Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is one of the causative agents for liver inflammation across the world. HEV is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus. Human HEV strains mainly belong to four major genotypes in the genus Orthohepevirus A, family Hepeviridae. Among the four genotypes, genotype 1 and 2 are obligate human pathogens, and genotype 3 and 4 cause zoonotic infections. HEV infection with genotype 1 and 2 mainly presents as acute and self-limiting hepatitis in young adults. However, HEV infection of pregnant women with genotype 1 strains can be exacerbated to fulminant hepatitis, resulting in a high rate of case fatality. As pregnant women maintain the balance of maternal-fetal tolerance and effective immunity against invading pathogens, HEV infection with genotype 1 might dysregulate the balance and cause the adverse outcome. Furthermore, HEV infection with genotype 3 can be chronic in immunocompromised patients, with rapid progression, which has been a challenge since it was reported years ago. The virus has a complex interaction with the host cells in downregulating antiviral factors and recruiting elements to generate a conducive environment of replication. The virus-cell interactions at an early stage might determine the consequence of the infection. In this review, advances in HEV virology, viral life cycle, viral interference with the immune response, and the pathogenesis in pregnant women are discussed, and perspectives on these aspects are presented.
- Hepatitis E virus (HEV)
- virology
- life cycle
- pathogenesis
- virus-cell interactions
- Hepatitis E in pregnancy
1. Introduction
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is one of the causative agents of viral liver infections. It is estimated that about 20 million HEV infections occur worldwide annually, with 3.3 million symptomatic cases of HEV infection and approximately 44,000 deaths [1]. The virus is usually transmitted via the gastrointestinal route from contaminated water or food of animal origin. Currently, at least four genotypes of HEV are known to infect humans [2]. Genotypes 1 and 2 viruses cause acute hepatitis in the general population, with a case fatality rate of 0.5%–3%. Infection of pregnant women with genotype 1 HEV may cause acute liver failure, leading to a case fatality rate of up to 30% (reviewed in [3]). Genotype 3 strains are the main causes of chronic HEV infection in elderly or immunocompromised patients, with a high risk of progressing to liver cirrhosis [3]. Sporadic cases of chronic infection by genotype 4 are also reported. The exact mechanisms for the different disease outcomes by genotypes are still unknown; however, recent research has provided some clues. The virus-cell interactions are complex and may determine the outcome of infection. A section below is dedicated to trying to shed light on this front, although there are many unknowns.
HEV is a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus with an icosahedral capsid. Two forms of HEV virions are known: quasi-enveloped and non-enveloped. The peak density of the naked, non-enveloped particles is 1.27 g/mL, while the quasi-enveloped particles have a density of 1.15 g/mL [4,5]. The HEV genome is about 7.2 kb and encodes three open reading frames (ORFs). An additional ORF, ORF4, is found only in genotype 1 strains [6]. ORF1 encodes the non-structural proteins for genome replication, ORF2 encodes the capsid protein, and ORF3 encodes a small multifunctional protein.
Contemporary studies have provided informative insights into the HEV life cycle. HEV was once considered as a non-enveloped virus, but quasi-enveloped virions are found in the blood circulation and cultured cells [7]. The lipid membrane shields the virions from neutralizing antibodies. There are multiple forms of ORF2 product in patient serum and cultured cells: the capsid protein associated with virions and the soluble protein glycosylated and secreted. These results reveal an interesting feature of the capsid protein biogenesis.
HEV infection interferes with cell signaling and evades the antiviral responses of innate immunity. HEV inhibits the induction of type I interferons [8] and can persist in the presence of type III interferons [9]. The viral proteins encoded by ORF1, 2, and 3 interact with cellular partners to downregulate antiviral factors and recruit elements to generate a conducive environment for HEV replication.
2. HEV Taxonomy and Distribution
HEV strains are classified into two genera: Orthohepevirus and Piscihepevirus, in the family Hepeviridae [10]. The genus Orthohepevirus contains four species, namely A, B, C, and D, which infect humans and animals. Piscihepevirus is isolated only from salmonid fish in North America so far. Orthohepevirus A consists of the previously known genotype 1–4 and the newly recognized genotype 5–8. Genotype 1 and 2 are restricted to humans [11]; genotype 3 and 4 are zoonotic and have been detected in a wide spectrum of hosts, including monkey, pig, sheep, cow, wild boar, deer, rabbit, and mongoose [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]; genotype 5 and 6 are reported to infect only wild boars [2], with genotype 5 having the potential for zoonotic infection [23]; genotype 7 and 8 are isolated from camels, with a sole case report of human infection from genotype 7 [23,24]. Orthohepevirus B consists of avian HEV [2]. Orthohepevirus C consists of rat and ferret HEV, while Orthohepevirus D contains only bat HEV [2]. A rat HEV strain of Orthohepevirus C was found in a patient with persistent hepatitis after liver transplantation, suggesting the zoonotic potential of this species [25]. The genomic variability and potential risk of cross-species infection of Orthohepevirus C strains have been reviewed elsewhere [26,27]. Along with the isolation of HEV from more wild and domestic animals, an evolution of the virus taxonomy is expected in the future.
