Lung diseases, such as pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary fibrosis, are life-threatening diseases and have common features of vascular remodeling. During progression, extracellular matrix protein deposition and dysregulation of proteolytic enzymes occurs, which results in vascular stiffness and dysfunction. Although vasodilators or anti-fibrotic therapy have been mainly used as therapy owing to these characteristics, their effectiveness does not meet expectations. Therefore, a better understanding of the etiology and new therapeutic approaches are needed. Endothelial cells (ECs) line the inner walls of blood vessels and maintain vascular homeostasis by protecting vascular cells from pathological stimuli. Chronic stimulation of ECs by various factors, including pro-inflammatory cytokines and hypoxia, leads to ECs undergoing an imbalance of endothelial homeostasis, which results in endothelial dysfunction and is closely associated with vascular diseases.
- lung disease
- endothelial to mesenchymal transition
- pulmonary hypertension
- pulmonary fibrosis
1. Introduction
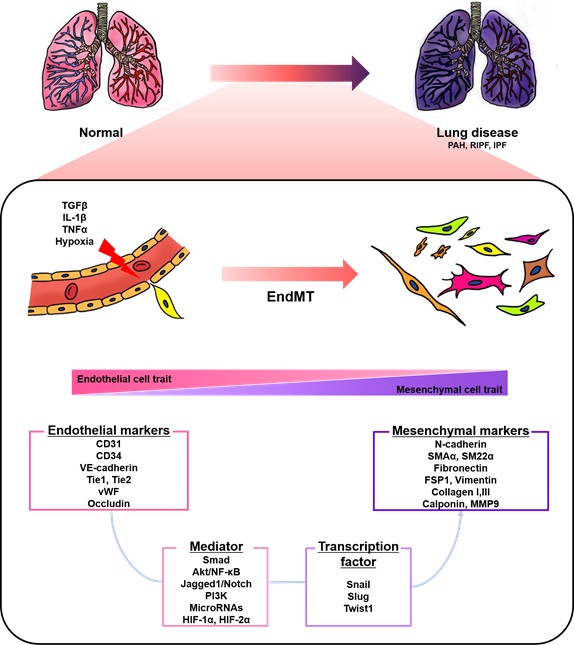
Endothelial cells (ECs), a monolayer composed of the inner cellular lining of the vascular lumen, play an important role in various physiological processes to maintain vascular homeostasis [1][2][3]. These cells are involved in the regulation of vascular tone, permeability, and inflammatory responses [4]. However, endothelial injury by stimuli, such as hypoxia, pro-inflammatory cytokines and abnormal mechanical forces, can induce endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT), resulting in endothelial dysfunction and destruction of homeostasis [2][5]. EndMT is the process by which ECs lose their cellular features and acquire mesenchymal characteristics [6]. EndMT-derived cells gain migration potential by losing endothelial markers, such as cluster of differentiation 31 (CD31) and vascular endothelial cadherin (VE-cadherin), which are involved in cell-to-cell contact [7][8]. Concomitantly, the expressions of mesenchymal markers, such as fibronectin, alpha-smooth muscle actin (SMAα), smooth muscle protein 22 alpha, vimentin, and neural cadherin (N-cadherin), are upregulated [7][8]. The morphology of ECs undergoing EndMT changes from a cobblestone monolayer to an elongated phenotype [9]. This phenomenon mainly occurs during embryonic cardiac development, but is also involved in various lung diseases, such as pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) and pulmonary fibrosis (PF) (Figure 1) [7][10][11][12][13].
Figure 1. A schematic representation of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) involved in lung diseases. Endothelial cells stimulated by transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ), interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), and hypoxia undergo EndMT. EndMT is characterized by phenotypic change from a cobblestone into an elongated shape, loss of endothelial markers, and the acquisition of mesenchymal markers. EndMT contributes to the pathogenesis of lung diseases, including pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis (RIPF), and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Various mediators and transcription factors are identified in this process.
