Transcription of protein-encoding genes starts with forming a pre-initiation complex comprised of RNA polymerase II and several general transcription factors. To activate gene expression, transcription factors must overcome the repressive chromatin structure, which is accomplished with multiprotein complexes. Histone Acetyl Transferases (HAT) catalyze acetylation of specific lysine residues in histone N-tails, which are involved in transcriptional regulation and other nuclear processes. HATs are parts of large multiprotein complexes, like the SAGA complex, where their activity is enhanced, and their substrate specificity is altered. The whole complex is recruited to target sequences on the genome with other components involved in protein-protein interactions. A prototypical HAT which acts as a transcriptional adaptor is known as General Control Nonrepressed protein 5 (GCN5), first identified in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. GCN5 was defined biochemically as the first transcription-linked HAT with specificity for histone H3 lysine 14 (H3K14). However, GCN5 could also acetylate additional histone lysine residues, such as H3K9, H3K18, H3K23, H3K27, H3K36, other histones such as H4 and H2B and non-histone nuclear proteins. In Arabidopsis, GCN5 is required for many developmental processes such as leaf development, apical dominance, root meristem activity, inflorescence, floral meristem function and flower fertility.
- Arabidopsis thaliana
- Viridiplantae
- GCN5
- ADA2b
- SGF29
- ADA3
- plant development
- plant stress responses
- SAGA
- histone acetylation
1. The Discovery of Histone Acetyltransferase GCN5 and the Associated SAGA Complex
Transcription of protein-encoding genes starts with forming a pre-initiation complex comprised of RNA polymerase II and several general transcription factors [1]. To activate gene expression, transcription factors must overcome the repressive chromatin structure, which is accomplished with multiprotein complexes [2]. Chromatin-modifying coactivators dynamically deposit or remove post-translational modifications (PTMs) on histones, creating or erasing docking surfaces for specific regulatory factors [2]. One class involves complexes that modify the nucleosomal histones through acetylation, phosphorylation, methylation and other modifications [3]. Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) catalyze acetylation of specific lysine residues in histone N-tails, which are involved in transcriptional regulation and other nuclear processes. HATs are parts of large multiprotein complexes, like the SAGA complex, where their activity is enhanced and their substrate specificity is altered. The whole complex is recruited to target sequences on the genome with other components involved in protein-protein interactions [4]. HATs and histone deacetylases (HDACs) can target promoters for either the activation or suppression of gene expression [2]. A prototypical HAT which acts as a transcriptional adaptor is known as GENERAL CONTROL NON-REPRESSED PROTEIN 5 (GCN5), first identified in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [5][6]. GCN5 was defined biochemically as the first transcription-linked HAT [7] with specificity for histone H3 lysine 14 (H3K14) [8]. However, GCN5 could also acetylate additional histone lysine residues, such as H3K9, H3K18, H3K23, H3K27, H3K36, and other histones such as H4 and H2B [9][10]. Furthermore, GCN5 was the HAT component of two distinct transcriptional adaptor complexes, SAGA (Spt-Ada-Gcn5-acetyltransferase) and ADA, capable of acetylating histones in nucleosomes [9]. These complexes are conserved in many eukaryotes [11] and have multiple distinct functions which lead to transcriptional activation. In yeast, SAGA is a large multi-subunit protein complex composed of at least 19 proteins [11][12]. These proteins are separated into four distinct modules, with two specific enzymatic activities: the HAT module that acetylates histones and contains GCN5, ADA2, ADA3, and SGF29; the deubiquitylase (DUB) module that triggers deubiquitination of histone H2B and includes UBP8, SGF11, SGF73, and SUS1; the suppressor of Ty (SPT) module that contains TRA1, ADA1, SPT3, SPT7, SPT8, and SPT20 (ADA5), and the TATA-binding protein (TBP)-associated factor (TAF) module that includes TAF5, TAF6, TAF9, TAF10, and TAF12 [4][12]. Recently, new structural studies showed that most of the proteins of SPT and TAF modules form a core module (COREm) [13][14]. The core module binds to TBP and consists of subunit TAF5, SPT20, and a histone octamer-like fold. The histone octamer-like fold comprises the heterodimers TAF6-TAF9, TAF10-SPT7, TAF12-ADA1, and two histone-fold domains in SPT3 [13][14]. SGF73 subunit is in association with DUBm and COREm. When a nucleosome binds to a SAGA complex, the HAT and the DUB modules are displaced from the COREm [14]. Several proteins in the SAGA complex have distinct protein-binding domains, writers, or readers domains (HAT, tudor, bromodomains etc.) that enable SAGA to associate with chromatin or other proteins through PTMs. Furthermore, SAGA proteins are also part of other complexes [11]. For instance, GCN5 is also part of the human ATAC complex [15]. TRA1 is also a component of the NuA4 acetyltransferase complex [16]. The proteins of the TAF module are also components of the TFIID complex [17].
