risks globally, where in developing countries don’t take safety seriously because they either don’t have or have inadequate legislation to reduce these are risks [2]. And addition poor and inadequate health and safety rules and regulations are lead to the occurrence of the accidents in developing countries [6,7]. Reference [13] referred to the main reason of accidents is lack of attention from leaders.
According to Reference [14], safety communication between managers and workers is one of the five necessary safety management practices that distinguish between high and low percentage accidents at the postal workplace. Reference [15] considered how communication problems and the difference in language, religion, and culture tend to prevent safety at worksite. Reference [12] also stated that the main difficulties in this for management stem from communication failures. As a result, lack of communication between managers and workers during construction can lead to poor workmanship, accidents, delays, and misreporting. These, in turn, can incur considerable costs and time because sometimes you cannot see the project manager on the site or just see them for only few hours [1].
Reference [16] expressed that training is designed to prevent human errors that may cause accidents and make workers able to perform a skillfully repetitive task. It is also the most effective tool for risk mitigation. And Reference [14] said the safety training is any attempt to improve performance on task that is a responsibility. In addition, the acquisition of ‘specific skills or knowledge’, ‘displaying poster’, ‘issuing of safety booklet [17]. As well Reference [18] has identified safety training as a major factor influencing H&S levels. And a lot of workers know that the training is very important, but they would not devote 30 min to an hour of training because their focus was to accomplish the task at a faster rate and get their wages [16]. Since safety programs in many sites are not conducted for the engineers, skilled, and unskilled laborers, orientation is given to the engineer, skilled, and unskilled laborers, but not referred to as hazard [15]. In India, as an example of developing countries, there are no training programs for staff and workers; thus, no guidance was given to new or employed staff. Workers had to learn from their own experiences [18].
The obligation of the owner and the participation of employees are key features of the implementation of the occupational health & safety management system (OHSMS); therefore, initiatives should be simple, short, clear, and relevant to specific tasks [12]. Reference [14] clarifies management commitment as a particular and decisive part of safety climate, which refers to workers’ understanding of the extent of their managers appreciation, as in their support of safe working and overall devotion to workers’ safety. As mentioned, management commitment to safety is foresight for worker job-related safety behaviors and accidents injuries.
Reference [15] has indicated that poor maintenance of equipment is also a major cause of accidents. Maintenance and inspection schedules are often not followed, and the equipment is repaired after damage and breakdown. This approach leads to time loss, unemployed workers, and project delays.
Regular safety inspections help management maintain safe working practices by monitoring unsafe practices at workplace. By helping your employees check safety, awareness remains high, and staff learn more about safety risks [16,17]. Reference [7] clarifies that failure of the management to conduct inspections of conditions, workers, materials, and equipment at sites will result in accidents. Additionally, the importance of the administration conducting the examination on a regular basis so that any weaknesses or problems occurring in the sites could be resolved in a timely manner and early action could be taken to prevent the accident.
A safety meeting is a pool in the workplace that includes all members of the construction team to discuss H&S issues [16]. Safety meetings provide an opportunity to provide new safety and information training. It also provides an opportunity for workers to review previously learned information. Without safety meetings, workers can relax with routine and slowly reduce vigilance and attention to safety while doing the same tasks day after day [17]. However, on many sites, safety meetings are not held [15].
According to Reference [18], developing countries suffer lack of various machines and equipment to process materials on the construction site, and this can be a major factor that causes a high level of injury, like those caused by lifting heavy, unusual, or irregular materials; when most of a country tends to have more labor-intensive construction industries, employers may resist the use of modern technology to reduce labor costs. In addition, because of government policy and high unemployment, public sector customers may require the most intensive use of labor.
Reference [19] clarifies big factors that contribute to the occurrence of accidents, such as most structures that are built are based on unsupported designs, many of which are inappropriate, poor quality materials, use of inappropriate construction methods/techniques; insufficient supervision is a major factor contributing to accidents at construction sites, as well as lack of commitment, weak implementation of H&S regulations, and lack of maintenance. There is also little regard for insurance, lack of experience, poor communication, and language barrier issues.
Other problems that can effect safety performance are inadequate personal protective equipment at work; lack of safety promotion; lack of documentation and organized safety management (SM) systems; safety practices approved at construction sites that are well below acceptable standards; lack of conducting safety meetings, monitoring safety performance, and the inclusion of safety issues at regular meetings; less support for incentive or punitive programs; lack of proper supervision; workers who are not protected because safety regulations were not fully established; lack of technical guidance; lack of experienced project managers; poor information flow; poor safety policies; insufficient safety budget; and lack of emergency plan and procedures [1,6,7,15,18].
