Metal-organic frameworks represent a porous class of materials that are build up from metal ions or oligonuclear metallic complexes and organic ligands. They can be considered as sub-class of coordination polymers and can be extended into one-dimension, two-dimensions, and three-dimensions. Depending on the size of the pores, MOFs are divided into nanoporous, mesoporous, and macroporous items. The latter two are usually amorphous. MOFs display high porosity, a large specific surface area, and high thermal stability due to the presence of coordination bonds. The pores can incorporate neutral molecules, such as solvent molecules, anions, and cations, depending on the overall charge of the MOF, gas molecules, and biomolecules. The structural diversity of the framework and the multifunctionality of the pores render this class of materials as candidates for a plethora of environmental and biomedical applications and also as catalysts, sensors, piezo/ferroelectric, thermoelectric, and magnetic materials.
- metal-organic frameworks
- coordination polymers
- synthesis
- applications
1. Introduction
Metal Organic Frameworks (MOFs) constitute a class of solid porous materials, which consist of metal ions or metallic clusters, which act as nodes, and polydentate organic ligands, which act as linkers between the nodes. The metal nodes (metal ions or metallic clusters) act as connection points and the organic ligands bridge the metal centers through coordination bonds, thus, forming networks of one-dimension, two-dimensions, or three-dimensions. The main structural features of the MOFs, which are directly related to their properties and applications, are the high porosity, the large volume of the pores, which can reach the 90% of the crystalline volume or more, the large specific surface area (several thousand m2·g−1), and the high thermal stability (250–500 °C) due to the presence of strong bonds (e.g., C–C, C–H, C–O, and M–O). An important sub-class of MOFs are the Isoreticular Metal Organic Frameworks (IRMOFs), which were first synthesized by the group of Yaghi [1]. The archetype IRMOF-1 was based on octahedral Zn-O-C clusters and 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid (BDC) bound to form a network with pcu topology. The series of IRMOFs retain the pcu topology and are based on varied organic linkers resulting in variable pore volumes and surface area. According to the terminology officially adopted by IUPAC on 2013 [2], MOFs are a sub-class of coordination networks (i.e., coordination compounds which extend to one-dimension, two-dimensions, or three-dimensions through repeating coordination entities), which are a sub-class of coordination polymers (i.e., coordination compounds with repeating coordination entities extending in 1, 2, or 3 dimensions, which do not need to be crystalline). MOFs are dynamic systems susceptible to structural changes upon external stimuli, such as temperature and pressure, and may not be crystalline.
The chemistry of MOFs has evolved rapidly in recent decades and it has become possible to adjust the size and shape of the pores, the network topology, and their surface area, so that the structures and properties of MOFs can be adapted to the needs of each application. The designed synthesis of new MOFs with desired physical and chemical properties in terms of Crystal Engineering principles requires the understanding of molecular and/or intermolecular interactions within the three-dimensional arrangement. The molecular interactions are the coordination bonds between the metal ions and the organic ligands, whereas the intermolecular interactions are the weak interactions such as hydrogen bonds, π–π interactions, etc. The designed synthesis of MOFs also requires complete control of the components and tools to be used, which is a fact that has been strongly argued by many researchers who believe that the complete control of all parameters of a chemical reaction is not feasible. On the other hand, lies the argument of the designed synthesis of IRMOFs, based on MOF-5, which resulted in a fairly large series of solids.
The structural characteristics of the MOFs are mainly affected by the large number of coordination geometries adopted by the metal ions and the use of oligonuclear metal clusters as nodes (secondary building units, SBUs), the geometrical characteristics, and the flexibility of the organic ligands, the role of the counterions, and the reaction solvent [3,4,5,6,7]. The network topology and dimensionality of the MOFs are strictly related to the different coordination geometries that can be adopted by the metal nodes, which vary depending on the electronic structure of the metal ions. Transition metal ions, especially those of the first row, lanthanides, and alkaline earth metals have been used because they display a wide variety of coordination numbers, geometries, and oxidation states, thus, offering synthetic and structural diversity. The use of rigid or flexible organic ligands plays a very important role in designing a MOF because the flexible ligands offer increased degrees of freedom with respect to the rigid ones and can lead to unpredictable crystal structures [8]. Organic molecules containing one or more N-donor or O-donor atoms are normally used as organic ligands to bridge between the metal ions in MOFs. Carboxylates (either aliphatic or aromatic containing one or more rings), pyridyl (e.g., pyrazine and 4.4′-bipyridyl derivatives) and cyano compounds, polyamines resulting from imidazole, oxalic acid, and benzene, phosphonates, sulfonates, and crown ethers are the most common ligands used. The anions counterbalance the positive charge of cationic MOFs and influence the supramolecular structure either being coordinated to the metal ions or by occupying the pores of the structure [9]. Organic cations can be hosted within the pores of anionic MOFs and can be exchanged by other cations, as in the case of bio-MOF-1, which hosts Me2NH2+ cations and solvate molecules and retains its crystallinity in solvent exchange experiments as well as during storage and release of cationic drug molecules [10]. Metal cations are usually coordinated to the original network, thus, altering its structural characteristics, whereas anionic metallic clusters require large porous structures and, in exceptional cases, can be exchanged by other cations for sensor applications [11]. The reaction solvent can affect the crystallization kinetics and the network topology through steric effects, fill coordination sites of the metal ions, complete the pores of the MOF, or participate in weak intermolecular interactions contributing to the crystal and thermal stability of the lattice.