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is categorized into five groups: PAH, PH due to left heart disease, PH due to lung diseases and/or hypoxia, PH due to pulmonary arterial obstructions, and PH with unclear and/or multifactorial mechanisms [14][15][16]. PAH has been defined as pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) ≥25 mmHg at rest and occurs as a result of multiple causes, such as heritable factors (mainly bone morphogenic protein receptor-2 (BMPR2) mutations), drugs and toxins, as well as association with other diseases; however, PAH without known causes is known as idiopathic PAH (IPAH) [14][17]. Vascular remodeling in PAH is characterized by the aberrant proliferation of pulmonary arterial ECs (PAECs) and smooth muscle cells (SMCs), which form occlusive neointima and vascular structural changes [18][19][20]. These progressive changes cause excess vasoconstriction and right ventricle hypertrophy and, ultimately, death [18][19][20]. Endothelial dysfunction is a key player in the pathogenesis of PAH [21]. Growing evidence suggests that EndMT potentially contributes to endothelial dysfunction and the vascular remodeling of PAH [7][11][22][23]. Indeed, many studies have demonstrated that various signaling pathways and mediators, including transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ), nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), Notch, and microRNA, are involved in the EndMT of PAH [24][25]. It has been reported that the endothelial-specific loss of BMPR2, known as the principal mutation factor of heritable PAH, induces EndMT in vitro and in vivo [7][11][23]. In addition, exposure to hypoxia or chronic stimulation with proinflammatory cytokines or TGFβ also induce EndMT in vitro and in vivo [26][27][28][29][30]. However, the contribution of EndMT to disease progression is not fully understood [2]. Current therapies for PAH, such as phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors, prostacyclin analogues, and endothelin receptor antagonists, can help relieve symptoms and slow progression, but there is no effective treatment [21][31]. Thus, targeting EndMT is emerging as a novel therapeutic approach by alleviating vascular remodeling and the PAH phenotype in vitro and in vivo [7][29][32][33][34][35][36].
Idiopathic PF (IPF) is chronic, progressive, and the most common interstitial lung disease without a definite etiology [37][38]. Various cell types, such as epithelial cells, pneumocytes, ECs, pericytes, fibrocytes, resident fibroblasts, and mesenchymal cells, are associated with the pathogenesis of IPF [25]. The injured epithelial cells, through aging, genetic susceptibility and repetitive microinjury, release fibrogenic factors and cytokines, resulting in the recruitment of contractile myofibroblasts, which are key cellular mediators of fibrosis [38]. Recruited myofibroblasts undergoing activation and proliferation induce extracellular matrix expansion, which consequently results in aberrant vascular remodeling in the lung [38]. The myofibroblasts are derived not only from the proliferation of resident mesenchymal cells, circulating fibrocytes, lung interstitium pericytes, epithelial–mesenchymal transition, but also EndMT. [38][39][40]. Many studies have demonstrated that EndMT occurs in the lung tissue of IPF patients and animal models, suggesting EndMT may play an important role in pathological processes in PF [25][41][42]. In addition, emerging evidence indicates that inhibiting EndMT can also be a therapeutic strategy in PF in vivo [41][43][44][45].
2. EndMT in Pulmonary Hypertension
PH is characterized by the muscularization of arterioles, medial thickening, plexiform region formation, intimal fibrosis, and the hyperproliferation of ECs and SMCs [15][16][46][47]. Most studies have identified EndMT by analyzing the co-expression of endothelial markers and mesenchymal markers in the lung tissue of patients and experimental PH animal models. EndMT has been observed in pathological lesions in the lungs of PH patients [7][30][32][48][49]. Endothelial (CD31, CD34, and VE-cadherin) and mesenchymal marker (SMAα) double-positive cells were observed in intimal and plexiform lesions in the lung tissue of PAH patients [7]. Another group also demonstrated that neointimal and plexiform lesions in the lung tissue of human PAH patients contain endothelial markers, CD31 or von Willebrand factor (vWF), and SMAα co-expressing cells [48]. Isobe et al. reported that the CD44 spliced variant form (CD44v) results from EndMT, and its positive cells also expressed vWF and SMAα in neointimal lesions of IPAH patients [32]. The 4 ± 1% of pulmonary arterioles in systemic sclerosis (SSc)-PAH patients showed vWF/SMAα co-localization [30]. CD31 and SMAα co-expressing cells were detected in endarterectomized tissues from patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) [49].