The regional prevalence of HEV genotypes is varied. Among the four major genotypes that infect humans, genotype 1 is mainly distributed in South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa [28,29], where the infection is predominantly due to poor sanitation and contaminated drinking water. Genotype 2 was initially discovered in Mexico and later found in Africa [30,31,32,33]. Genotype 3 contributes to pockets of hepatitis E cases in industrialized countries [34,35,36] and also widely spreads in some developing countries in Latin America [37,38] and China [39]. The most frequent route of transmission of genotype 3 HEV in humans is the consumption of HEV-contaminated uncooked/undercooked pork or sausage [40,41]. Genotype 4 is most prevalent in China but also detected in other countries, such as South Korea, Japan, and France [42,43,44]. Like genotype 3, genotype 4 HEV can be transmitted via contaminated food. The co-infection of genotypes 3 and 4 in patients with acute hepatitis was reported in Japan [45].
In addition to the gastrointestinal route, HEV has been demonstrated to be transmitted via blood transfusion in some countries [46,47]. Genotype 1 HEV has also been detected in blood donors in India [48].
Despite the genetic difference, the four genotypes belong to a single serotype. The antibody against the neutralization epitopes of the capsid protein of HEV genotype 3 can neutralize the other different geographic HEV strains in genotype 1 and 2 [49]. Commercial enzyme immunoassays and rapid immunochromatographic kits based on genotype 1 HEV ORF2/ORF3 antigens can detect the presence of IgM or IgG antibodies induced by the four major genotypes of HEV [50,51].
3. HEV Life Cycle
HEV virions are conventionally viewed as non-enveloped particles, ranging from 20–40 nm in diameter. However, HEV particles from cultured cells and serum samples are found to be quasi-enveloped. HEV virions from cultured cells and monkey feces have different densities and sedimentation coefficients. The virions from cell culture supernatant possess lipid and vp13, while those from feces do not [88]. The non-enveloped virions are enterically transmitted and possibly enter the bloodstream after the first round of replication in an unknown cell type in the gut. The virions then reach hepatocytes from the bloodstream. The enveloped virions in the uncooked/undercooked meat may also be enterically transmitted and the envelop is presumably removed during passage in the gastrointestinal tract. The enveloped virions that are transmitted via blood reach hepatocytes and extra-hepatic target cells from the bloodstream. The HEV cell entry has been reviewed elsewhere [102]. Non-enveloped virions require heparan sulfate proteoglycan (HSPG) for attachment to target cells, but the enveloped virions (eHEV) attach to the cells independent of HSPG [4]. Both types of virions enter the cells through clathrin-mediated and dynamin-2-dependent endocytosis (Figure 5). During the endocytosis of HEV, low pH is required but not enough for the uncoating of eHEV [4]. However, the mechanism of uncoating is not well understood.
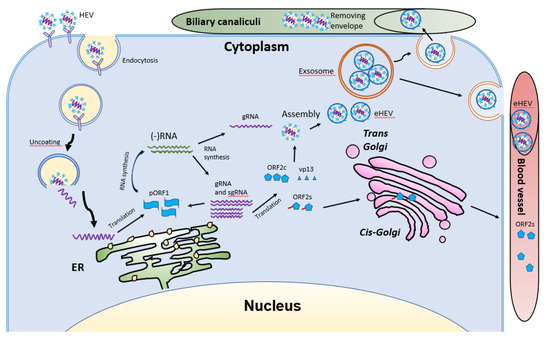
After uncoating, the positive-sense RNA genome is released into the cytosol and serves as the template for the translation of ORF1. The 7-methylguanosine cap structure at the 5′UTR of the HEV genome recruits the 40S ribosomal subunit to initiate cap-dependent translation. Once produced, RdRp will initiate transcription of the viral genomic RNA by binding to its 3′UTR to produce the negative-sense intermediate RNA [64]. This intermediate RNA serves as the template for the synthesis of progeny positive-sense viral genomes. HEV replication requires Golgi-specific brefeldin A-resistant guanine nucleotide exchange factor 1 (GBF1) [101,103]. The ubiquitin-proteasome system also contributes to HEV replication as inhibition of the system abolishes the viral replication [103,104]. For viral encapsidation and assembly, the capsid protein interacts with a 76nt region specifically in the 5′ end of the HEV genome [104]. The N-terminal 111 amino acid residues of the capsid protein appear to not be involved in the interaction.
