Malaria is among the deadliest infectious diseases in the world caused by Plasmodium parasites.
- acridine derivatives
- antimalarial
- hybrid molecules
- malaria
1. Introduction
A century has elapsed since Laveran described Plasmodium parasites and Ross confirmed that they were transmitted by mosquitoes [1]. Still, malaria remains a leading cause of mortality and morbidity worldwide [2]. Although we have been witnessing the decrease in malaria burden over the last decade, prospects for malaria eradication are now threatened by resistance to artemisinin-based combination therapies, the current first-line antimalarial treatment [3], urging the development of new classes of antimalarials. While a vaccine remains elusive, we depend on chemotherapeutic agents to both treat infections and prevent disease. Most available antiplasmodials target the pathogenic blood stages in humans [4]. However, to eradicate malaria, it is mandatory to develop compounds that block parasite transmission, cure the asymptomatic hepatic infection and clear the latent forms in the liver [5]. Therefore, elimination efforts require identification of new drug classes acting at multiple stages of the parasite life cycle. One strategy to accelerate development of antimalarials is to recycle known drug scaffolds [4].
Acridine (AC, Figure 1) derivatives have attracted much attention due to their broad spectrum of biological activity, such as antimicrobial, antitumoral, anti-Alzheimer, antiprionic, antileishmanial and antimalarials agents [4,6,7]. Although different modes of action seem to be exerted by AC derivatives depending on their therapeutic targets, the most consensual mechanism of action (MOA) of AC analogues against different diseases is interaction with DNA [8]. However, other MOAs have been suggested to elucidate the antimalarial activity of AC derivatives, such as inhibition of the parasite’s (i) type II topoisomerases, (ii) mitochondrial bc1 complex, or (iii) hemozoin formation [4]. The interest in AC-based structures as antimalarials occurred from early findings on antiprotozoan/antimicrobial activity of the classic synthetic dyes methylene blue (MB, Figure 1) and, later, acridine orange (ACO, Figure 1) with IC50 values of 7.8 and 465.7 nM (for MB and ACO, respectively) against Plasmodium falciparum (Pf) 3D7 strain [9]. Both the tendency to induce skin coloration and toxicity of MB soon triggered the pursuit for more suitable antimalarial substitutes, which led to the synthesis of quinacrine (QN, Figure 1), in 1932 [10]. QN was thus the first clinically tested synthetic antimalarial drug and was widely used as an antimalarial by soldiers during WWII but was soon superseded by chloroquine (CQ, Figure 1), whose bioavailability, safety and efficiency were substantially superior [4,11]. However, with the widespread resistance of Pf to CQ, the search for more efficient QN derivatives or analogues remains vigorous. Amongst different approaches reported in the literature, chemical modifications and the combination or conjugation of AC-based compounds with known relevant pharmacophores have been addressed, in an attempt to outwit resistance mechanisms to classical antimalarials and to produce safer and synergistic or multi-target action compounds. In this context, the present review will focus on efforts made in the last two decades for the development of AC-based compounds as a tool for the rescuing or repurposing of the classical antimalarial quinacrine.
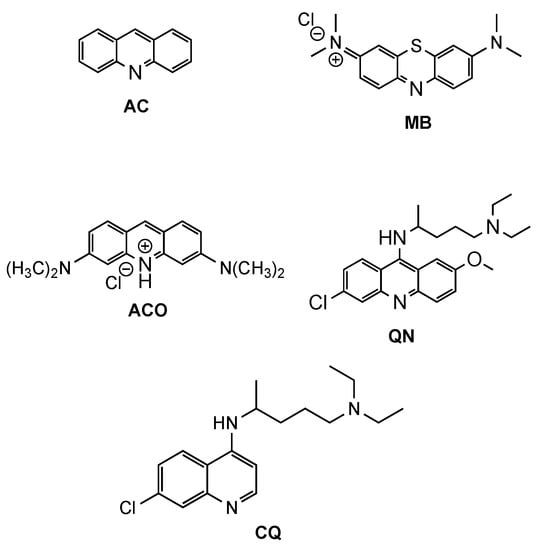
Figure 1. Chemical structure of acridine (AC), methylene blue (MB), acridine orange (ACO), quinacrine (QN) and chloroquine (CQ).
