Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) represents a challenging pregnancy complication in which women present a state of glucose intolerance. GDM has been associated with various obstetric complications, such as polyhydramnios, preterm delivery, and increased cesarean delivery rate. Moreover, the fetus could suffer from congenital malformation, macrosomia, neonatal respiratory distress syndrome, and intrauterine death.
- inflammation
- oxidative stress
- gestational diabetes
- plant foods
- antioxidants
1. Introduction
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) represents a challenging pregnancy complication in which women present a state of glucose intolerance that is diagnosed for the first time during pregnancy. It has been estimated that 5 to 7% of pregnancies are complicated by diabetes, and almost 80% is GDM [1,2,3]. Diagnosis of GDM is achieved by the 75 g oral glucose tolerance test, although thresholds vary among different health and diabetes associations [4].
GDM has been associated with various obstetric complications, such as polyhydramnios, preterm delivery, shoulder dystocia, and increased rates of cesarean delivery [5]. Moreover, the fetus could suffer from congenital malformations, macrosomia, neonatal respiratory distress syndrome, hypoglycemia, and intrauterine death [5]. GDM presents a challenging diagnosis, and its management can be difficult. Ethnicity is a risk factor for the development of GDM, as the incidence of GDM is increased among Hispanic and African women [6]. Obesity, a family history of type 2 diabetes (T2D), and a prior history of GDM could also increase the risk of GDM.
There is increasing evidence that GDM presents a genetic component like T2D and aggregates within families [7]. Women with a diabetic sibling had an 8.4-fold increased risk of GDM [8]. In addition, specific gene variants of melatonin receptor 1B (MTNR1B), transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2), and insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) have been found to be associated with GDM [9,10]. It has been speculated that a high sugar intake and increased weight gain during pregnancy might be responsible for an inflammatory pathway that impacts on the onset of insulin resistance [11,12]. Findings from other studies correlated heme iron levels with GDM but not non-heme iron derived from plant-based foods such as grains, vegetables, and seeds [13,14,15].
The first line therapy for GDM is based on a lifestyle approach with a low glycemic diet and an increase in physical activity. If these measures are not effective in reaching the desired glycemic control, a drug approach with insulin can be started. In view of the above, the role of the diet is crucial during pregnancy. Additionally, other pregnancy-related diseases such as hypertension and fetal growth restriction could be affected by dietary patterns [16].
Several studies have been performed about the effects of different dietary patterns on GDM, but the findings are not conclusive [17,18]. A plant-based diet could represent a suitable option for preventing inflammation through a wide range of antioxidant-rich foods [19]. The literature suggests that a high intake of vegetables, fruits, grains, fish, and legumes, according to the Mediterranean diet (MedDiet), presents a low glycemic pattern and may lower the risk of GDM in a low-risk population [20,21,22].
Zamani et al. revealed that food quality can also impact on GDM. In fact, following unhealthy dietary patterns seems to increase the risk of GDM [23].
The balance between oxidant and antioxidant molecules also represents a pivotal aspect of treating the inflammatory state in GDM [24]. Oxidative stress is characterized by a critical imbalance between antioxidant defenses and reactive oxygen species (ROS) [25]. Hyperglycemia could facilitate ROS production, thus creating an inflammatory state and increasing insulin resistance.
Vascular impairment is another mechanism involved in GDM related to oxidative stress [26]. Chronic exposure to ROS could lead to the increased production of mediators that drive stress-signaling pathways and cause potential tissue damage to key target organs, such as the vasculature and pancreas [26]. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) has a pivotal role in insulin resistance as its concentrations are raised in GDM [27].
2. The Impact of a Plant-Based Diet on Gestational Diabetes
The term “plant-based” presents a wide definition as it could either partially include a limited amount of foods derived from animals or include only plant foods such as fruits, vegetables, and legumes [28].
A MedDiet is characterized by food derived from plants without a complete exclusion of animal-source foods. In contrast, both vegetarian and vegan diets exclude meat, chicken, and fish, and a vegan diet additionally excludes dairy and eggs.
A plant-based diet is rich in fibers, magnesium, potassium, and antioxidants but presents a lower intake of saturated fatty acids.
A plant-based diet can exert its role in the prevention of GDM via multiple mechanisms of action. Figure 1 summarizes some beneficial effects of this dietary pattern.