The three-dimensional structure of MOFs is formed due to strong coordination bonds between the metal ions and the organic ligands and displays cavities and inner surfaces, which are occupied by counterions, guest molecules, and/or solvate molecules. Other types of interactions, such as hydrogen bonds, metal-metal bonds, and π–π interactions can occur and contribute to the stability of the MOFs. However, coordination bonds are stronger and provide more stable networks. Depending on the size of the cavities/pores, the MOFs are divided into nanoporous materials, with pores less than 20 Å in diameter, mesoporous materials (20–500 Å in diameter), and macroporous materials (over 500 Å in diameter). Most of the mesoporous and macroporous MOFs are amorphous materials [12]. Increasing the size of the pores is still a challenge since interpenetration prevents the presence of free empty space in a network. Interpenetration is favored by organic ligands with aromatic rings capable of the development of π–π interactions. Highly porous MOFs have been prepared by using poly-carboxylato and rigid alkyne-type ligands, as well as SBUs with large dimensions, which determine the size of the pores [13].
2. Applications of MOFs
MOFs display a range of structural features, namely large surface area, high porosity, crystallinity and thermal stability, and functionality of pores and frameworks, which render them promising materials for environmental and biomedical applications, as catalysts, sensors, absorbers for toxic gases, and metal ions.
2.1. Gas Adsorption/Separation/Storage for Energy and Environmental Applications
MOFs have been extensively studied for applications in gas storage. For example, H2 and CH4 represent alternative energy resources for future vehicles, and their effective usage still remains a challenge for the automotive industry. The capture of toxic industrial gases, such as NH3 and H2S, and volatile hydrocarbons, like benzene, as well as the removal of SO2 and NOx from flue gas, are of great importance for environmental protection. A very critical step in the chemical industry is the separation of mixtures of gases, such as CO2 capture and CO2/CH4, CO2/N2 separation, O2 purification, and so on.
CO2 is the main greenhouse gas and is responsible for global warming and for water acidification. MOF-74-Mg, which is the magnesium analogue of MOF-74, shows the highest CO2 uptake capacity of 228 and 180 cm3·g−1 at 273 and 298 K and 1 bar, respectively (Figure 2) [57]. The exceptional CO2 uptake by MOF-74-Mg is attributed to the increased ionic character of the Mg-O bond, which imparts additional uptake beyond weight effects while maintaining the reversibility of adsorption. MOF-210 has a very high surface area of 10,450 m2·g−1 and shows a CO2 uptake value of 2400 mg·g−1 (74.2 wt %, 50 bar at 298 K), which is larger than that of MOF-177 or MIL-101(Cr) (60 wt % and 56.9 wt %, respectively) [58,59,60]. MOF-200 has a similar CO2 uptake as MOF-210 under similar conditions. Other MOFs, which show considerably higher CO2 uptake compared with other solid materials, are the NU-100 (69.8 wt %, 40 bar at 298 K), the MOF-5 (58 wt %, 10 bar at 273 K), and the HKUST-1 (19.8 wt %, 1 bar at 298 K).
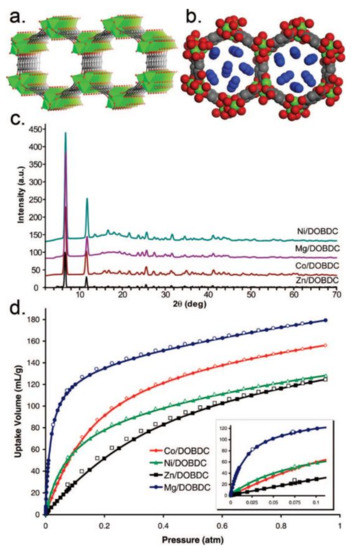
Figure 2. (a) The 1D channels of MOF-74-Mg, Mg-DOBDC (solvents omitted). (b) Space-filling model of the pore structure of MOF-74-Mg (Mg, green. C, grey. O, red). (c) PXRD data for the isostructural MOFs M-DOBDC (M = Zn, Co, Mg, Ni). (d) CO2 sorption isotherm (296K, 0 to 1 atm) of the isostructural MOFs M-DOBDC (inset: CO2 sorption isotherms at 296 K, 0 to 0.1 atm). Reprinted with permission from J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10870–10871 ([57]). Copyright 2008 American Chemical Society.
Synthetic strategies for the preparation of MOFs with efficient CO2 uptake capacity have been developed and include amine incorporation, introduction of functional groups, and additional metal ions and control of pore size. The method used in the industry for CO2 separation is the amine scrubbing, which is high-energy consuming and presents disadvantages, such as amine degradation and equipment corrosion. Alternatively, MOFs incorporating amines have been examined as potential candidates for CO2 separation. For example, incorporation of N,N′-dimethylethylenediamine (mmen) within the [Mg2(dobpdc)] MOF (dobpdc4− = 4,4′-dioxido-3,3′-biphenyldicarboxylate) afforded [mmen-Mg2(dobpdc)], which displays an exceptional capacity for CO2 adsorption at low pressures, 2.0 mmol·g−1 (8.1 wt %) at 0.39 mbar, and 25 °C and 3.14 mmol·g−1 (12.1 wt %) at 0.15 bar and 40 °C, at conditions relevant to removal of CO2 from air and flue gas, respectively [61]. In addition, [en-Mg2(dobpdc)] and [dmen-Mg2(dobpdc)] (en = ethylenediamine, dmen = N,N′-dimethylethylenediamine) display significant CO2 uptakes (3.63 mmol·g−1 and 3.77 mmol·g−1, respectively) at 0.15 bar [62]. Bio-MOF-11, [Co2(ad)2(CH3CO2)2]·2dmf·0.5H2O (ad− = adeninate) contains pyrimidine and amino groups within the pores of the framework and exhibits high CO2 capacity (~6 mmol·g−1 at 273 K) and exceptional selectivity for CO2 over N2 at 273 K (81:1) and 298 K (75:1) [63]. MOFs functionalized with low-molecular weight polymers containing amino groups, such as PEI (polyethyleneimine), have shown impressive CO2 uptake, which were many times larger than the respective MOFs. For example, PEI-MIL-101-125 display CO2 uptake of 3.95 and 4.51 mmol·g−1, respectively, over four times than that of MIL-101-125, and PEI@UiO-66 shows