2. Hybrids Containing the 9-Aminoacridine Scaffold
Another noteworthy approach used for recycling the QN scaffold and obtaining faster and available new antimalarial treatments is based on the concept of hybrid drugs. A hybrid molecule is formed through the covalent link between two known chemical moieties with different biological modes of action. This methodology was developed aiming to obtain molecules with better biologic activity, solubility profile and stability than the parent drugs, as well as less susceptibility to the development of drug resistance (Scheme 1). In the last decade, this strategy has attracted attention, mainly in the field of the development of antimalarial drugs due to the urgency of novel compounds to fight malaria disease [23,24].
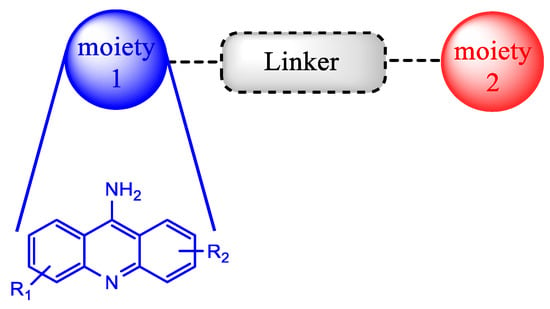
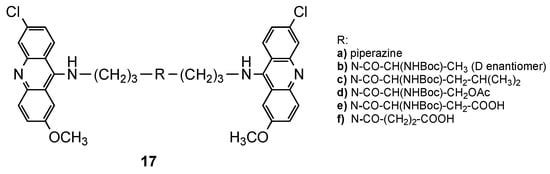
2.1. Bisacridine Hybrids
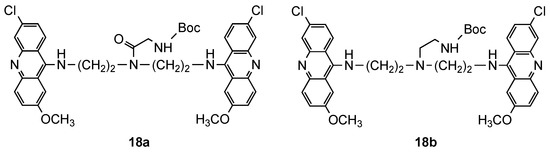
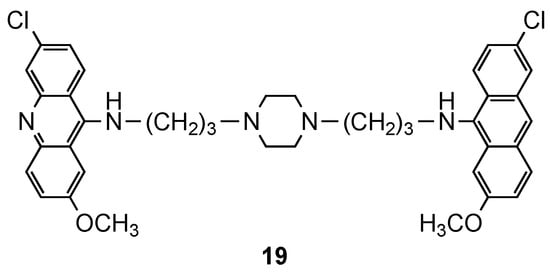
2.2. Acridine–Artemisinin Hybrids
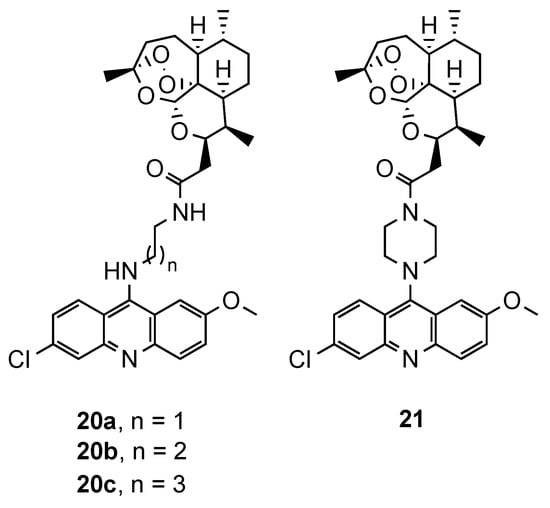
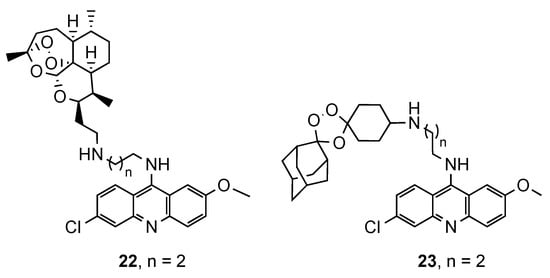
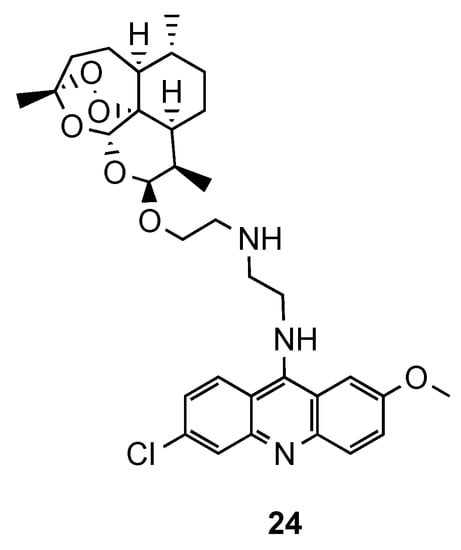
2.3. Acridine–Aminoquinoline Hybrids
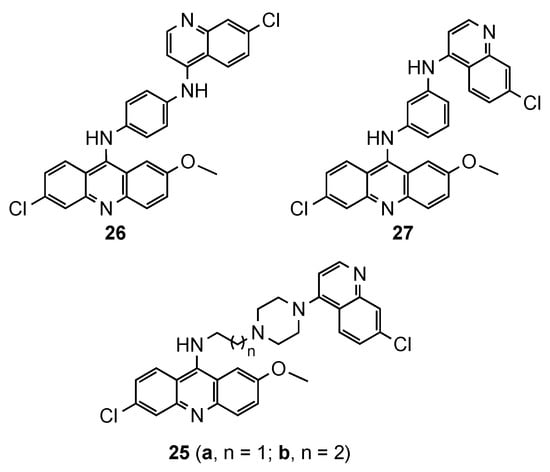