At the end, Reference [18] clarified that the successful H&S management system program is based on the premise that management and line functions are responsible for H&S.
1.2. Culture Barriers
Culture is a phenomenon that has been created by people, represents the way communities live, and determines how everyone appears at work [2,3]. Culture is the behavior of people, how to create systems of work, procedures, and routines to follow, and how can anyone formally or unofficially agree to follow such processes so that they can become the norm [3]. The United Kingdom executive director of H&S described safety culture as “the product of individual and collective values, attitudes, competencies and behavior patterns that define commitment to the organization’s H&S program” [20]. The “set of beliefs, criteria, attitudes and expectations shared by members of a community, organization or group” was another definition by Reference [21]. For decades, “culture” has been used as a management feature [3,22]. The safety culture is the key component of the SM system of an organization [23]. Where the considered the relationship between safety culture and safety performance is both qualitative and quantitative of theoretical study and experimental Reference [23]. Reference [24] said the strengthening of SM is always the highest priority in construction work. Promoting a safety culture will be one of the most effective ways. At the same time, Reference [25] said safety culture should be understood as an expression of organizational culture. And establishing a culture of safety is a priority for senior management, and the safety culture at the project level is also reflected in the behavior of the project manager [25]. But staff are responsible for following procedures and thinking about how they work, where additional duty should not be considered [2].
SM can reflect and affect the company’s safety culture [25]. And organizations with a positive safety culture are characterized by trust-based communication through shared perceptions of the importance of safety and confidence in the efficiency of preventive measures [26].
Safety culture plays critical role in the safety of employees in the workplace [25]. Almost every workplace has safety culture problems. For a good reason, cultures in the workplace grow slowly and can be killed quickly [27]. There are factors that cause a particular problem of safety cultures and lead to negative attitudes towards safety and increase resistance to safety initiatives. Reference [28] said it has been proven that a strong safety culture has a positive impact on safety performance in many industrial conditions.
The lack of a safety culture may be due to a lack of commitment to safety or occupational safety and health administration (OSHA) requirements [1]. Showing commitment at all levels of the organization is an important cultural factor [27]. The commitment is a personal responsibility where employees are committed to applying the safety culture at work [3]. Thus, they will work to safely communicate, learn, adapt, and modify behavior based on committed mistakes [29]. According to Reference [20], safety culture refers not only to the level of compliance with HSE but also refer to the obligation of senior management, which plays main role in its implementation. Whereas senior management should formulate a policy that indicates compliance with safety, management’s commitment was the most important measure for determining the impact of unsafe site performance [21]. Reference [29] mention the main contractors reduce prices or cost by considering the cost of safety first and then paying responsibility to their subcontractors to afford the extra costs when it comes to bidding projects. This behavior, whether they realize it or not, is a guarantee of a culture of safety.
One of the factors impacting safety performance in the AEC industry is the absence of superintendence by the responsible supervisor. There is no regular supervision or project manager staying on site for a few hours at least once a week. The supervisor was found as an intermediary broker to make sure safety practice in the construction project. The conduct of the safety supervisor can affect safety measures that prevent an unexpected accident [1]. In addition, the worker may not report any accident or say anything to the responsible person in site [1]. Reference [15] said, in general, the injury is not documented. Whereas many incidents occur because of careless attitudes of workers regardless of their neglect, from direct monitoring, that indifference should be noted [1]. Reference [18] clarifies lack of a suitable H&S culture in the AEC industry in developing countries, and workers are less responsive to H&S issues.
Safety rules and procedures can reduce accidents caused by unsafe conditions because they give a clear picture and limits to the implementation of the safety program of the construction project. The problems that are often identified are that the rules and procedures are difficult to understand and implement and are not appropriate for the current situation and the specifications [21].
Reference [2] indicate that exploitation and corruption is another example of the factors that affect safety performance; for example, with exploitation in developing countries, the exploitation of labor to work for a long time and cheap salaries is a result of absence or inadequacy of OHS systems or little enforcement. This happens not only for legislative lands but also because of social standards paid for poverty. Corruption plays a negative role in developing safety culture by reducing levels of occupational safety measures. Sometimes legislation exists, but those responsible for enforcing the law do not perform their duties honestly. Unscrupulous organizations exploit this to distance themselves from spending money on safety measures by spending some money as bribes. The management also blames individuals for being responsible for accidents, where the responsibility for the incidents is considered to belong to certain persons [26]. This approach is prominent in organizations based on penal culture, and this approach corresponds to the community’s desire to identify a clear cause of the incident [30]. Reference [26] explained that another reason affecting the safety culture is the feedback loop not being closed after an accident; after an accident, the focus is on the employee, often being committed. The priority is to reduce damage and return to production.