CO2 uptake up to 1.65 mmol·g−1 and CO2/CH4 selectivity 111, which are much larger values than UiO-66 [64,65]. Yaghi and co-workers reported the functionalization of the organic ligand of IRMOF-74-III with primary amine through ligand modification, thus, yielding six analogs with different functional groups (–CH3, –NH2, –CH2NHBoc, –CH2NMeBoc, –CH2NH2, and –CH2NHMe). Spectroscopic data revealed that CO2 binds chemically to IRMOF-74-III-CH2NH2 and IRMOF-74-III-CH2NHMe to form carbamic species. The CO2 uptake of IRMOF-74-III-CH2NH2 is 3.2 mmol·g−1 at 800 Torr and 298 K [66]. Introduction of polar functional groups in the pores of MOFs through direct synthesis or post-synthesis modification was proved an efficient method to enhance the adsorption capacity and selectivity of CO2. For example, UPC-12 exhibits high selectivity for CO2 due to the formation of H-bonds between the CO2 molecules and the -COOH groups within the pores and the π–π stacking interactions between the CO2 molecules and the bpy moieties of the MOF [67]. NbO-type MOFs retain the NbO-type structure upon functionalization with different groups, such as amide, nitro groups, and N-heterocycles, and display higher CO2 uptake than the parent MOFs [68,69,70,71,72]. Ligand functionalized UiO-66, UiO-66(Zr)-(COOH)2 shows high CO2/N2 selectivity of 56 upon a 15/85 CO2/N2 gas mixture at 303 K and 1 bar, and UiO-67 functionalized BUT-10 and BUT-11 show enhanced CO2 adsorption uptakes (50.6 and 53.5 cm3·g−1, respectively) and separation selectivity over N2 and CH4 (18.6 and 31.5 for a 15/85 CO2/N2 gas mixture, and 5.1 and 9.0 for a 10/90 CO2/CH4 gas mixture) [73,74]. The control of the pore size of the MOFs allows inclusion of smaller guests (e.g., CO2 3.30 Å) and enables ultra-high selectivity. However, the precise control of pores with a size of 3–4 Å is very difficult. Examples of isoreticular MOFs, SIFSIX-2-Cu, SIFSIX-2-Cu-i, SIFSIX-3-Zn, and SIFSIX-3-Cu showed more efficient CO2 capture for the latter, which exhibits the smallest pore size [75,76]. The approach of ‘Single Molecule Trap’ (SMT) for the capture of a single CO2 molecule was developed by Zhou and co-workers who prepared paddlewheel dicopper complexes (SMT-1-2) with intramolecular metal-metal distance of 7.4 Å, suitable for the accommodation of one CO2 molecule. Incorporation of SMT-1 to the 3D framework of PCN-88 enhanced the CO2 uptake to 4.20 mmol·g−1 at 296 K and 1 bar with respect to 0.63 mmol·g−1 for SMT-1 under identical conditions [77]. MOFs based on heterometallic SBUs of the general formula [MII2MIII(OH)(COO)6], CPM-200s, display excellent CO2 uptake capacity, 207.6 and 190.9 cm3·g−1 for CPM-200-Fe/Mg and CPM-200-In/Mg, respectively, at 273 K and 1 bar, comparable to the value of MOF-74-Mg [78]. Other examples of heterometallic MOFs such as MIL-101(Cr,Mg) and UiO-66(Li,Na,K,Pb) display higher CO2 uptake with respect to the parent MOF, but is much smaller than MOF-74-Mg and CPM-200s, which hold the highest values [79,80,81,82]. The mixed-metal solid-solution MOFs [(AlOH)1−x(VO)xL] (x = 0–1, L = 1,4-benzenedicarboxylate) display a total uptake of 11–14 mmol·g−1 at 1 bar for the low vanadium content species, which is comparable with the values found for other members of the MIL-53 family [83].
Light hydrocarbon separation is a very important and crucial process in the petroleum industry, and their efficient separation will reduce the energy consumption and cost. Ethylene (C2H4) and propylene (C3H6) are used in the production of polymers. During the production of C2H4, an impurity of ~1% of C2H2 is also produced. The microporous MOF [Cu(atbdc)] (H2atbdc = 5-(5-amino-1H-tetrazol-1-yl)-1.3-benzenedicarboxylic acid), UTSA-100, displays high C2H2/C2H4 selectivity and high C2H2 uptake from mixtures containing 1% acetylene. At 296 K and 1 atm, the acetylene and ethylene uptake amount of UTSA-100 are 95.6 and 37.2 cm3·g−1, respectively, which is much higher than that of M’MOF-3 [84,85]. Other examples of MOFs exhibiting high C2H2 uptake are UTSA-300 (3.41 mmol·g−1 at 273 K and 1 bar) [86], SIFSIX-1-Cu (8.50 mmol·g−1 at 298 K and 1 bar) [87], [Mn3(bipy)3(H2O)4][Mn(CN)6]·2(bipy)·4H2O (3.2 mmol·g−1 at 27–83 K and 1 bar) [88], and NOTT-300 (6.34 mmol·g−1 at 293 K and 1 bar) [89]. In addition, the raw propylene (C3H6) product contains trace impurity of propyne (C3H4), which is highly undesirable. Chen and co-workers reported a flexible-robust MOF, ELM-12, which shows strong binding affinity and suitable pore confinement for propyne, and obtained propylene with a purity over 99.9998%, which is the propyne impurity removed to a concentration below 2 ppm [90]. The separation of C2H4 and C3H6 from their mixtures with the respective alkanes by using distillation processes shows low efficiency because of the similarity of their boiling points. Their separation can be alternatively achieved by the formation of π-complexes of olefins with transition metal cations [91,92], and by using MOFs, such as KAUST-7, which contains channels allowing the adsorption of C3H6 but does not permit the C3H8 to diffuse/adsorb into the pore system [93,94]. Another important and difficult process in the chemical industry is the separation of benzene and cyclohexane, as well as C2H2/CO2 separation. Conventional distillation is high energy consuming. Therefore, alternative methods involving the use of suitable MOFs containing open metal sites, or introducing π–π stacking interactions of the π-electron deficient pore surface and π-rich guest molecules have been developed [95,96,97,98].