2.4. Acridine–Chalcone Hybrids
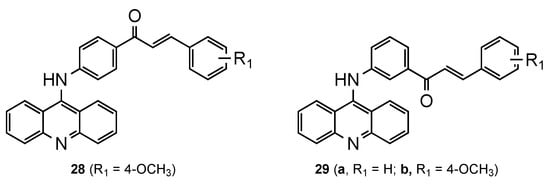
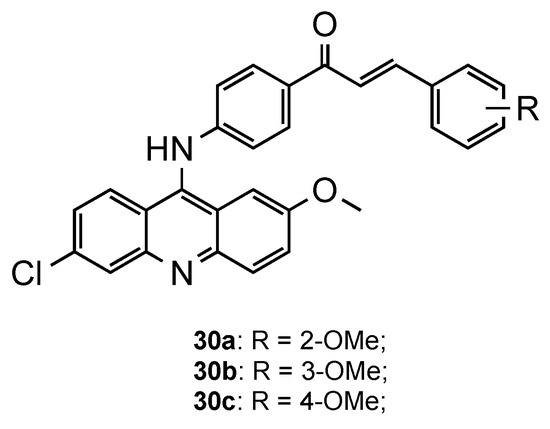
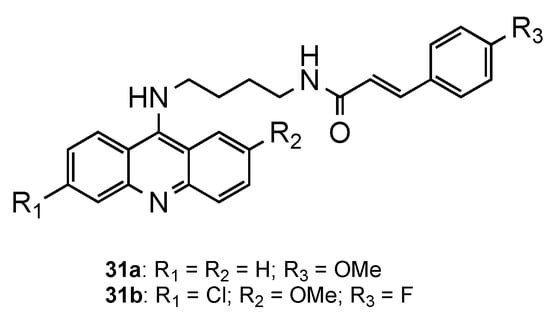
2.5. Acridine–Cinnamoyl Hybrids
2.6. Other Acridine Hybrids
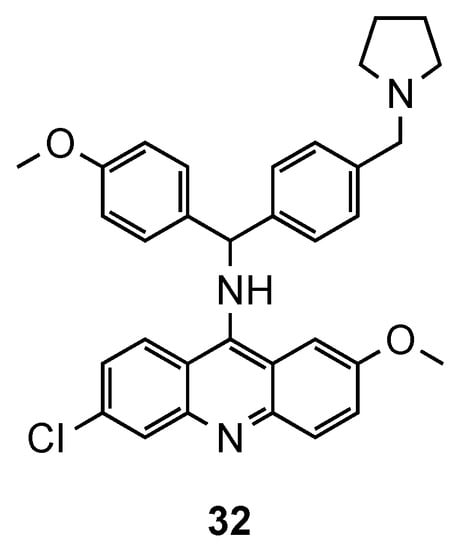
The synthesis of hybrids containing the acridine and clotrimazole-like pharmacophore was first described by Sandra Gemma et al. [48,49]. In previous works [48,49], the authors changed the chemical structure of clotrimazole, an antimycotic drug, to improve its antimalarial activity. In their more recent work [50], this resulting compound was next linked to 9-aminoacridine and assessed against three Pf CQS (D10, 3D7 and NF54) and two CQR (W2 and K1) strains. In the in vitro assays, except for the CQS D10 strain, compound 32 (Figure 21) exhibited better activities (IC50 values ranging from 1.0 to 49 nM for CQS D10, 3D7, and NF54 strains and from 9.0 to 59 nM for CQR W2, and K1 strains) than the reference CQ. This compound has a polyarylmethyl, which gives it the ability to selectively interact with the free heme-iron center and consequently accumulate into the food vacuole, promoting the generation of toxic radical species for plasmodium’s parasites [50].