In addition to performing the double staining of endothelial and mesenchymal markers, ECs isolated from the lung have also been used for studying EndMT [49][50]. Endothelial-like cells isolated from the vascular tissue of patients with CTEPH underwent disruption of the endothelial monolayer and abnormal growth even after sorting with CD31 [49]. In addition, conditioned media from myofibroblast-like cells isolated from CTEPH patients induced phenotypic changes and mesenchymal marker expression in pulmonary microvascular ECs (PMVECs) [49]. Pulmonary vascular ECs (PVECs) isolated from patients with IPAH exhibited molecular characteristics of EndMT and a spindle-shaped morphology, which was similar to that of normal PVECs treated with TGFβ1, a well-known factor of EndMT [50]. Pulmonary arteries isolated from PAH patients showed increased mRNA levels of mesenchymal markers and EndMT-related factors, which also supports EndMT [7].
Animal models have also been used to demonstrate EndMT. Monocrotaline (MCT) injection causes endothelial injury and pulmonary vascular remodeling, and is commonly used to induce severe PH [50][51]. Several groups observed the reduction of endothelial markers and the induction of mesenchymal markers, as well as the co-staining of SMAα and endothelial marker (CD31 or CD34), in the lung tissue of MCT-induced PH rats [7][28][29][50][52]. Zhang et al. found that changes in endothelial and mesenchymal cell marker expressions occurred in a time-dependent manner during MCT-induced PAH development [51]. Chronic hypoxia also contributes to the vascular remodeling of small pulmonary arteries [27][53]. With this, it has been demonstrated that three weeks of hypoxia induces EndMT in the pulmonary arteries of rats and mice [26][53]. EndMT was further identified within the intimal layer of small pulmonary arteries, but not in large arteries, in chronic hypoxia-induced PH rats [27]. The combination of SU5416, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor antagonist, and a chronic hypoxia model (SuHx) has been used for severe PH owing to the similarity of pathological lesions to plexiform lesions of human PAH [53]. In the lung of the SuHx model that had over 80 mmHg of right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP), transitions of vWF+ vimentin− ECs to vWF− vimentin high mesenchymal-like cells were observed in pulmonary vascular lesions [7]. Tie2+ vimentin+ and Tie2+ SMAα+ cells were also found in occlusive lesions [7]. In addition, 6 ± 1% of pulmonary vessels had vWF/SMAα double-positive ECs, which contrasts with normal tissues having only 1% transitional EndMT cells in SuHx mice [30].
In general, endothelial and mesenchymal marker double-positive cells are considered EndMT-induced cells. However, this approach has the limitation of not being able to distinguish complete EndMT (cEndMT), where there are lost endothelial markers, and partial EndMT (pEndMT) cells. To overcome this problem, several studies have used endothelial-specific fluorescence transgenic animals [48][54]. Qiao et al. established VE-cadherin Cre or Tie2 Cre-mTomato/mGFP lineage-tracing mice [48]. Histological analysis identified SMAα-expressing neointima in an experimental PH animal model derived from the endothelium in VE-cadherin Cre or Tie2 Cre-mTomato/mGFP lineage-tracing mice [48]. Furthermore, cEndMT cells isolated from SuHx-induced Cdh5-Cre/CAG-GFP double-transgenic mice showed a spindle-like morphology and were characterized by mesenchymal-like functions, such as high proliferation and migration ability [54]. Additionally, conditioned media from cEndMT had a paracrine effect on the proliferation and migration of non-endothelial mesenchymal cells, suggesting that EndMT contributes directly and indirectly to the vascular remodeling of PAH [54].