Do not provide resources for success that are also factors that affect safety culture. Staff need some basic resources, such as knowledge and skills, whereas you cannot expect people to follow safety procedures if they do not know the right way to do it or lack the skills to actually implement it [27]. The knowledge, skills, and ability of workers to work, particularly with regard to hazards and risks in their work, may reduce accidents. These competencies can be enhanced through training and chosen suitable workers [21]. Time is also another resource, where work injuries cannot be avoided when production is more important than security and the time of purchase or production approaches faster. These factors can weaken the safety culture, when it may sound like the only safety resources that the company needs to provide to employees are personal protective equipment [27].
1.3. Behavior Barriers
Construction is one of the most dangerous industries in the world, with a large numbers of accidents that lead to death of workers, injuries, and work-related diseases, as well as other serious direct and indirect losses [31]. Safety behaviors are actual behaviors performed by individuals at work [32]. References [33,34] concluded unsafe behavior is the most important element in the cause of site crashes. Where unsafe acts can be defined as human work that is outside the control of risks or work procedures on which the person was trained or aware informed, causing unnecessary exposure to the person [35], unsafe procedures and behaviors cause 80% to 90% of construction accidents [36] and deteriorate a project’s cost and schedule performance [37].
References [37,38,39,40] indicated that construction accidents in the workplace occur because of three basic reasons, like failure to determine an unsafe state which existed prior to the commencement of the activity or which were developed after the commencement of the activity; making a decision to continue the work activity after the worker has identified an unsafe condition; and making a decision to act unsafe regardless of the initial conditions of the work environment. Reference [41] clarify that the Behavioral actions are not limited to impact workers but also include senior management and corporate management personnel.
There are a variety of factors that influence the safety conduct of construction workers. These factors can be broadly grouped into two main groups, both personal and organizational [42], including: marital status, educational level, knowledge of safety, drinking habits, work-related pressure, and work-mates’ safety behavior [42].
Safety knowledge also plays critical role in improving employee behavior and safety [42]. Safety knowledge includes awareness of OHS hazards [43]. Moreover, experts have also made it clear that, if the worker has a lack of safety knowledge and does not understand basic construction specifications, or even does not want to understand the reason or important of safety in construction, there is a greater chance for them to act unsafe during working hours [44]. Therefore, safety knowledge is very important for the development of on-site safety behaviors [42]. As a result, most experienced workers in the industry are unlikely to behave in an unsafe manner during their work. It is normal for workers with years of experience in the industry to get used to safer behaviors than those with less experience, and young workers are more prone to accidents than older workers. Some workers do not have long-term experience in construction work, which leads to less knowledge of the construction environment. However, over time, workers gain greater experience and are, therefore, aware of safety requirements [42,44,45]. Additionally, educational level has a positive influence on workers’ safety behaviors. It is easier to maintain safety standards when the workforce is composed of individuals with a sound educational background [42].
Drinking habits can affect workers’ safety behaviors. Alcohol use at work can expose the drinker and others to greater risk of injury, especially in the workplace where heavy machinery is located. It is estimated that 20–25% of workplace accidents are related to alcohol. According to experts, the excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages leads to decrease productivity, less efficiency, and affects the person’s attitude of safety, as well as his performance. Whether alcohol is used before reaching the workplace, or during work, has an impact on the individual’s behavior and job perception [42,46,47].
Reference [42] clarifies some factors that affect safety behavior, such as marital status and number of dependents; workers also tend to be more cautious in what they do when their social responsibilities are higher. Experts have argued that married workers with more dependents in their families tend to follow safety instructions and guidelines on-site more than others. The worker who does not have a family or does not support anyone is not interested in safety or in its application, and their behavior is random and sometimes insecure. In addition, the worker is influenced by the behavior of his colleagues in the work; if the worker does not wish to highlight the negative features in safety, he is motivated to follow the safety procedures, but sometimes the worker is not motivated and provided guidance to follow the safety, so he follows the negative behavior of his colleagues [42].
The socialization of the worker affects the work of the individual. Organizational socialization is defined as ‘‘the process by which an individual acquires the social knowledge and skills necessary to assume an organizational role”. The process of socialization of new workers as the only mechanism through which employees are trained on safety, as well as the socialization of family and friends and previous experiences, all have an influence on the behavior of the individual at work. In the organization, members explain to them the nature of the organization and the norms and behaviors used in the work, but, unfortunately, the behaviors become a rule. The behaviors are often unsafe [48].