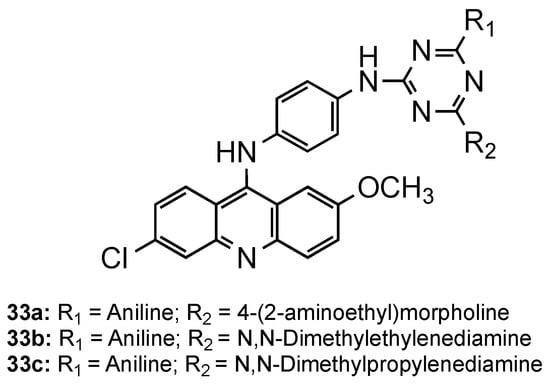
Kumar et al. directed their attention to triazine–acridine hybrids (33, Figure 22) [51]. The synthesized compounds were evaluated for their in vitro antimalarial activity against the CQS Pf strain and their cytotoxicity on the VERO cell line. Of the whole set, compounds 33a–c exhibited good antimalarial activities in vitro with a high selectivity index, some of them being better than CQ (33a: IC50 = 6.97 nM, SI = 2896.02; 33b: IC50 = 4.21 nM, SI = 295.02; 33c: IC50 = 4.27 nM, SI = 315.39; CQ: IC50 = 8.15 nM, SI = 8983). Compound 33a was further subjected to in vivo study against the CQR N-67 strain of P. yoelii orally in Swiss mice at a dose of 100 mg/kg for four days. Although the compound could suppress the infection in 96.59%, it could not provide significant protection to the treated mice in 28 days survival assay [51].
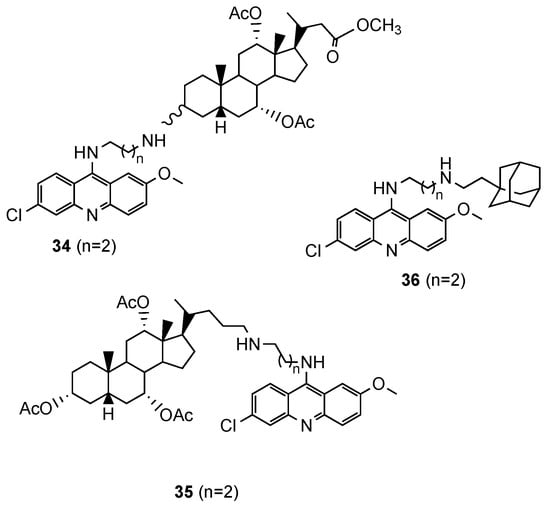
Based on reports concerning the good inhibitory activity of steroidal 4-aminoquinolines, and adamantyl-aminoquinolines [52], Tot et al. [53] expanded their work towards the synthesis and in vitro antimalarial activity of news 9-aminoalkylaminoacridine derivatives possessing steroid and adamantane carriers (34 and 35, and 36, respectively; Figure 23). Compound 36, an adamantyl derivative, presented an antimalarial activity comparable to that of artemisinin and better than CQ against the Pf CQS D6, CQR W2 and multi-drug resistant TM91C235 strains (36: IC50(W2) = 8.6 nM, IC50(D6) = 9.3 nM, IC50(TM91C235) = 5.8 nM; Artemisinin: IC50(W2) = 6.70 nM, IC50(D6) = 9.00 nM, IC50(TM91C235) = 13.40 nM; CQ: IC50(W2) = 456.20 nM, IC50(D6) = 12.27 nM, IC50(TM91C235) = 138.82 nM). Compound cytotoxicity was evaluated in the human liver carcinoma cell line HepG2, and compound 36 exhibited the best selectivity index (SI(W2) = 352; SI(D6) = 326; SI(TM91C235) = 522) [53].
