Anaplastic lymphoma kinase-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ALK+ NSCLC) is a model disease for the use of targeted pharmaceuticals in thoracic oncology. This entry summarizes the state-of-the-art treatment for these tumors as of January 2021, with a special emphasis in the sequential use of various compounds as well as the growing importance of molecular profiling and monitoring for patient management.
- ALK+ non-small-cell lung cancer
- tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- EML4-ALK fusion variant 3
- chemotherapy
- sequential therapies
1. The New Era of Second-Generation ALK Inhibitors
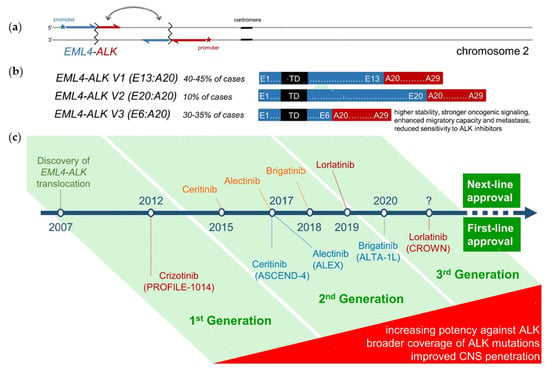
1.1. Best-First for Longer Survival
1.2. Best-First before Chemotherapy
1.3. When Should Brain Radiotherapy Be Offered?
1.4. Safety and Tolerability
2. State-of-the-Art after the First Line
2.1. Oligoprogressive Patients
2.2. Systemic Treatment after Alectinib or Brigatinib
2.3. Systemic Treatment after Crizotinib
2.4. Treatment with ALK Inhibitors after Lorlatinib
| First Line: | Crizotinib | Ceritinib | Alectinib | Alectinib | Brigatinib | Ensartinib | Lorlatinib | Lorlatinib |
| study [ref.] |
PROFILE-1014 [12,29] |
ASCEND-4 [46] |
J-ALEX [76,77] |
ALEX [1,28] |
ALTA-1L [5,78] |
eXalt3 [4] |
CROWN [10] |
global phase II [61] (EXP1) |
| comparator | chemo | chemo | crizotinib | crizotinib | crizotinib | crizotinib | crizotinib | single arm |
| patients (n) | 172 | 189 | 103 | 152 | 137 | 143 | 149 | 30 |
| ORR (%) | 74 | 73 | 76 | 83 | 76 | 75 | 76 | 90 |
| mPFS (mo) | 10.9 | 16.6 | 34.1 | 25.7 */34.8 ** | 24.0 */29.4 ** | 25.8* | NR | NR |
| HR | 0.45 | 0.50 | 0.34 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 0.52 | 0.28 | N/A |
| Post Crizotinib: | Ceritinib | Ceritinib | Alectinib | Alectinib | Brigatinib | Brigatinib | Ensartinib | Lorlatinib |
| study [ref.] |
ASCEND-1 [31] |
ASCEND-2 [79] |
global phase II [13] |
phase II [14] |
phase I/II [15] |
ALTA 90/180 mg [16,17] |
phase I/II [80] |
global phase II [61,62] (EXP2/3A) |
| patients (n) | 163 | 140 | 138 | 87 | 70 | 110 | 29 | 59 |
| ORR (%) | 56 | 38 | 50 | 48 | 71 | 55 | 69 | 70 |
| mPFS (mo) | 6.9 | 5.7 | 8.9 | 8.1 | 13.4 | 12.9/16.7 | 9 | 11.1 |
| Post Alectinib (or other 2G TKI): | Ceritinib | Ceritinib | Brigatinib | Brigatinib | Brigatinib | Brigatinib | Lorlatinib | |
| study [ref.] |
phase II [81] (Japan) |
retrospective [82] (Japan) |
ALTA-2 [83] |
Phase II (IIT, USA) [64] |
retrospective [65] |
EAP (EU) [70] |
global phase II [61,62] (EXP3B/4/5) |
|
| patients (n) | 20 | 9 | 103 | 19 | 18 | 111 | 139 | |
| ORR (%, (n)) | 25 (4/20) | 44 (4/9) | pending | 47 (9/19) | 17 (3/18) | n/a | 41 (52/127) | |
| mPFS (mo) | 3.7 | 4.4 | 6.4 | 4.4 | n/a | 6.9 | ||
| mTNT (mo) | 8.7 | |||||||
| Post Lorlatinib: | Brigatinib | |||||||
| study [ref.] |
EAP (EU) [70] |
|||||||