3. EndMT in Pulmonary Fibrosis
IPF characterizes matrix deposition and fibrotic tissue remodeling, and it has been demonstrated that fibroblasts are involved in pathogenesis; thus, efforts to identify the origin of fibroblasts have been made [42][55]. In the lung tissue of radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis (RIPF) patients and radiation-exposed mouse models, the co-localization of CD31 and SMAα was significantly elevated compared to that of the control group, indicating EndMT [41]. The same group also reported endothelial heat shock protein beta 1 (HSPB1)-dependent EndMT in the PF of lung cancer [45]. The bleomycin-induced PF in animal models is the most commonly used model to study human IPF by causing damage to epithelial cells and alveolar inflammation [56][57]. Another group reported significant alterations of EC markers in the lungs of bleomycin-treated endothelial-specific autophagy-related 7 (ATG7) knockout mice compared to bleomycin-treated WT mice [58]. Hashimoto et al. established a Tie2-Cre/CAG-CAT-LacZ double transgenic mice model to track endothelial-derived fibroblasts in bleomycin-induced PF [42]. The 16.2% of lung fibroblasts isolated from bleomycin-treated mice were X-gal-staining-positive and 14.8% of X-gal-positive cells were SMAα- and Collagen I-double positive (myofiboblast), while the other 85.2% were SMAα-negative and Collagen I-positive, suggesting that a significant number of fibroblasts are EC-derived [42]. Suzuki et al. demonstrated that PVECs isolated from lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced mouse lungs undergo EndMT using the double staining of CD31 and SMAα or S100A4 [59]. Flow cytometry analysis showed that the number of SMAα + PVECs and S100A4 + PVECs increased, while the total number of PVECs decreased [59].
Taken together, EndMT may play a key role in the pathogenesis of lung diseases. Many studies describe EndMT based on the evidence of co-expression of EC markers and mesenchymal markers in the lung tissue of animal disease models or human patients, which has a primary limitation because EndMT is a switching process; thus, the underlying molecular mechanisms are not yet fully understood. The methods to clarify partial and complete EndMT processes have been improved using endothelial-specific fluorescence transgenic mice; however, further investigation with human samples is needed. Thus, the clinical relevance of EndMT should be thoroughly assessed.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/biomedicines8120639
References
- Scott Potenta; Elisabeth M Zeisberg; Raghu Kalluri; The role of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer progression. British Journal of Cancer 2008, 99, 1375-1379, 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604662.
- Jin Gu Cho; Aram Lee; Woochul Chang; Myeong-Sok Lee; Jongmin Kim; Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition Represents a Key Link in the Interaction between Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction. Frontiers in Immunology 2018, 9, 294, 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00294.
- Sang-Min Kim; Sang-Min Kim Jae-Wan Huh; Eun-Young Kim; Min-Kyung Shin; Ji-Eun Park; Seong Who Kim; Wooseong Lee; Bongkun Bongkun Choi & Eun-Ju Chang; Eun-Ju Chang; Endothelial dysfunction induces atherosclerosis: increased aggrecan expression promotes apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells. BMB Reports 2019, 52, 145-150, 10.5483/bmbrep.2019.52.2.282.
- Cristina Sena; Ana M. Pereira; Raquel Seiça; Endothelial dysfunction — A major mediator of diabetic vascular disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease 2013, 1832, 2216-2231, 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.08.006.
- Guido Krenning; Valerio G. Barauna; José E. Krieger; Martin C. Harmsen; Jan-Renier A. J. Moonen; Endothelial Plasticity: Shifting Phenotypes through Force Feedback. Stem Cells International 2016, 2016, 1-15, 10.1155/2016/9762959.
- Harika Sabbineni; Arti Verma; Payaningal R. Somanath; Isoform-specific effects of transforming growth factor β on endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Journal of Cellular Physiology 2018, 233, 8418-8428, 10.1002/jcp.26801.
- Benoît Ranchoux; Fabrice Antigny; Catherine Rucker-Martin; Aurélie Hautefort; Christine Péchoux; Harm Jan Bogaard; Peter Dorfmüller; Séverine Remy; Florence Lecerf; Sylvie Planté; et al. Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Pulmonary Hypertension. Circulation 2015, 131, 1006-1018, 10.1161/circulationaha.114.008750.
- Fernanda Ursoli Ferreira; Lucas Eduardo Botelho De Souza; Carolina Hassib Thomé; Mariana Tomazini Pinto; Clarice Origassa; Suellen Salustiano; Vitor Marcel Faça; Niels Olsen Saraiva Camara; Simone Kashima; Dimas T. Covas; et al. Endothelial Cells Tissue-Specific Origins Affects Their Responsiveness to TGF-β2 during Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 458, 10.3390/ijms20030458.