Alternative technologies for H2 storage and its potential use as renewable fuel for vehicle applications have long explored during the early years of MOFs development. The required materials should meet the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) requirements, which are 5.5 wt % H2 gravimetric capacity achievable in the temperature range of −40 to 60 °C with a maximum pressure of 100 bar. Well-known MOFs, such as MOF-5, MOF-177, and UiO-66 display H2 uptake 5 wt % (77 K, 90 bar), 7.5 wt % (77 K, 80 bar), and 4.2 wt % (77 K, 60 bar), respectively [99,100,101]. Recent advances include the synthesis of a series of Pd-doped MIL-101 samples with different Pd content affecting their H2 storage performances, Pt nanoparticles on the outer surface of MOF-5, and then coating with hydrophobic microporous carbon black (CB/Pt/MOF-5 composite), which displays 41% higher H2 uptake than that of MOF-5, incorporation of polarized organic units into MOFs to improve the binding energy of H2 (e.g., MOF-649 and MOF-650 with internally polarized 2,6-azulenedicarboxylate), and carbon nanodots functional MOFs, Cdots@UMCM-1a, with efficiently enhanced H2 storage capacity attributed to specific interactions between the H2 adsorbate and polar groups on the surface of the Cdots [102,103,104,105].
Great progress has been made during recent decades on MOFs for applications on storage of CH4, which is the primary component of natural gas. For vehicle applications, an ideal MOF should have both high CH4 storage capacity and high CH4 deliverable capacity. Promising examples, which meet the volumetric target set by DOE (263 cm3·cm−3 at 35 bar), are HKUST-1 with total uptake 267 and 272 cm3·cm−3 at 65 and 80 bar, respectively, and working capacity of 190 and 200 cm3·cm−3 at 65 and 80 bar, respectively, UTSA-76 with total uptake of 257 cm3·cm−3 at 65 bar, and working capacity of 197 cm3·cm−3 at 80 bar, Ni-MOF-74 with total uptake of 251 and 267 cm3·cm−3 at 65 and 80 bar, respectively, and working capacity of 129 and 152 cm3·cm−3 at 65 and 80 bar, respectively, NJZU-53 with total uptake 241 cm3·cm−3 at 65 bar, and working capacity of 190 cm3·cm−3 at 65 bar, PCN-14 with total uptake of 230 and 250 cm3·cm−3 at 65 and 80 bar, respectively, and working capacity of 157 and 178 cm3·cm−3 at 65 and 80 bar, respectively, and MOF-519 with total uptake of 279 cm3·cm−3 at 80 bar, and working capacity of 230 cm3·cm−3 at 80 bar (Figure 3) [106,107,108,109].
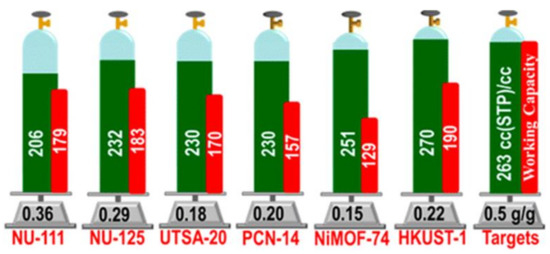
Figure 3. Methane uptake properties (green) and working capacity (red) of selected MOFs. Reprinted with permission from J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 11887–11894 ([107]). Copyright 2013 American Chemical Society.
2.2. Sensing Applications
MOFs are especially attractive as novel sensing materials because they display a high surface area, which enhances detective sensitivity, specific structural features (open metal sites, tunable pore sizes, etc.), which promote host-guest interactions and selectivity, and flexible porosity, which enables reversible release and uptake of small molecules, cations and anions, biomolecules, and so on. The guest molecules can induce visible changes including a shift of the emission spectrum or change in the emitting color, and change in the fluorescence intensity such as ‘turn-on’ and ‘turn-off’ processes.
A thermostable Mg-based MOF, [Mg(pdda)(dmf)] (H2pdda = 4,4′-(pyrazine-2,6-diyl) dibenzoic acid), which contains nanoholes and non-coordinating nitrogen atoms inside the walls of the holes, displays high selectivity for Eu3+ ions at low concentrations in aqueous solutions [125]. A luminescent Ln-MOF, [Me2NH2][Tb(bptc)] (H4bptc = 3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic acid) exhibits rare chiral helical channels despite the achiral nature of the organic ligand. Luminescent studies showed highly selective fluorescence quenching response to Fe3+ ions in a liquid suspension, rendering it as a potential chemo-sensor for Fe3+ ions [126]. A bimetallic Eu-Tb MOF with 1,4-benzenedicarboxylate ligands showed Pb2+ selectivity in polluted environmental waters. The color of the luminescent Ln-MOFs could be fine-tuned from green to red by doping the MOFs with different Tb/Eu ratios, and, in the presence of Pb2+, the emission color of the MOFs changes from red-orange to green, which is visually observed by naked eyes [127]. A Cd-MOF, [Cd(edda)] (H4edda = 5,5′-ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy)]diisophthalic acid), exhibits ratiometric fluorescence response to Hg2+ for the first time with a fast response (~15 s) and especially high sensitivity of ~2 nM below the permissible limits in drinking water set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. This behavior is attributed to the collapse of the crystal structure of the Cd-MOF induced by Hg2+ [128]. MOFs have been proven as very promising materials for the uranium extraction during radionuclide separation and seawater mining due to their ability for post grafting with functional groups with strong affinity for the uranium ions and porous functionalization for storage of hydrated U(IV) ions. HKUST-1, UiO-66, MILs, and ZIF-8 display stability under gamma irradiation. The phosphoryl-urea-functionalized UiO-68(Zr) MOF was the first organo-modified MOF that exhibited uranium extraction behavior. Examples of phosphonate-functionalized, amidoxime-functionalized, amine-functionalized MOFs, among others, display adsorption capacity up to 360 mg·g−1 [129].