Following the assembly, the viral progeny are transported by multivesicular bodies and released by the cellular exosomal pathway [105]. The HEV assembly and release are reviewed elsewhere [106]. Most infectious HEV particles in the form of eHEV are released from the apical side of the hepatocytes into the biliary canaliculi, where the eHEV are converted to non-enveloped particles by the detergent in the bile (Figure 5). A small portion of eHEV particles is released into the blood via the basolateral side of the hepatocytes. After the virion release, only non-enveloped HEV can be detected in bile and feces, but in blood and urine virions are likely to be enveloped [107,108]. The eHEV envelope possesses the trans-Golgi network protein 2 (TGOLN2), one of the markers of the trans-Golgi network, suggesting that the membrane-associated HEV particles are derived from the intracellular membrane but not the cell surface [7]. The eHEV particles are shown to contain the capsid and vp13 proteins, while the non-enveloped particles only contain the capsid protein. It is important to note that, due to the surrounding of an envelope, the eHEV cannot be neutralized by capsid-specific monoclonal antibodies. The absence of vp13 in the naked virions suggests that this protein is only required for the release but not the entry of the virus. In addition to the reduced recognition by antibodies, the attachment efficiency of the eHEV virions to hepatocytes is one-tenth that of the naked virions [4]. Conversely, the infectivity of the eHEV particles is shown to increase after the removal of the lipid layer. Considering the gastrointestinal transmission route for HEV, the eHEV is the source of naked virions and may contribute to dissemination.
During the formation of eHEV in the cells, the virus acquires the envelope mainly from the intracellular membrane. During this process, how the virus alters the process of the host fatty acid is still unknown. The presence of the lipid envelope seems to assist the virus in evading neutralizing antibodies. However, the shorter duration of viremia than the presence of non-enveloped virions in feces suggests that the eHEV might have a minor role in HEV transmission. The HEV life cycle has been reviewed elsewhere [109].
HEV infection can evoke a series of physiological and immunological alterations in the host. Viremia in acute hepatitis E patients normally lasts for one month, during which the anti-HEV IgM is the major antibody produced [110,111]. Anti-HEV IgM can still be detected in about 40% of patients until 12 months. Viral RNA can become undetectable when the patients come to clinical attention (reviewed in [110]). However, with the newly developed pan-genotypic PCR-based assay that is more sensitive than the commercial kits and detects the entire spectrum of the genotypes in Orthohepevirus A [112], detection and quantification of HEV in clinical samples could be significantly improved. Thus, HEV infection might be less underestimated, and viral RNA can be detectable in clinical settings with a better possibility. IgG production usually peaks at 20 weeks post-infection and can be detected after two years, in around 37% of cases. Immunohistochemical analysis of liver biopsies shows the infiltration of activated CD8+ T cells, which may lead to liver damage during acute liver failure [113,114].
Both innate and adaptive immune responses are needed to clear the virus. HEV has evolved a series of strategies to evade immune responses. HEV-specific T-cell responses in patients with chronic hepatitis E are absent but detectable after viral clearance, suggesting an association with impaired T-cell immune response [115,116]. Robust HEV-specific T cell responses predominantly targeting the capsid protein are present during acute infection, while low-level response is seen in immunosuppressed patients [117]. A recent study defines the T cell receptors that target HEV-specific CD8+ T cell epitopes in HEV helicase and RdRp, which are explored for immunotherapy of chronic hepatitis E [118].
4. HEV Infection of Pregnant Women
HEV infection during pregnancy can result in poor prognosis [196] and vertical transmission. Unlike HBV and HCV, which normally do not cause death cases in acute infection of pregnant women [197,198], HEV infection by genotype 1 strains in pregnant women results in up to 30% case fatality, while infection by genotype 3 strains is usually subclinical [3].