Perceived-risk individuals who are aware of the risks that they can encounter at work, and the effects of them, are more committed to safety, while individuals who are not aware of the risks or are not exposed to a health hazard by working are the people who most often conduct unsafe behavior and are not concerned about safety [48]. When workers always sense that they are working in safe conditions, and therefore neglect the safety procedures required by rules and regulations [16], there is a kind of knowledge and awareness of the dangers, but he still behaves unsafe behavior [48]. Reference [49] showed in his study that a harsh working environment also affects the behavior of the individual, as most activities are carried out under the sun and exposed to weather conditions.
Incentive programs may inadvertently encourage unsafe behavior. If employees realize that the performance of unsafe work practices will increase production, for example, and therefore garner rewards, this behavior will be inadvertently enhanced to continue such behavior [48]. For this reason, production incentives must be relevant and in line with the good performance of safety [45,50].
Improving safety behaviors to reduce unsafe work by employees becomes a confirmed need. As a result, it is believed that strengthening the behavior-based approach of occupational H&S management is to ensure a way to reduce infection rates [42]. Reference [51] pointed to some of the things that can reduce unsafe behavior, like enhancement of the safety of the leaders, improvement of the safety environment of the construction project and supervision of the project safety, and training and consolidation of safety and participation positions.
1.4. Awareness Barriers
Safety awareness is an “individual’s own awareness of safety issues” [51]. With workers’ awareness in construction, OHS is of great importance as it defines individual and organizational behavior. However, the majority of construction workers have low safety awareness, a condition that can have a negative influence on workers and the organization [52]. In global projects, one of the critical safety problems is the viewpoint of local contractors and workers towards safety. Local workers in India and Taiwan have a low level of safety awareness at the construction site [16].
Safety toolbox meetings are one of the main safety programs that organized weekly, monthly, and annually for different stages of workers [53]. In addition, the toolbox or safety meeting is one way of educating workers, where all workers gather in one place and safety officer informs them of safety issues [16]. References [6,52] pointed out how safety meetings work to increasing awareness and to put their safety as their first. When they do not conduct safety meetings before starting work, where they do not apply what they have been taught or have been exposed to, H&S will undoubtedly take a low priority in discussions and budgets.
Poor data management or recordkeeping make it difficult to measure the extent of risk impact and, many countries cannot produce basic data on safety and cannot determine its quantification; thus, it is difficult determine where the problem lies, and then it becomes difficult to take corrective action [2,53].
The main problem with the issue of safety in construction sites is the attitude of workers, and it is found that most workers did not wear personal protective equipment properly due to ignorance, neglect, apathy, and excessive trust [16]. They have less awareness of the importance of wearing appropriate personal protective equipment [15,53]. Reference [20] observe that awareness about the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) reduces the risk of injury. When an accident occurs, workers may receive first aid and medical care, but, in most cases, no specialized medical treatment or compensation is available, and there may be no first aid [15,54].
Reference [51] suggests that there is a direct and positive impact of safety awareness on safety behavior. The effect of awareness on behavior is mainly based on the theory of behavior and behavior. In the meantime, by increasing self-awareness of safety, individual safety behavior could be improved.
2. Management Barriers
Figure 1 shows 29 management barriers from 64 general safety barriers that hinder the implementation of safety in AEC industry beside that, “Lack of safety training” was in first position between the rest barriers based on the number of sources that considered it as a barrier that hinders the implementation of safety in AEC industry. Reference [14] said the safety training is any attempt to improve performance on task that is the responsibility. In addition, ‘specific skills or knowledge acquisition’, ‘poster display’, ‘safety booklet issuance’ [17]. Reference [18] has identified safety training is a major factor influencing H&S levels. And a lot of workers know that the training is very important, but they would not devote 30 min to an hour of training because their focus was to accomplish the task at a faster rate and get their wages [16].
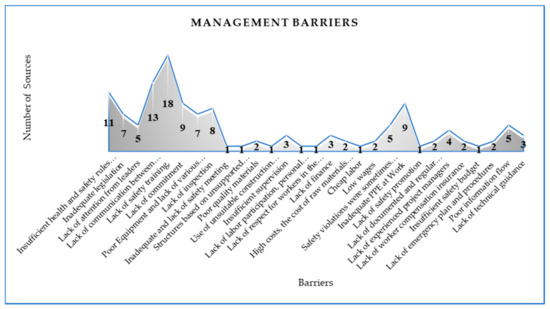
Figure 1. Management barriers based on number of sources.