- Gonzalo Sanchez-Duffhues; Amaya García De Vinuesa; Peter Ten Dijke; Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cardiovascular diseases: Developmental signaling pathways gone awry. Developmental Dynamics 2018, 247, 492-508, 10.1002/dvdy.24589.
- Shuhong Guan; Jun Zhou; CXCR7 attenuates the TGF-β-induced endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and pulmonary fibrosis. Molecular BioSystems 2017, 13, 2116-2124, 10.1039/c7mb00247e.
- Christian Hiepen; Jerome Jatzlau; Susanne Hildebrandt; Branka Kampfrath; Melis Goktas; Arunima Murgai; Jose Luis Cuellar Camacho; Rainer Haag; Clemens Ruppert; Gerhard Sengle; et al. BMPR2 acts as a gatekeeper to protect endothelial cells from increased TGFβ responses and altered cell mechanics. PLOS Biology 2019, 17, e3000557, 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000557.
- Elisabeth M. Zeisberg; Oleg Tarnavski; Michael Zeisberg; Adam L. Dorfman; Julie R. McMullen; Erika Gustafsson; Anil Chandraker; Xueli Yuan; William T. Pu; Anita B. Roberts; et al. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition contributes to cardiac fibrosis. Nature Medicine 2007, 13, 952-961, 10.1038/nm1613.
- Duong Thi Bich Thuan; Hatem Zayed; Ali H. Eid; Haissam Abou-Saleh; Gheyath K. Nasrallah; Arduino A. Mangoni; Gianfranco Pintus; A Potential Link Between Oxidative Stress and Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Systemic Sclerosis. Frontiers in Immunology 2018, 9, 1985, 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01985.
- Gérald Simonneau; David Montani; David S. Celermajer; Christopher P. Denton; Michael A. Gatzoulis; Michael Krowka; Paul G. Williams; Rogerio Souza; Haemodynamic definitions and updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. European Respiratory Journal 2019, 53, 1801913, 10.1183/13993003.01913-2018.
- Jun-Dae Kim; Aram Lee; Jihea Choi; Youngsook Park; Hyesoo Kang; Woochul Chang; Myeong-Sok Lee; Jongmin Kim; Epigenetic modulation as a therapeutic approach for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Experimental & Molecular Medicine 2015, 47, e175-e175, 10.1038/emm.2015.45.
- Aram Lee; Danielle McLean; Jihea Choi; Hyesoo Kang; Woochul Chang; Jongmin Kim; Therapeutic implications of microRNAs in pulmonary arterial hypertension. BMB Reports 2014, 47, 311-317, 10.5483/bmbrep.2014.47.6.085.
- J. W. Roos-Hesselink; Felix Zijlstra; Pulmonary hypertension, how to diagnose and who to treat?. Netherlands Heart Journal 2011, 19, 493-494, 10.1007/s12471-011-0221-2.
- Melissa A. Lyle; Jonathan P. Davis; Frank V. Brozovich; Regulation of Pulmonary Vascular Smooth Muscle Contractility in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Implications for Therapy. Frontiers in Physiology 2017, 8, -, 10.3389/fphys.2017.00614.
- G G Pietra; W D Edwards; J M Kay; S Rich; J Kernis; B Schloo; S M Ayres; E H Bergofsky; B H Brundage; K M Detre; et al. Histopathology of primary pulmonary hypertension. A qualitative and quantitative study of pulmonary blood vessels from 58 patients in the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Registry.. Circulation 1989, 80, 1198-1206, 10.1161/01.cir.80.5.1198.
- Marlene Rabinovitch; Molecular pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2012, 122, 4306-4313, 10.1172/jci60658.
- Benoît Ranchoux; Lloyd D. Harvey; Ramon J. Ayon; Aleksandra Babicheva; Sebastien Bonnet; Stephen Y. Chan; Jason X.-J. Yuan; Vinicio A. De Jesus Perez; Endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary arterial hypertension: an evolving landscape (2017 Grover Conference Series). Pulmonary Circulation 2017, 8, -, 10.1177/2045893217752912.