Volatile organic molecules and explosive compounds can be efficiently detected by MOFs based on guest-dependent luminescent responses either by shifting of the emission spectrum or by changes in the luminescent intensity [130,131,132].
Various anions have been successfully detected by MOF-based sensors. [Ln2(bpdc)(bdc)2(H2O)2] (Ln = Eu, Tb; H2bpdc = 2,2′-bipyridine-3,3′-dicarboxylic acid) can detect F− ions based on a significant decrease in fluorescence, and [Ln2Zn(L)3(H2O)4](NO3)2 (Ln = Eu, Tb; L = 4,4′-dicarboxylate-2,2′-dipyridine anion) shows high selectivity and sensitivity to I− ions [133,134]. An Ln-mucinate MOF shows CO32− sensing ability through the greatest luminescence enhancement over other anions, and MOF-based thin-film show selectivity on CO32− over other anions, e.g., SO42−, PO43−, ClO4−, etc., in aqueous solution through a turn-off response [135,136]. The highly toxic CrO42− and Cr2O72− anions found in wastewater can be efficiently detected by MOFs, such as [Ln4(OH)4(bpdc)3(bpdca)0.5(H2O)6](ClO4) (Ln = Tb, Gd, bpdca2− = biphenyl-4,4′-dicarboxylate), and [Cd(tptz)(H2O)2(HCOOH)(ipa)2] (tptz = {4-[4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl]phenyl}-1H-1,2,4-triazole, ipa = isophthalic acid) [137,138]. The cationic MOF [CuL2(H2O)0.5](NO3)2 displays characteristic colors in response to specific anions, such as Cl−, Br−, I−, SCN−, and N3− (Figure 4) [139]. The isostructural heterometallic MOFs, In/Eu-CBDA, and In/Tb-CBDA (CBDA = 5,5′-(carboxylbis(azanediyl))-diisophthalic acid) can detect 1,4-dinitrobenzene and Cr2O72− with high selectivity and sensitivity [140]. ZnO quantum dots on MOF-5 is an effective fluorescent sensing platform for the phosphates tested for the assessment of phosphates in environmental aqueous samples [141], and CdSe/CdS/Cd0.5Zn0.5S/ZnS quantum dots on MOF-5, QD@MOF-5 composite display size-selective thiol sensing [142].
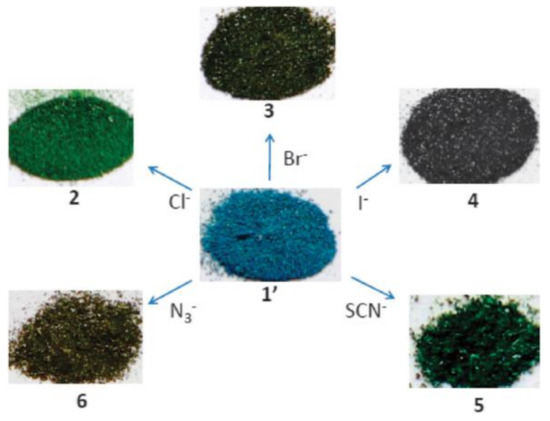
Figure 4. Color change of [CuL2(H2O)0.5](NO3)2 (1′) upon exchange of nitrates by the indicated anions. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 2946–2948 ([139])—Reproduced by permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry.
MOF-based sensors for humidity measurements have been studied based on changes of fluorescence or electrochemical signals, such as CuMOF, thin-film of HKUST-1, Cu-BTC film, and amine-functionalized MOF nanoparticles NH2-MIL-125(Ti) [143,144,145,146,147]. pH and temperature sensors based on luminescent MOFs have been extensively studied for monitoring pH changes in biological environments and for luminescent thermometers. For example, among others, [Eu3(C14H6N2O4)4(OH)(H2O)4]·2H2O displays a linear photoluminescence response in the 5–7.5 pH range, UiO-66-N=N-ind3h synthesized by post-synthetic modification of UiO-66-NH2 exhibits pH-dependent fluorescence in the 1–12 pH range, (Tb-THBA) nanoparticles (THBA = tris[(2-hydroxy-benzoyl)-2-aminoethyl]amine) show a temperature-dependent luminescent intensity in the range of 20–65 °C, and [Zn3(TDPAT)(H2O)3] (TDPAT = 2,4,6-tris(3,5-dicarboxylphenylamino)-1,3,5-triazine) can detect a temperature from 164 to 276 K [148,149,150,151].
Core-shell nanocomposites with an MOF core have been developed for sensing biological molecules, such as human serum albumin, bacterial endospores, and cancer cell apoptosis [152,153,154]. Luminescent MOFs are also successful in detecting DNA, RNA, protein, and other biomolecules and present advantages over other sensing materials for biomolecules (e.g., single-walled carbon nanotubes, graphene oxide, carbon nanoparticles, gold nanoparticles), such as structural diversity, high sensitivity, and biodegradability. Biocompatibility and non-toxic metal clusters need to be developed in order for in vivo sensing to be realized [155].