“Lack of respect for workers in the building construction industry”, “Structures based on unsupported designs, many of which are inappropriate”, “Use of unsuitable construction methods/techniques”, “Lack of labor participation, personal risk assessment and work pressure”, “High costs, the cost of raw materials and telecommunications”, “Cheap labour”, “Safety violations were sometimes ignored in order to maintain the project schedule”, “Lack of safety promotion”, and “Insufficient safety budget” were in last position between the rest of the barriers based on the number of sources that considered it as a barrier that hinders the implementation of safety in AEC industry; but, remaining barriers need to be considered because, based on Reference [63], lack of labor involvement, personal risk assessment and work pressure, lack of respect for workers in the construction industry, lack of finance, high costs, high costs of raw materials, and telecommunications lead to poor performance. According to Reference [64], the availability of cheap labor means that workers are forced to assume unacceptable risks due to fear of being dismissed. And low wages leading to fatigue and slow rate of work due to the inability to afford proper nutrition. In addition, Reference [74] says that additional safety violations were sometimes ignored in order to maintain the project schedule.
3. Culture Barriers
Figure 2 shows 13 culture barriers from 64 general safety barriers that hinder the implementation of safety in AEC industry; beside that, “Lack of commitment” was in first position between the rest of the barriers based on the number of sources that considered it as a barrier that hinders the implementation of safety in AEC industry. This result is due to the fact that on-site staff appear to be unaware of safety issues, probably because they have not been informed of the statistics on serious and fatal accidents at the site, as well as the number of disabilities resulting from such accidents. Unfortunately, the government, represented by the Ministry of Labor, has few and incorrect safety records on construction projects. There is, therefore, little chance for employees to gain any insight into the impact and the number of safety issues involved. This result shows the high importance placed on the availability of safety data by management personnel who use it during orientation sessions for their employees [89]. This result agrees with Reference [90], who clarifies that workers who lack knowledge and skills cannot work safely.
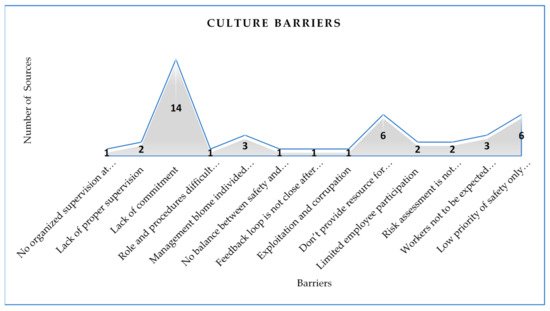
Figure 2. Culture barriers based on number of sources.
“Role and procedures difficult understand and implement”, “No organized supervision at least once a week”, “No balance between safety and profitability “, “Feedback loop is not close after accidents”, and “Exploitation and corruption” were in last position between the rest of the barriers based on the number of sources that considered it as a barrier that hinders the implementation of safety in AEC industry. Some research and scientific sites mentioned some reasons for poor performance and safety culture, including: Reference [26], who indicated that no balance between safety and profitability—profitability is the only attention in the organization. H&S are seen as a cost, and the only priority is to avoid further increases, while researchers, like References [28,70], also explained the factors that affect safety culture and how these factors are limited worker participation where the participation of workers is very important in building workers’ awareness of safety programs [21], in addition, to giving a positive effect to the performance of the company’s safety [91], whilst Reference [37] revealed that successful management in work is built from a positive safety attitude within a group of workers that can be achieved through a culture of good safety.
4. Behavior Barriers
Figure 3 shows 12 behavior barriers from 64 general safety barriers that hinder the implementation of safety in AEC industry; besides that, “Work pressure is high when deadlines are approaching” was in first position between the rest of barriers based on the number of sources that considered it as a barrier that hinders the implementation of safety in AEC industry. It is common that work pressure is high when deadlines are approaching [48]. As a result, work safety among workers was not observed because they were urged to take shortcuts while performing their duties [42,45]. Experts also pointed out that, when a company had to finish a project in a timely manner, workers had to quickly accomplish the task rather than work safely. Workers conduct unsafe behavior to please their bosses and to avoid negative consequences. In this time, the individual suffers overload, and the safety motive is reduced by workers. Thus, the value of safety on performance pressure is often ignored, not only by workers but also management, where they focus on performance rather than safety and consider productivity more important than safety, so it increase accident rates [34,42,48,53]. This result is due to managers’ interest in productivity, saving time and money, pressuring workers to end work, and prioritizing productivity rather than safety.
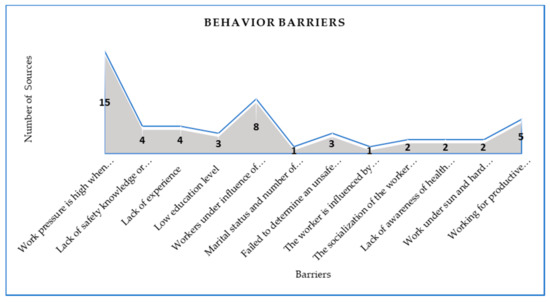
Figure 3. Behavior barriers based on number of sources.