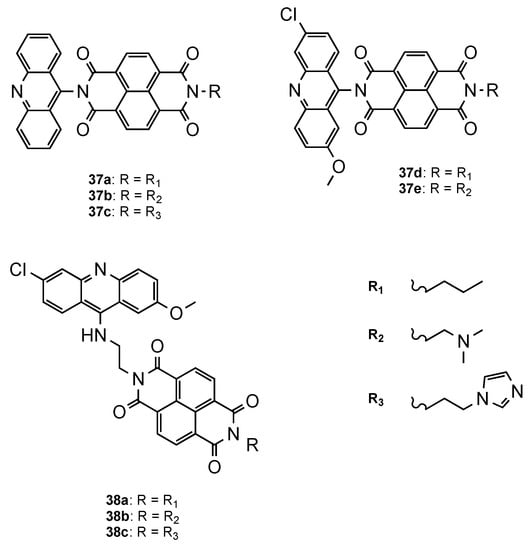
Another approach was proposed by Dana et al. [54], who developed a novel class of hybrids integrating acridine and redox-active naphthalenediimide (NDI) scaffolds either directly linked (37a–e, Figure 24) or through a flexible linker (38a–c, Figure 24). Both series were further evaluated against Pf CQS 3D7 and CQR W2 strains. Overall, the compounds showed better activities than the parent drugs NDI and acridine (NDI: IC50 = 260 nM; Acridine: IC50 = 26.4 nM). The orthogonal series (37a–e) displayed considerably less antiplasmodial activity than the flexible series (38a–c), which demonstrated the influence of the spacer linker on the antimalarial activity (37a–e: 419 < IC50 < 4197 nM; 38a–c: 3.65 < IC50 < 8.44 nM). Moreover, structure–activity relationship studies proved once again the importance, for antiplasmodial activity, of the incorporation of the substituents 6-chloro and 2-methoxy in the acridine core. Hybrids 38a and 38b presented the best activities, alongside no cytotoxic in mammalian fibroblast NIH3T3 cells (38a: IC50(3D7) = 3.65 nM, IC50(W2) = 52.20 nM; 38b: IC50(3D7) = 4.33 nM, IC50(W2) = 28.53 nM; CQ: IC50(3D7) = 12.56 nM, IC50(W2) = 430.60 nM) [54].
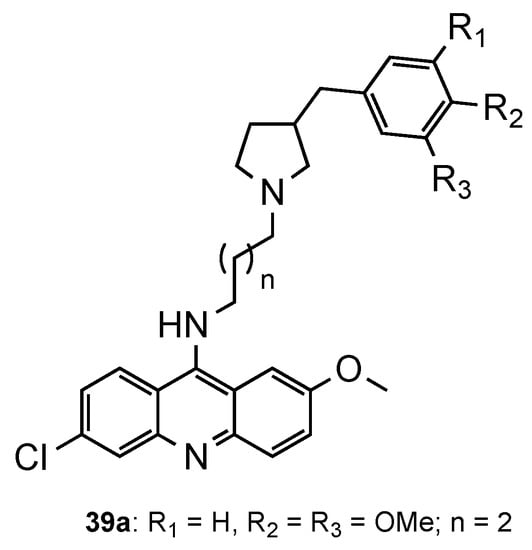
Considering the recent reports of resistance to ACT [3], Pandey et al. [55] developed a series of pyrrolidinoaminoalkane–acridine hybrids (39, Figure 25) to posteriorly use them as potential partners with artemisinin derivatives for the ACT. The two points of structural variations were the phenyl ring and the alkane spacer. When evaluated against the CQS 3D7 and the CQR K1 strains, compound 39a performed better (39a: IC50 (3D7) = 9.3 nM, IC50 (K1) = 5.2 nM). Then, 39a was evaluated in vivo in Swiss mice infected with the MDR strain P. yoelii nigeriensis at a dose of 100 mg/kg per day for 4 days via the oral route, showing > 90% suppression of parasitaemia on day 4. The authors further showed that, when tested in combination with artemether, arteether or artesunate, compound 39a serves as a good partner in ACT, namely, with artemether [55].