2. The Plant SAGA Complex
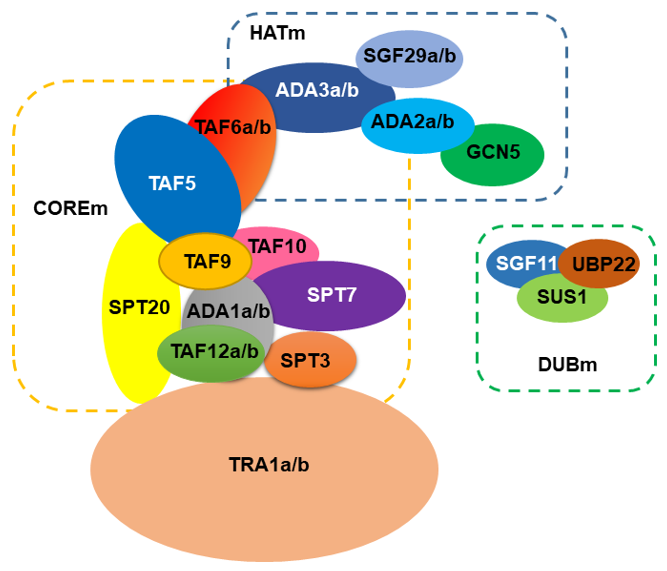
Using the genome of Arabidopsis thaliana as a reference for plants, the SAGA complex is comprised of approximately 24 proteins (Figure 1). Using the current structure of the yeast SAGA complex [13][14] the HAT module (HATm) in Arabidopsis consists of the same proteins, GCN5, ADA2, ADA3, and SGF29. However, the Arabidopsis HATm contains two subunits of ADA2, ADA3, and SGF29 (designated as ADA2a, ADA2b, ADA3a, ADA3b, SGF29a, and SGF29b, respectively). Based on this structure, the Arabidopsis COREm consists of similar TAF proteins (TAF5, TAF6, TAF9, TAF10, and TAF12), and the adaptor proteins ADA1 and SPT20. The yeast SPT module consists of another three subunits SPT3, SPT7, and SPT8, distinct from the plant homologues. For instance, in Arabidopsis genome, SPT8 is not encoded; however, the presence of multiple WD40 domains in yeast Spt8 makes the evolutionary information challenging [15]. Furthermore, Arabidopsis SPT3 homologue is like TAF13, whereas SPT7 homologues appear to have a conserved bromodomain found in AtHAF1 (TAF1) subunit. Interestingly, several subunits from the COREm are duplicated in Arabidopsis including ADA1, TAF6, and TAF12. The COREm occupies a central position in the complex and is connected to the TRA1 module through TAF12-SPT20 interaction [13][14]. In Arabidopsis, TRA1 has two homologues (TRA1a and TRA1b). In yeast, Tra1 recruits SAGA to promoters through the interaction with transcription factors [16]. In Arabidopsis, TRA1a and TRA1b promote H2A.Z deposition at the whole-genome level as part of the activity of SWR1 complex [18]. Finally, the DUB module (DUBm) is partially present in Arabidopsis genome, consisting of the UBP22 protein that deubiquitinates histone H2B, a second enzymatic activity of the complex, and the associated proteins SGF11 and ENY2. The fourth subunit of yeast DUBm, SGF73, is absent in Arabidopsis, suggesting that DUBm may function as H2Bub1 deubiquitinase independent from SAGA complex [19][20].
Figure 1. A model for the organization of SAGA complex in Arabidopsis.
In multi-cellular eukaryotes, SAGA (or GCN5-containing) complexes appear to have an essential role in development [21]. Likewise, in Arabidopsis, gcn5 mutants have pleiotropic effects on every development aspect (Table 1) [22][23]. Furthermore, mutations in another HATm subunit ADA2b, result in pleiotropic phenotypes on every part of the whole plant life cycle; however, some are different from gcn5 mutants [22][24]. Moreover, both gcn5 and ada2b mutants are implicated in plant responses to abiotic and biotic stress [22][25][26][27]. The other components of HATm in Arabidopsis do not affect plant development; however, the role of ADA2a on plant development is made redundant by the ADA2b function, since the Arabidopsis double mutant ada2aada2b phenocopies the gcn5 mutation [28]. Mutation in SGF29a is implicated in salt stress responses by having an auxiliary role to ADA2b [29]. These genetic interactions, together with the biochemical data showing that GCN5 acts through ADA2b and ADA2a [30][31], suggest that different versions of GCN5-containing (SAGA) complexes may exist in plants.