“Marital status and family members to support” was in last position between the rest of the barriers based on the number of sources that considered it as a barrier that hinders the implementation of safety in AEC industry. This finding is due to that the fact that a person who has a family is careful to take care and work in safety, unlike the individual who is living alone and has some kind of carelessness and indifference. But there are some opinions that sometimes a person with a family is rushing to get back to his family and doing the work quickly and without taking the safety factors seriously so as to get back to his family faster. That is the same as the: “The worker is influenced by the behavior of his colleagues in the work, Negative behavior” barrier.
5. Awareness Barriers
Figure 4 shows 10 awareness barriers from 64 general safety barriers that hinder the implementation of safety in AEC industry; beside that, “Low level educated, lack of experience and lack of knowledge” was in first position between the rest barriers based on the number of sources that considered it as a barrier that hinders the implementation of safety in AEC industry. Most construction workers are poorly educated, which is a barrier to improved safety performance [6,63]. Workers have practical skills but lack knowledge and theoretical applications. They do the specific work only to do their duty as a worker, and their main concern is to carry out the task given. Differences in age show a different level of awareness. Young workers often do not have the experience of recognizing and avoiding workplace hazards. The lack of experience sets young workers at greater risk of injury, illness, and death [1]. Reference [42] found that older workers showed more positive attitudes towards safety. Experts have also noticed that older workers are more concerned about safety at work than younger workers in the industry. Young people are enthusiastic and sometimes careless, but, as they age, along with the physical endurance and daringness of workers, they begin to act more responsibly to protect themselves. This result is due to the fact that education, experience, and knowledge are related to the extent to which risks and accidents can be avoided and the extent to which employees comply with H&S standards on site.
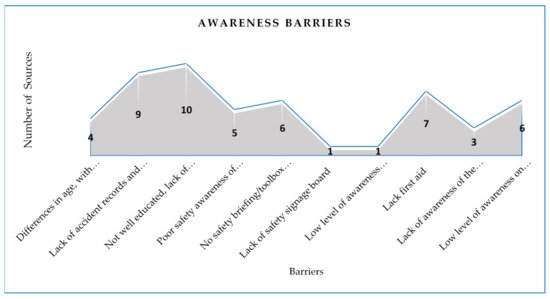
Figure 4. Awareness barriers based on number of sources.
“Lack of safety signage board” and “Low level of awareness among contractors of the importance and need for training” were in last position between the rest of the barriers based on the number of sources that considered it as a barrier that hinders the implementation of safety in AEC industry. In promoting safety in the AEC industry, H&S training plays an important role. However, the level of awareness among contractors of the need for such training is unsatisfactory. They often believe that their money should be better spent on meeting their training allocations [16]. Reference [19] clarifies that there is lack of awareness of the H&S regulations provided in the companies, as well as poor awareness of OHS [52].
During the process of identification and classifying of the barriers in the sources which were reviewed, many ways to improve safety performance in AEC industry were found, such as the following:
Identify Clear Goals and Objectives: The goals and objectives of the program must be clearly defined and provide a specific timetable contain this goal. The goals serve as a strategy that needs to be frequently measured and improved in the short term (one year), intermediate (3 years) and long term (5 years) [92]. Reference [35] explained that setting goals can contribute to reducing the unsafe acts of workers, whereas unsafe acts can be closely monitored by goal setting, and policies and procedures to limit them are identified. In addition, goal setting should be communicated through writing the safety plan clearly and comprehensively [93].
Safety regulation: Studies [40,78] mentioned that, in Kuwait and China, respectively, there was agreement among survey participants that safety regulation is important to reduce accidents at construction sites. The conclusion is that accidents are caused by a vast range of factors, some of which is a lack of awareness of safety regulation and failure to implement safety rules.
Obtain Commitment from Management: Managers must adhere to the safety program and not just a paper program [92], but through the formation of a committee composed of supervisors, workers, agents of main contractors, agents of the owner, and consultants of OHS in order to address safety issues. A regular meeting should be held by this committee (e.g., weekly or biweekly) to address H&S by conducting an examination, discussing job hazard analysis, or steering safety and training meetings [93]. In addition, they must allocate adequate resources and adequate funding to the program [92,93,94].
Effective communication between site staff: The communication is an effective strategy, where it is one of the key components with regard to managing personnel in the construction sector. Poor communication is a key factor in seven percent of accidents on site. There should be a way staff member at the site can communicate their views and opinions regarding the H&S aspects of the site. This process helps to develop a culture of safety through on-site communication. In addition, site staff are supported to discuss the different problems identified between them, as well as with the site’s management [95].