| patients (n) | 37 | |||||||
| ORR (%) | n/a | |||||||
| mPFS (mo) | n/a | |||||||
| mTNT (mo) | 7.5 | |||||||
| ALK+, First Line: | Crizotinib | Ceritinib | Alectinib | Brigatinib | Ensartinib | Lorlatinib |
| study [ref.] |
ALTA1L-ALEX (asympt. BM) [1,5] |
ASCEND-4 (stable BM) [46] |
ALEX (asympt. BM) [1] |
ALTA-1L (asympt. BM) [5] |
eXalt3 (asympt. BM) [4] |
CROWN (asympt. BM) [10] |
| patients (n) for iORR: |
21–22 | 22 | 21 | 18 | 13 | 14 |
| iORR (%) | 29–50 | 73 | 81 | 78 | 75 | 82 |
| patients (n) total: | 138–151 | n/a | 152 | 137 | 143 | 149 |
| brain progression at 1 year: | 19–41 | n/a | 9.4 | 8.8 | 4 | 2.8 |
| ALK+, Post Crizotinib: | Ceritinib | Alectinib | Brigatinib | Ensartinib | Lorlatinib | |
| study [ref.] |
ASCEND-2 [79] |
phase I/II pooled [84] |
ALTA (180mg) [85] |
phase I/II [80] |
phase II [61] |
|
| patients (n) | 20 | 50 | 18 | 6 | 37 | |
| iORR (%) | 45 | 64 | 67 | 83 | 68 | |
| iORR (%) 1L | 73 | 81 | 78 | 75 | 75 | |
| ΔiORR 2L-1L | −29% | −17% | −11% | 8% | −7% | |
| (% of 1L) | (−39%) | (−21%) | (−14%) | (+11%) | (−9%) | |
| EGFR+, First Line and beyond: | Gefitinib/Erlotinib | Osimertinib | Radiotherapy /+ΤΚΙ | |||
| study [ref.] |
FLAURA [39] (stable BM) |
FLAURA [39] (stable BM) |
various studies [86,87,88] |
|||
| patients (n) for iORR: | 19 | 22 | ||||
| iORR (%) | 68 | 91 | 50–60 / 85 | |||
| patients (N) total: | 277 | 279 | ||||
| brain progression at 1 year: | 24 | 8 | ||||
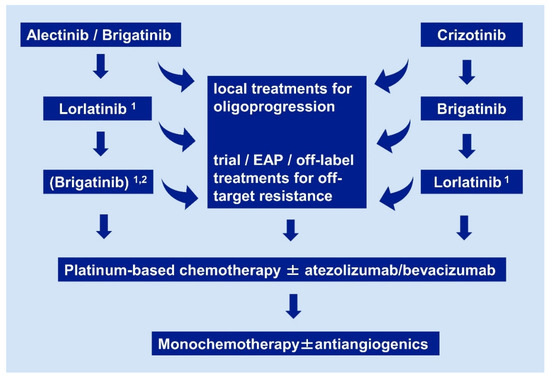
2.5. Do We Need Rebiopsies and Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) Testing?
2.6. The Emerging Concept of Molecular Risk and Value of Disease Monitoring in ALK+ NSCLC
2.7. Treatment after TKI
3. Summary and Conclusions
ALK+ NSCLC is a model disease for the management of OPD, use of targeted pharmaceuticals, and clinical utility of advanced molecular profiling in thoracic oncology. Standard first-line treatments are currently the second-generation ALK inhibitors alectinib and brigatinib. Lorlatinib and brigatinib are the preferred next-line therapies after progression under second-generation TKI and crizotinib, respectively, except for cases with off-target resistance detected in tissue or liquid rebiopsies, which require special therapeutic maneuvers. Presence of the EML4-ALK fusion variant 3 and/or TP53 mutations identify high-risk cases with earlier treatment failure and shorter survival, regardless of the applied therapy. The potential clinical utility of serial ctDNA assays for improved guidance of treatment in these cases is currently a subject of intense investigation. Major pharmaceutical challenges for the field are the development of more potent, fourth-generation TKI and effective immunotherapies, which will be essential in order to cure ALK+ NSCLC in the future.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ph14020080