2.3. Catalytic Applications
MOFs have been extensively used as heterogeneous catalysts for the synthesis of fine chemicals, which are extremely important in the chemical industry. The properties that render MOFs suitable for heterogeneous catalysts are related to the robust nature, which is required for catalysis under extreme conditions, the porosity, and large surface area, which facilitated the catalytic activity as well as the presence of pores and channels, which are needed for catalytic selectivity and the organic ligands that can tune the catalytic reactivity and selectivity. The catalytic active sites of MOFs may be the metal nodes, the functionalized ligands, and the pores of the structure. The synthesis of fine chemicals is most commonly realized through oxidation reactions (e.g., epoxidation, sulfoxidation, aerobic oxidation), 1,3-cycloaddition reactions, transesterification reactions, C–C bond formation reactions (e.g., Heck reaction, Sonogashira coupling, and Suzuki coupling), and hydrogenation reactions of unsaturated organic molecules. The MOFs as heterogeneous catalysts may act as Lewis acids through the metal ions or metal nodes as well as the organic ligands, or as support for the moieties that carry the oxygen or the noble metals necessary for the catalytic reaction. The Zn MOF-5 was partially substituted with manganese and the bimetallic MnFe-MOF-74 was used for the epoxidation of the alkene with high selectivity (up to 99%, Figure 5) [166,167]. Composites of metal complexes immobilized on MOF can also act as Lewis acids in epoxidation reactions, such as post synthetically modified (Cr)NH2-MIL-101, post synthetically modified UiO-66 and UiO-67 with salicylaldehyde molybdenum complex, and copper functionalized UiO-66 [168,169,170]. The aerobic oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes or ketones requires the presence of noble metals inside the pores of the MOF or attachment to the modified ligands. Palladium and gold nanoparticles introduced into the nanoporous MOF are used for selective aerobic oxidation [171,172]. Cu-based MOFs are usually used as catalysts for 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reactions, which is the formation of five-membered ring compounds [173,174]. Several examples of MOF catalysts in transesterification reactions have been reported, such as UiO-66 and UiO-67 [175,176]. C-C bond formation reactions such as Heck reactions, Sonogashira coupling, and Suzuki coupling are extremely important for organic synthesis and require the presence of palladium or palladium nanoparticles as catalysts, which are incorporated in the pores or are attached to the functionalized organic ligands. For example, palladium complexes, such as bis(tri(1-piperidinyl)phosphine) palladium chloride or bis(triphenylphosphine) palladium dichloride incorporated in a Ni-MOF for the Heck reaction of estragole with iodobenzene [177], palladium incorporated in a Zr-MOF based on 2,2′-bipyridine-5,5′-dicarboxylate ligands applied in the carbonylative Sonogashira coupling at atmospheric pressure in the presence of CO [178], and palladium dichloride immobilized on a mixed-ligand MOF containing bipyridyl and biphenyl moieties for Suzuki catalysis [179]. Palladium nanoparticles incorporated in Zr MOF-808 is an excellent heterogeneous catalyst for Heck reaction without an additional base [180], whereas palladium nanoclusters in NH2-UiO-66 (Zr) used in the Suzuki catalysis in the presence of light give 99% conversion and selectivity of biphenyl compounds [181]. A wide range of unsaturated organic compounds, such as α,β-unsaturated aldehydes, cinnamaldehyde, nitroarene, and nitro compounds, alkenes and alkynes, quinoline, benzene, and other aromatic compounds, can be hydrogenated with a very high yield and selectivity under mild conditions in the presence of MOFs and derived materials as heterogeneous catalysts. For example, Pt nanoparticles incorporated within MIL-101(Fe,Cr) used as catalysts for the hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes to unsaturated alcohols [182]. MIL-120 incorporated with Ni particles showed a better result on gas-phase benzene hydrogenation than the Ni/Al2O3 catalyst [183], which is a well-defined hollow Zn/Co ZIF composite with rhombic dodecahedron shape that displayed superior activity and selectivity toward the semi-hydrogenation of acetylene [184], and Ir nanoparticles encapsulated in ZIF-8 used in the hydrogenation of phenylacetylene [185]. The catalytic activity for the CO2→CO reduction with [Ru3(btc)2-x(pydc)xXy] catalysts (X = Cl, OH, OAc, x = 0.1, 0.2, 0.6, 1.0; 0 ≤ y ≤ 1.5, H3btc = benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid, H2pydc = pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid) as monitored by UHV-FTIR spectroscopy, showed peaks characteristic of the presence of (CO)Ruδ+ species. The CO2→CO conversion at 90 K is attributed to charge transfer from the 3d Ru orbitals to the 2πu CO2 antibonding orbital, possibly yielding chemisorbed CO2δ− species that might act as a reaction intermediate to produce CO [111]. These defect-engineered MOFs also act as olefin hydrogenation catalysts after activation with H2 to produce Ru-H species, assisted by the presence of the basic pyridyl-N atom of the pydc linkers [111]. Cu-based MOFs, [Cu3(btc)2] HKUST-1 (btc3− = benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylate) and [Cu3(btb)2] MOF-14 (btb3− = benzene-1,3,5-tribenzoate) display high catalytic activity toward CO oxidation at low temperatures (105 K), which is related to the CO species adsorbed on the Cu2+ coordinatively unsaturated metal ion sites upon exposure to various amounts of O2 [186]. Several MOFs, for example NU-1000, UiO-66, HKUST-1, and MIL-101(Cr)-DAAP, have been tested as heterogeneous catalysts for the catalytic destruction of the phosphate ester bonds and phosphate-fluoride bonds, in chemical warfare agents, such as DMNP (dimethyl 4-nitrophenyl phosphate), DENP (diethyl 4-nitrophenyl phosphate), BNPP (bis(4-nitrophenyl) phosphate), and the highly toxic GD (O-pinacolyl methylphosphonofluoridate), known as Soman [187].
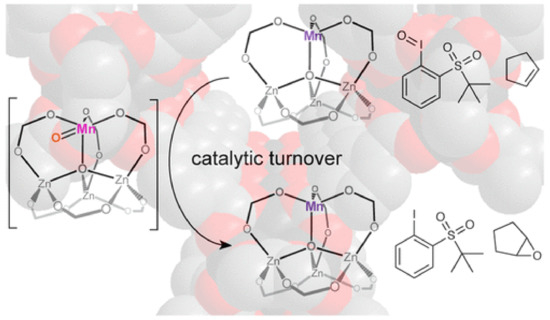
Figure 5. Schematic view of the selective catalytic activity of MnFe-MOF-74 for the epoxidation of the cyclic alkenes in the presence of tBuSO2PhIO. Reprinted with permission from ACS Catal., 2018, 8, 596–601 ([166]). Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society.