- Vallerie V. McLaughlin; Stephen L. Archer; David B. Badesch; Robyn J. Barst; Harrison W. Farber; Jonathan R. Lindner; Michael A. Mathier; Michael D. McGoon; Myung H. Park; Robert S. Rosenson; et al. ACCF/AHA 2009 Expert Consensus Document on Pulmonary Hypertension. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2009, 53, 1573-1619, 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.01.004.
- Rachel K. Hopper; Jan-Renier A.J. Moonen; Isabel Diebold; Aiqin Cao; Christopher J. Rhodes; Nancy F. Tojais; Jan K. Hennigs; Mingxia Gu; Lingli Wang; Marlene Rabinovitch; et al. In Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension, Reduced BMPR2 Promotes Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via HMGA1 and Its Target Slug. Circulation 2016, 133, 1783-1794, 10.1161/circulationaha.115.020617.
- Anastasia Gorelova; Ms. Mariah Berman; Imad Al Ghouleh; Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 2020, , , 10.1089/ars.2020.8169.
- Archana Vijay Gaikwad; Mathew Suji Eapen; Kielan D. McAlinden; Collin Chia; Josie Larby; Stephen Myers; Surajit Dey; Greg Haug; James Markos; Allan R. Glanville; et al. Endothelial to mesenchymal transition (EndMT) and vascular remodeling in pulmonary hypertension and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine 2020, 14, 1027-1043, 10.1080/17476348.2020.1795832.
- Ting Liu; Xiao-Zhou Zou; Ning Huang; Xiao-Yue Ge; Mao-Zhong Yao; Hong Liu; Zheng Zhang; Chang-Ping Hu; miR-27a promotes endothelial-mesenchymal transition in hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension by suppressing BMP signaling. Life Sciences 2019, 227, 64-73, 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.038.
- Bo Zhang; Wen Niu; Hai‑Ying Dong; Man‑Ling Liu; Ying Luo; Zhi‑Chao Li; Hypoxia induces endothelial‑mesenchymal transition in pulmonary vascular remodeling. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 2018, 42, 270-278, 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3584.
- Jingjing Wang; Min Yu; Jian Xu; Yusheng Cheng; Xiang Li; Guihong Wei; Hong Wang; Hui Kong; Wei-Ping Xie; Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) mediates the protective effects of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibition on pulmonary hypertension. Journal of Biomedical Science 2019, 26, 6, 10.1186/s12929-019-0496-y.
- Haiyan Zhao; Yang Wang; Xiaoli Zhang; Yingying Guo; Xiaofei Wang; miR-181b-5p inhibits endothelial-mesenchymal transition in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension by targeting endocan and TGFBR1. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 2020, 386, 114827, 10.1016/j.taap.2019.114827.
- Robert B. Good; Adrian J. Gilbane; Sarah L. Trinder; Christopher P. Denton; Gerry Coghlan; David J. Abraham; Alan M. Holmes; Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition Contributes to Endothelial Dysfunction in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. The American Journal of Pathology 2015, 185, 1850-1858, 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.03.019.
- Sanjiv J. Shah; Pulmonary Hypertension. JAMA 2012, 308, 1366-1374, 10.1001/jama.2012.12347.
- Sarasa Isobe; Masaharu Kataoka; Jin Endo; Hidenori Moriyama; Shogo Okazaki; Kenji Tsuchihashi; Yoshinori Katsumata; Tsunehisa Yamamoto; Kohsuke Shirakawa; Naohiro Yoshida; et al. Endothelial–Mesenchymal Transition Drives Expression of CD44 Variant and xCT in Pulmonary Hypertension. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 2019, 61, 367-379, 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0231oc.
- Li Zhang; Yu-Mei Li; Xi-Xi Zeng; Xiao-Yan Wang; Shao-Kun Chen; Long-Xin Gui; Mo-Jun Lin; Galectin-3- Mediated Transdifferentiation of Pulmonary Artery Endothelial Cells Contributes to Hypoxic Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 2018, 51, 763-777, 10.1159/000495331.