Several subunits of the COREm, like TAF5 and TAF6a, are required for plant viability [32][33]. In addition, both TRA1 genes are also essential for plant life cycle [33]. These functions may not be specific to SAGA complex since TAF5 and TAF6 are also present in the TFIID complex, and TRA1 is also a component of the NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex. The other members of COREm, like the SPT20 and TAF10, are implicated in environmental stresses [34][35]. TAF12b (also known as EER4 or CHK1) is involved in ethylene and cytokinin responses [36][37]. Finally, the DUBm components in Arabidopsis are not crucial for proper plant development [20][38].
Table 1. Comparison between Arabidopsis and known yeast SAGA subunits.
|
SAGA Modules |
Yeast |
Arabidopsis thaliana |
Arabidopsis Mutant Phenotype |
|
HATm |
GCN5 |
GCN5 (AT3G54610, HAG1) |
Pleiotropic effects on development and responses to stress [22][23][25][26] |
|
ADA2 |
ADA2b (AT4G16420, PRZ1) |
Pleiotropic effects on development and responses to stress [22][24][27] |
|
|
ADA2a (AT3G07740) |
No developmental abnormalities [28] |
||
|
ADA3 |
ADA3a (AT2G19390) |
Involved in flowering (Vlachonasios, under review) |
|
|
ADA3b (AT4G29790) |
No developmental abnormalities [39] |
||
|
SGF29 |
SGF29a (AT3G27460) |
No developmental abnormalities [29] |
|
|
SGF29b (AT5G40550) |
No developmental abnormalities [29] |
||
|
COREm |
ADA1 |
ADA1a (AT2G24530) |
Not available |
| ADA1b (AT4G31440) |
Not available |
||
|
SPT3 |
TAF13 (AT1G026280) |
Seed development [40] |
|
|
SPT7 |
HAF1 (AT1G32750, HAC13, TAF1) |
Light responses [41] |
|
|
SPT8 |
Not detected |
|
|
|
SPT20 |
SPT20 (AT1G72390) |
Late flowering [34] |
|
|
TAF5 |
TAF5 (AT5G25150) |
Lethal [31] |
|
|
TAF6 |
TAF6a (AT1G04950) |
Lethal [32] |
|
|
TAF6b (AT1G54360) |
|
||
|
TAF9 |
TAF9 (AT1G54140) |
Not available |
|
|
TAF10 |
TAF10 (AT4G31720) |
Involved in osmotic stress [35] |
|
|
TAF12 |
TAF12a (AT3G10070) |
|
|
|
TAF12b (AT1G17440, EER4, CKH1) |
|||
|
TRA1m |
TRA1 |
TRA1a (AT2G17930) |
Early flowering [33] |
|
TRA1b (AT4G36080) |
No developmental abnormalities [33] |
||
|
DUBm |
SGF73 |
Not detected |
|
|
SGF11 |
SGF11 (AT5G58575) |
No developmental abnormalities [38] |
|
|
UBP8 |
UBP22 (AT5G10790) |
No developmental abnormalities [20] |
|
|
SUS1 |
SUS1 (AT3G27100, ENY2) |
No developmental abnormalities [38] |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/plants10020308
References
- Roeder, R.G. The role of general initiation factors in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1996, 21, 327–335.
- Li, B.; Carey, M.; Workman, J.L. The role of chromatin during transcription. Cell 2007, 128, 707–719.
- Bannister, A.J.; Kouzarides, T. Regulation of chromatin by histone modifications. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 381–395.
- Strahl, D.B.; Briggs, S.D. The SAGA continues: The rise of cis- and trans-histone crosstalk pathways. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Reg. Mechan. 2020, 194600.
- Berger, S.L.; Pina, B.; Silverman, N.; Marcus, G.A.; Agapite, J.; Reiger, J.L.; Triezenberg, S.J.; Guarente, L. Genetic isolation of ADA2: A potential transcriptional adaptor required for function of certain acidic activation domains. Cell 1992, 70, 251–265.
- Georgakopoulos, T.; Thireos, G. Two distinct yeast transcriptional activators require the function of the GCN5 protein to promote normal levels of transcription. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 4145–4152.
- Brownell, J.E.; Zhou, J.; Ranalli, T.; Kobayashi, R.; Edmondson, D.G.; Roth, S.Y.; Allis, C.D. Tetrahymena histone Acetyltransferase a: A homolog to yeast Gcn5p linking histone acetylation to gene activation. Cell 1996, 84, 843–851.