Two-dimensional MOFs have been recently developed as catalysts of outstanding intrinsic reactivity, as support materials for catalysts, and as catalysts with multifunctional catalytic activity for diverse organic transformations. Their enhanced catalytic activity is associated with the ultra-thin thickness and more accessible active sites, which decrease the diffusion resistance and increase the host-guest interactions, rendering these materials much better than the corresponding bulk MOFs [188]. For example, 2D MOFs based on tetrakis(4-carboxyphenyl)-porphyrin display unique photochemistry and high efficiency in light-harvesting applications and showed catalytic activity in photooxidation reactions (Figure 6) [189,190,191]. Incorporation of nanoparticles or enzymes as well as post-synthetic modification provided new materials with enhanced catalytic activities [192]. For example, [Zr12O8(OH)14(BPYDC)9] (H2BPYDC = 2,2′-bipyridine-5,5′-dicarboxylic acid), MON-19, loaded with platinum nanoparticles, displays efficient hydrogenation of C=C bonds under mild conditions without external high-pressure hydrogen [193].
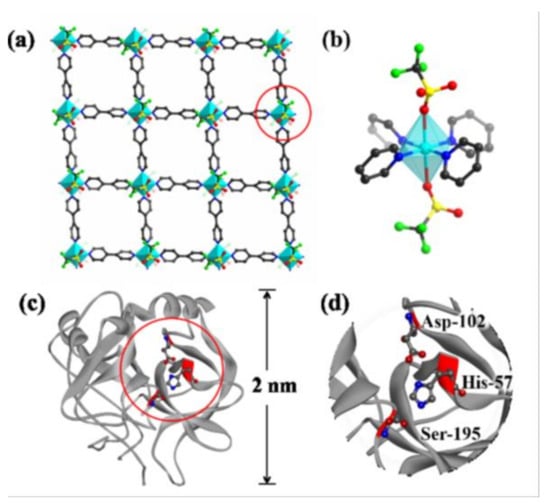
Figure 6. (a) Schematic representation of a single-layered 2D nanosheet of Cu-MOF. Color code: C, gray. O, red. S, yellow. F, green. Cu polyhedral, blue. H-atoms not shown. (b) Schematic representation of a Cu(II) center in the nanosheets. (c) Molecular structure of a-chymotrypsin. (d) The polychrome sections in this structure are the active site with residues Asp-102, His-57, and Ser-195. a-chymotrypsin can be effectively inhibited by 2D Cu-MOF, [Cu(bpy)OTf)2] (bpy = 4,4′-bipyridine, OTf = trifluoromethanesulfonate). Reprinted with permission from J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 8312–8319 ([189]). Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society.
2.4. Piezo/Ferroelectric, Thermoelectric, and Dielectric Applications
The piezoelectric materials convert mechanical energy into electrical energy through the direct piezoelectric effect and can be considered as energy harvesters to generate energy when direct electricity or batteries are not available. A subclass are the ferroelectric materials, which exhibit spontaneous electric polarization whose direction can be reversed by applying external electric fields. Piezo/ferroelectric materials, such as crystalline and ceramic materials, polymers, and liquid crystals find potential applications in piezoelectric quartz crystals as ultrasonic transducer, sensors and actuators, filters, ultrasonic motors, energy harvester, optical devices and so on. Besides traditional piezo/ferroelectric materials, MOFs have investigated for potential applications, among these [Zn2(mtz)(nic)2(OH)]·0.5H2O (Hmtz = 5-methyltetrazole, Hnic = nicotinic acid), [Zn(phtz)(nic)]2 (Hphtz = 5-phenyltetrazole), [Cd(tib)(p-BDC-OH)]·H2O (tib = 1,3,5-tris(1-imidazolyl)benzene, p-BDC-OH = 2-OH-1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid), [In(C16H11N2O8]·1.5H2O, and [Mn5(NH2bdc)5(bimb)5]·0.5H2O (NH2bdcH2 = 2-amino-1,4-benzene dicarboxylic acid, bimb = 4,4′-bis(1-imidazolyl)biphenyl) show significant ferroelectric properties with spontaneous polarization values of Ps of 6.26, 5.27, 11.65, 3.81, and 2.556 μC·cm−2, respectively [165,220,221,222]. The piezoelectric properties of MOFs have been rarely studied. For example, a MOF based on [Cd(imazethpyr)] displays a piezoelectric coefficient d33 value of 60.10 pC·N−1, which is smaller than that of BaTiO3, but was the first MOF with such piezo/ferroelectricity (Figure 7) [223]. ZIF-8-based MOFs exhibit ‘soft’ piezo/ferroelectricity and water soluble MOFs such as NUS-series and UiO-series exhibit piezoelectric coefficient as dzz up to 3.5 pm·V−1 [224,225,226].
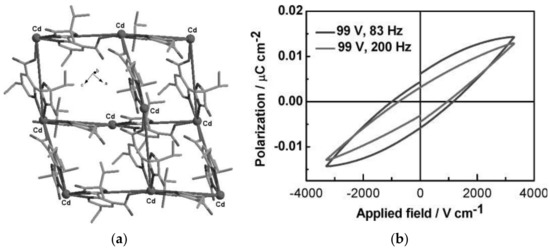
Figure 7. (a) The diamond-like net of MOF based on [Cd(imazethpyr)] and (b) electric hysteresis loop of the MOF. Dalton Trans. 2008, 3946–3948 ([223])—Reproduced by permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry.