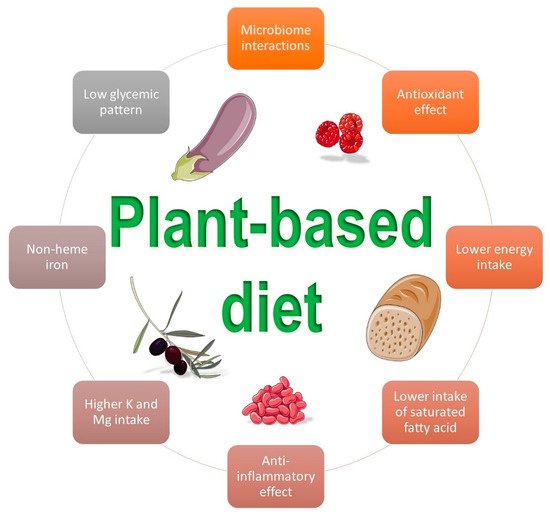
Figure 1. Beneficial influences of a plant-based diet on gestational diabetes mellitus (Images by smart.sevier.com).
Most dietetic associations agree that a well-planned vegetarian diet presents an adequate amount of nutrients and is helpful for the prevention and treatment of several diseases [29,30]. Although plant-based diets are associated with an increased risk of nutritional deficiencies such as vitamin B12, the available evidence also supports a well-planned vegetarian or vegan diet as a safe option during pregnancy and lactation [31,32]. However, they require strong awareness and monitoring to achieve a balanced intake of all the key nutrients. In a retrospective study of 1419 women, Kesary et al. found that a maternal vegan diet might act as a protective factor from maternal weight gain but that it also increases the occurrence of lower birth weight in the neonate [19]. In a different study, a calorie-restricted vegetarian diet was found to increase insulin sensitivity compared to a conventional diabetic diet over 24 weeks of gestation [33]. Moreover, physical activity along with a low calorie diet had a positive effect on oxidative stress marker levels. A vegetarian diet was also reported to reduce intramyocellular lipid concentrations and visceral fat, favorably impacting on insulin sensitivity and enzymatic oxidative stress markers [33].
Zulyniak et al., in 2017, analyzed 3997 full-term Canadian mothers and found that a plant-based diet was associated with increasing numbers of neonates with a low birth weight in women of Caucasian ethnicity, while, at the same time, the same dietary pattern was associated with increasing numbers of neonates with a higher birth weight in women of Asiatic ethnicity living in Canada [34].
The MedDiet and its role in the prevention of GDM has also been the subject of several investigations. A prospective study by García de la Torre et al. analyzed 1066 normoglycemic women before 12 gestational weeks following a MedDiet with extra-virgin olive oil (EVOO) and pistachio supplementation and found that GDM incidence and maternal–fetal outcomes were lower than in the control group [35]. In a different prospective study including 1076 pregnant women adhering to a MedDiet pattern, better glucose tolerance and a decreased incidence of GDM was highlighted [36].
A case-control study of 299 pregnant women affected by GDM found that a high adherence to the MedDiet before pregnancy was strongly associated with a decreased risk in GDM, suggesting a dose-dependent fashion [37].
Mak et al. performed a prospective cohort study of 1337 Chinese pregnant women and did not find a significant association between the risk of GDM and early pregnancy dietary patterns. However, the authors found that a high protein–low starch diet decreased the risk for GDM among obese women [38].
In a different study, the Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension (DASH) was found to be effective to prevent GDM in 200 pregnant women [39]. The DASH, which was created to lower blood pressure, emphasizes a lower sodium intake and prefers foods rich in potassium, magnesium, and calcium [39].
Jali et al. analyzed 325 pregnant women undergoing screening for GDM and found out that 52 (16%) presented GDM. Particularly, authors have revealed an increased prevalence of GDM in patients following a non-vegetarian diet compared to a vegetarian diet (65.5% vs. 38.5%) [40].
Another Indian study analyzed 5100 pregnant women and revealed that non-vegetarianism was associated with an increased risk of developing GDM [41].
According to the available evidence, several possible mechanisms could explain the beneficial effects of a plant-based diet on GDM: the presence of fibers and vegetable proteins, a higher intake of antioxidants, a lower intake of saturated fat, and a higher intake of non-heme iron [42,43].
Table 1 summarizes the available studies and the main findings concerning the link between a plant-based diet and GDM.