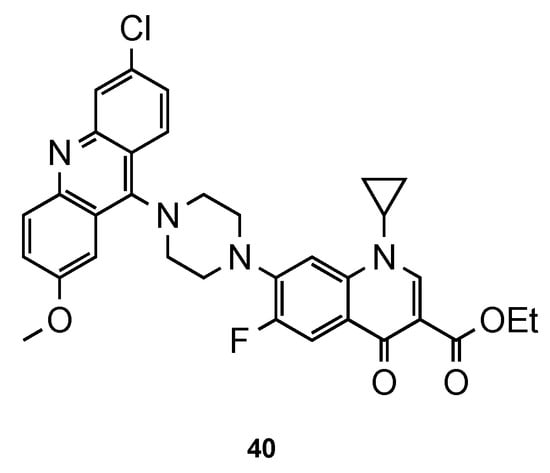
Recently, Dana et al. [56] focused their work on ciprofloxacin–acridine hybrids. Ciprofloxacin (CFX) is a second-generation fluoroquinolone-based antibiotic, known to be active against the in vitro culture of Pf [57,58]. In this work, the authors functionalized CFX in the N-terminal of the piperazine moiety with acridine scaffold. Hybrid 40 (Figure 26) was tested for its in vitro antimalarial activity against the CQS 3D7 strain of Pf. Although the activity of 40 was improved in comparison to that of CFX, it was not better than the reference CQ (3D7: IC50 (40) = 359.40 nM, IC50 (CFX) = 45350.0 nM, IC50 (CQ) = 12.56 nM). However, it is noteworthy that compound 40 did not show any hemolysis of infected RBCs or uninfected RBCs at their highest tested concentrations (10–45 µM), which may suggest minimal toxic effects in vivo [56].
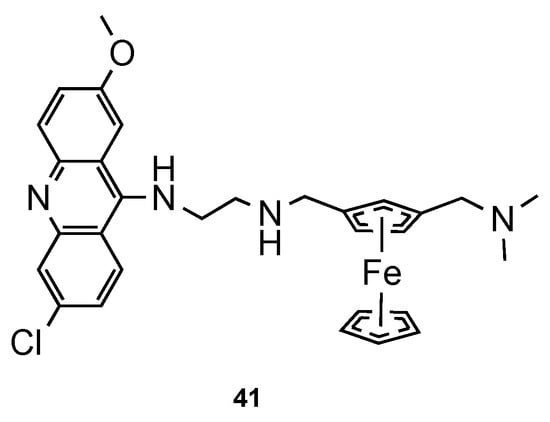
Blackie et al. [59] established the role of ferrocenyl moiety in the antiplasmodial activity of ferroquine, another import scaffold in antimalarial derivatives [60]. The authors concluded that ferrocenyl fragment serves simply as a hydrophobic spacer group. Next, they synthesized compound 41 (Figure 27) and tested them against CQS 3D7 and CQR K1 strains of Pf. It is noteworthy that hybrid 41 showed potent antimalarial activity (ED50 = 1 and 8 nM against CQS 3D7 and CQR K1 Pf strains, respectively), comparatively to CQ (ED50 = 8.52 and 290 nM against CQS 3D7 and CQR K1 Pf strains, respectively) [59].
This review depicts a brief background of the development of antimalarials based on the heteroaromatic core of QN focused on the last two decades. Despite the potent antimalarial activity of QN, its toxicity was among the reasons for its rapid substitution by CQ. Thus, all the modifications described in this review were mainly driven to increase the antimalarial activity of QN derivatives but also to improve their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties, as well as overcome problems of cytotoxicity. The classical modifications in the side-chain of acridine reported in this paper emphasized the importance of the substituents methoxy and chlorine at positions 2 and 6 of the acridine ring, respectively. Still, it was also clear that small changes in the chemical structure of the molecules cause major impacts in their antimalarial activity. Alongside these modifications, this review also summarized the advances made towards hybrid molecules holding the acridine moiety. By joining two different molecules with a distinct mechanism of action, it is possible not only to improve the antiplasmodial activity but also to overcome resistance problems, often associated with classical antimalarial compounds. Although this approach does not always fulfill its purpose, it highlights the importance of the nature of the linker between the two moieties. It is noteworthy that the reported efforts have been progressively unveiling novel acridine-based derivatives as promising leads that will hopefully guide future research on the development of acridine-related molecules for the treatment of malaria.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/molecules26030600