The thermoelectric materials, which can generate electric potential from a temperature difference, constitute an environmentally-friendly approach of energy generation from waste heat. Besides inorganic compounds, such as oxides and alloys, the approach of conductive MOFs as new potential thermoelectric materials has been developed. This approach includes first-row transition metal MOFs with thiolate ligands, such as [Cu(pdt)2] (pdt = 2,3-pyrazinedithiolate), inclusion of guest molecules in known MOFs, such as TCNQ@HKUST-1 (HKUST-1 = [Cu3(BTC)2], BTC = benzene tricarboxylate), I2 and metal nanoclusters in order to improve the conductivity of the material. 2D MOF nanosheets of bis(thiolato) ligands and light transition metals, i.e., π-d conjugated systems, and post-synthetically modified MOFS, i.e., guest@MOFs and conductive-polymer grafted MOFs, are promising candidates for the fabrication of thermoelectric devices due to their excellent conductivity [227].
Semiconducting devices are based on dielectric materials, which display ultra-low dielectric constants (κ < 3.9 as in SiO2). MOFs feature ultra-low dielectric constants, which are considered as promising materials for the future microelectronics industry. The requirements of doing so are thermal stability at a high temperature, predictable mechanical behavior, electrical insulation, and adhesion to other interlayers. DFT calculation on various MOFs, such as IRMOF-1 family, UiO-66, UiO-67, MIL-140, and MOF-74-M (M = Mg, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Zn), revealed the influence of the structural and chemical characteristics on their electronic and dielectric properties, demonstrating their ability to behave as insulators and low-dielectric constant materials, and predicted dielectric constants in the range of 1.25 to 2.0 [228,229]. Surface-anchored HKUST-1 thin films grown by liquid phase epitaxy (LPE) were studied by spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE) to determine an optical constant of n = 1.39 at a wavelength of 750 nm (κ~1.93) [230]. ZIF-8 thin films deposited on silicon wafers studied by SE and the dielectric constant was measured by impedance analysis at different frequencies and temperatures yielding κ = 2.33 at 100 kHz [231]. Other MOFs, which display ultra-low dielectric constants (below that of SiO2) are, for example, [Sr2(1,3-dbc)2(H2O)2] (bdc = 1,3-bis(4,5-dihydro-2-oxazolyl)benzene), which retains its crystallinity up to 420 °C with κ~2.4 [232], [Zn2(Hbbim)2(bbim)] (H2bbim = bisbenzimidazole) with κ~3.05 [233], [Pb(tab)2(4,4′-bipy)](PF6) (tab = 4-(trimethylammonio)benzenethiolate) with κ~2.53, [Zn2(L-trp)2(bpe)2(H2O)2] (L-trp = L-tryptophane, bpe = 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethylene) with κ~2.53, [Mn2(D-cam)2(2-Hpao)4] (D-cam = D-camphoric acid, 2-Hpao = 2-pyridinealdoxime) with κ~2.8, and [Co2(D-cam)2(3-abpt)2(H2O)3] (3-abpt = 4-amino-3,5-bis(3-pyridyl)-1,2,4-triazole) with κ~3.0 [234].
2.5. Proton-Conducting and Magnetic Materials
Recently, MOFs have attracted considerable interest as proton-conducting materials and their potential applications in electrochemical devices, sensors, hydrogen fuel cells, etc. MOFs can accommodate various proton carriers in their pores/channels and can provide useful insight into the proton-conducting pathway and mechanism, and these advantages render them excellent materials for such applications. While the negative charge of the lattice is not a prerequisite for conducting protons, many of them are anionic MOFs whose charge is offset by small protonated amines or protons attached to the solvent molecules by hydrogen bonds, or protons weakly attached to functional groups of the ligands (less frequently in carboxylates, more often in sulfonic and phosphonate ligands). For example, {H[(N(CH3)4)2][Gd3(NIPA)6]}·3H2O (H2NIPA = 5-nitroisophthalic acid) displays high proton conductivity of 7.17 × 10−2 S·cm−1 at high relative humidity, which is among the highest values for proton-conducting MOFs [235], and the bimetallic complex {NH(prol)3}[MnCr(ox)3] (NH(prol)3+ = tri(3-hydroxypropyl)ammonium, ox = oxalate), which consists of oxalate-bridged bimetallic layers interleaved by NH(prol)3+ ions and shows proton conduction of ~10−4 S·cm−1 under 75% relative humidity due to the presence of an extensive H-bonded network between the anionic MOF, the NH(prol)3+ ions, and water molecules [236]. Some examples of neutral MOFs, which display high proton conductivity, are [Tb4(TTHA)2(H2O)4]·7H2O (H6TTHA = 1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triamine hexaacetic acid) with high proton conductivity over 10−2 S·cm−1 at 295–358 K temperature range due to an extensive H-bond network formed between water solvates and carboxyl groups [237], [Ln(L)(H2O)2] (LnIII = Dy, Er, Gd; H3L = (HO)2P(O)CH2CO2H) with proton conductivity values of 1.13 × 10−6, 2.73 × 10−3, and 6.27 × 10−6 S·cm−1, respectively, at high temperatures (>348 K) and 95% relative humidity [238], and [Ln2(CO3)(ox)2(H2O)2]·3H2O (LnIII = Ce, Pr, Nd, Tb) with proton conductivity above 10−3 S·cm−1 without an additional humidity (Figure 8) [239].
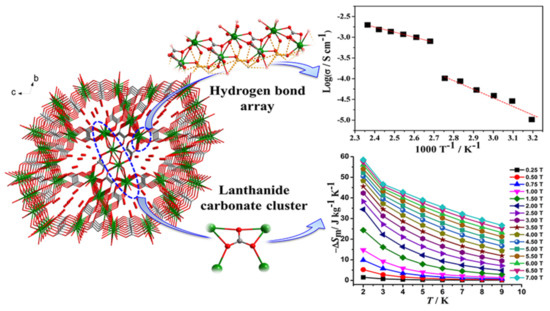
Figure 8. The 3D framework of {[Gd2(CO3)(ox)2(H2O)2]·3H2O, which contains an ordered one-dimensional pore channel along the a-axis, which serves as a 1D hydrogen bond pathway. The compound shows high proton conductivity (up right) and a large magnetocaloric effect (down right). Reprinted with permission from Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 9020–9027 ([239]). Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ma14020310