Table 1. Main findings of the studies concerning the impact of a plant-based diet on gestational diabetes mellitus.
| Reference | Type of Study | Main Outcome | Number of Participants | Event | Definition of Plant-Based Diet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arora et al., India [41] | Observational, cross-sectional | An increased risk of developing GDM was associated with a non-vegetarian diet | 5100 women | The prevalence of GDM was 35% using WHO 2013 criteria | Vegetarian diet |
| Barrett et al., Australia [44] | RCT | A vegetarian diet in early pregnancy increased the presence of short-chain fatty acid bacteria producers without any influence on GDM risk | 9 following a vegetarian diet and 18 an omnivorous one | Microbiome alpha diversity was similar, while beta diversity was reduced, in vegetarians | Vegetarian diet |
| De Filippis et al., Italy [42] | Observational | An increased consumption of plant foodstuffs based on a MedDiet was associated with beneficial microbiota improvements | 51 vegetarians, 51 vegans, and 51 omnivores | Positive correlation between consumption of vegetables and short-chain fatty acids, Prevotella, and Firmicutes in the gut microbiome | MedDiet |
| García de la Torre et al., Spain [35] | Observational, prospective | Following a MedDiet with EVOO and pistachio supplementation before 12 gestational weeks showed a lower GDM incidence and better maternal–fetal outcomes | 932 women | The incidence of GDM was lower in the intervention group than in the controls (RR 0.81) | MedDiet |
| Izadi et al., Iran [39] | Observational, case-control | Adherence to the DASH and MedDiet was associated with a reduced risk for GDM | 200 women with GDM and 260 without GDM | A higher adherence to DASH was related to 71% reduced risk for GDM | DASH and MedDiet |
| Jali et al., India [40] | Observational, cross-sectional | Non-vegetarian pregnant women showed an increased risk for glucose intolerance | 325 women: 202 vegetarian and 123 non-vegetarian | 52 women (16%) presented GDM. An increased prevalence of GDM in patients following a non-vegetarian diet compared to a vegetarian diet (65.5% vs. 38.5%) | Vegetarian diet |
| Kahleova et al., Czech Republic [33] | RCT | A low calorie vegetarian diet improved insulin sensitivity | 37 following a vegetarian diet and 37 following a conventional diabetic diet | A vegetarian diet improved adipokine levels and oxidative stress markers compared to a conventional diabetic diet over 24 weeks | Vegetarian diet |
| Karamanos et al., Mediterranean countries [36] | Observational, prospective | Adhering to a MedDiet pattern decreased the incidence of GDM | 1076 women | The incidence of GDM was lower in subjects with better adherence to the MedDiet (8.0% vs. 12.3%) | MedDiet |
| Kesary et al., Israel [19] | Observational, retrospective | A vegan diet is a protective factor from maternal weight gain but increased the risk for a lower birth weight | 234 vegans, 133 vegetarian, and 1052 omnivores | A vegan diet in pregnancy was associated with a lower birth weight centile compared to omnivores (42.6 ± 25.9 vs. 52.5 ± 27.0; p < 0.001) | Vegan and vegetarian diet |
| Mak et al., China [38] | Observational, prospective | Following an early pregnancy dietary pattern did not significantly increase the risk of GDM in patients. However, a high protein–low starch diet was associated with a decrease in risk for GDM among obese women | 1337 women | 199 women (14.9%) developed GDM | Plant-based and a high protein–low starch pattern diet |
| Olmedo-Requena et al., Spain [37] | Observational, case-control | A high adherence to a MedDiet before pregnancy was strongly associated with a decreased risk in GDM | 291 with GDM and 1175 without GDM | A high MedDiet adherence was associated with lower GDM risk (aOR 0.61; p = 0.028), while a very high MedDiet adherence was more strongly associated (aOR 0.33; p = 0.005) | MedDiet |
| Zhang et al., USA [45] | Observational, prospective | A low fiber and high sugar intake diet increased the risk for GDM | 13,100 women | 758 with GDM. Each 10-g/day increment in total fiber intake was associated with a 26% reduction in GDM risk | Diet rich in fiber |
| Zulyniak et al., Canada [34] | Observational, prospective | A plant-based diet was associated with lowering the birth weight for women of Caucasian ethnicity and increasing it in Asiatic women living in Canada | 3997 women | The plant-based diet was inversely associated with birth weight (β = −67.6 g per 1-unit increase; p < 0.001) | Plant-based diet |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/antiox10040557