- Kuo, M.H.; Brownell, J.E.; Sobel, R.E.; Ranalli, T.A.; Cook, R.G.; Edmondson, D.G.; Roth, S.Y.; Allis, C.D. Transcription-linked acetylation by Gcn5p of histones H3 and H4 at specific lysines. Nature 1996, 383, 269–272.
- Grant, P.A.; Duggan, L.; Côté, J.; Roberts, S.M.; Brownell, J.E.; Candau, R.; Ohba, R.; Owen-Hughes, T.; Allis, C.D.; Winston, F.; et al. Yeast Gcn5 functions in two multisubunit complexes to acetylate nucleosomal histones: Characterization of an Ada complex and the SAGA (Spt/Ada) complex. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 1640–1650.
- Morris, S.A.; Rao, B.; Garcia, B.A.; Hake, S.B.; Diaz, R.L.; Shabanowitz, J.; Hunt, D.F.; Allis, C.D.; Lieb, J.D.; Strahl, B.D. Identification of histone H3 lysine 36 acetylation as a highly conserved histone modification. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 7632–7640.
- Lee, K.K.; Workman, J.L. Histone acetyltransferase complexes: One size doesn’t fit all. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 284–295.
- Baker, S.P.; Grant, P.A. The SAGA continues: Expanding the cellular role of a transcriptional co-activator complex. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5329–5340.
- Wang, H.; Dienemann, C.; Stützer, A.; Urlaub, H.; Cheung, A.C.M.; Cramer, P. Structure of the transcription coactivator SAGA. Nature 2020, 577, 717–720.
- Papai, G.; Frechard, A.; Kolesnikova, O.; Crucifix, C.; Schultz, P.; Ben-Shem, A. Structure of SAGA and mechanism of TBP deposition on gene promoters. Nature 2020, 577, 711–716.
- Helmlinger, D.; Tora, L. Sharing the SAGA. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2017, 42, 850–861.
- Brown, C.E.; Howe, L.; Sousa, K.; Alley, S.C.; Carrozza, M.J.; Tan, S.; Workman, J.L. Recruitment of HAT complexes by direct activator interactions with the ATM-related Tra1 subunit. Science 2001, 292, 2333–2337.
- Lee, T.I.; Causton, H.C.; Holstege, F.C.; Shen, W.C.; Hannett, N.; Jennings, E.G.; Winston, F.; Green, M.R.; Young, R.A. Redundant roles for the TFIID and SAGA complexes in global transcription. Nature 2000, 405, 701–704.
- Luo, Y.X.; Hou, X.M.; Zhang, C.J.; Tan, L.M.; Shao, C.R.; Lin, R.N.; Su, Y.N.; Cai, X.W.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; et al. A plant-specific SWR1 chromatin-remodeling complex couples histone H2A.Z deposition with nucleosome sliding. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e102008.
- Grasser, K.D.; Rubio, V.; Barneche, F. Multifaceted activities of the plant SAGA complex. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gene Regul. Mech. 2020, 194613.
- Nassrallah, A.; Rougée, M.; Bourbousse, C.; Drevensek, S.; Fonseca, S.; Iniesto, E.; Ait-Mohamed, O.; Deton-Cabanillas, A.F.; Zabulon, G.; Ahmed, I.; et al. DET1-mediated degradation of a SAGA-like deubiquitination module controls H2Bub homeostasis. eLife 2018, 7, e37892.
- Wang, L.; Dent, S.Y.R. Functions of SAGA in development and disease. Epigenomics 2014, 6, 329–339.
- Vlachonasios, K.E.; Thomashow, M.F.; Triezenberg, S.J. Disruption mutations of ADA2b and GCN5 transcriptional adaptor genes dramatically affect Arabidopsis growth, development, and gene expression. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 626–638.
- Bertrand, C.; Bergounioux, C.; Domenichini, S.; Delarue, M.; Zhou, D.-X. Arabidopsis histone acetyltransferase AtGCN5 regulates the floral meristem activity through the WUSCHEL/AGAMOUS pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 28246–28251.
- Sieberer, T.; Hauser, M.-T.; Seifert, G.J.; Lusching, C. PROPORZ1, a putative Arabidopsis transcriptional adaptor protein, mediates auxin and cytokinin signals in the control of cell proliferation. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 837–842.
- Vlachonasios, K.E.; Kaldis, A.; Nikoloudi, A.; Tsementzi, D. The role of transcriptional coactivator ADA2b in Arabidopsis abiotic stress responses. Plant Signal. Behav. 2011, 6, 1475–1478.