- Takeo Tsutsumi; Tetsutaro Nagaoka; Takashi Yoshida; Lei Wang; Sachiko Kuriyama; Yoshifumi Suzuki; Yuichi Nagata; Norihiro Harada; Yuzo Kodama; Fumiyuki Takahashi; et al. Nintedanib ameliorates experimental pulmonary arterial hypertension via inhibition of endothelial mesenchymal transition and smooth muscle cell proliferation. PLOS ONE 2019, 14, e0214697, 10.1371/journal.pone.0214697.
- Yucai Chen; Tianyi Yuan; Huifang Zhang; Yu Yan; Danshu Wang; Lianhua Fang; Yang Lu; Guanhua Du; Activation of Nrf2 Attenuates Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling via Inhibiting Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: an Insight from a Plant Polyphenol. International Journal of Biological Sciences 2017, 13, 1067-1081, 10.7150/ijbs.20316.
- A. M. Reynolds; M. D. Holmes; S. M. Danilov; P. N. Reynolds; Targeted gene delivery of BMPR2 attenuates pulmonary hypertension. European Respiratory Journal 2011, 39, 329-343, 10.1183/09031936.00187310.
- Talmadge E. King; Annie Pardo; Moisés Selman; Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. The Lancet 2011, 378, 1949-1961, 10.1016/s0140-6736(11)60052-4.
- Luca Richeldi; Harold R Collard; Mark G Jones; Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. The Lancet 2017, 389, 1941-1952, 10.1016/s0140-6736(17)30866-8.
- Moises Selman; Annie Pardo; Alveolar epithelial cell disintegrity and subsequent activation: a key process in pulmonary fibrosis.. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2012, 186, 119-21, 10.1164/rccm.201206-0997ED.
- Thomas A Wynn; Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. The Journal of Pathology 2008, 214, 199-210, 10.1002/path.2277.
- Seo-Hyun Choi; Zhen-Yu Hong; Jae-Kyung Nam; Hae-June Lee; Junho Jang; Ran Ji Yoo; Yong Jin Lee; Chang Young Lee; Kyung Hwan Kim; Seungwoo Park; et al. A Hypoxia-Induced Vascular Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Development of Radiation-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Clinical Cancer Research 2015, 21, 3716-3726, 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-14-3193.
- Naozumi Hashimoto; Sem H. Phan; Kazuyoshi Imaizumi; Masaki Matsuo; Harunori Nakashima; Tsutomu Kawabe; Kaoru Shimokata; Yoshinori Hasegawa; Endothelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 2010, 43, 161-172, 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0031oc.
- Shina Song; Yunxia Ji; Guanghua Zhang; Xue Zhang; Bin Li; Defang Li; Wanglin Jiang; Protective Effect of Atazanavir Sulphate Against Pulmonary Fibrosis In Vivo and In Vitro. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology 2018, 122, 199-207, 10.1111/bcpt.12871.
- Toshio Suzuki; Yuji Tada; Santhi Gladson; Rintaro Nishimura; Iwao Shimomura; Satoshi Karasawa; Koichiro Tatsumi; James West; Vildagliptin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis in lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury by inhibiting endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Respiratory Research 2017, 18, 177, 10.1186/s12931-017-0660-4.
- Seo-Hyun Choi; Jae-Kyung Nam; Bu-Yeo Kim; Junho Jang; Young-Bae Jin; Hae-June Lee; Seungwoo Park; Young Hoon Ji; Jaeho Cho; Yong Jin Lee; et al. HSPB1 Inhibits the Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition to Suppress Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Tumorigenesis. Cancer Research 2016, 76, 1019-1030, 10.1158/0008-5472.can-15-0952.
- Xuexin Lu; Jiannan Gong; Phyllis A. Dennery; Hongwei Yao; Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition: Pathogenesis and therapeutic targets for chronic pulmonary and vascular diseases. Biochemical Pharmacology 2019, 168, 100-107, 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.06.021.
- Jongmin Kim; Yujung Kang; Yoko Kojima; Janet K. Lighthouse; Xiaoyue Hu; Micheala A. Aldred; Danielle L. McLean; Hyekyung Park; Suzy A. Comhair; Daniel M. Greif; et al. An endothelial apelin-FGF link mediated by miR-424 and miR-503 is disrupted in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nature Medicine 2013, 19, 74-82, 10.1038/nm.3040.