Role of Government: The government plays a key role in safety, as it requires each contractor to offer necessary documents, such as a building authorization and the location of the area. The government will impose a contractor’s insurance fee, which will be refunded if the contractor complies with the safety requirements at the end of the work [78,82]. The government will arrange visits to construction sites to ensure that site safety measures are implemented [40,82].
Training programs: Lack of training indicates that workers are unable to do their jobs well. Training clearly has a role to play in identifying management practices to enhance safety performance and should provide proper training for all their workers [35,71]. While Reference [96] was found that training is not associated to the implementation of H&S in construction sites. Most companies do not have continuous training on safety because of the cost reason. In addition, they do not have enough time to train.
The type of employees training must of course depend on the type of work [35,71]. It is essential that anybody working on the site have at least eight hours of safety training or training in information safety [78]. Training usually begins with the direction of workers and carries on where workers need to be more educated about the particular features of the work they do [82]. As we know, training will make workers more efficient in their job performance and increase the awareness of staff about hazardous tasks, thus increasing the company’s income. Therefore, the company should not neglect training [35,71]. Safety training has several advantages, wherein workers learn safe behavior and technical skills. It can be used to teach safe behaviors, provide practice time, and motivate workers to perform operations safely [20]. And safety training may include reviewing project-specific or task specific hazard communication, methods of safe works behavior company, policies, and H&S objectives [93], as well as worker orientation, safety induction, and toolbox talks [82]. It may include topics, such as workers’ rights and responsibilities, falling downhill, hot work, electrical safety, personal protection equipment, first aid, and emergency procedures [35,40].
Safety record system: Useful information that can be used effectively to reduce or even eliminate expected risks can be provided in the safety record [78]. The accident reporting program in Hong Kong was found to be the most significant contributor to reducing the on-site recurrence of incidents [78]. Recordkeeping activities include records of all incidents, including data, such as time, location, workplace conditions, or cause. This also includes data analysis of incidents to detect trends and weaknesses in company safety programs or poor implementation of the program. Then, the manager spends his time finding a solution to the issue [82,93].
Conduct regular safety meetings to inform staff of external problems at the site: Regular meetings on H&S are necessary for communicating H&S data to all stakeholders [78,82]. And a well-planned safety meeting creates excellent spirits [40]. When the employee is satisfied that the employer is interested with safety at the workplace, the employee will comply with H&S guidelines and perform the work in a safe manner [40,82]. The safety program has to provide monthly, if not weekly, meetings to talk about workplace risks, conditions that may affect safety. And, to find a solution, they should also to encourage all workers to express their views and make recommendations without any repercussions or insults [95]. To make safety meetings more effective, more substantive and current material is needed by a variety of qualified speakers. It may also be appropriate to hold smaller meetings for specific crafts, with more discussion on immediate problems [40].
Select contractors with High Safety Performance: Contractual contractors shall be appointed with a good safety performance record during the bidding process by the consultant. Contractor’s attitudes towards safety range from minimum commitment to full compliance, and the owners concerned should, therefore, take into consideration the previous safety performance of the contractors during the bidding process and upon awarding the contract. [71,92,93,94].
Personnel Selection: Some accidents occur as a result of wrong personal behavior. Some employees are more susceptible to accidents than others, while some other employees have a preventive attitude towards accidents. Employees are selected based on personal behavior, family stability, and alcohol and drug testing, which are examined before the employee is approved [71,97].
Inform employees of risks and potential issues before starting work: Timely information is one of the main aspects of efficient management of employees in the AEC industry and extremely impacts site safety level, such as providing an overview of the various safety requirements of the site and related problems [95].
Use signage to help the movement of individuals in and around the site: It is essential that all construction sites have a uniform signaling system that all stakeholders understand to prevent risk. Signal symbols should appear in appropriate locations and must be obtainable in the safety manual. However, it is the responsibility of the contractor to make certain that all the signers are conscious of all the signs they must recognize. The color of the warning signs should attract viewer’s attention [82].
Establish the Responsibilities of Safety Supervisor: Managers and supervisors adopt teamwork to develop and manage the safety program [92]. The best way to develop this is to assign a full-time safety supervisor [82,98]. The primary responsibility of this individual is to perform and guide the implementation of the elements of the H&S program [93], such as inspect and monitor site safety, as well as monitor the implementation of site safety laws and policies [98]. While H&S inspections are a way for management to identify the H&S conditions of sites [82], they can also help to identify the nature of the safety conditions on the site [40]. In addition, through inspection, it is ascertained whether workers apply the knowledge they receive through the safety training [16]. The use of safety inspections has had a positive impact on the Company’s initiative to control losses [40]. It was noted that the accident rates were low in the projects where inspections were conducted regularly [40,82].