- Benhamed, M.; Bertrand, C.; Servet, C.; Zhou, D.-X. Arabidopsis GCN5, HD1, and TAF1/HAF2 interact to regulate histone acetylation required for light-responsive gene expression. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 2893–2903.
- Kim, S.; Piquerez, S.J.M.; Ramirez-Prado, J.S.; Mastorakis, E.; Veluchamy, A.; Latrasse, D.; Manza-Mianza, D.; Brik-Chaouche, R.; Huang, Y.; Rodriguez-Granados, N.Y.; et al. GCN5 modulates salicylic acid homeostasis by regulating H3K14ac levels at the 5’ and 3’ ends of its target genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 5953–5966.
- Hark, A.T.; Vlachonasios, K.E.; Pavangadkar, K.A.; Rao, S.; Gordon, H.; Adamakis, I.D.; Kaldis, A.; Thomashow, M.F.; Triezenberg, S.J. Two Arabidopsis orthologs of the transcriptional coactivator ADA2 have distinct biological functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1789, 117–124.
- Kaldis, A.; Tsementzi, D.; Tanriverdi, O.; Vlachonasios, K.E. Arabidopsis thaliana transcriptional co-activators ADA2b and SGF29a are implicated in salt stress responses. Planta 2011, 233, 749–762.
- Mao, Y.; Pavangadkar, K.A.; Thomashow, M.F.; Triezenberg, S.J. Physical and functional interactions of Arabidopsis ADA2 transcriptional coactivator proteins with the acetyltransferase GCN5 and with the cold-induced transcription factor CBF1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1759, 69–79.
- Mastorakis, E. Chromatin Remodeling during Plant-Pathogen Interactions. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Warwick, Coventry, UK, 2017.
- Mougiou, N.; Poulios, S.; Kaldis, A.; Vlachonasios, K.E. Arabidopsis thaliana TBP-Associated Factor 5 is essential for plant growth and development. Mol. Breed. 2012, 30, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, C.; Clerici, E.; Dreni, L.; Horlow, C.; Caporali, E.; Colombo, L.; Kater, M.M. The Arabidopsis TFIID factor AtTAF6 controls pollen tube growth. Dev. Biol. 2005, 285, 91–100.
- Endo, M.; Tanigawa, Y.; Murakami, T.; Araki, T.; Nagatani, A. Phytochrome-dependent late-flowering accelerates flowering through physical interactions with phytochrome B and constans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18017–18022.
- Gao, X.; Ren, F.; Lu, Y.T. The Arabidopsis mutant stg1 identifies a function for TBP-associated factor 10 in plant osmotic stress adaptation. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006, 47, 1285–1294.
- Robles, L.M.; Wampole, J.S.; Christians, M.J.; Larsen, P.B. Arabidopsis enhanced ethylene response 4 encodes an EIN3-interacting TFIID transcription factor required for proper ethylene response, including ERF1 induction. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 2627–2639.
- Kubo, M.; Furuta, K.; Demura, T.; Fukuda, H.; Liu, Y.G.; Shibata, D.; Kakimoto, T. The CKH1/EER4 gene encoding a TAF12-like protein negatively regulates cytokinin sensitivity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 629–637.
- Pfab, A.; Bruckmann, A.; Nazet, J.; Merkl, R.; Grasser, K.D. The Adaptor Protein ENY2 Is a Component of the Deubiquitination Module of the Arabidopsis SAGA Transcriptional Co-activator Complex but not of the TREX-2 Complex. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 1479–1494.
- Srivastava, R.; Rai, K.M.; Pandey, B.; Singh, S.P.; Sawant, S.V. Spt-Ada-Gcn5-Acetyltransferase (SAGA) complex in plants: Genome wide identification, evolutionary conservation and functional determination. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134709.
- Lindner, M.; Simonini, S.; Kooiker, M.; Gagliardini, V.; Somssich, M.; Hohenstatt, M.; Simon, R.; Grossniklaus, U.; Kater, M.M. TAF13 interacts with PRC2 members and is essential for Arabidopsis seed development. Dev. Biol. 2013, 379, 28–37.
- Bertrand, C.; Benhamed, M.; Li, Y.F.; Ayadi, M.; Lemonnier, G.; Renou, J.P.; Delarue, M.; Zhou, D.-X. Arabidopsis HAF2 gene encoding TATA-binding protein (TBP)-associated factor TAF1, is required to integrate light signals to regulate gene expression and growth. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 1465–1473.