- Lina Qiao; Toshihiko Nishimura; Lingfang Shi; Dane Sessions; Ama Thrasher; James R. Trudell; Gerald J. Berry; Ronald G. Pearl; Peter N. Kao; Endothelial Fate Mapping in Mice With Pulmonary Hypertension. Circulation 2014, 129, 692-703, 10.1161/circulationaha.113.003734.
- Seiichiro Sakao; Hiroyuki Hao; Nobuhiro Tanabe; Yasunori Kasahara; Katsushi Kurosu; Koichiro Tatsumi; Endothelial-like cells in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: crosstalk with myofibroblast-like cells. Respiratory Research 2011, 12, 109-109, 10.1186/1465-9921-12-109.
- Haiyang Tang; Aleksandra Babicheva; Kimberly M. McDermott; Yali Gu; Ramon J. Ayon; Shanshan Song; Ziyi Wang; Akash Gupta; Tong Zhou; Xutong Sun; et al. Endothelial HIF-2α Contributes to Severe Pulmonary Hypertension by Inducing Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 2018, 314, L256-L275, 10.1152/ajplung.00096.2017.
- Huili Zhang; Yanjun Lin; Yiwen Ma; Junfeng Zhang; Changqian Wang; Protective effect of hydrogen sulfide on monocrotaline‑induced pulmonary arterial hypertension via inhibition of the endothelial mesenchymal transition. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 2019, 44, 2091-2102, 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4359.
- Jian Xu; Jingjing Wang; Mengyu He; Honghao Han; Weiping Xie; Hong Wang; Hui Kong; Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-4) inhibition alleviates pulmonary arterial remodeling in experimental pulmonary hypertension. Laboratory Investigation 2018, 98, 1333-1346, 10.1038/s41374-018-0080-1.
- Harika Sabbineni; Arti Verma; Sandeep Artham; Daniel Anderson; Oge Amaka; Fang Liu; Subhadra P. Narayanan; Payaningal R. Somanath; Pharmacological inhibition of β-catenin prevents EndMT in vitro and vascular remodeling in vivo resulting from endothelial Akt1 suppression. Biochemical Pharmacology 2019, 164, 205-215, 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.04.016.
- Toshio Suzuki; Erica J. Carrier; Megha H. Talati; Anandharajan Rathinasabapathy; Xinping Chen; Rintaro Nishimura; Yuji Tada; Koichiro Tatsumi; James West; Isolation and characterization of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition cells in pulmonary arterial hypertension. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 2018, 314, L118-L126, 10.1152/ajplung.00296.2017.
- Dilip Nataraj; Armin Ernst; Raghu Kalluri; Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is associated with endothelial to mesenchymal transition.. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 2010, 43, 129-30, 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0044ED.
- Yong Zhou; Ping Li; Jia-Xi Duan; Tian Liu; Xin-Xin Guan; Wen-Xiu Mei; Yong-Ping Liu; Guo-Ying Sun; Li Wan; Wen-Jing Zhong; et al. Aucubin Alleviates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in a Mouse Model. Inflammation 2017, 40, 2062-2073, 10.1007/s10753-017-0646-x.
- Marios A. Mouratis; Vassilis Aidinis; Modeling pulmonary fibrosis with bleomycin. Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine 2011, 17, 355-361, 10.1097/mcp.0b013e328349ac2b.
- Krishna K. Singh; Fina Lovren; Yi Pan; Adrian Quan; Azza Ramadan; Pratiek N. Matkar; Mehroz Ehsan; Paul Sandhu; Laura E. Mantella; Nandini Gupta; et al. The Essential Autophagy GeneATG7Modulates Organ Fibrosis via Regulation of Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2015, 290, 2547-2559, 10.1074/jbc.m114.604603.
- Toshio Suzuki; Yuji Tada; Rintaro Nishimura; Takeshi Kawasaki; Ayumi Sekine; Takashi Urushibara; Fumiaki Kato; Taku Kinoshita; Jun Ikari; James West; et al. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury drives a progenitor cell-like phenotype. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 2016, 310, L1185-L1198, 10.1152/ajplung.00074.2016.