The company must design a suitable work schedule for each department that fits its mode of working in order to reduce fatigue and stress of workers: Workers feel tired and stressed due to excessive work, pressure, and irregular work schedule, reducing work performance and causing accidents occur. Therefore, work should not be done for long periods (extra work). Workers who work at night must receive adequate rest on the day and qualify to continue their work at night. To minimize accidents caused by fatigue, the worker must feel comfortable even if he has been working hard all day, as that provides an appropriate working environment reduces the fatigue of workers [35].
Job hazard analysis (JHA): Job hazard analysis is one of the management tools that are used in the fields of professional safety training and accident prevention, and it provides staff with a guide to each step so as to perform each step safely and efficiently [99]. It may begin by reviewing construction process-related activities and by identifying potential serious exposures that may result in injury. Other sources may use OSHA records, reports of infringements, reports of accident investigations, workers interviews, or just intuition to identify risks and accidents [93]. The cooperation between the designer and the client will result in safety risk analysis for each project option.
Risk Assessment: Risk assessment is the extent to which people can be hurt and how severe. Construction activities are exposed to many risks, so it is necessary to assess and manage these risks through an organized risk assessment process so that appropriate controls can be taken on the basis of potential and potential risk. The risk should be assessed by the employees; if the worker’s experience is not sufficient, the company must provide the person have experience to assist him [71,82].
Emergency plan: Create an emergency plan for use in the event of death or emergency, and then put either the owner or the insurance company and resources responsible to solve it [82,93]. The plan aims to seek medical and other support services in the area and to ensure that the first aid store is adequately equipped to meet all potential emergencies identified [40,89,99].
Reward Policy: To improve workplace safety culture in construction, the establishment of a reward system is essential in parallel with safety education and training. Further, the safety based on incentive program enhances the reporting of accidents or any unsafe act that leads to an accident. As incentives work to encourage workers to monitor their safety behaviors and avoid stray and unsafe behaviors [71,82,100].
Reference [45] suggested that production incentive should be in compliance with high safety performance. The reward system can be either a monetary or an upgrade. Disciplinary action is a form of punishment for a worker who violates on-site safety instructions. Therefore, the combination of reward and punishment can be seen as a strategy for learning safe behaviors among site workers [61,71,89,101].
Providing Safe Equipment and Tools: The use of safe machinery and facilities is necessary to keep the H&S of site workers. With technology in the AEC industry, the design of machines has been improved. Although this approach has reduced the number of accidents, it is at the same time causing a new type of accident. For example, new workers who are not familiar with enterprise technology are causing accidents on construction projects [71].
Provide first-aid: Provide primary care for the injured person by a specialist. First aid will not eliminate the risks but only to reduce potential risks to the person who may be exposed. It is, therefore, necessary to provide first aid at each site [82].
Provide Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): PPE as any equipment worn by a person at work to protect him or her from hazards to H&S and any additional accessories is designed to protect him or her while performing the task. In order to achieve a safe and healthy condition in construction sites, it is necessary to have PPE for workers. Among the obligations of senior management is to make sure that the safety equipment is sufficient [16]. Personal protective equipment (PPE) includes hard hats, gloves, boots, and eye/face goggles [19]. Companies that do not provide personal protective equipment to their workers assert that such preventive measures are too expensive or that personal protective equipment often reduces workers’ ability to move and productivity. In addition, there are also workers’ who make their own decision not to use personal protection equipment because of religious values [89,102,103,104]. Practical recommendations and safety measures towards the importance of the application of PPE in infrastructure projects like avoiding of the transmission of the COVID-19 [105].
Safety budget: It is important to provide safety budget where, when provided, all strategies suggested can be implemented [16].
Figure 5 summarizes ways to improve safety performance.
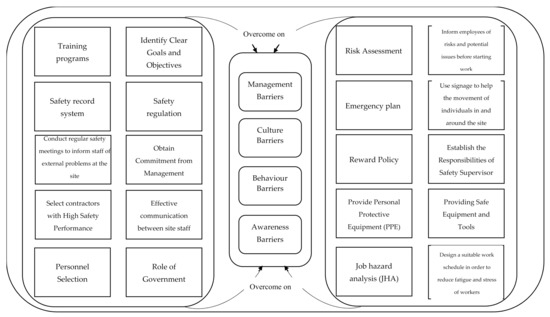
Figure 5. Ways to improve safety performance.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/su13063316
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