A fine balance is maintained during pregnancy between maternal-fetal tolerance and mounting an effective innate and adaptive immunity against invading pathogens. Dysregulation of the mechanisms maintaining the balance can lead to disorders. Early studies show that the number of T cells decreases during pregnancy [199,200,201]. There is a clear shift of the Th1:Th2 paradigm with an apparent Th2 bias, which could create maternal-fetal tolerance for fetus development [202]. Regulatory T cells are also considered to play a role in maternal-fetal tolerance during pregnancy [203]. Th2 bias in pregnant women with acute hepatitis E due to genotype 1 HEV is more prominent than in non-pregnant patients with acute hepatitis E and healthy pregnant women [204]. The obvious Th2 alteration might attribute to the physiological changes of pregnancy or the consequence of virus infection. These data suggest that genotype 1 HEV might be able to dysregulate the balance between tolerance and immunity.
Early antiviral response is critical for the host to control virus infection. In pregnant women with acute infection of genotype 1 HEV, the expression of TLR3, 7, and 9 in monocytes and macrophages is upregulated. But when acute liver failure (ALF) develops, their expression is reduced, which may account for the defective immune response in ALF patients [205]. Also, the IFN response in placental cells is reported to be weaker than hepatocytes for genotype 1 but not genotype 3 HEV [206]. These data suggest that genotype 1 HEV might be able to evade the early antiviral response in a certain population of pregnant women and cause an adverse consequence.
Genotype 1 HEV infection might interfere with adaptive immunity in some subjects. One study shows that in the second and third trimester of pregnancy, HEV-infected pregnant women with fulminant hepatic failure (FHF) have lower CD4+ T cell counts and higher CD8+ T cell counts than HEV-negative women with FHF [207]. Other studies show a significant infiltration of activated CD8+ T cells containing granzymes in liver biopsies from HEV-infected patients with FHF, which suggests the role of CD8+ T cells in the liver injury [113,114]. Clinical investigation in HEV-infected women with acute liver failure revealed that the cytokine level, such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ, is higher than in non-infected pregnant women, and the level of these cytokines are positively correlated to adverse pregnancy outcome [136]. These data suggest that genotype 1 HEV induces an overactive inflammatory response leading to a poor prognosis in a certain population of pregnant women.
The genotype 1 HEV is also implicated in invading the placenta more effectively than genotype 3. A recent study demonstrates that the genotype 1 HEV grows much more dynamically than genotype 3 HEV in the ex vivo maternal-fetal interface model using the decidua basalis and fetal placenta [208]. Genotype 1 HEV induces a higher level of apoptosis of decidua and placenta cells than genotype 3 HEV and provokes a higher level of IL-6, CCL-3, and CCL-4, which positively correlates with the viral load. Meanwhile, UV-treated culture supernatant harvested from genotype 1 HEV-infected explants causes more tissue injury in fresh decidua and placenta organ culture than the genotype 3 HEV-infected cultures [208]. Further studies are needed to compare the genetic characteristics of genotype 1 and 3, and identify the key factors in genotype 1 infection that determine severe disease outcome.
In addition to immunological factors, hormone variation during pregnancy may contribute to viral replication. Pregnant women with acute HEV hepatitis have increased estrogen and progesterone level [207]. These hormones are known to dampen the cell-mediated immune response [209,210]
Similarly, the estradiol level in HEV-infected pregnant women during the third trimester is significantly higher than HEV-negative pregnant women. An in vitro experiment shows that the estradiol treatment facilitates HEV replication in A549 cells [211]. Thus, the variation in hormone level is also speculated to be one of the factors that contribute to the severe disease progress of HEV-infected pregnant women.
Collectively, the immune-tolerant environment may subject pregnant women to become more vulnerable to HEV infection. HEV infection with genotype 1 might dysregulate the balance maintaining the maternal-fetal tolerance and effective immunity, or alter the immunological mechanisms that maintain the balance, which leads to the dire consequence of FHF in pregnant women. The potential mechanisms that genotype 1 HEV employs to produce the mortality of pregnant women need to be investigated. Why infection of different genotypes results in different disease outcomes and what determines the chronicity of HEV infection remain unclear. Both virus and host factors possibly contribute to the disease’s progress. In terms of the viral factors, genetic variations of the different genotypes and host adaptability may account for the different outcomes. Conversely, the immune-tolerant environment and associated factors that may be better exploited by genotype 1 HEV in a certain vulnerable population might contribute to the development of ALF in infected pregnant women. So far, most fatality cases of HEV infection during pregnancy are found in South Asia. Due to the different geographical environments and food habits, the gut microbiota in South Asia might vary from other areas and might be a risk factor for ALF development in HEV-infected pregnant women. Further research on this front is needed to address this speculation.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/v13020267
